Basic Tree
Tree
- Definition
- Terminology
- Property
- Storing
- Traversal
- Binary Tree
- Complete Binary Tree
What is a tree ?

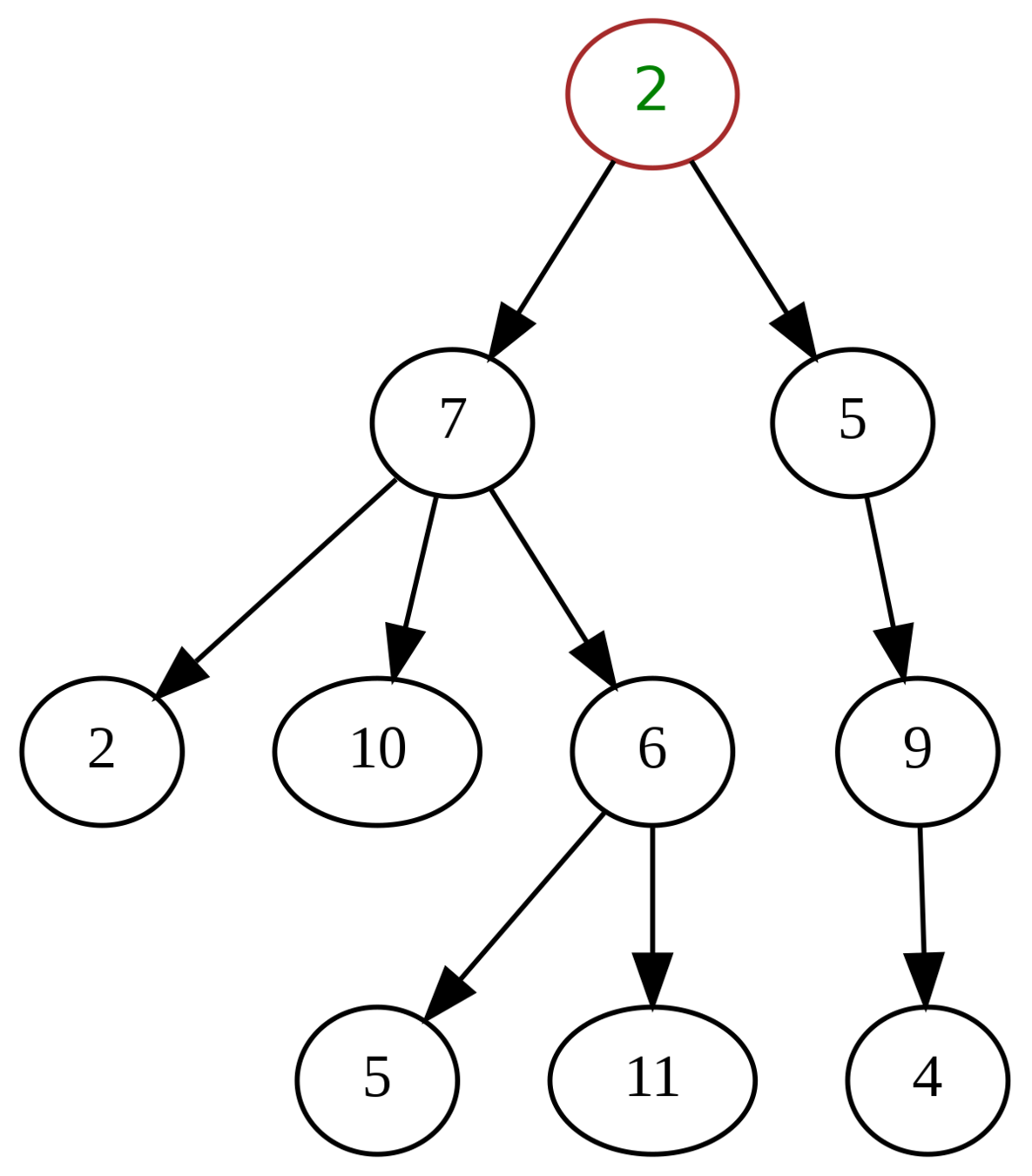
Tree - Definition
Definition: non-cyclic connected graph
Wait... what is cyclic? what is connect? graph?
Tree - Definition
Definition: non-cyclic connected graph
Wait... what is cyclic? what is connect? graph?
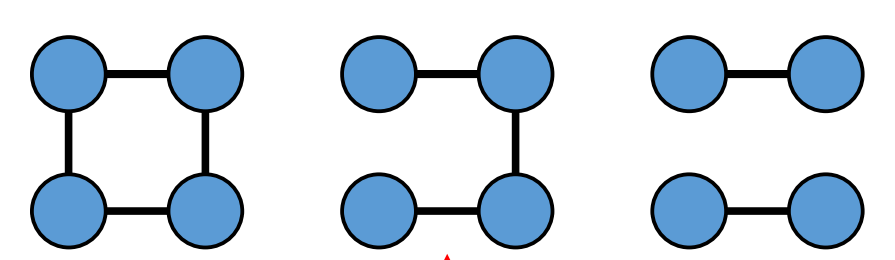
Cyclic
Connected
non-cyclic
Connected
non-cyclic
not connected
cyclic and not connected is possible
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth

Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
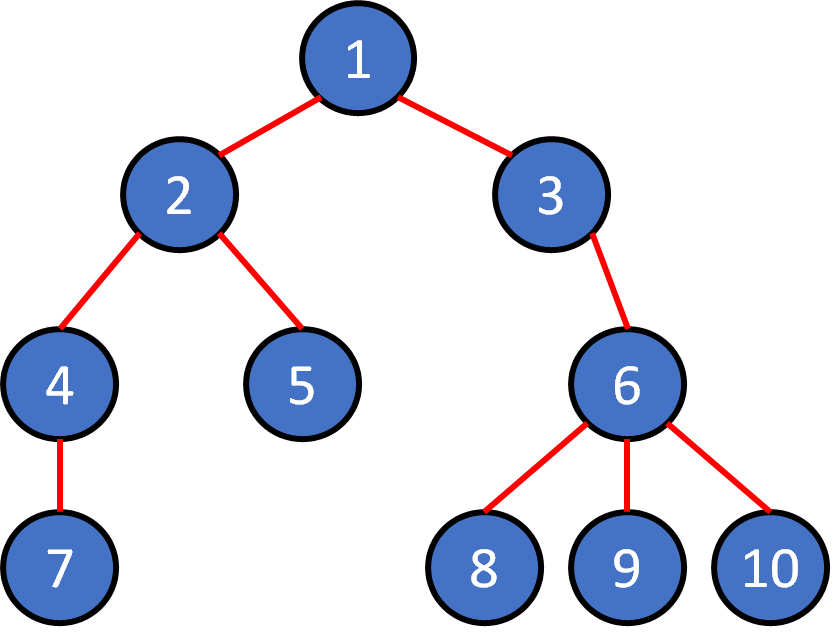
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
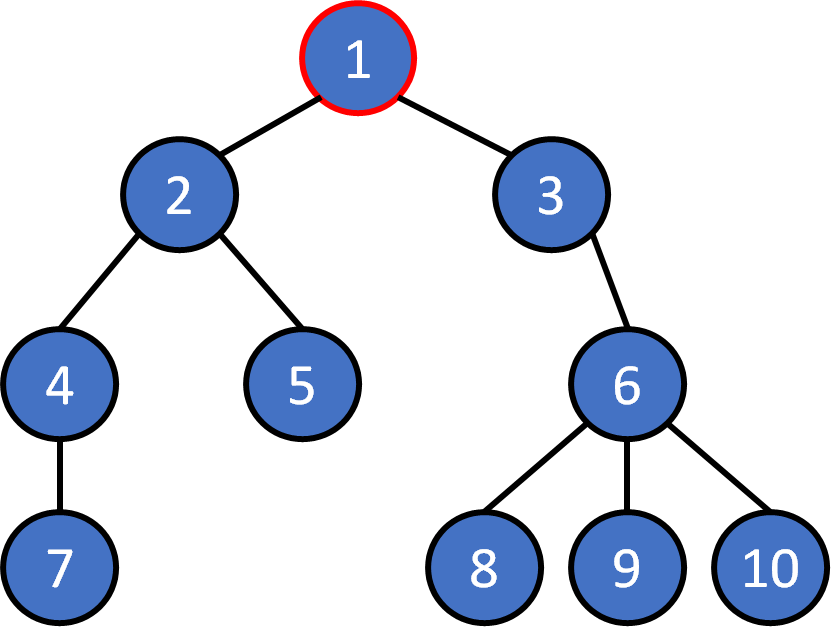
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
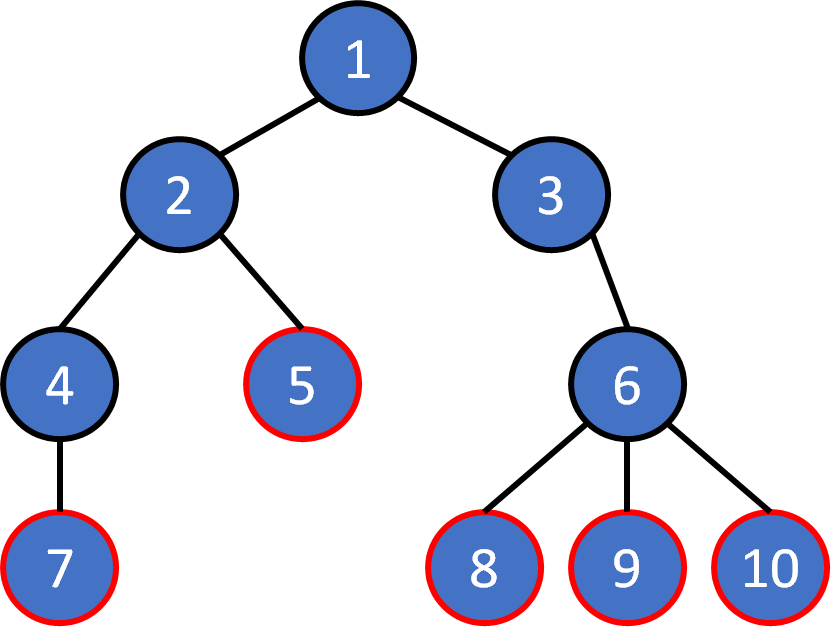
