Feudal society
UNIT 2

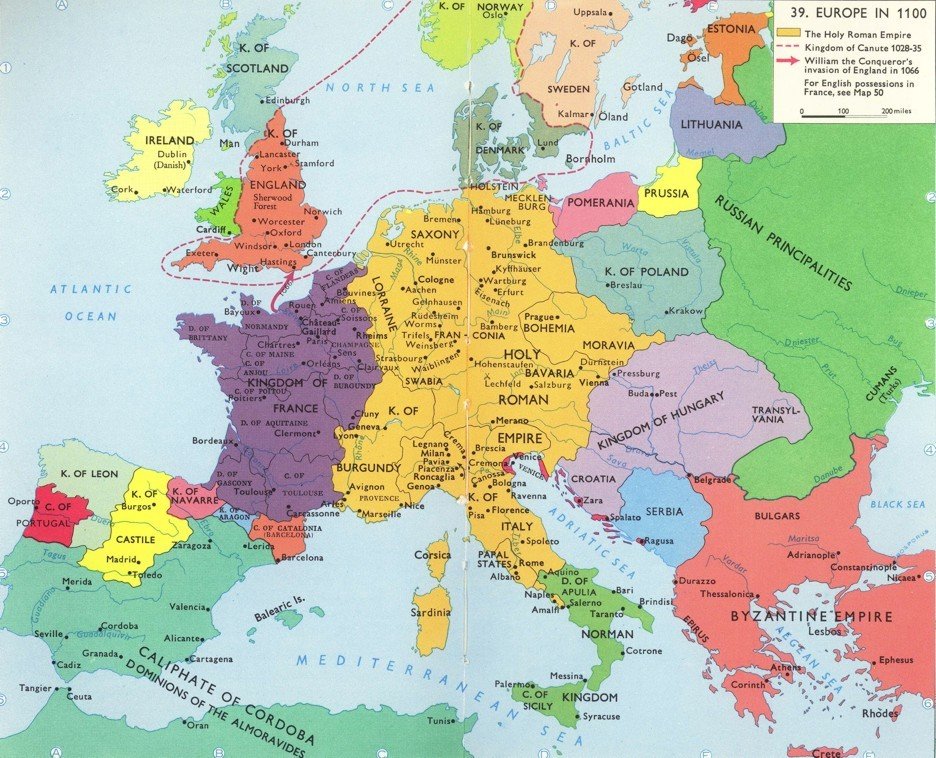
New
Invasions
9th -10th Centuries
Western Europe
was invaded by
VIKINGS
MAGYARS
and SARACENS
and...

Feudalism
This new wave of invasions caused insecurity and violence ...
created
a new form of society...
Small kingdoms
were created and
united by
Religion
Trade
and Social structure
The main religion -Roman Christianity
in the East
Orthodox Cristianity

Overland trade routes made communication and trade better

Social structure -
nobility/clergy and peasants/serfs
Monarchies lost power
- Didn't control all their terrritory
Kingdoms divided
between king's children
so
smaller, weaker kingdoms
- Didn't have large armies
- Couldn't collect taxes

- Depended on lords/nobility to provide soldiers
Beginning of new social, political and economic structure called FEUDALISM
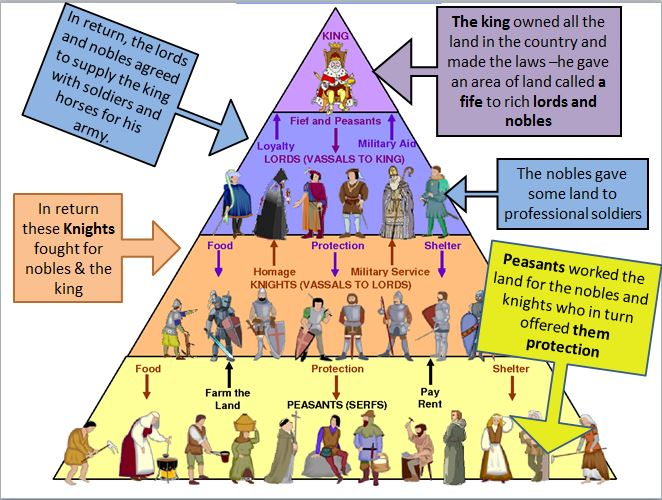
FEUDAL TIES
KNIGHTS / SOLDIERS
(vassals to the lord)
FREE PEASANTS / SERFS
LORDS/NOBILITY
(vassals to the king/queen)
KING or QUEEN
provide military assistance
provide land / fief
provides land / fief
provide military assistance
work the land
protection / place to live
Important words
homage
swear/swore
allegiance
vassal
loyalty
lords/nobles/baron
fief/manor
grant
Rendir homenaje
jurar lealtad
vasallo
lealtad
señor feudal
feudo/ grant of land
dar

Ceremony of homage
A vassal (noble) promised loyalty and military assistance
to the king
This video explains
FEUDALISM - a new social and political system that started in the 9th and 10th Century in Western Europe
1. Explain the agreement/deal that the kings made with the nobles/lords.
a) What did the kings give the nobles
b) What did the nobles give the king
2. Explain the order of society.
3. What role did the peasants have?
4. Why was FEUDALISM a benefit for people during the Middle Ages?
5. Why were castles important
FEUDALISM
Watch the video and answer the questions
FIEF...

