ES7
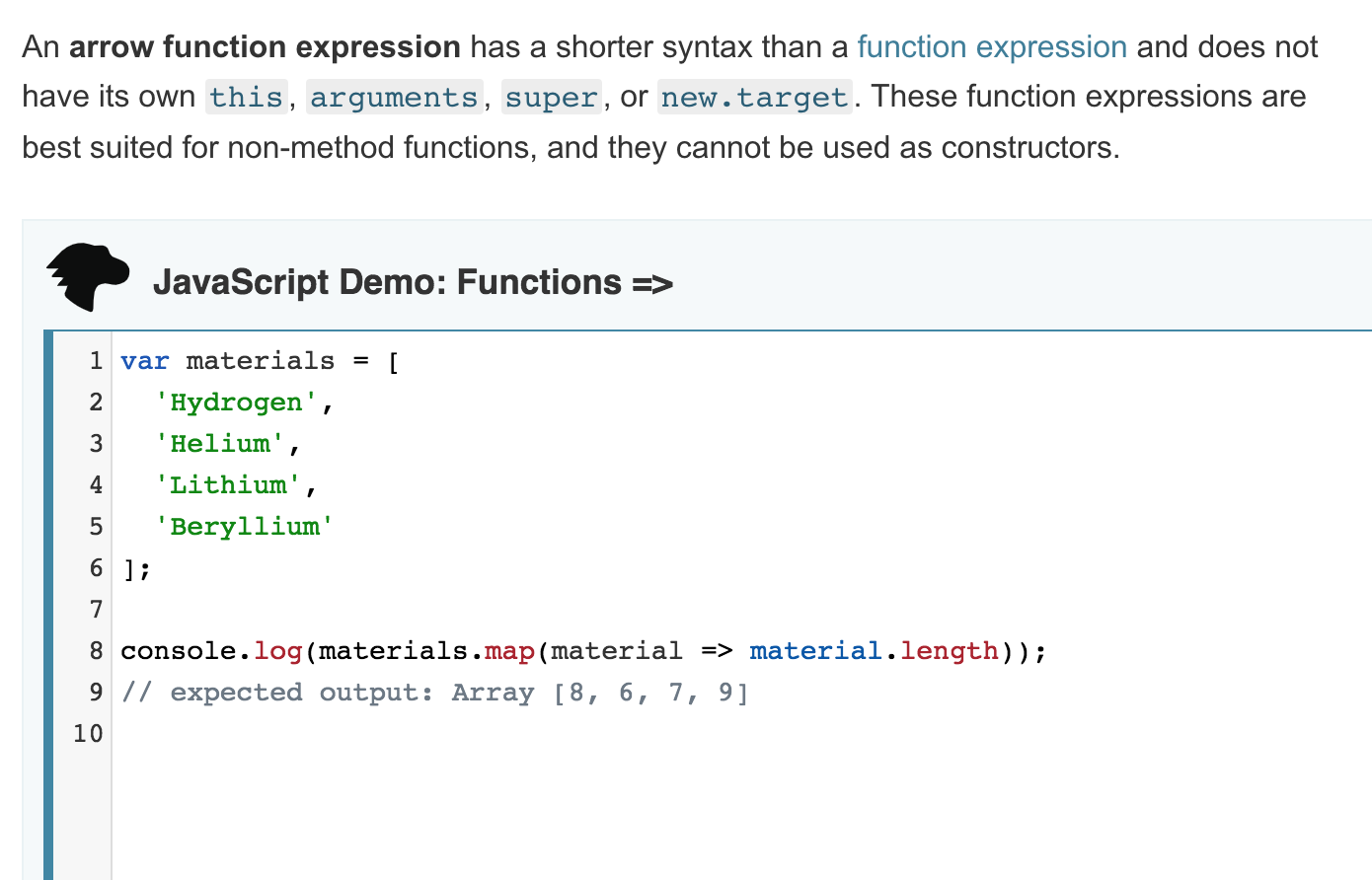
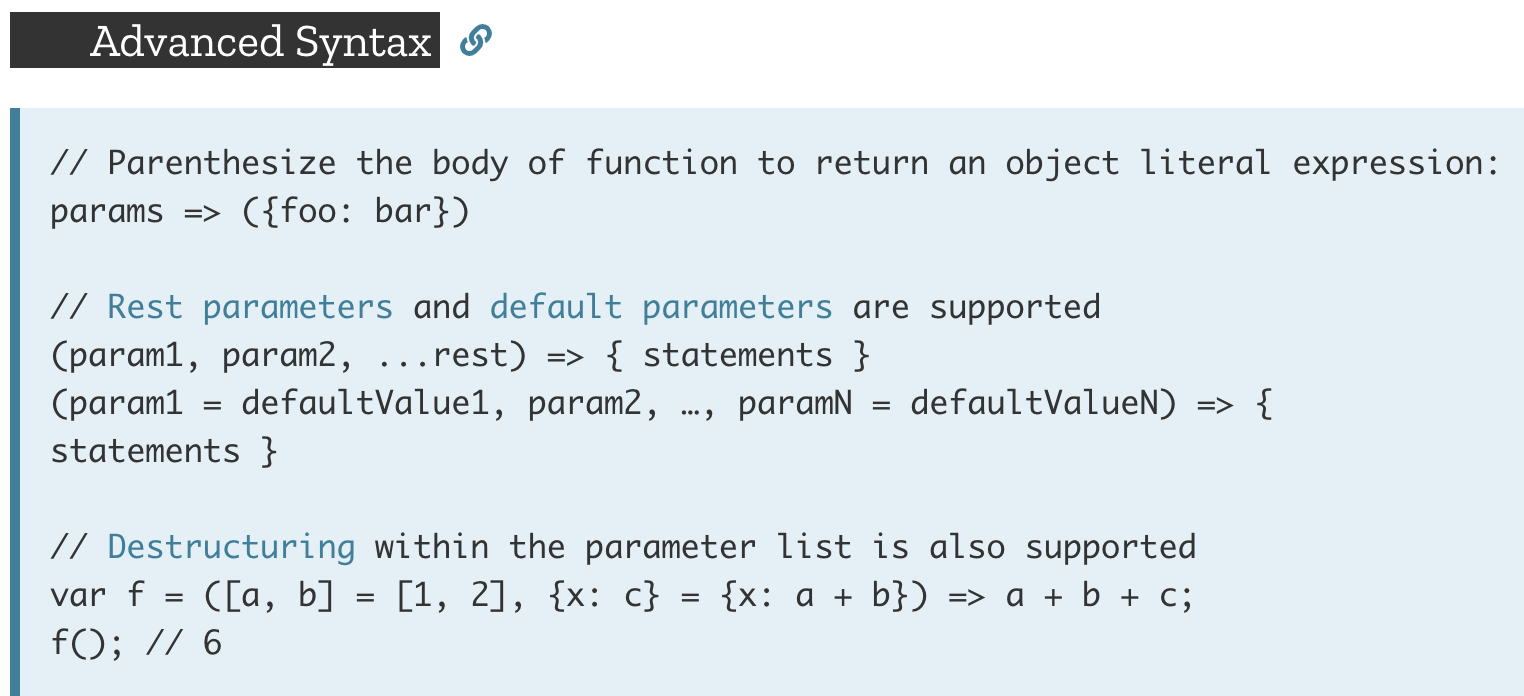
Arrow functions