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
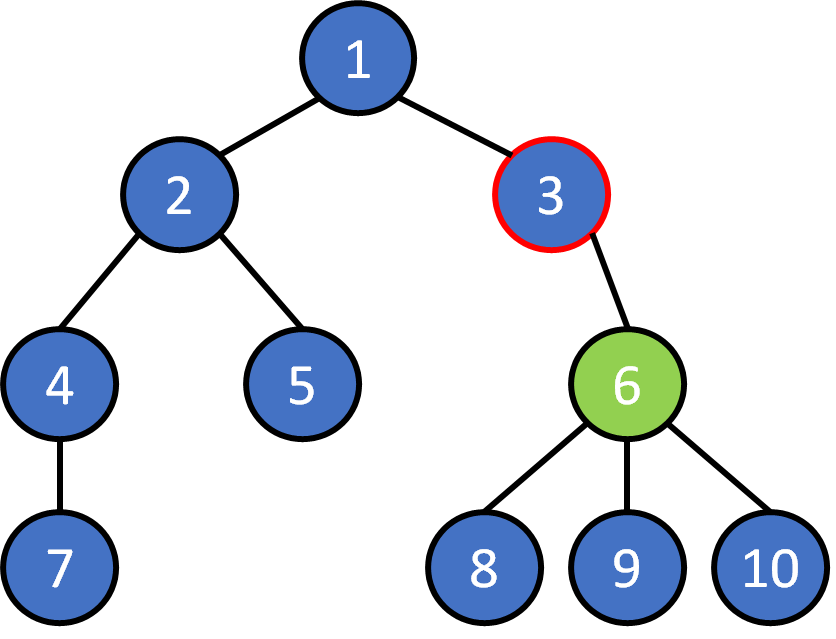
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
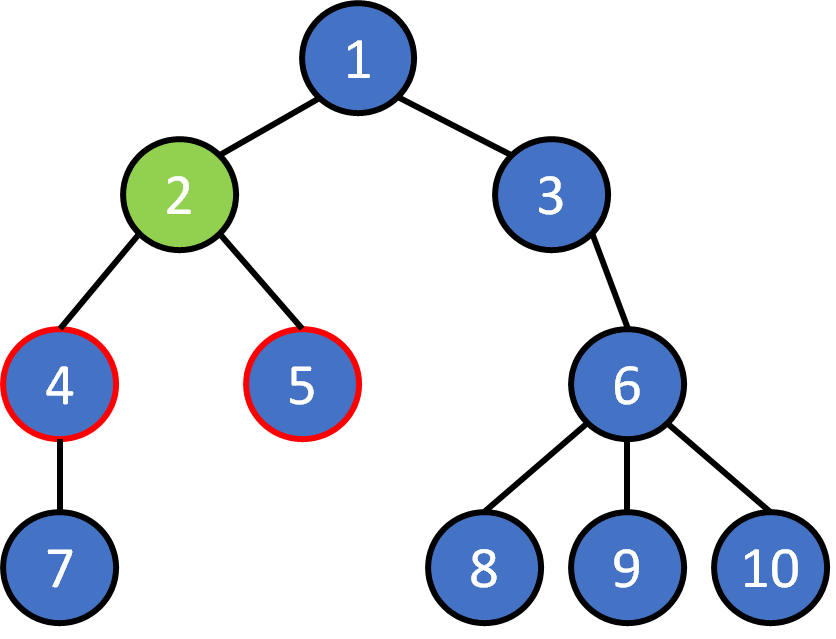
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
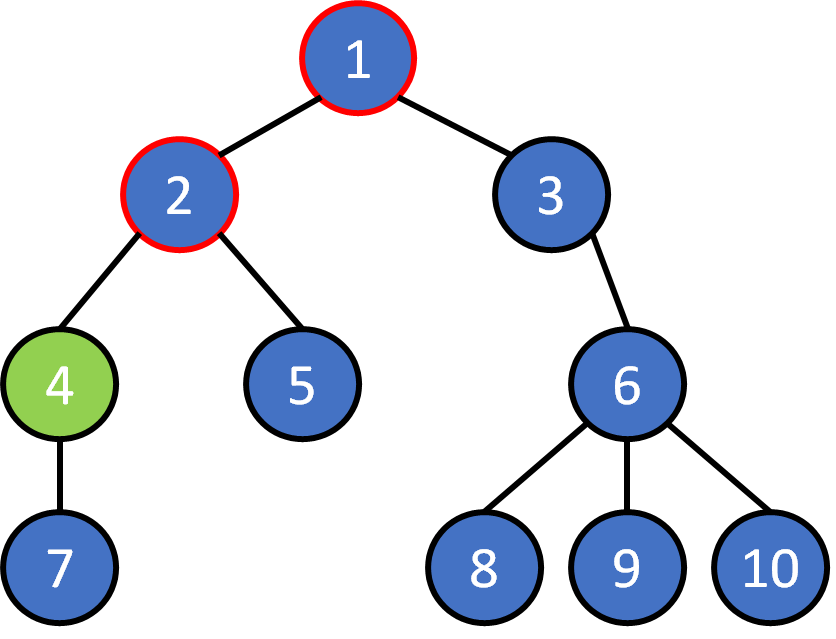
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
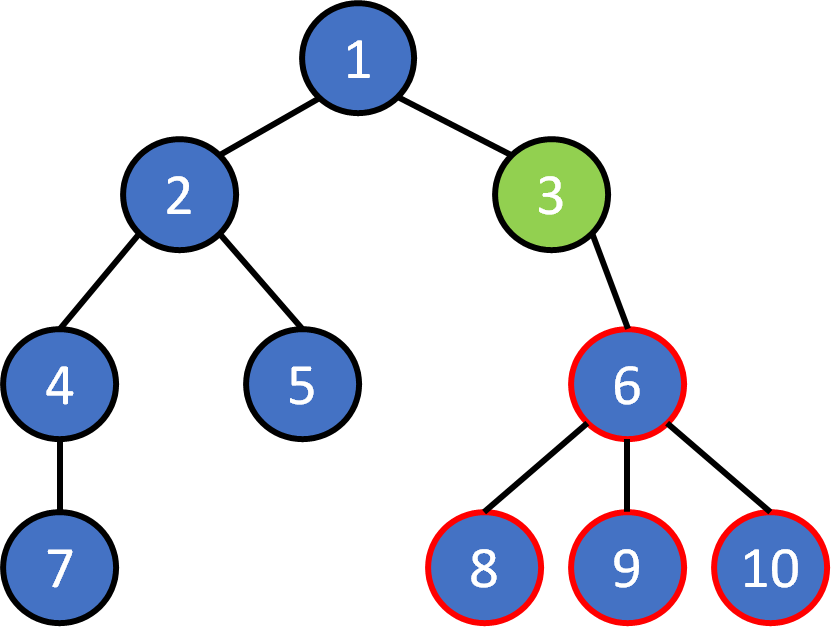
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
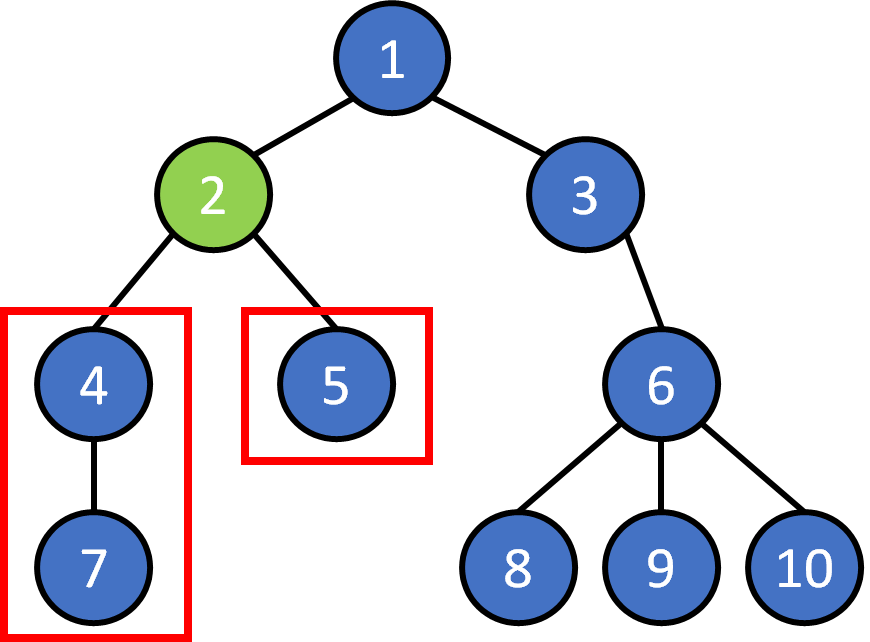
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
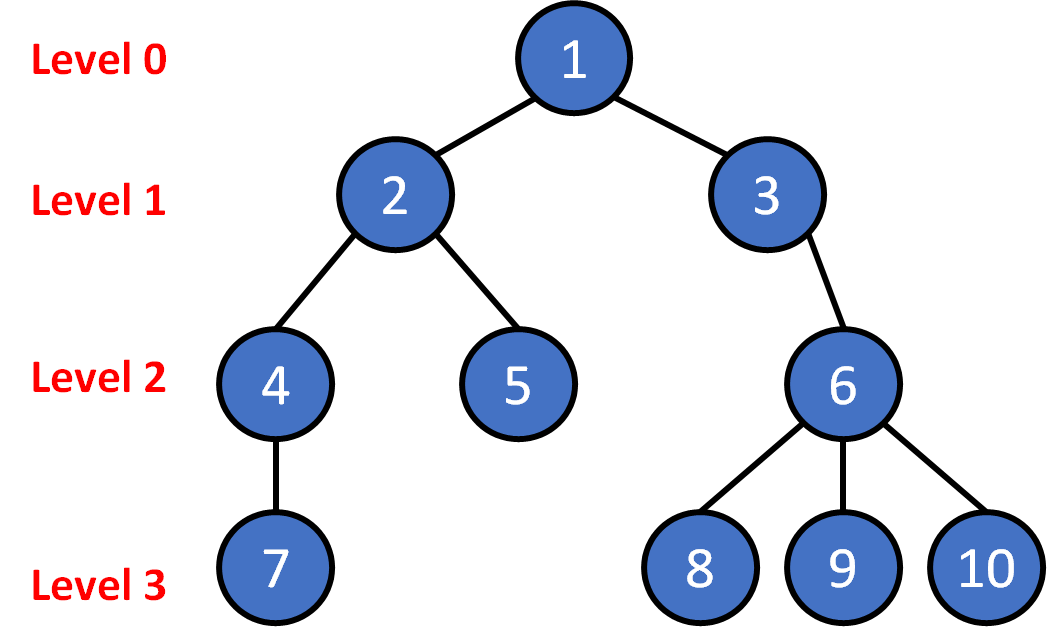
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
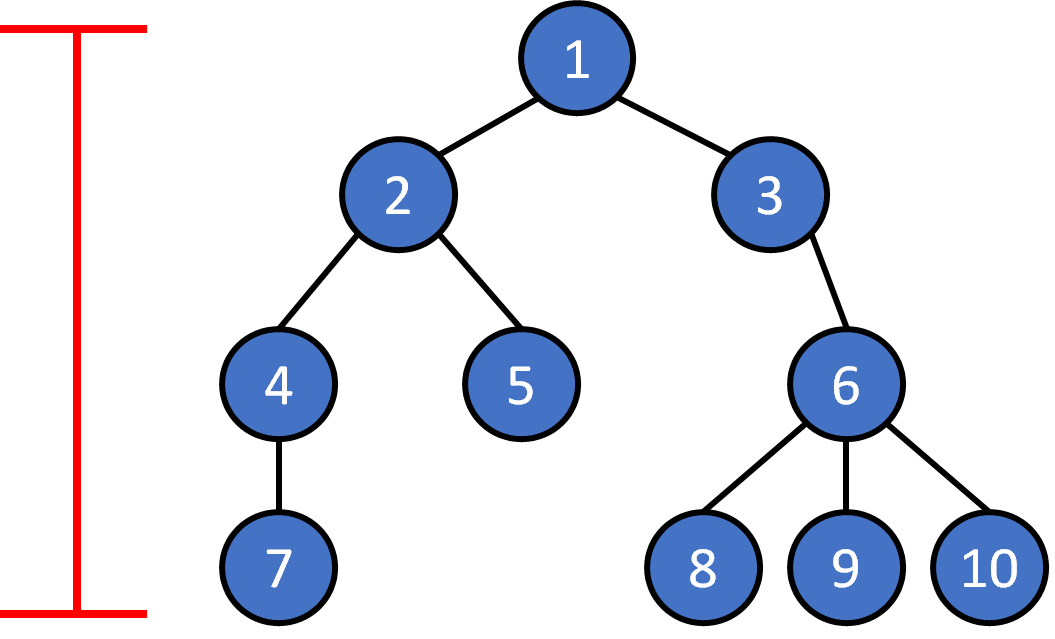
0
1
2
3
Tree Terminology
- node
- edge
- root
- leaf
- parent
- child
- ancestor
- descendant
- subtree
- level
- depth
- height
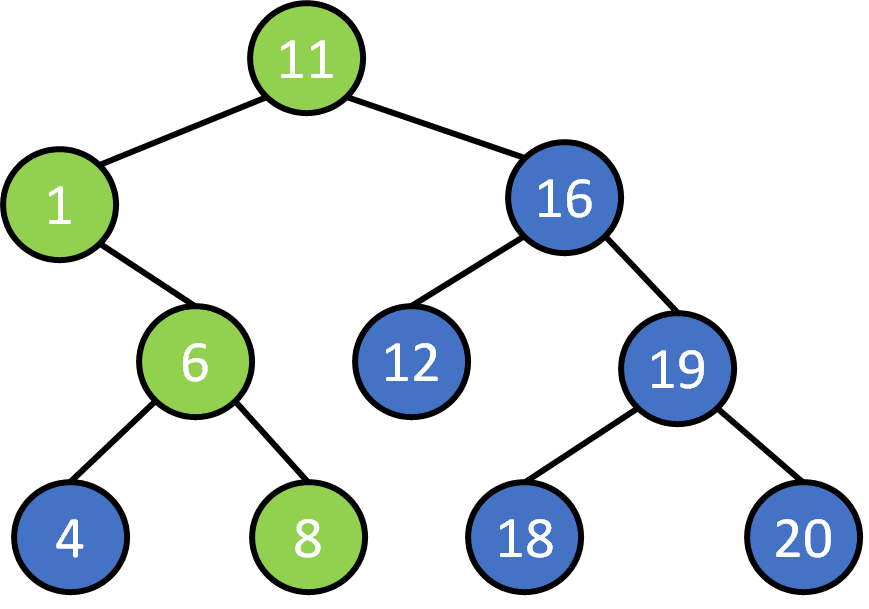
height = 3
height = 2

