Graph
Graph
- Introduce, Definition
- How to store a Graph
- DFS, BFS on Graph
- Connected Component number
- Bipartite Graph
Graph
Introduce, Definition
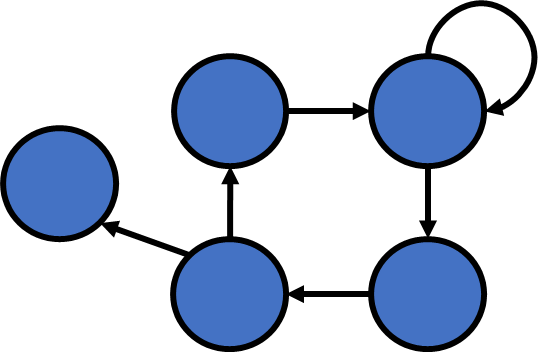
Definition
- Vertex
- Edge
- Graph: a set of vertex and a set of edges
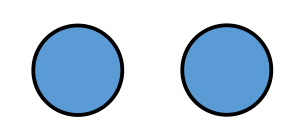

Definition
- Directed Edge
- Undirected Edge
- Directed Graph
- Undirected Graph
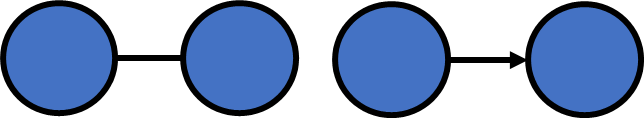
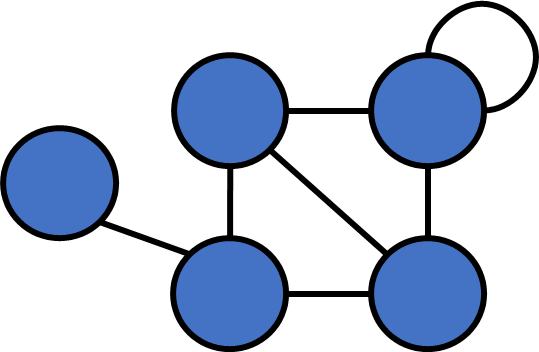
Definition
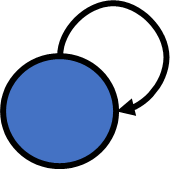
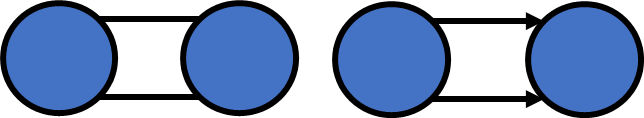
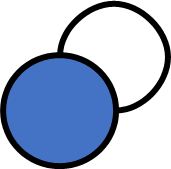
- Multiple edges
- Self loop
Definition
- degree: number of edges related to a vertex V
- in-degree: number of edges that go into a vertex V
- out-degree: number of edges that come out from a vertex V
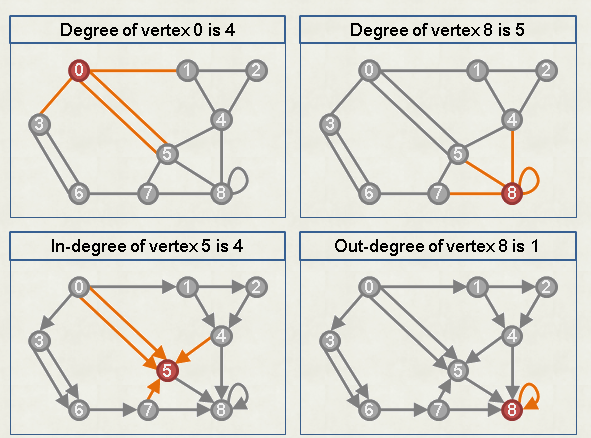
Definition
- degree: number of edges related to a vertex V
- in-degree: number of edges that go into a vertex V
- out-degree: number of edges that come out from a vertex V
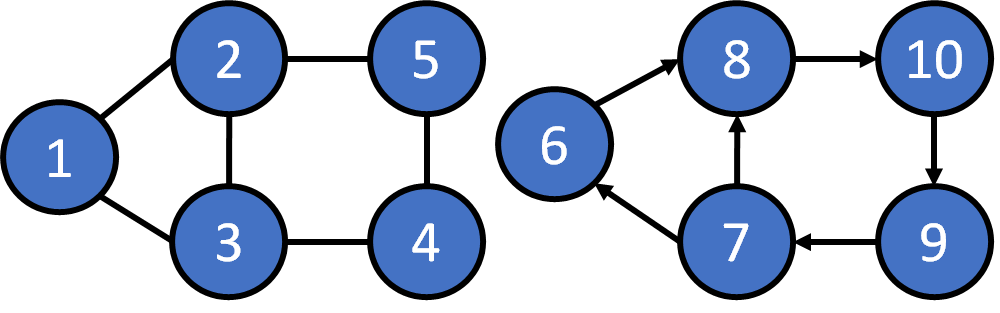
Definition
- path: a set of edges that join a sequence of vertices
- a path from vertex A to vertex B
- length of the path:
- the number of edges on the path
- The sum of the weight of edges on the path.