Text
the DEMESNE, PLOTS of land
and VILLAGES

King/lord/noble lived here
DEMESNE included the castle...

Everything on the demesne belonged to the Lord.
The peasant paid to use the lord's land.
...and farmland, meadows and forest
Forest - hunting and wood
Farmland - to grow food


The serfs/peasants needed the Lord's permission to HUNT or get WOOD for fire
worked the land and gave the lord the products in exchange for living on the fief


Village - where the free peasants lived
Plots of land
peasants worked
Mill -
grind grains
to make
bread

Oven - to cook food


Press - make wine and oil

Privileged Estates
Three Estates
NOBLES and
KNIGHTS
COMMONERS
serfs and
free peasants
CLERGY
monks/nuns
military power
defended the land
pray,
kept records
worked the land
traded, made crafts
SERFS
Serfs - Not free to leave the fief
Didn't recieve money for work
Received food and shelter for work
Born a serf,
died a serf

Free Peasants
Free to make personal decisions
Owned small pieces of land called plots
Lived in villages
Paid taxes to the lord
to use
the MILL, PRESS and OVEN


Peasants's and Serf's daily work

Main crops - cereal and vegetable

Kept animals


Serf's Agricultural work
Everyone in the family
worked all day long
Typical farming tools
Roman Plough

TWO YEAR ROTATION
No fertiliser to grow food.
GOOD because
the cultivated land more fertile
BAD because
only used half the land
cultivated less food
fallow


Lived in small villages
Houses made of wood and mud
had small vegetable gardens
Shared the house with the animals
Peasants' Villages
Self-sufficient:
Cultivated their own food
Made their own clothes
Furniture and houses
Outside the villages
Had vineyards,
olives and grain


In the forest -
collected wood, fruit and
hunted
The Nobility
Lower Nobility


Upper Nobility
owned large estates(fiefs)
had titles:
DUKE, COUNT, MARQUIS
Knights -
came from rich families
owned horse and weapons

Provided protection for
the King
or other
richer nobles
Responsible to
defend
the population
Knights

A 7 year old boy
from weathly family
went to live with a knight
as his servant and student
PAGE
How to become a knight
Learned to read, sing, fight and play chess
SQUIRE

When he showed that he had learnt everything...
A 15 year old boy
trained with the knight
and helped him.
KNIGHTS

...the SQUIRE became a knight in a special ceremony.

When the king didn't need military help
the knights practised in tournaments
MEDIEVAL KNIGHTS
What were the steps to become
a knight?
Name some of the responsibilities that a squire had?
What was CHIVALRY?
Name some of the WEAPONS and ARMOUR?
What did knights do in TOURNAMENTS?
Watch the video and answer these questions
NOBLE WOMEN

Arranged marriages
Better educated than men
Took care of house & children
Made clothes
Unmarried women
went to convents
Recieved higher level
of education

CLERGY
Baptism
Marriage
Last Rites
when and where a child was born, his/her name and parents' names
who was married and
who were their children
when a person died, where they were buried
Monks, priests, nuns performed religious functions
and produced important records/archives
about the population. For example...

Lived in monasteries
Isolated from other people
CLERGY
Had political power, economic power
and cultural power
Political Power

Catholic Church
Only church in Western Europe/Christiandom
Could EXCOMMUNICATE the King
King lost all his vassals and became unprotected and weak.
The POPE was the head of the Catholic Church
Economic Power

Recieved money and land
Peasants gave some of their harvest (a tithe)
to the Church
Had serfs to do all manual work
Copied and translated ancient written works
Culture

Created manuscripts and copied artwork
in the scriptorium
Spread of Christianity
in the 11th-13th century
CURSADES
Military expeditions to recover JERUSALEM from the Muslims
TEMPLARES
Military orders
of monks and knights
that fought against
the Muslims

Life in a Castle
CLERGY

KIngs did not have
a permanent residence
Monarchies travelled with
the COURT - family, soldiers and
palace officials
The CURIA were
church and palace officials,
lawyers, nobles and soldiers
The CURIA
helped the kings rule