height = 4
distance to the farest leaf
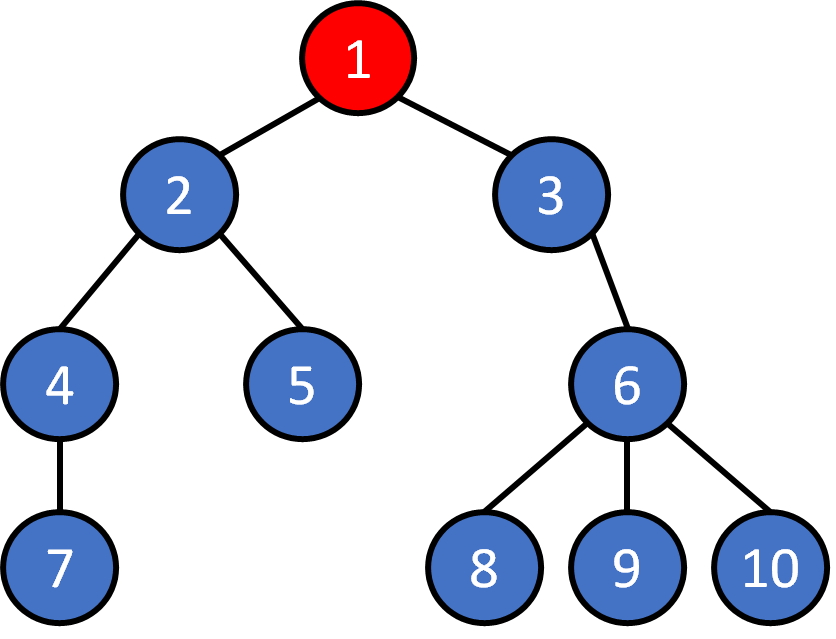
Tree - Property
-
Each node can be root
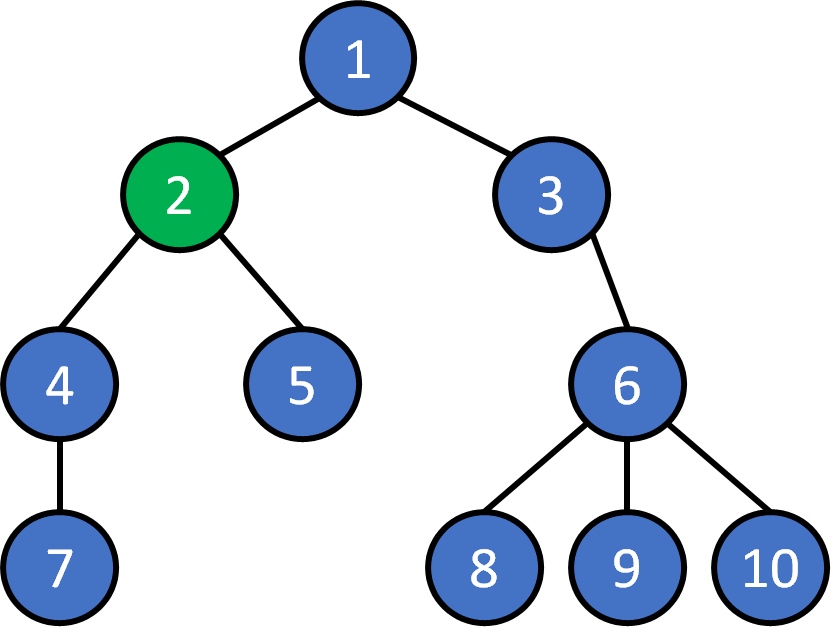
-
Each node can be root
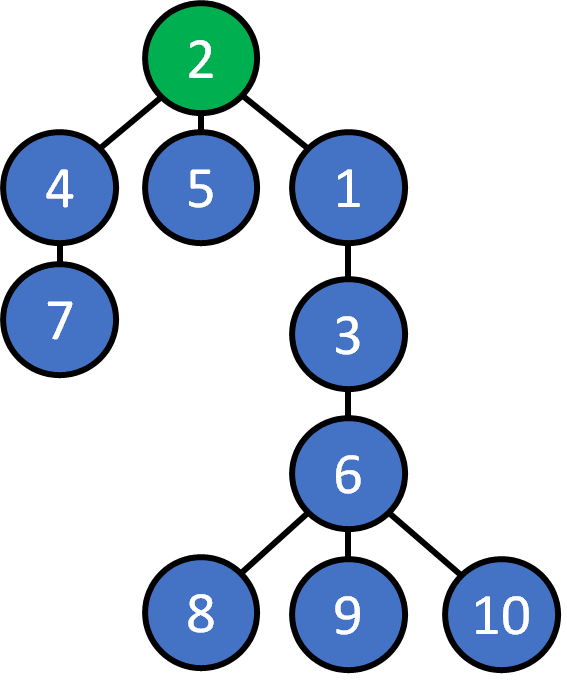
2. Given any pair of nodes, there exists a unique path that doesn't visit a node twice.
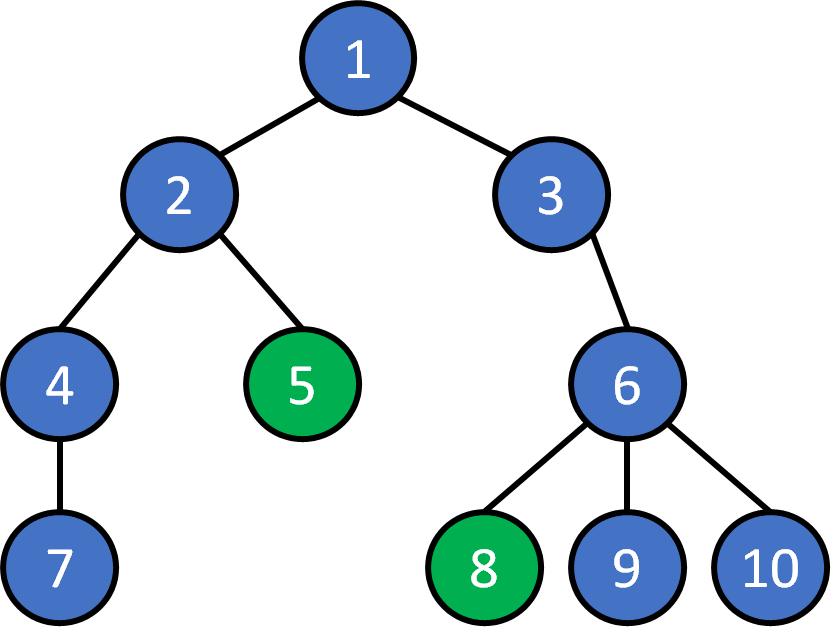
2. Given any pair of nodes, there exists a unique path that doesn't visit a node twice.
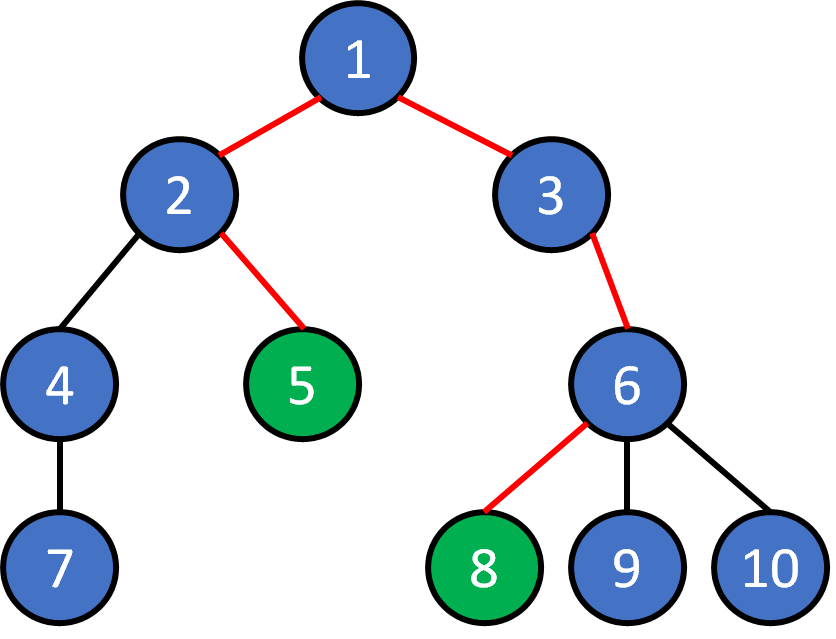
2. Given any pair of nodes, there exists a unique path that doesn't visit a node twice.
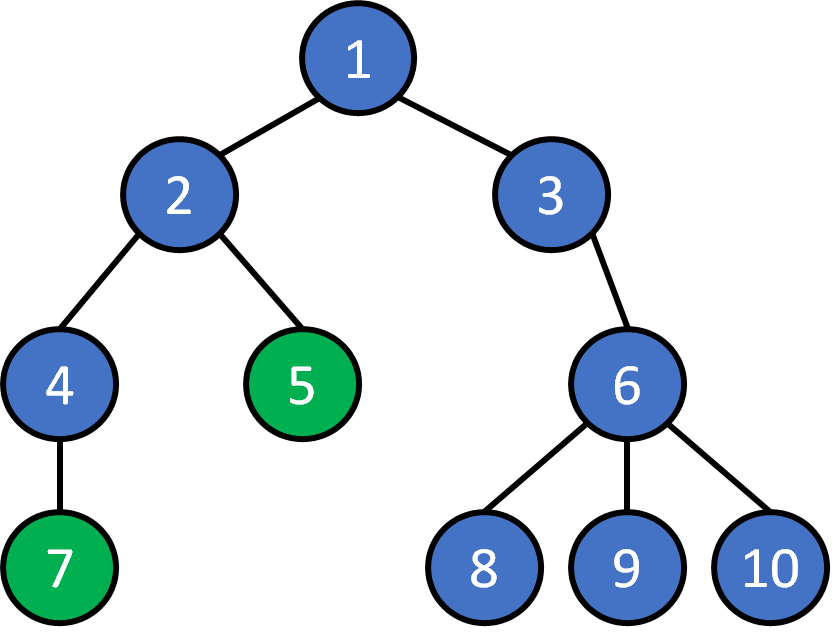
2. Given any pair of nodes, there exists a unique path that doesn't visit a node twice.
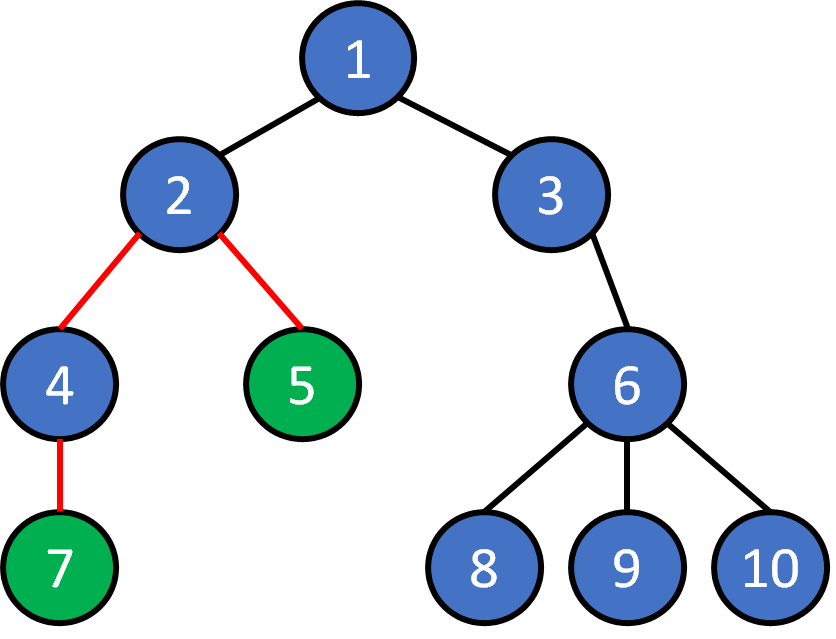
3. A tree have N nodes has exactly (N-1) edges
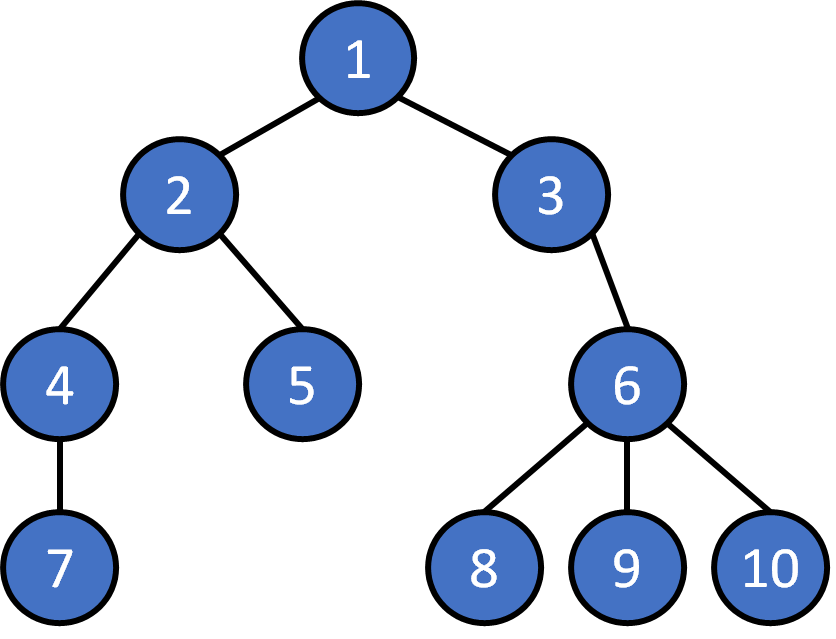
Tree - Storage
Tree - Storage
Tree - Storage
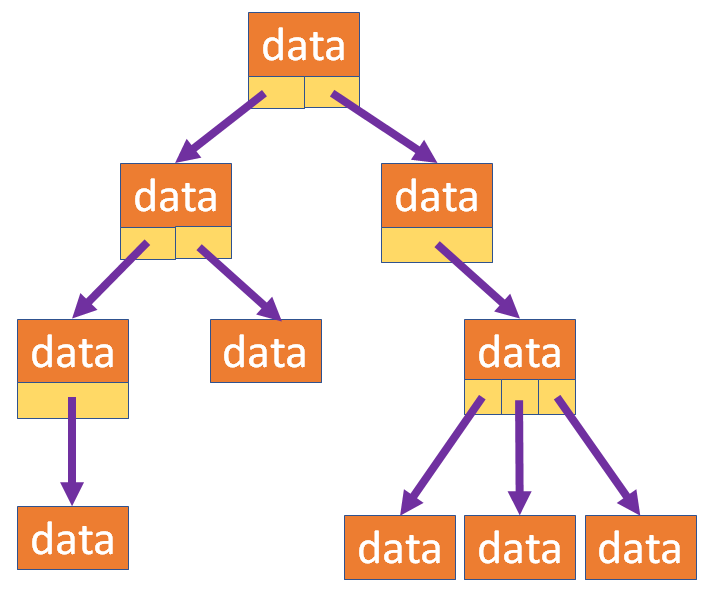
How to store a tree structure
Node is like a linked list !
Question : how many pointers needed?
struct Node{
int _data;
Node *_child1, *_child2, *_child3, ...?