Definition
- cycle: a path starts and ends in the same vertex
- if not specified, a path can contain cycles
Definition
- Connected Graph : there must exist a path between two distince vertices in the graph
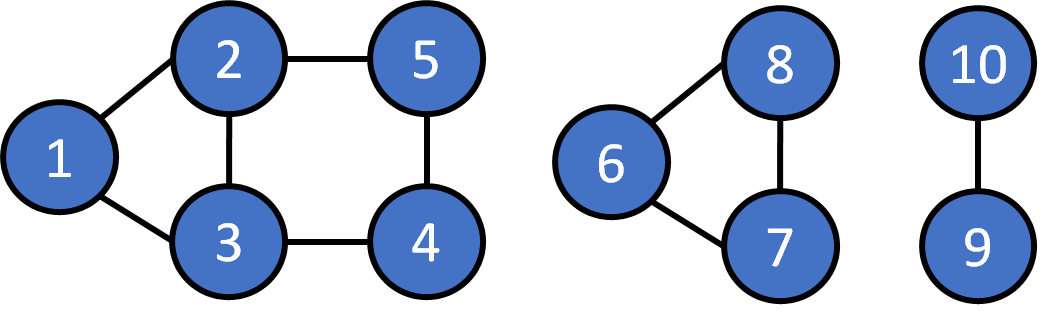
How to store a graph
- Use linked list, take a vertex as a node, use pointer to recode the neighbor of the vertex
- cons: complicated implementation
- Undirected edge can be treat as two directed edges