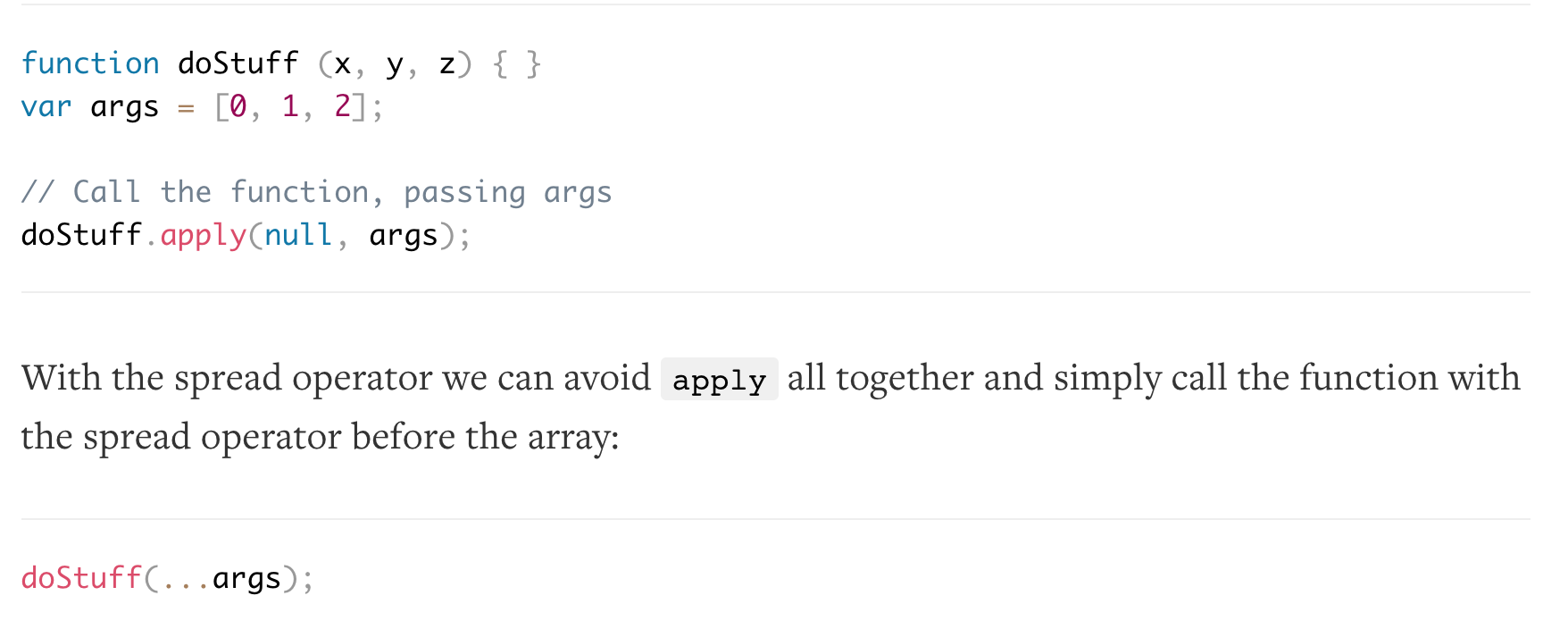
spread ...

let { x, y, ...z } = { x: 1, y: 2, a: 3, b: 4 };