(Node*)* array;
int index;
}
void addNode(Node * parent, int val){
if(index == N)
array = new Node*[2*N];
array[index] = new Node(val);
index++;
}
Node::Node(){
malloc(sizeof(Node*) * N);
}
Tree - Storage
Solution : use linked list or dynamic array (STL vector)
#include <vector>
struct Node{
int _data;
vector<Node*> _childs;
}Tree - Storage
Another Solution : Use array of dynamic array (STL vector)
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int data[SIZE];
vector<int> child[SIZE];
void addChild(int parent, int child){
child[parent].push_back(child);
}Use when the Probelm gives the index of each node.
Tree - Traversal
Tree - Traversal
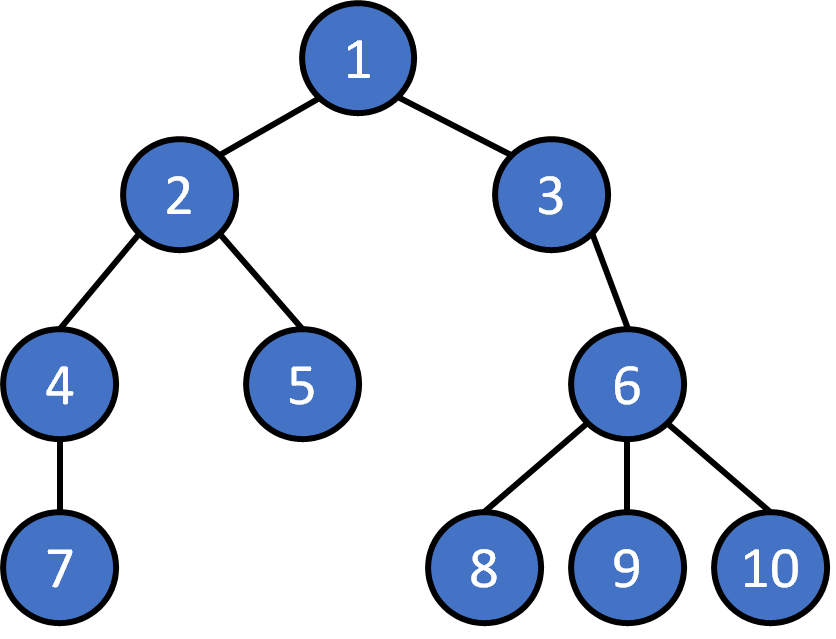
Depth First Search (DFS)
Tree - Traversal
DFS
Tree - Traversal
DFS
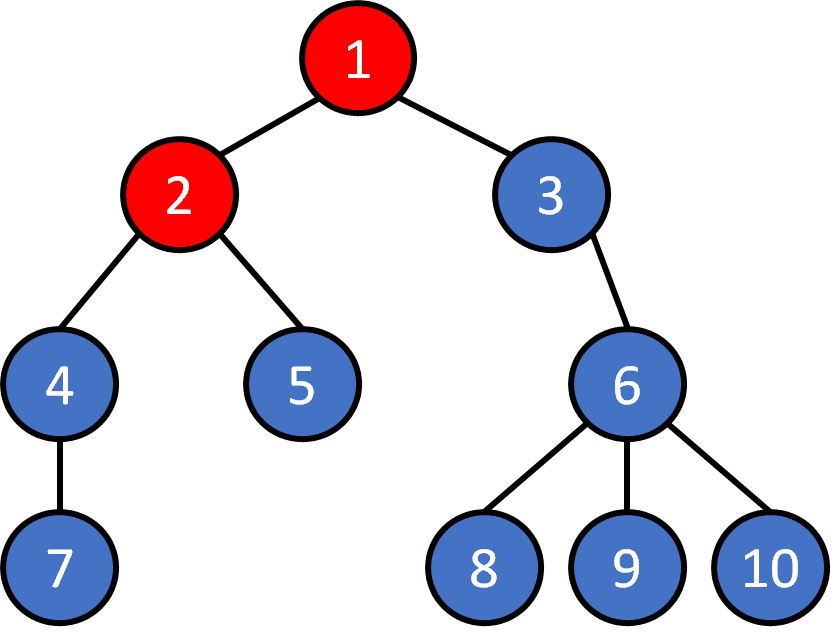
Tree - Traversal
DFS
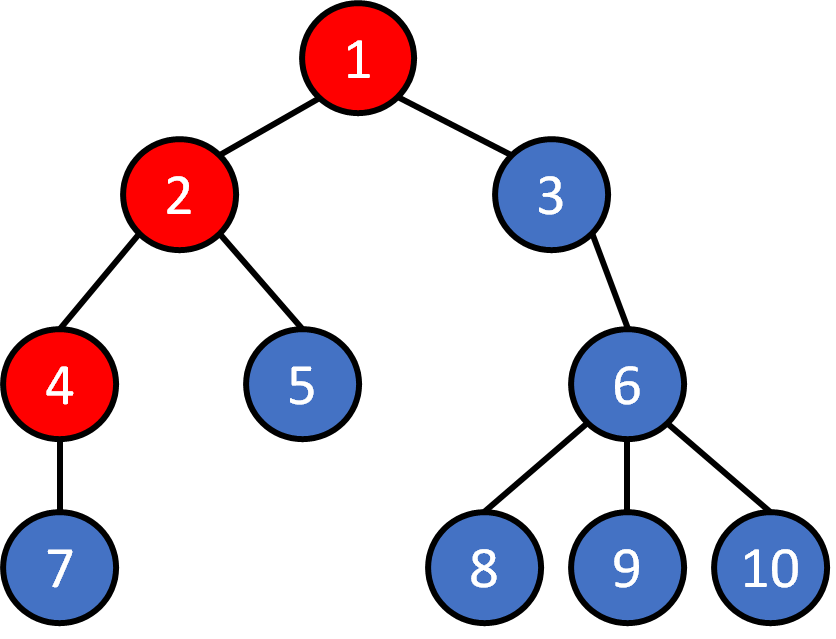
Tree - Traversal
DFS
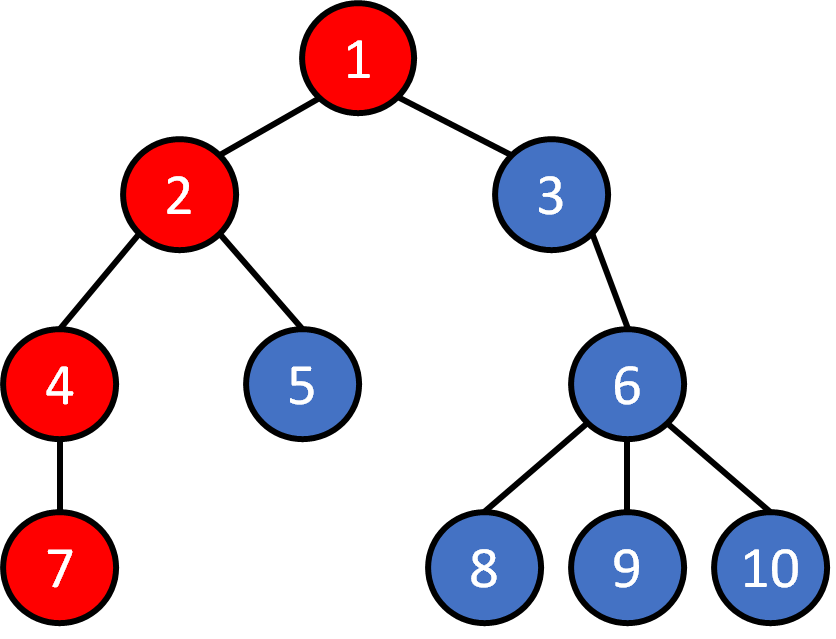
Tree - Traversal
DFS
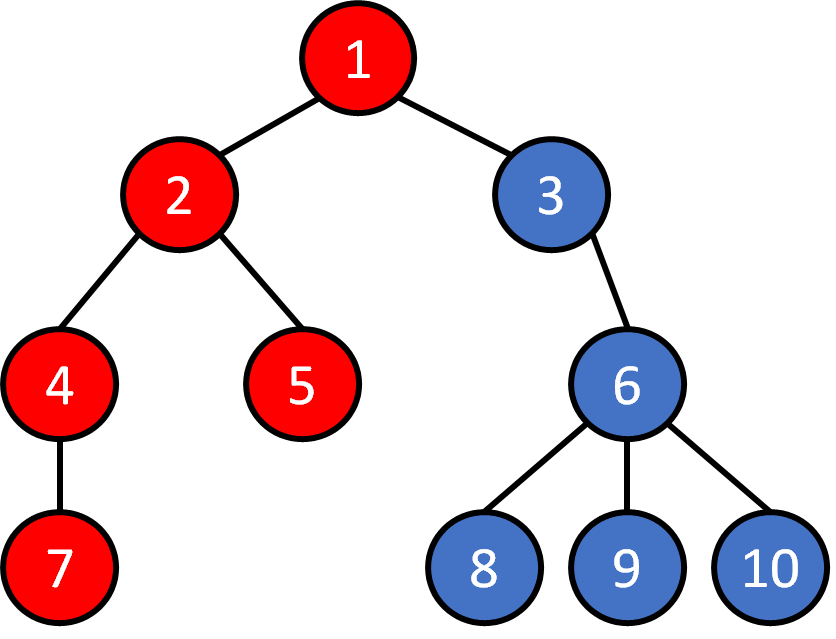
Tree - Traversal
DFS
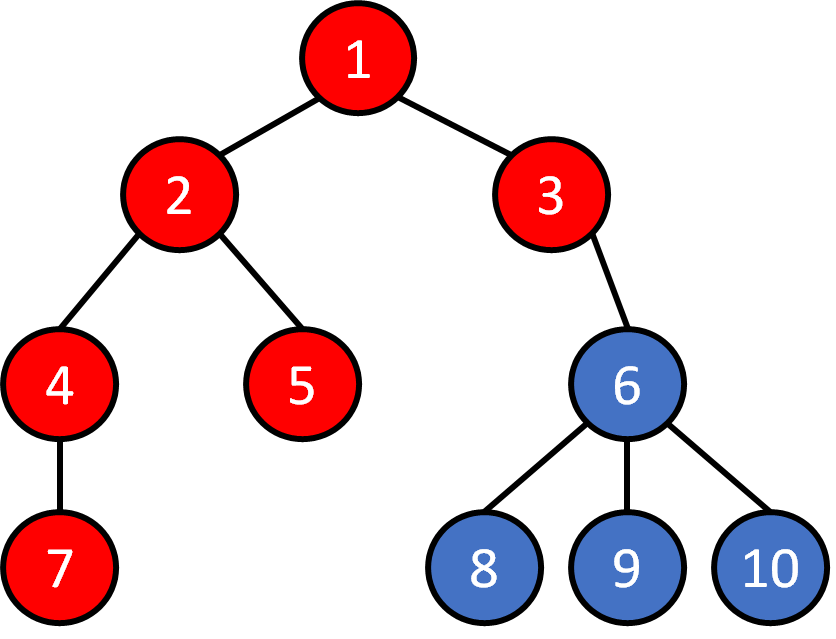
Tree - Traversal
DFS
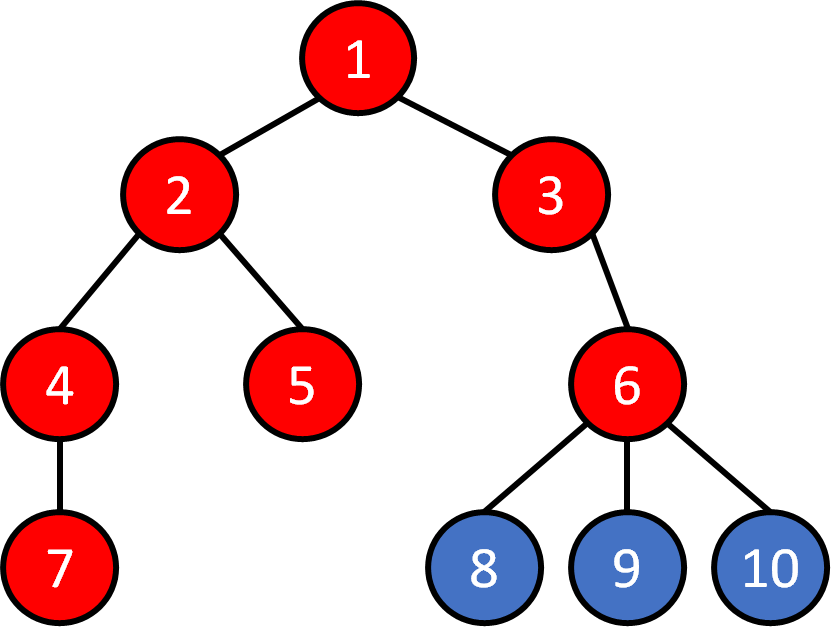