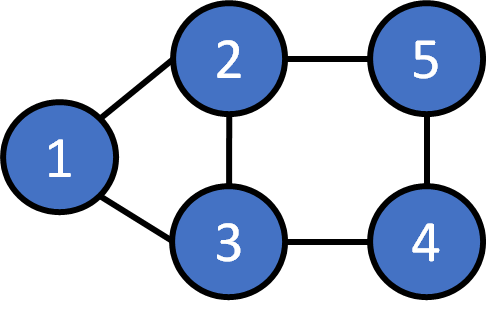
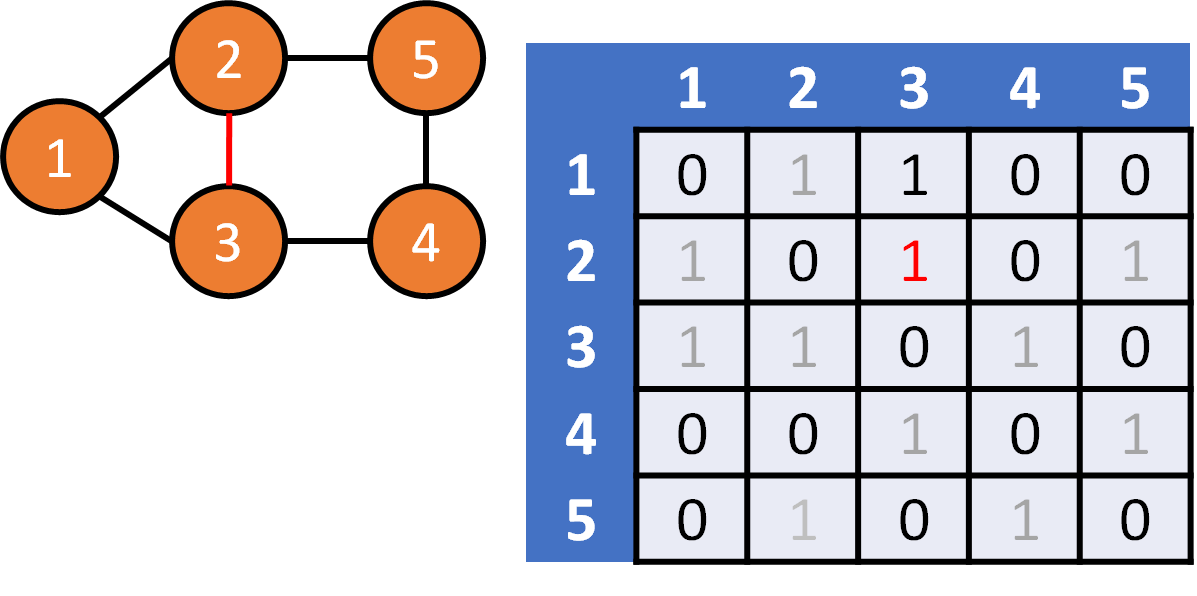
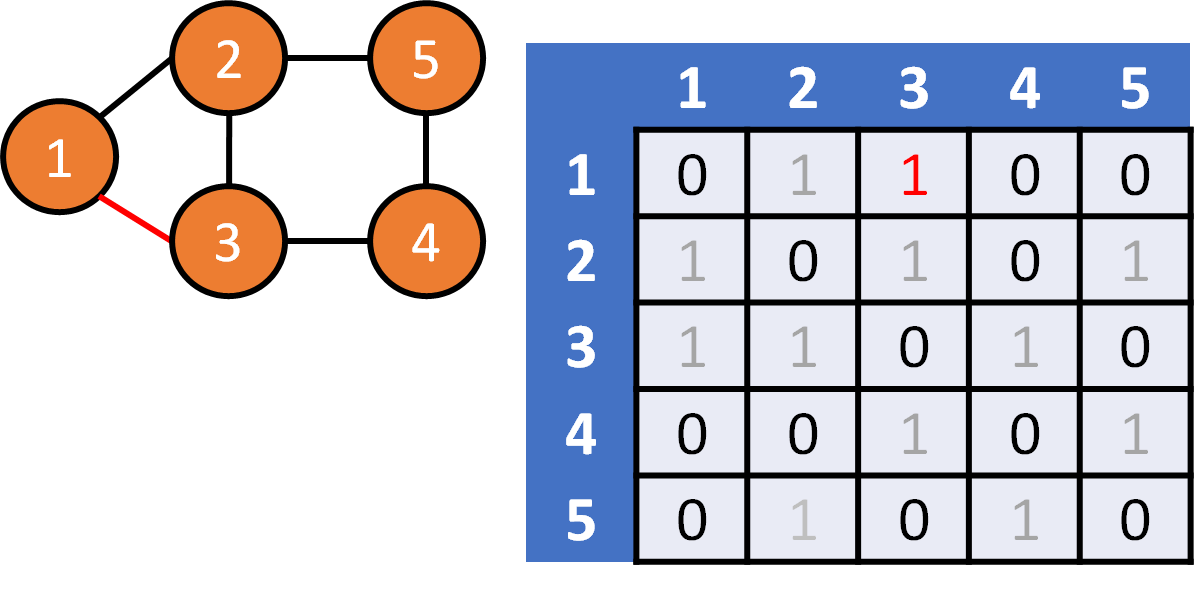
adjacency matrix
Undirected Graph
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
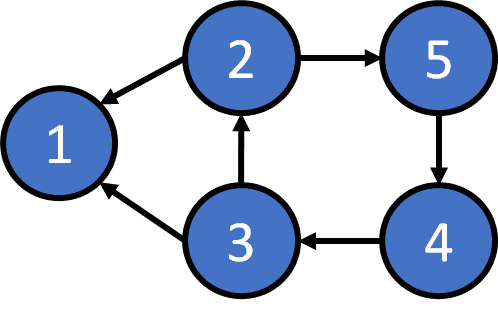
adjacency matrix
Directed Graph
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
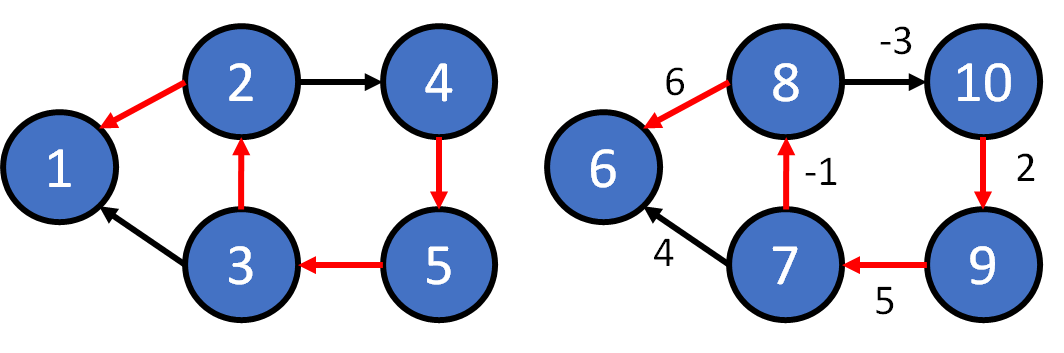
adjacency matrix
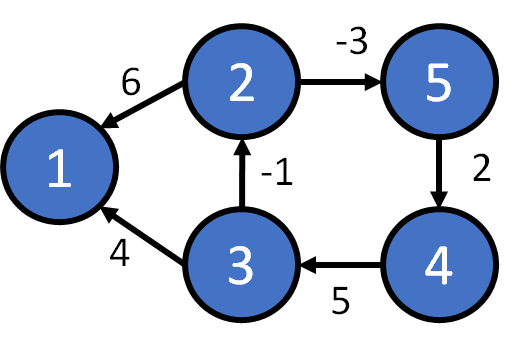
Directed Graph + weight on edges