Tree - Traversal
DFS
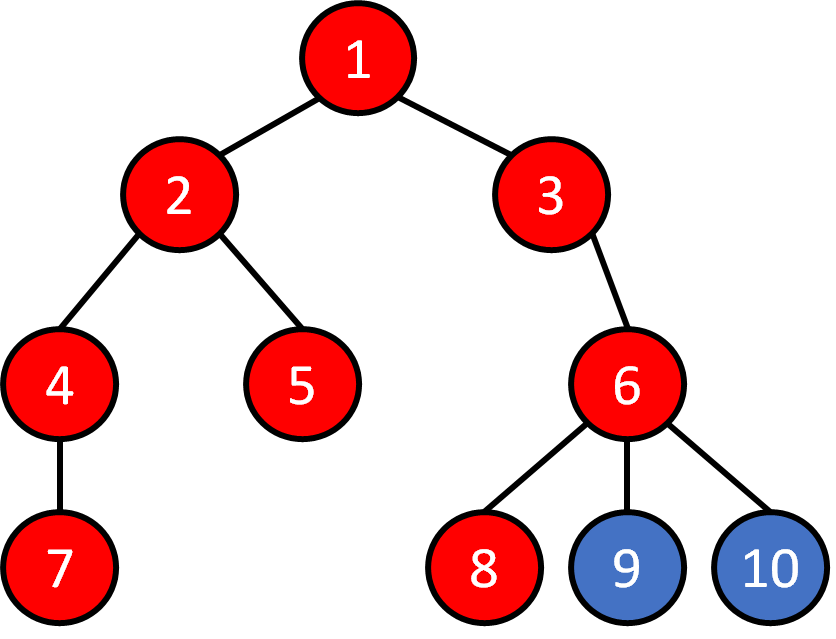
Tree - Traversal
DFS
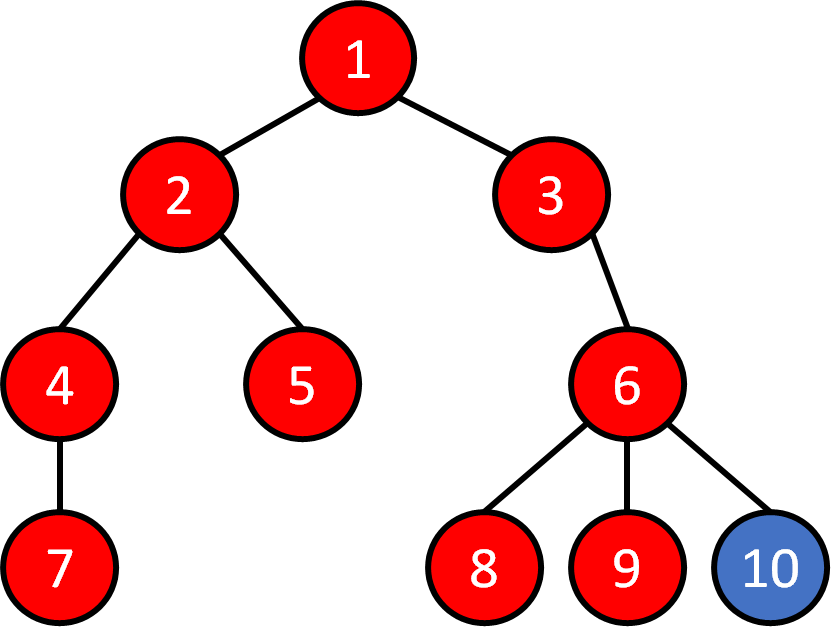
Tree - Traversal
DFS
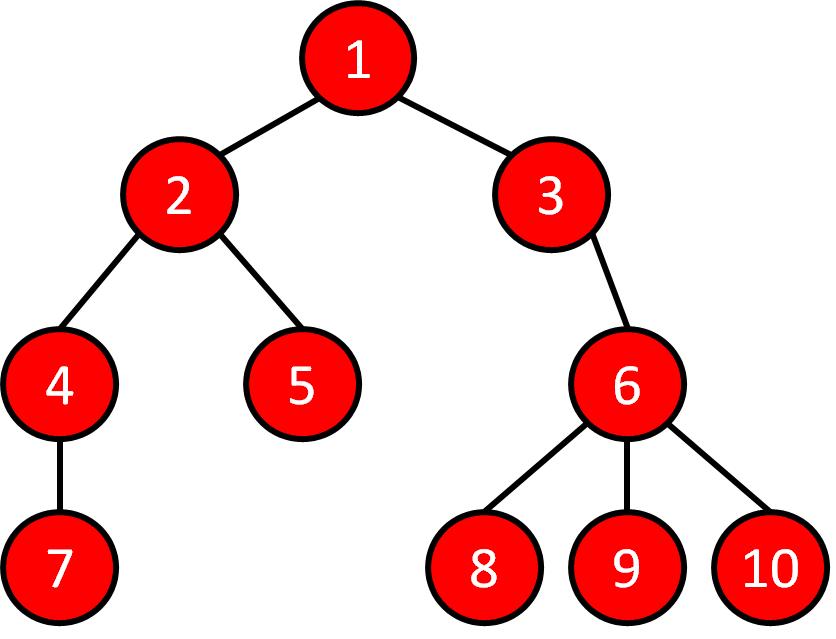
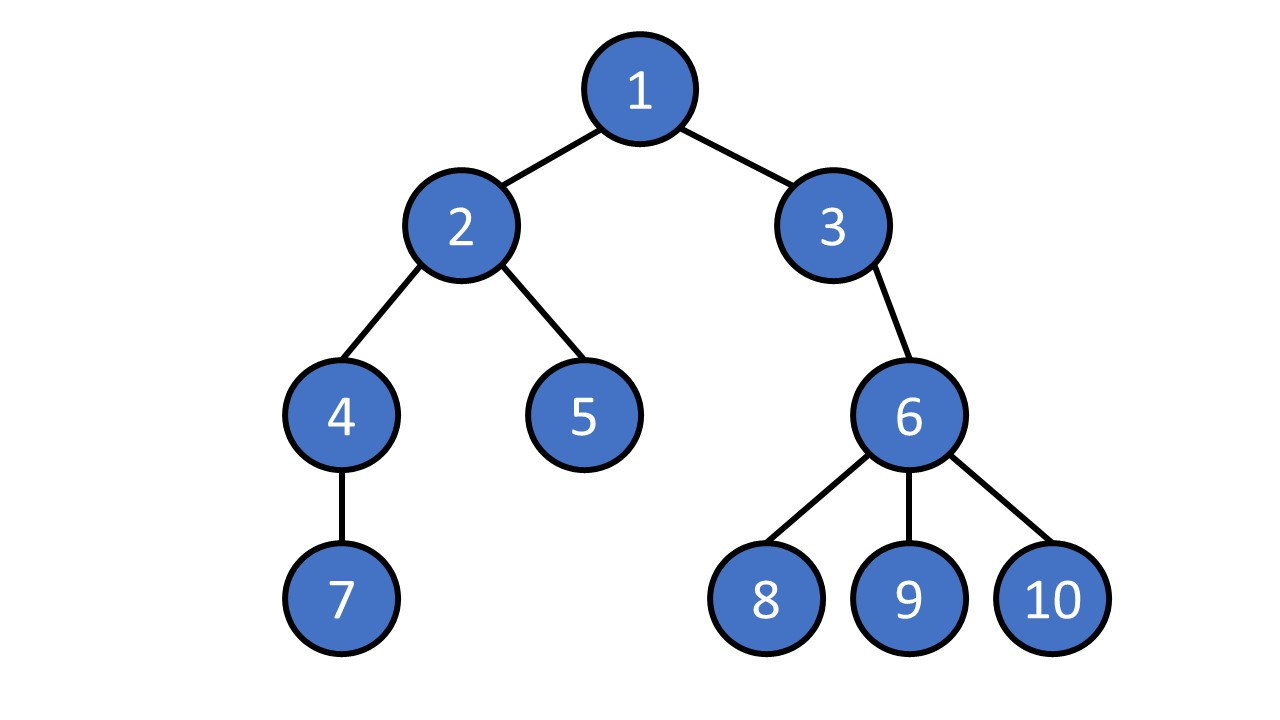
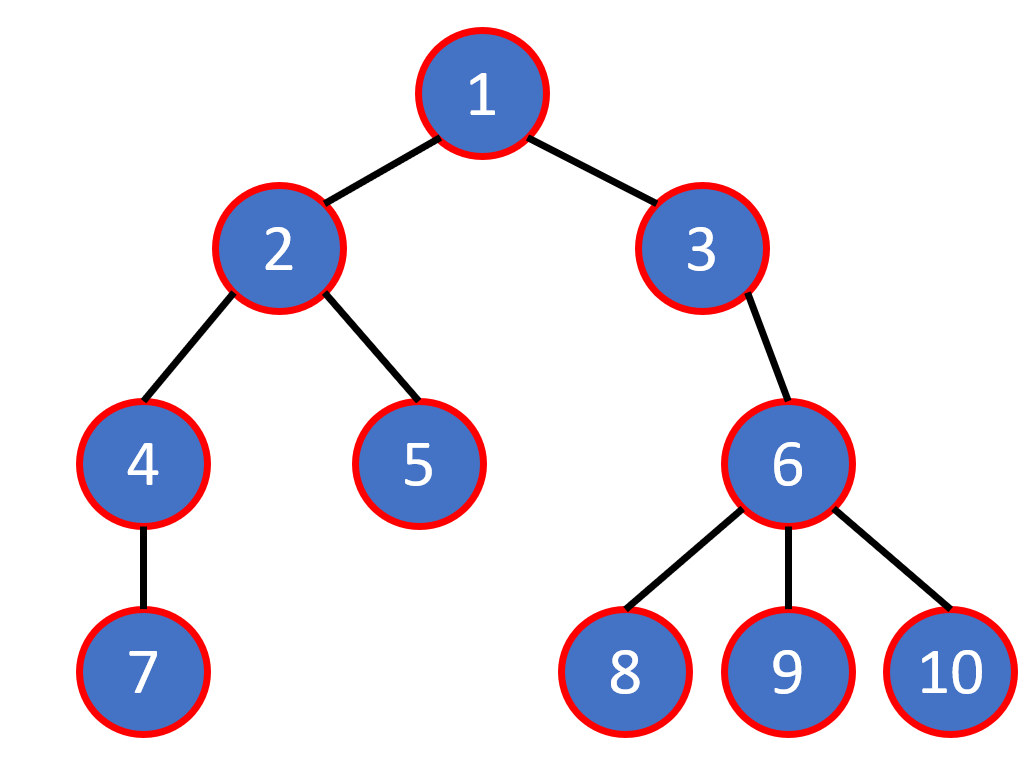
1 2 4 7 5 3 6 8 9 10
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
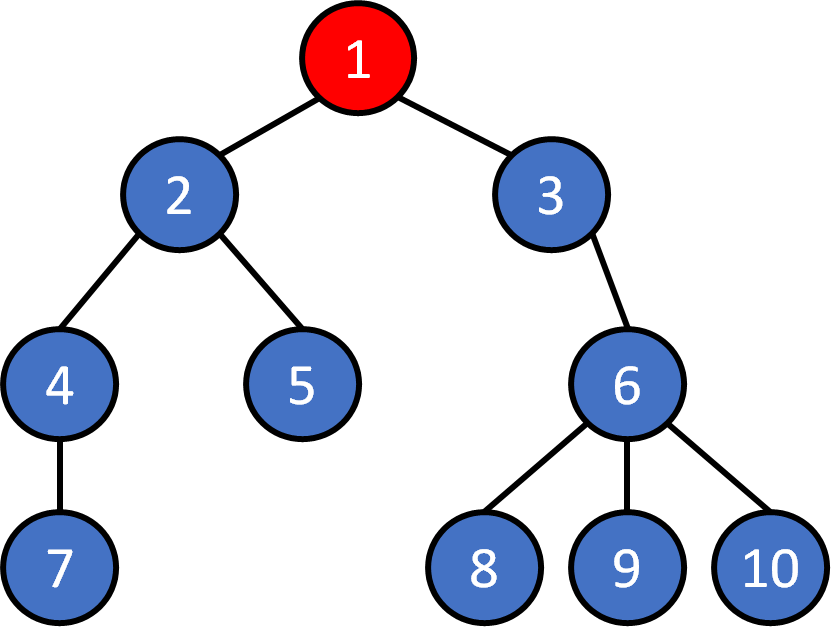
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
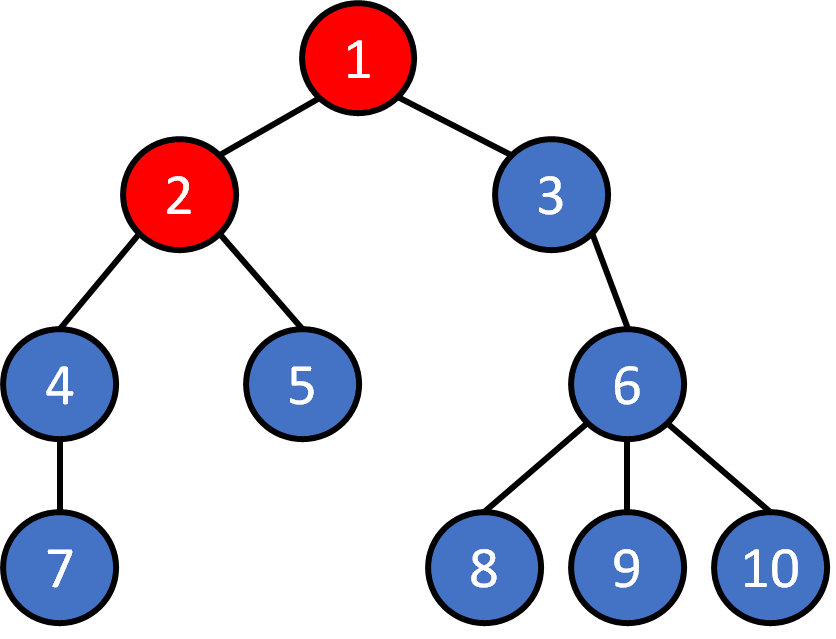
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
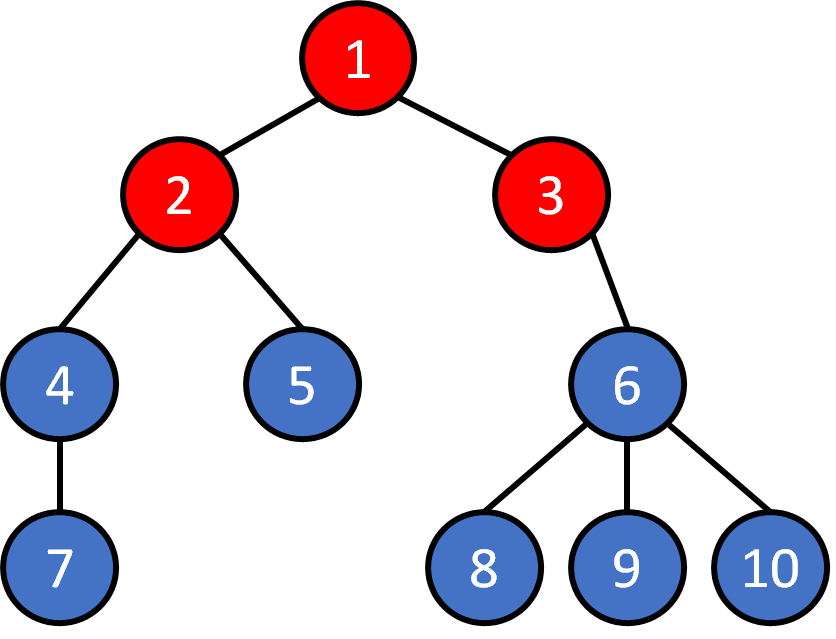
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
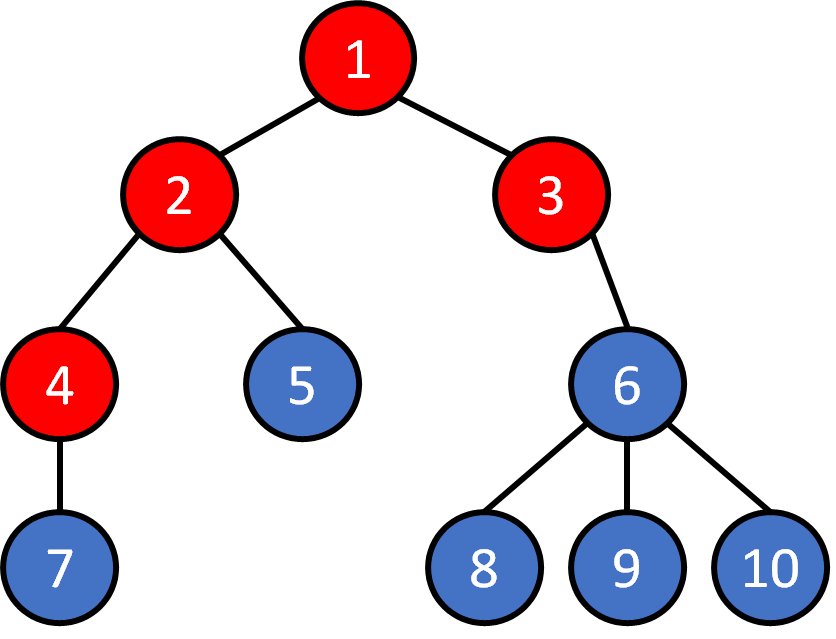
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
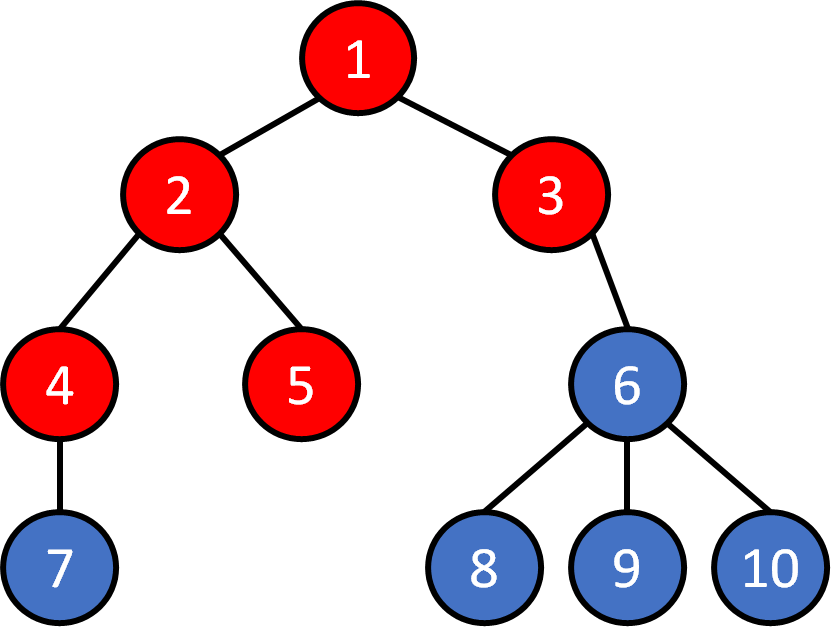
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
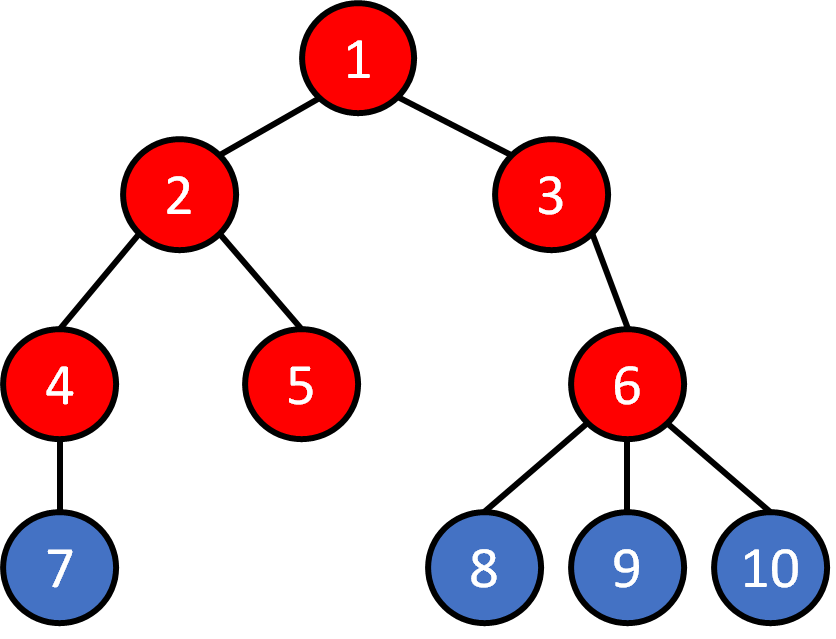
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
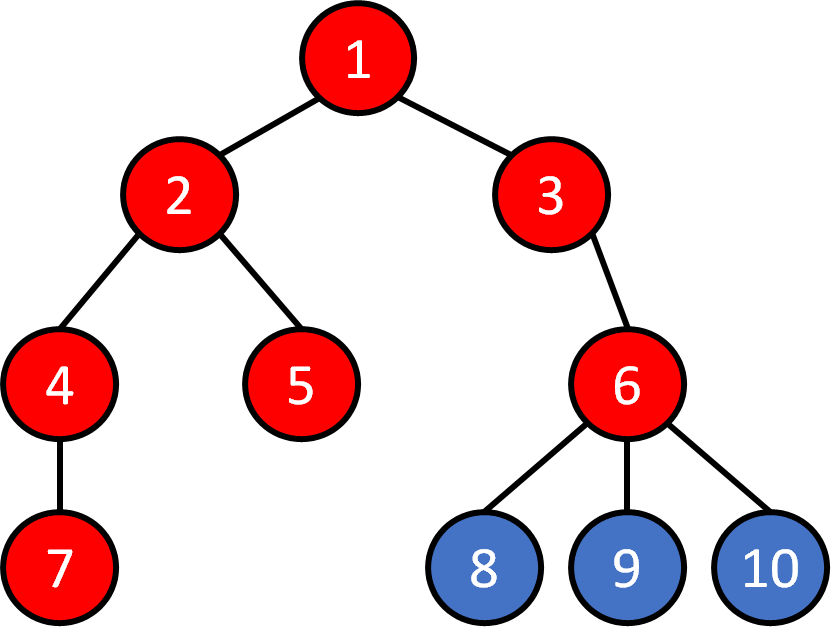
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
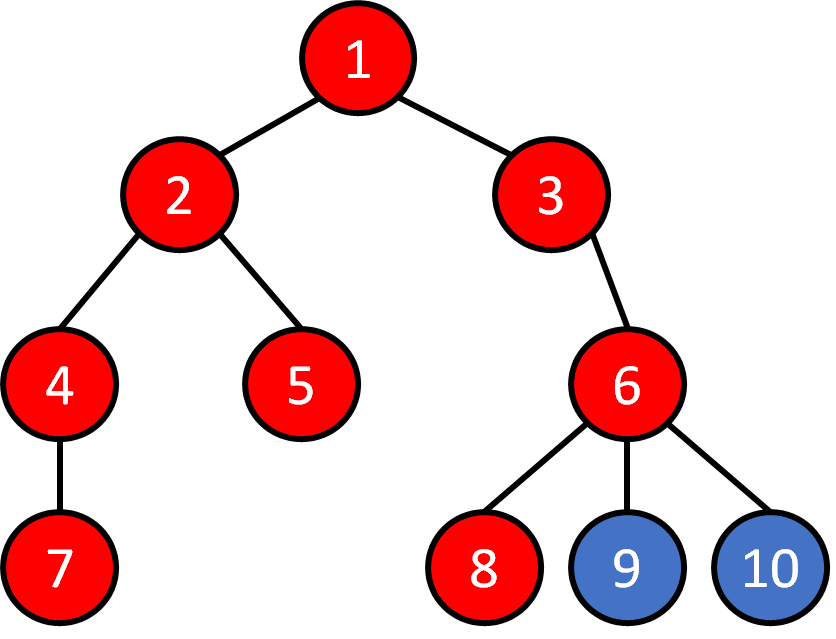
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
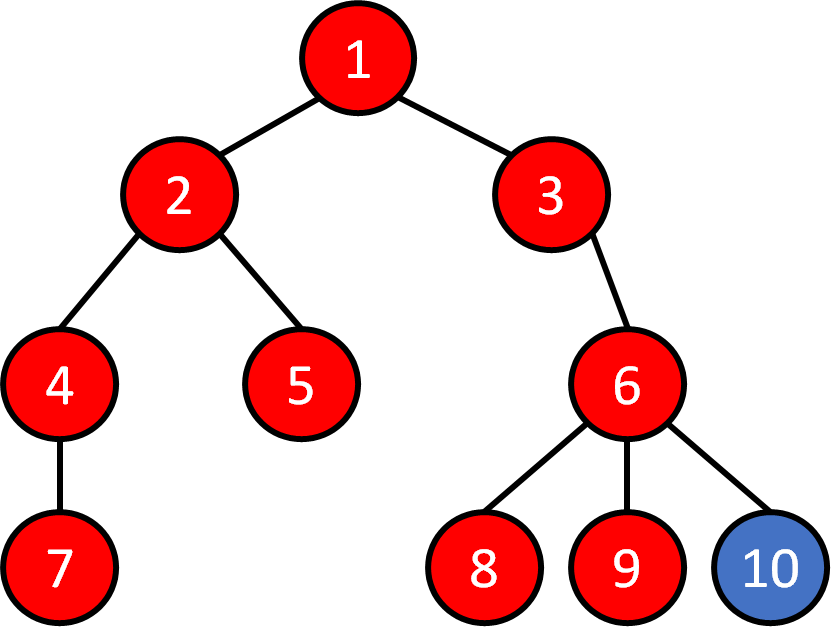
Tree - Traversal
Breadth First Search (BFS)
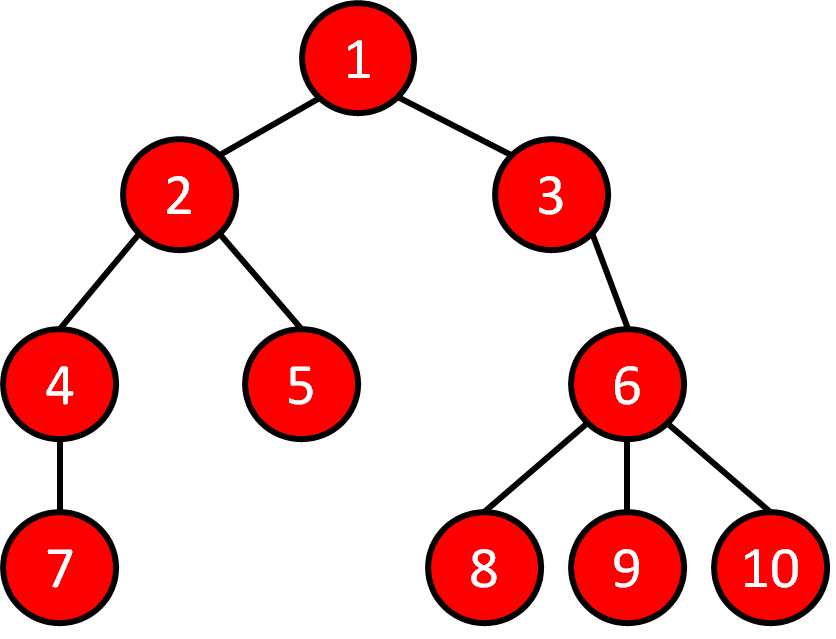
Tree Traversal - Code
Tree Traversal - Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int data[MAXN];
vector<int> child[MAXN];
void DFS_recursive(int root){
cout << data[root] << " ";
for(int i = 0; i < child[root].length(); i++){
DFS_recur(child[root][i]);
}
}
void DFS_iterative(int root){
stack<int> tovisited;
tovisited.push(root);
while(!tovisited.emtpy())
{
int cur = tovisited.top();
cout << cur << " ";
tovisited.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < child[cur].length(); i++){
tovisited.push(child[cur][i]);
}
}
}
void BFS(int root){
queue<int> tovisited;
tovisited.push(root);
while(tovisited.empty())
{
int cur = tovisited.front();
cout << cur << " ";
tovisited.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < child[cur].length(); i++){
tovisited.push(child[cur][i]);
}
}
}Binary Tree
Binary Tree
- Each Node has a most two child node
- level k has at most nodes
- a binary tree with depth k has at most
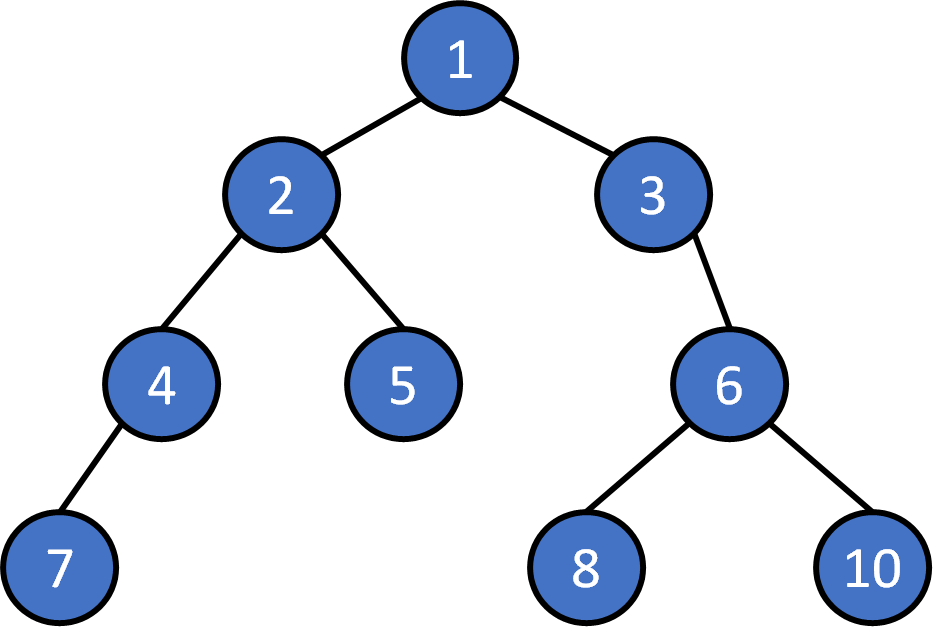
how to traversal ?