(unweight => weight = 1)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 2 | ? | 6 | ? | ? | -3 |
| 3 | 4 | -1 | ? | ? | ? |
| 4 | ? | ? | 5 | ? | ? |
| 5 | ? | ? | ? | 2 | ? |
Method 2: adjacency list
Undirected Graph
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |
| 4 | 3 | 5 | ||
| 5 | 2 | 4 |

each vertex stores a list of its neighbors
(one of the implementations: linked-list)
Directed Graph
Method 2: adjacency list

| 1 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 5 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 4 | 3 | |||
| 5 | 4 |
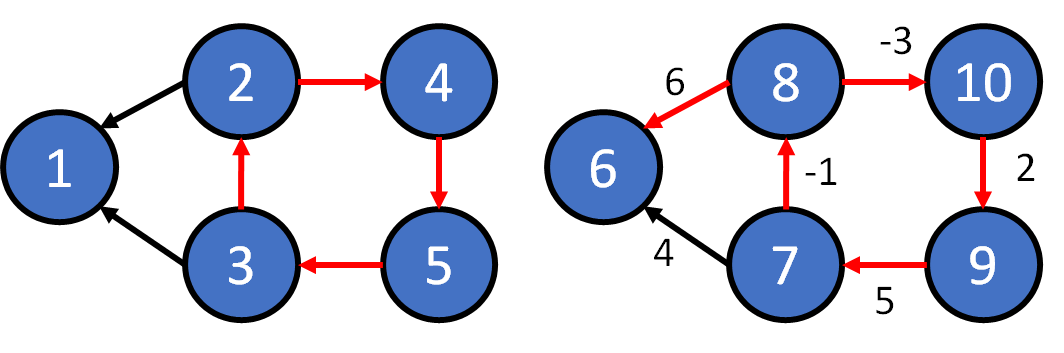
Method 2: adjacency list
Directed Graph + weight on edges
in u's list we store (v, cost)
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | (1, 6) | (5, -3) | ||
| 3 | (1, 4) | (2, -1) | ||
| 4 | (3, 5) | |||
| 5 | (4, 2) |

Comparison
| Adjacency Matrix | Adjacency List | |
|---|---|---|