pre/ in/ post order
Complete Binary Tree
- every level is full except the last level
- last level is filled in left first.
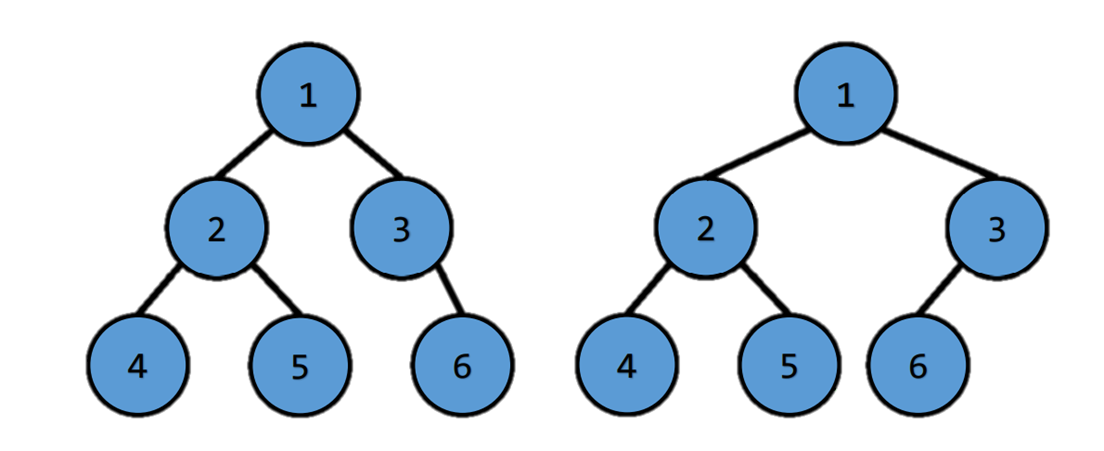
Complete Binary Tree
- indexs of childs of node k are 2k and 2k+1
- parent of node k is [k/2]
- depth of a N node complete binary tree is about log(n)
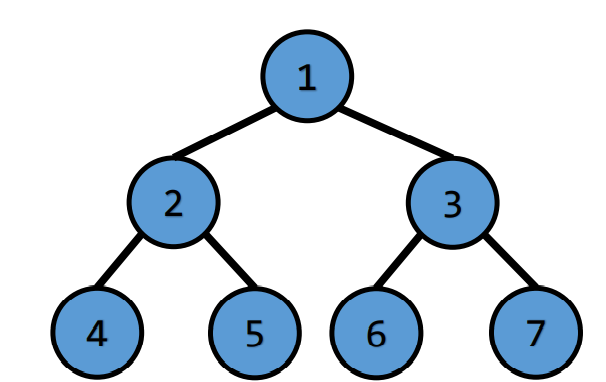
Complete Binary Tree
- So we can store it in an array !

| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|
Why storing a normal binary tree in array is not good ?
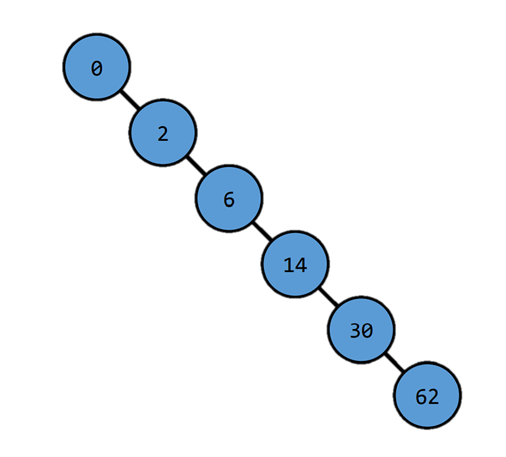
Binary Search Tree !
Binary Search Tree - Property
Definition :
- if a node has a left subtree, the value of any node on its left subtree is less than the value of itself.
- if a node has a right subtree, the value of any node on its right subtree is greater than the value of itself.
- left/right subtree of any node is also a binary search tree itself
- no duplicate nodes (same value)
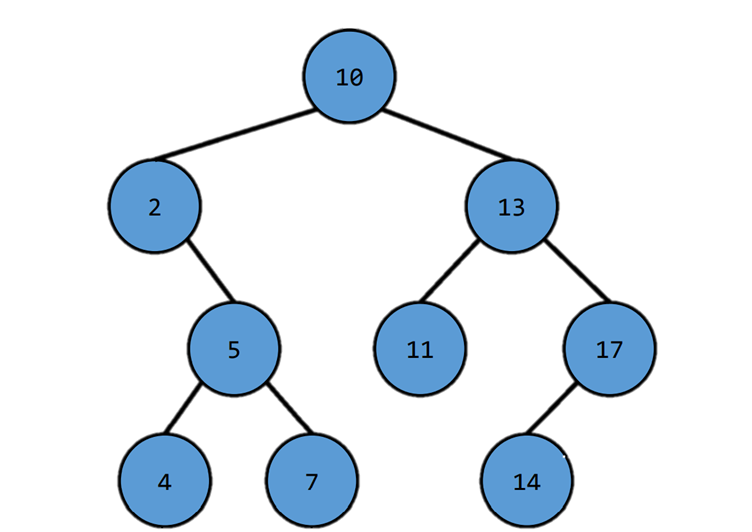
Search 8?
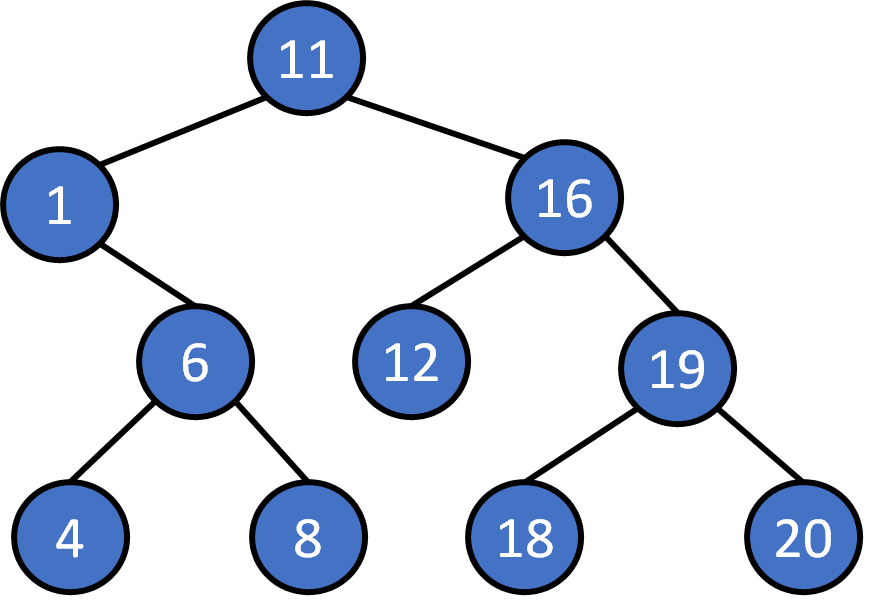
Search 8?
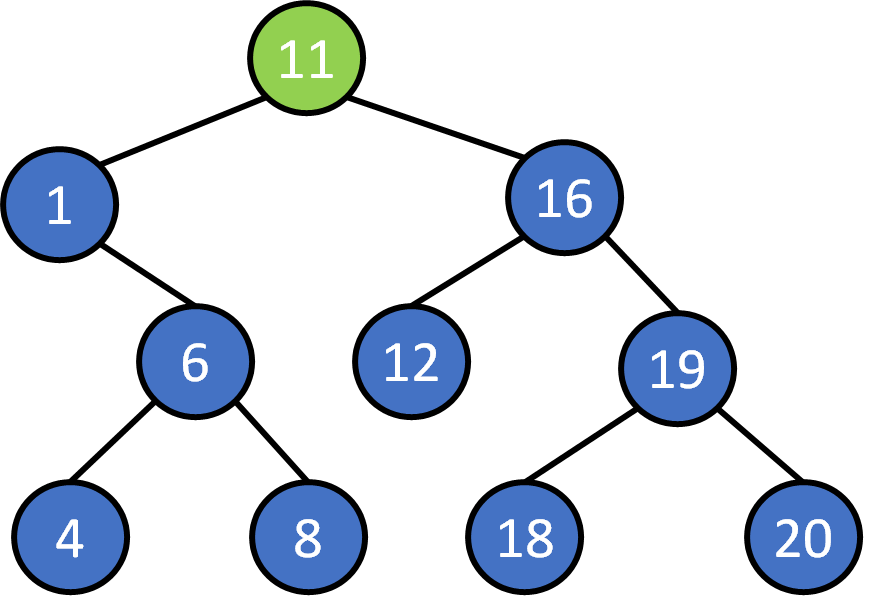
Search 8?
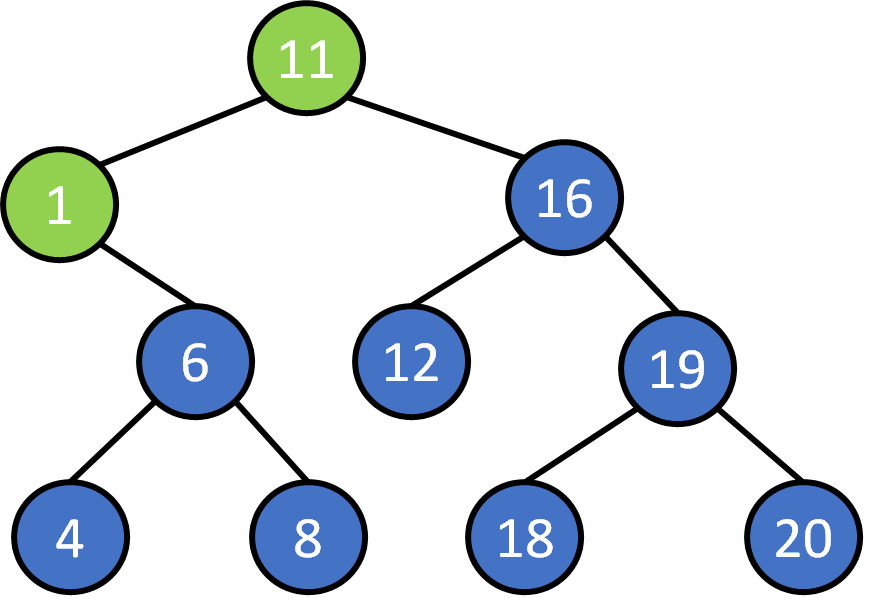
Search 8?
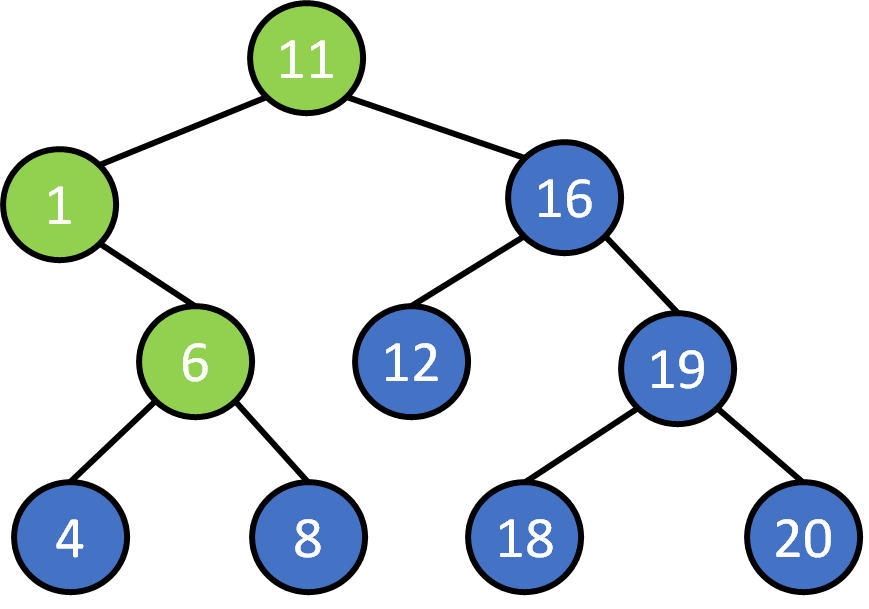
Search 8?
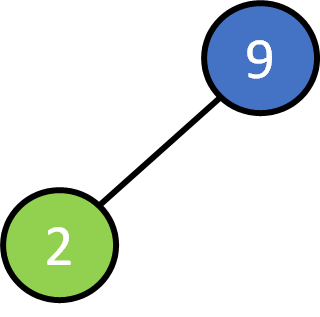
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7

9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
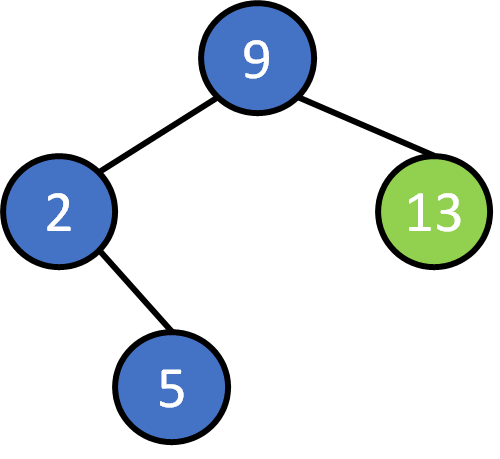
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7

9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
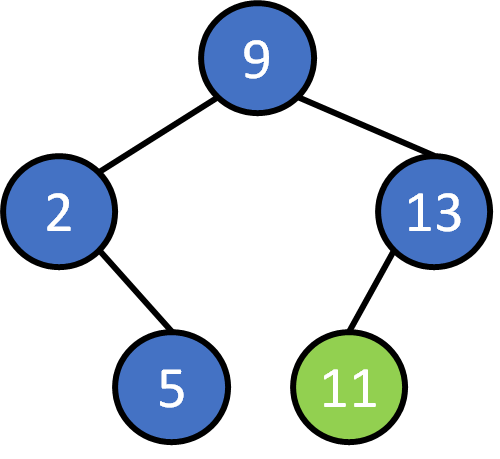
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
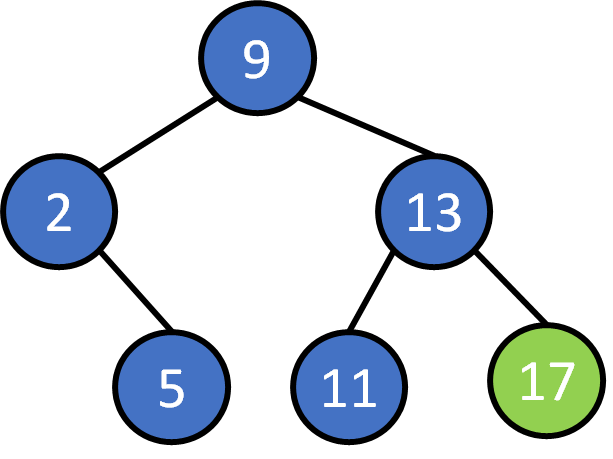
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
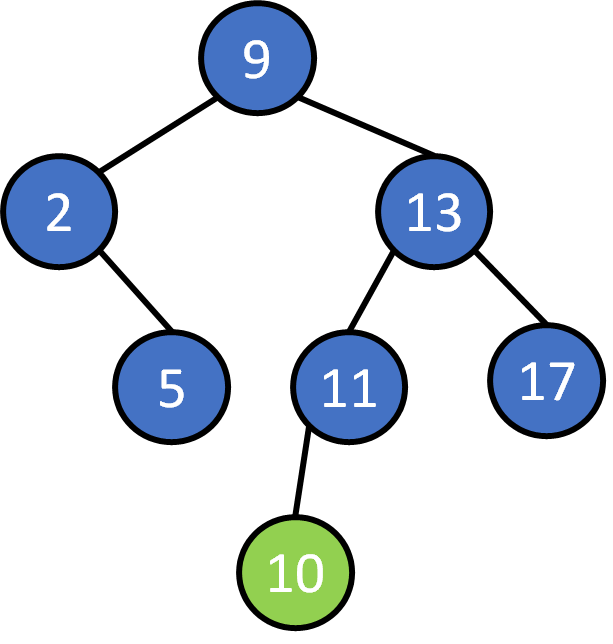
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
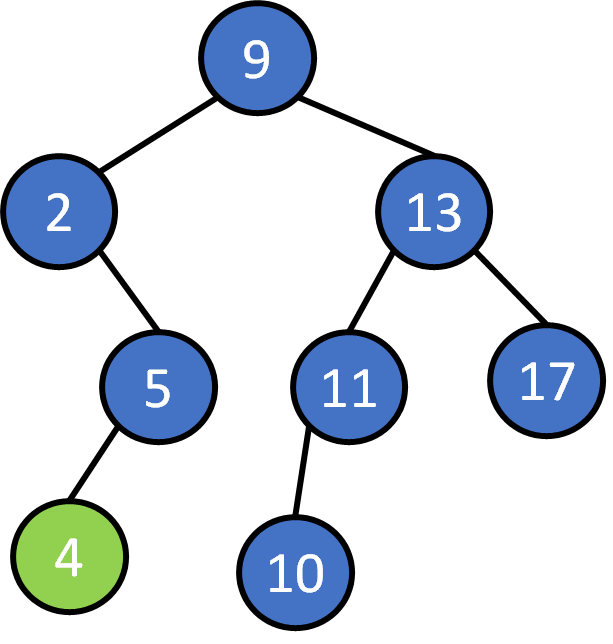
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
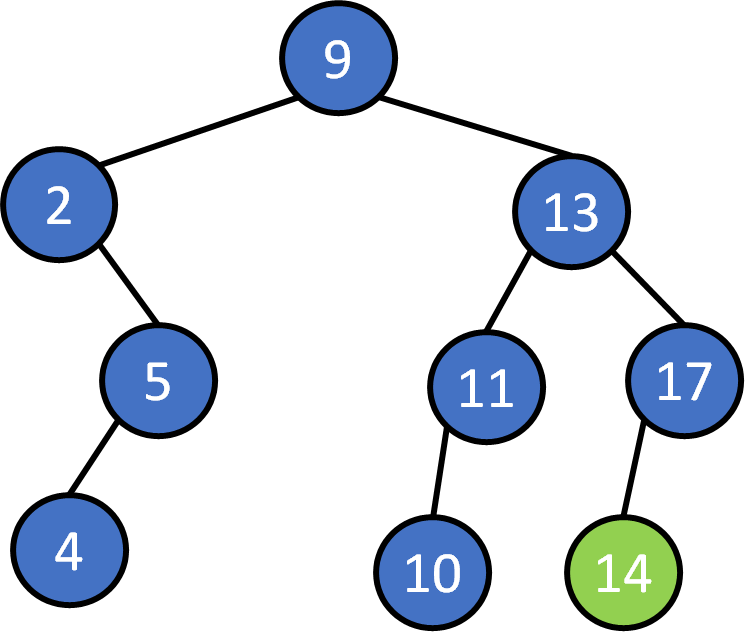
9, 2, 5 ,13, 11, 17, 10, 4, 14, 7
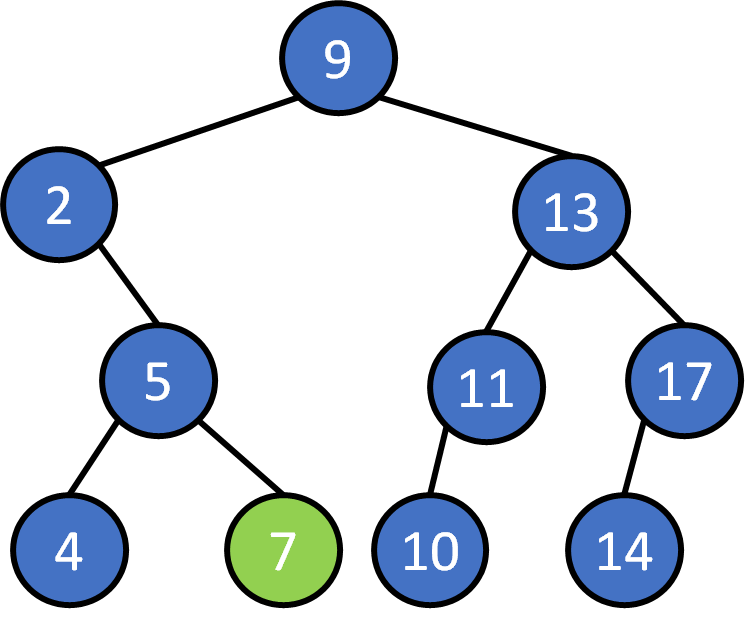
delete 13 ?
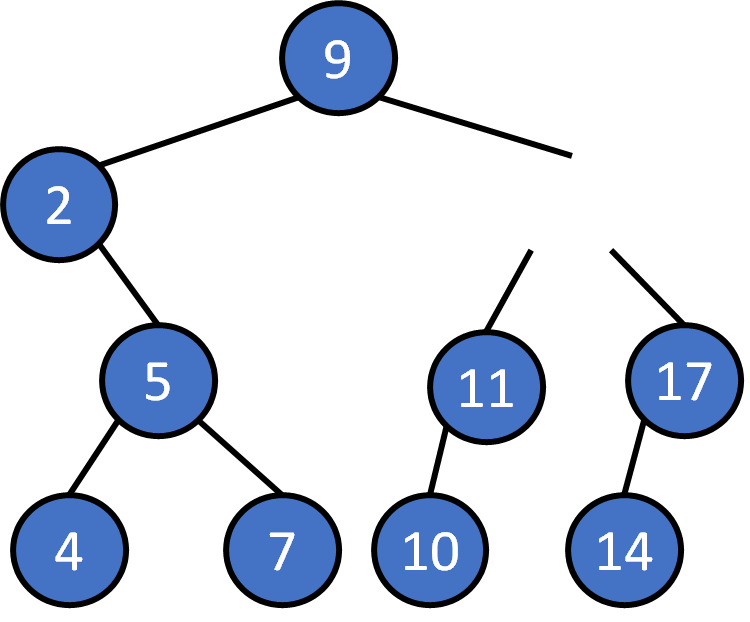
delete 13 ?
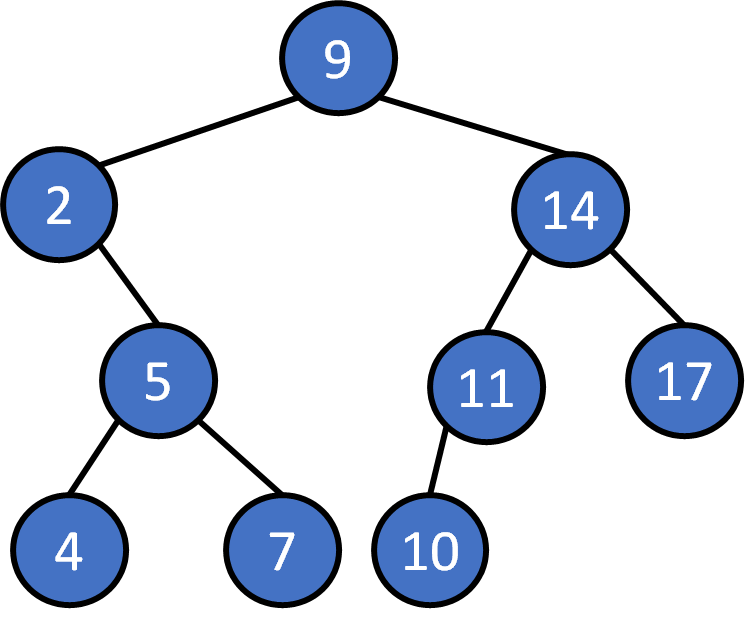
Time complexity ?
- add Node
- O(h), h is the depth of the tree
- search a value
- O(h), h is the depth of the tree
- delete a value
- O(h), h is the depth of the tree
- When binary tree with N nodes, time complexity is O(log N)
?

Insert in what order ?
depth -> log N N