| Space Complexity |
||
| Ask if there is an edge between two node | ||
| Iterate every edge of a node |
O(V^2)
O(1)
O(V)
O(E)
O(\text{degree}(V))
O(\text{degree}(V))
DFS, BFS on Graph
Similiar with DFS, BFS on tree
DFS on Graph
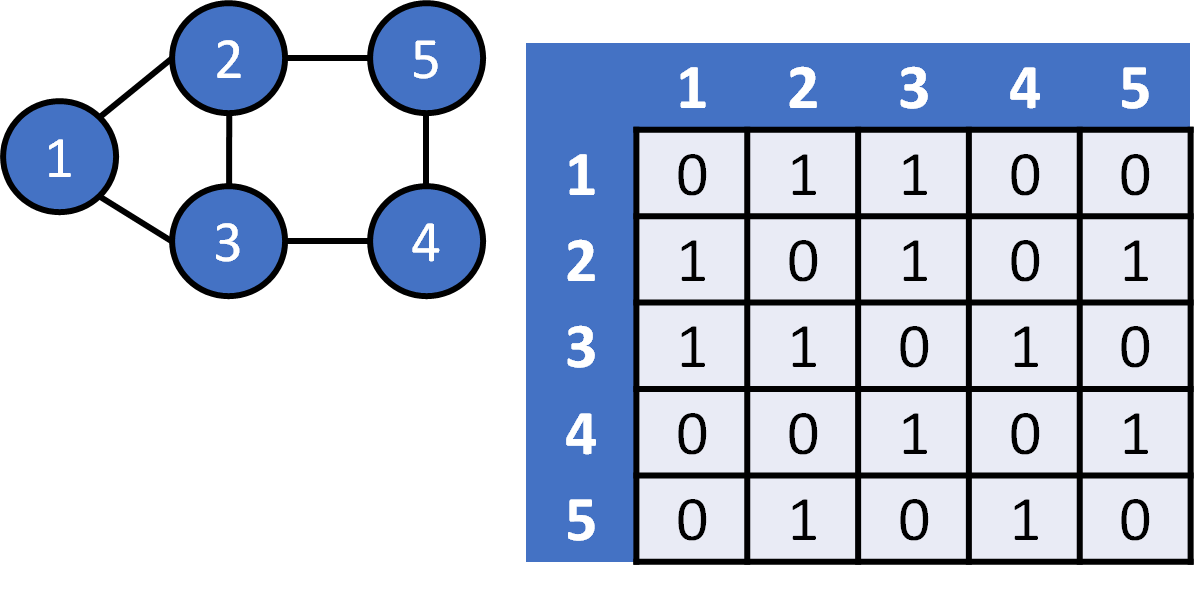
DFS on Graph
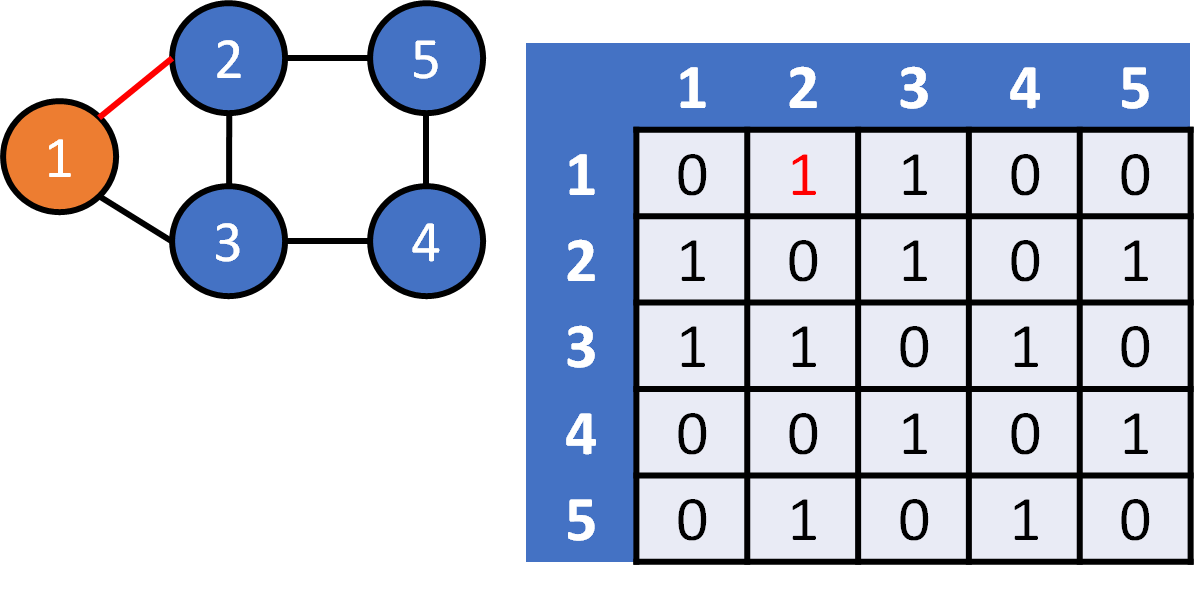
DFS on Graph
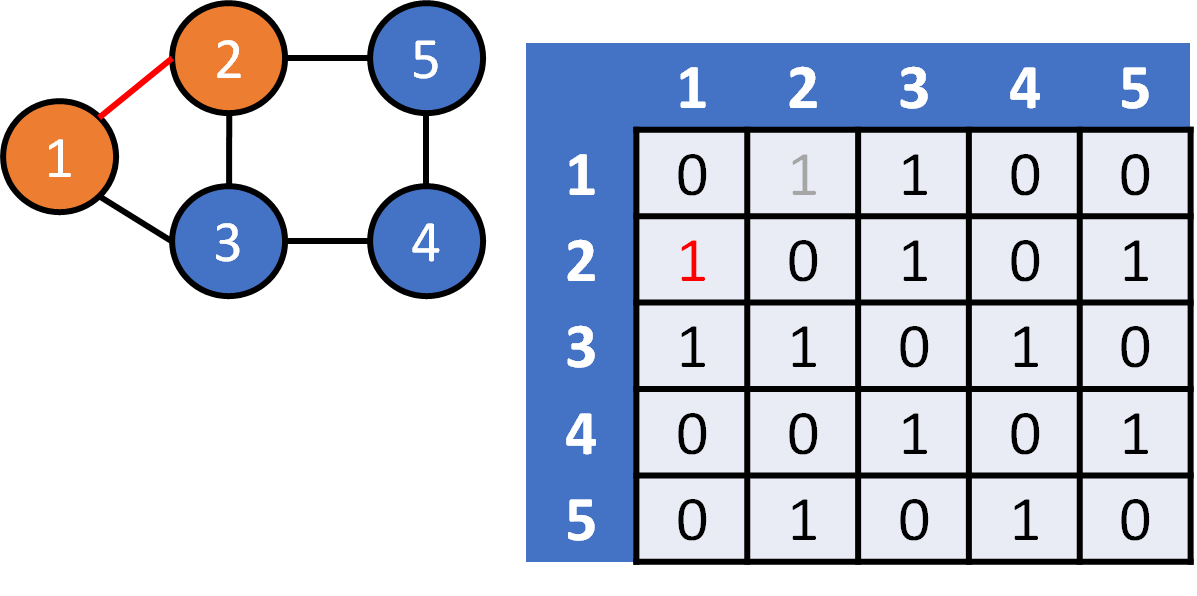
DFS on Graph
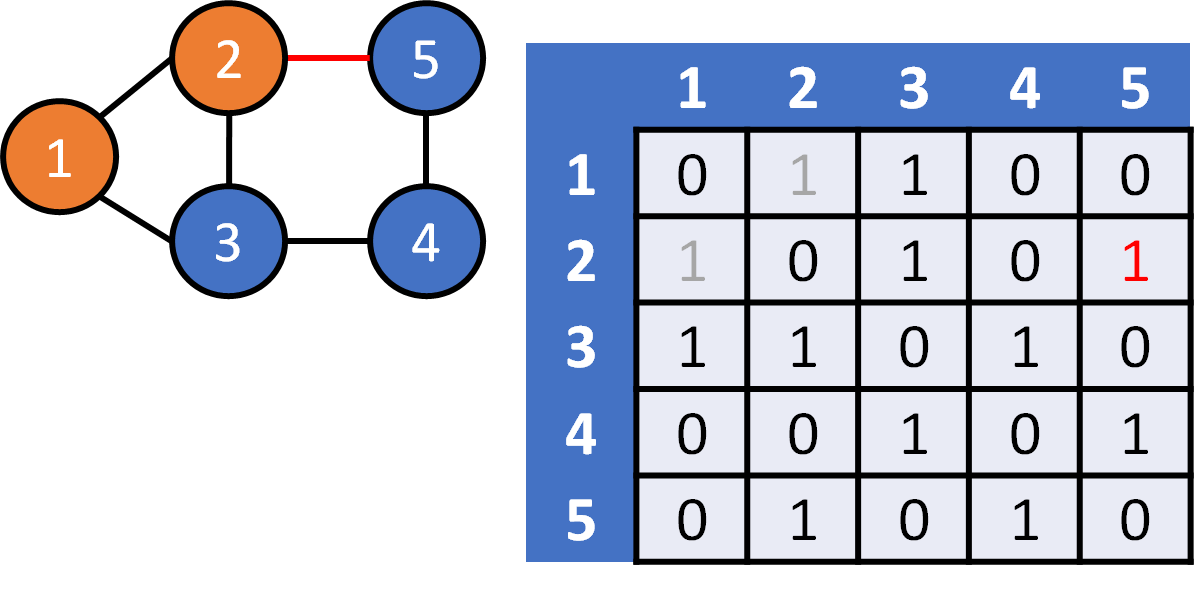
DFS on Graph
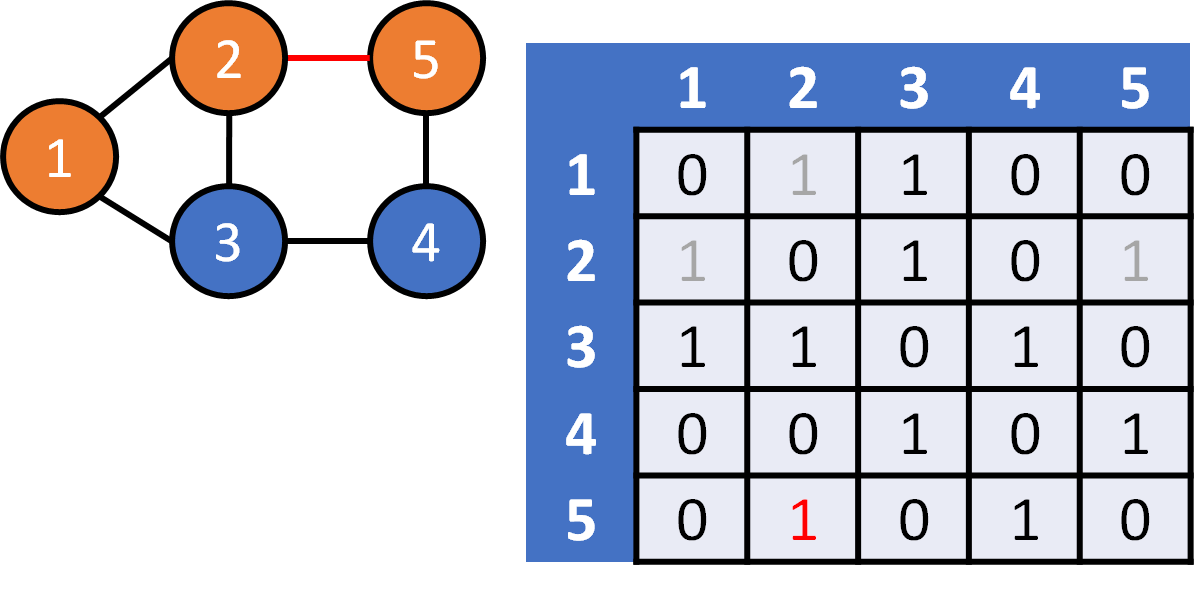
DFS on Graph
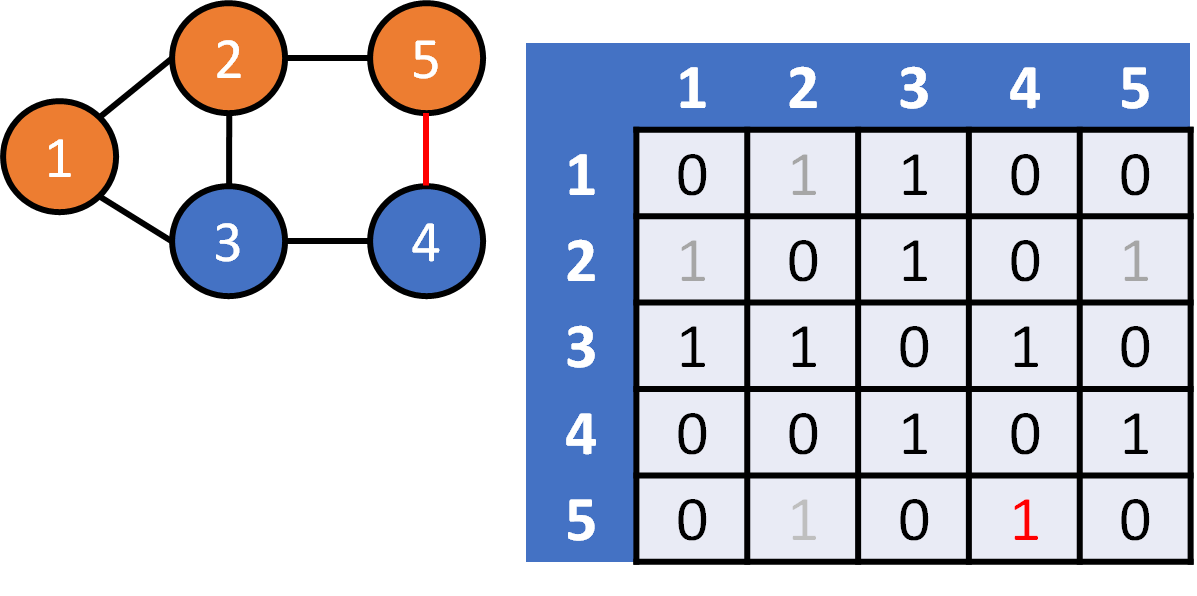
DFS on Graph
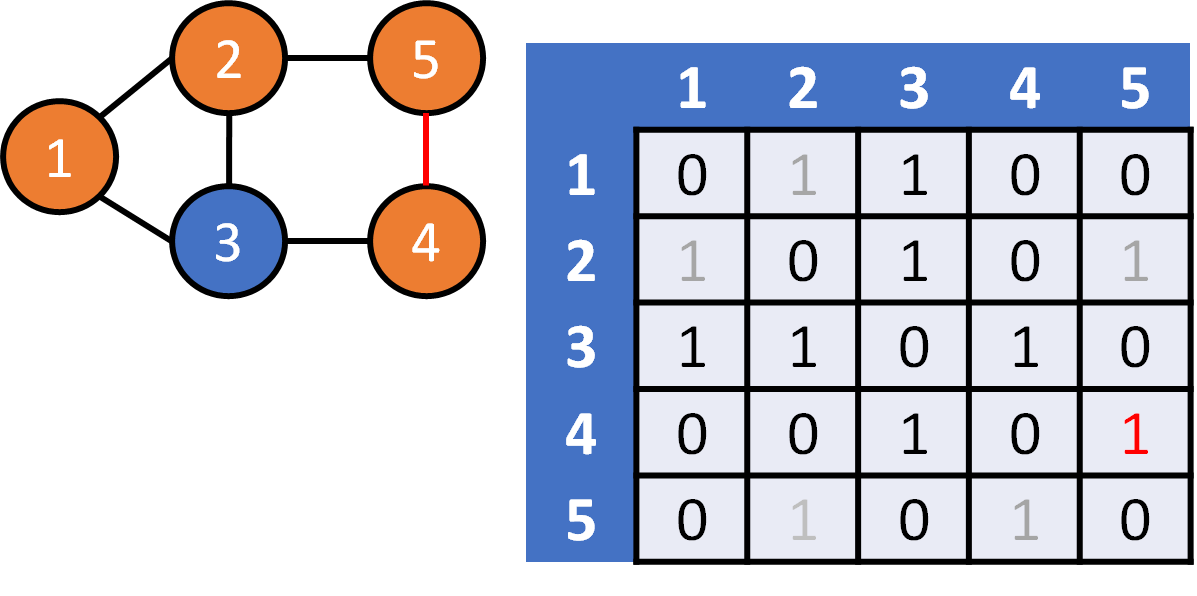
DFS on Graph
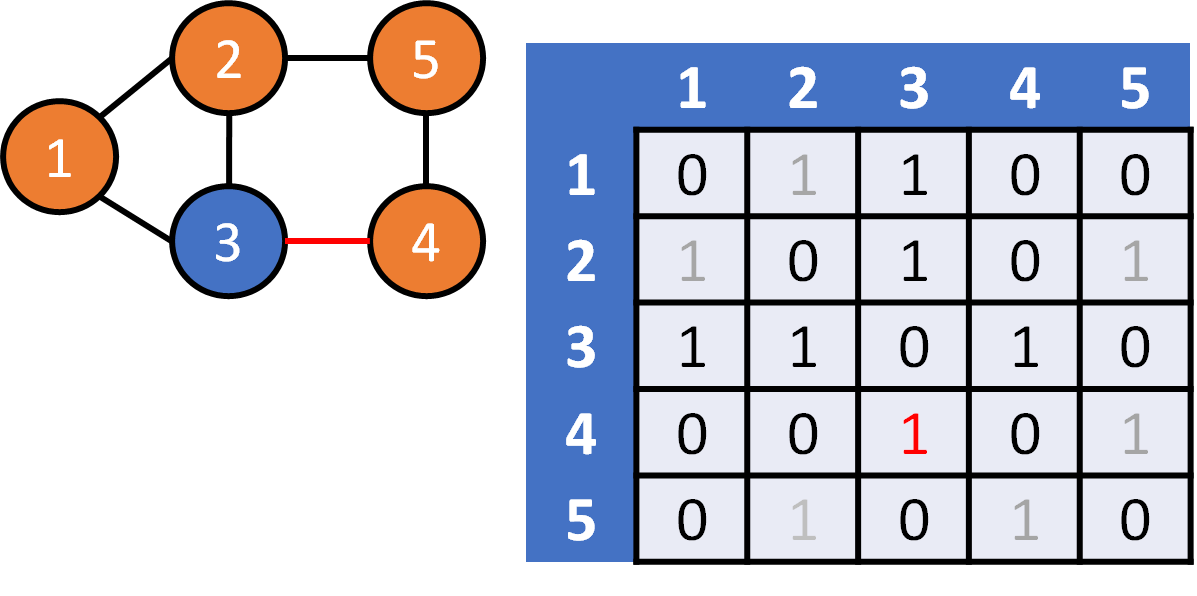
DFS on Graph
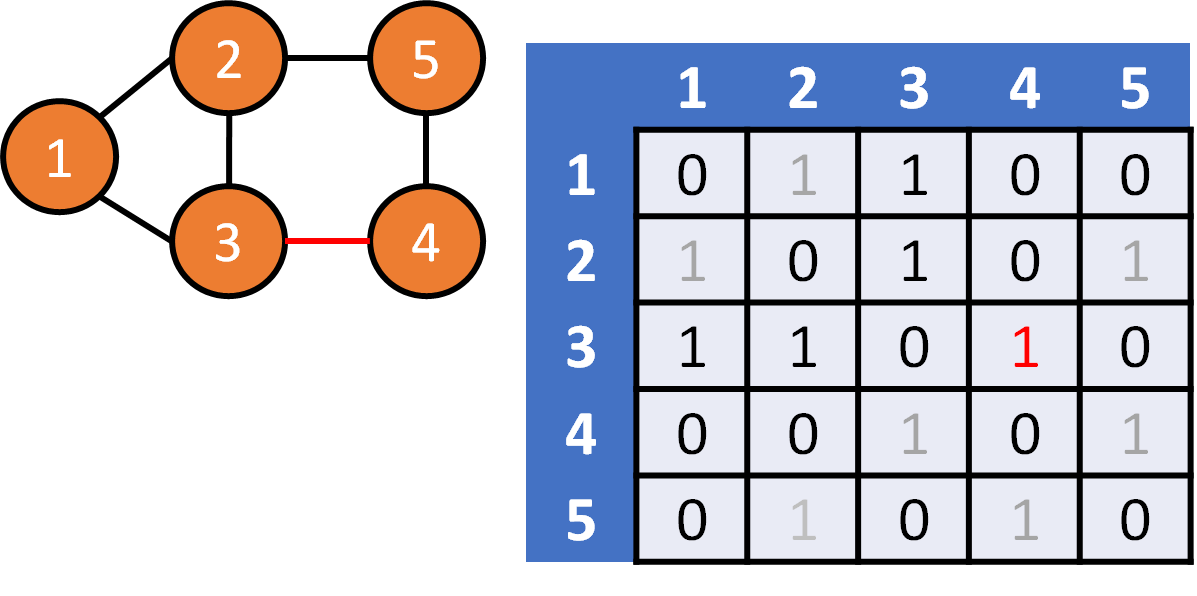
DFS on Graph
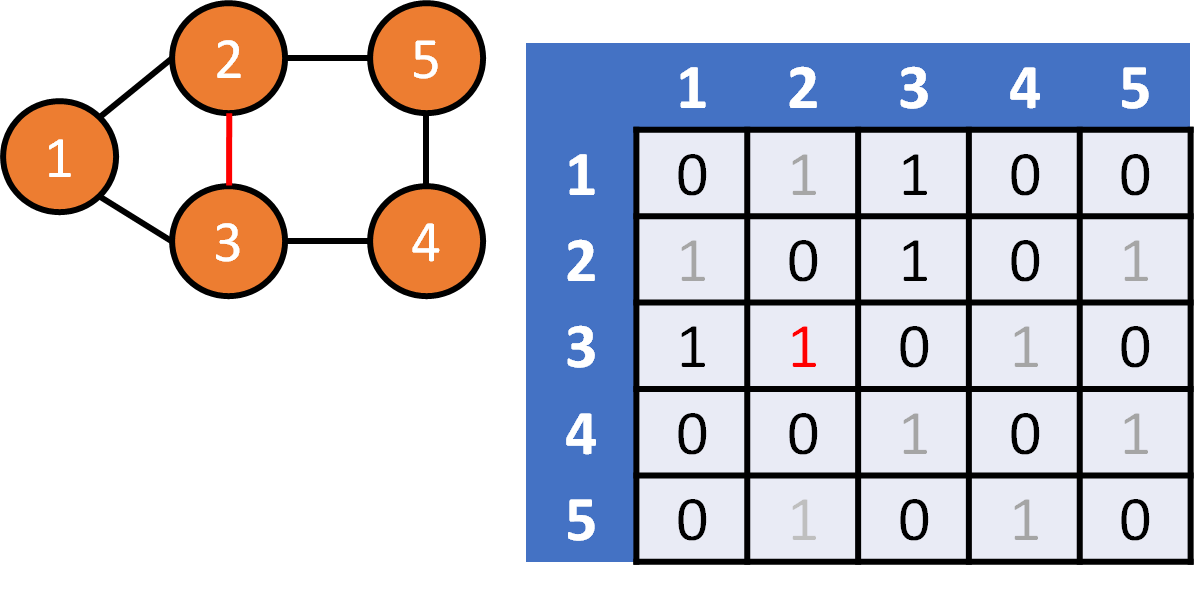
DFS on Graph
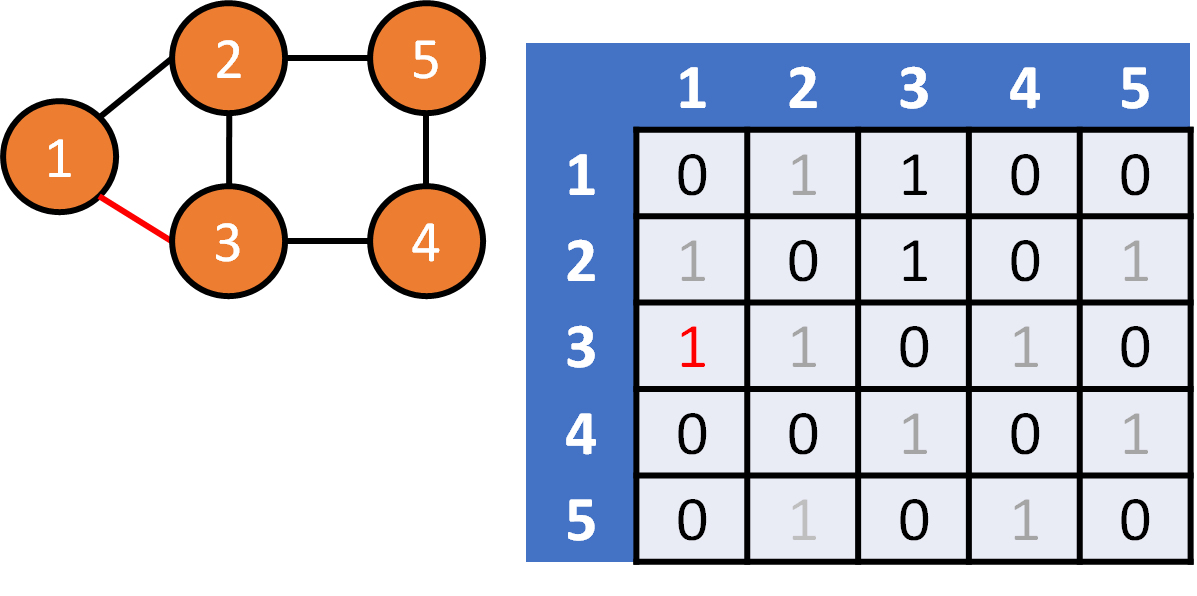
DFS on Graph
DFS on Graph
DFS, BFS on Graph
- Record if a vertex has been visited to prevent visit multi-times.
- Check if a vertex is visited before visiting it.
- Remember to mark a vertex as visited after visiting it.
Main cause of RE, TLE
Code of DFS((adjacency matrix)
const int n = 10000;
int G[n][n]; // edge index;
bool visited[n];
void init()
{
for(int u = 0; u < n; u++)
visited[u] = false;
}
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
G[u][v] = 1;
G[v][u] = 1;
}
void DFS(int u)
{
visited[u] = true;
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++)
{
if(G[u][v] == 1)
{
if(visited[v] == false)
DFS(v);
}
}
}
Code of DFS(adjacency list)
const int n = 10005
vector<int> G[n]; // adjacency list
bool visited[n];
void init()
{
for(int u = 0; u < n; u++)
{
visited[u] = false;
}
}
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u); // if undirected
}
void DFS(int u)
{
visited[u] = true;
for(int i = 0; G[u].length(); i++)
{
int v = G[u][i];
if(visited[v] == false)
{
DFS(v);
}
}
}Code of BFS
void bfs(int v){
queue<int> tv; // tovisited
tv.push(v);
while(!tv.empty())
{
int u = tv.top();
tv.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); i++){
if(visited[G[u][i]])
continue;
visited[G[u][i]] = true;
tv.push(G[u][i]);
}
}
// G[v] is a array store all neighbor of a vertex v
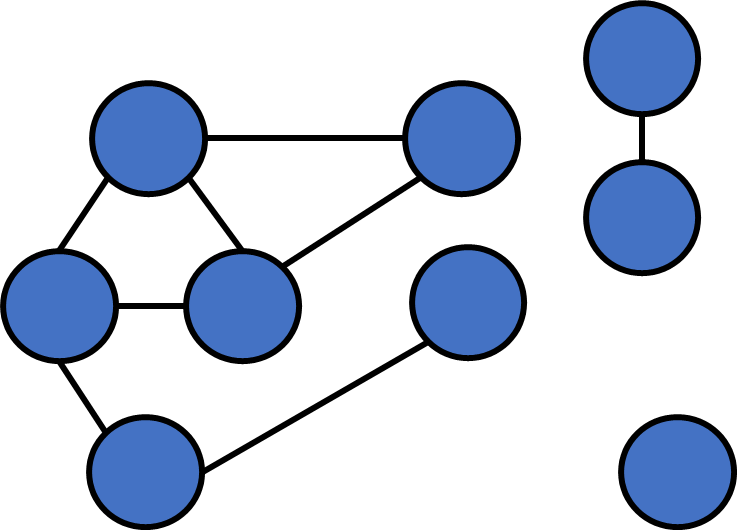
}Numbers of connected components?
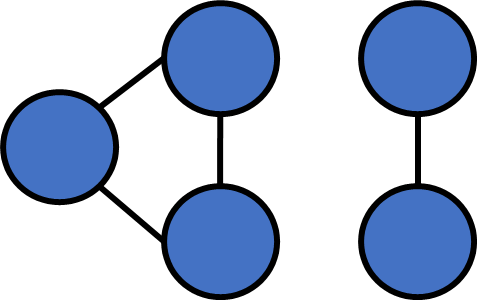
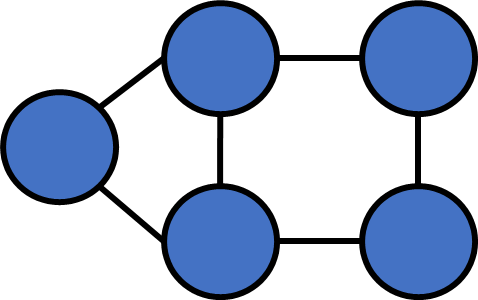
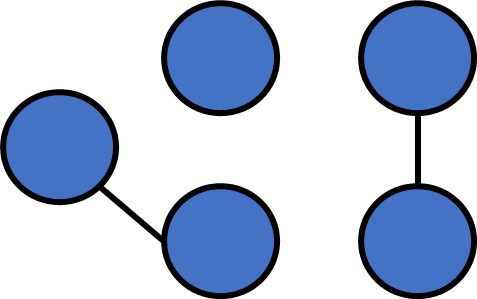
Number of connected components
After a single round of DFS, all vertices in the same c.c will be visited.
In contrast, vertices that aren't in the same c.c. won't be visited.
Number of connected components
After a single round of DFS, all vertices in the same c.c will be visited.
In contrast, vertices that aren't in the same c.c. won't be visited.
We can just count how many rounds DFS it takes to visit all vertices!
Number of connected components
int cnt = 0; // count
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) // 0 ~ V-1
{
visited[i] = false;
}
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
if(!visited[i]){
dfs(i);
cnt++;
}
}Homework