console.log(x); // 1
console.log(y); // 2
console.log(z); // { a: 3, b: 4 }

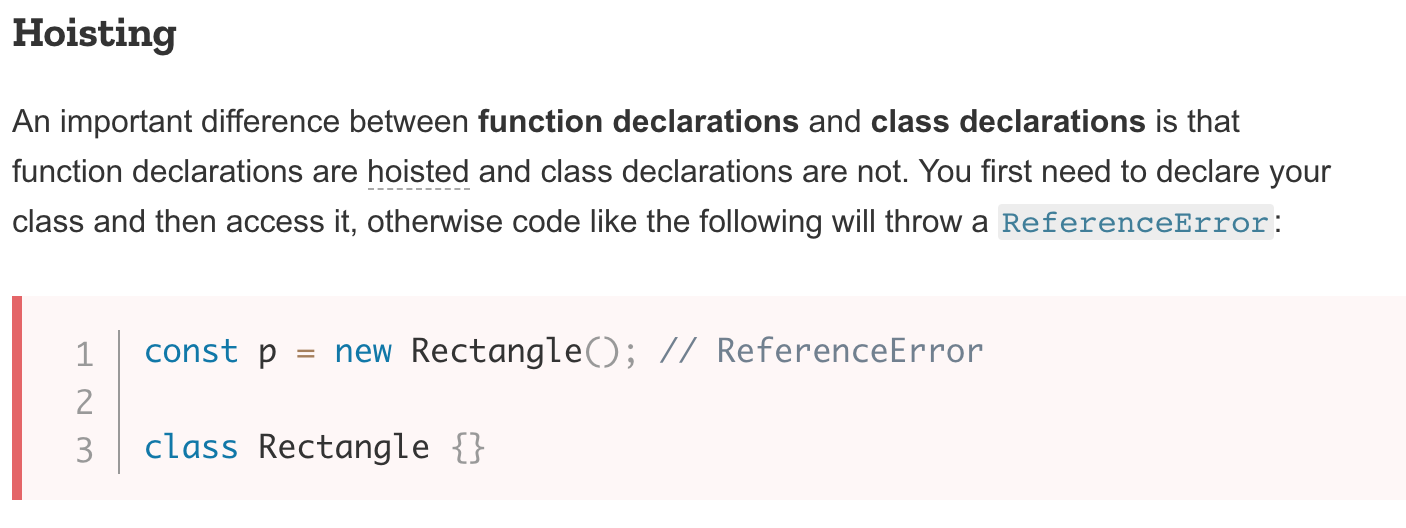
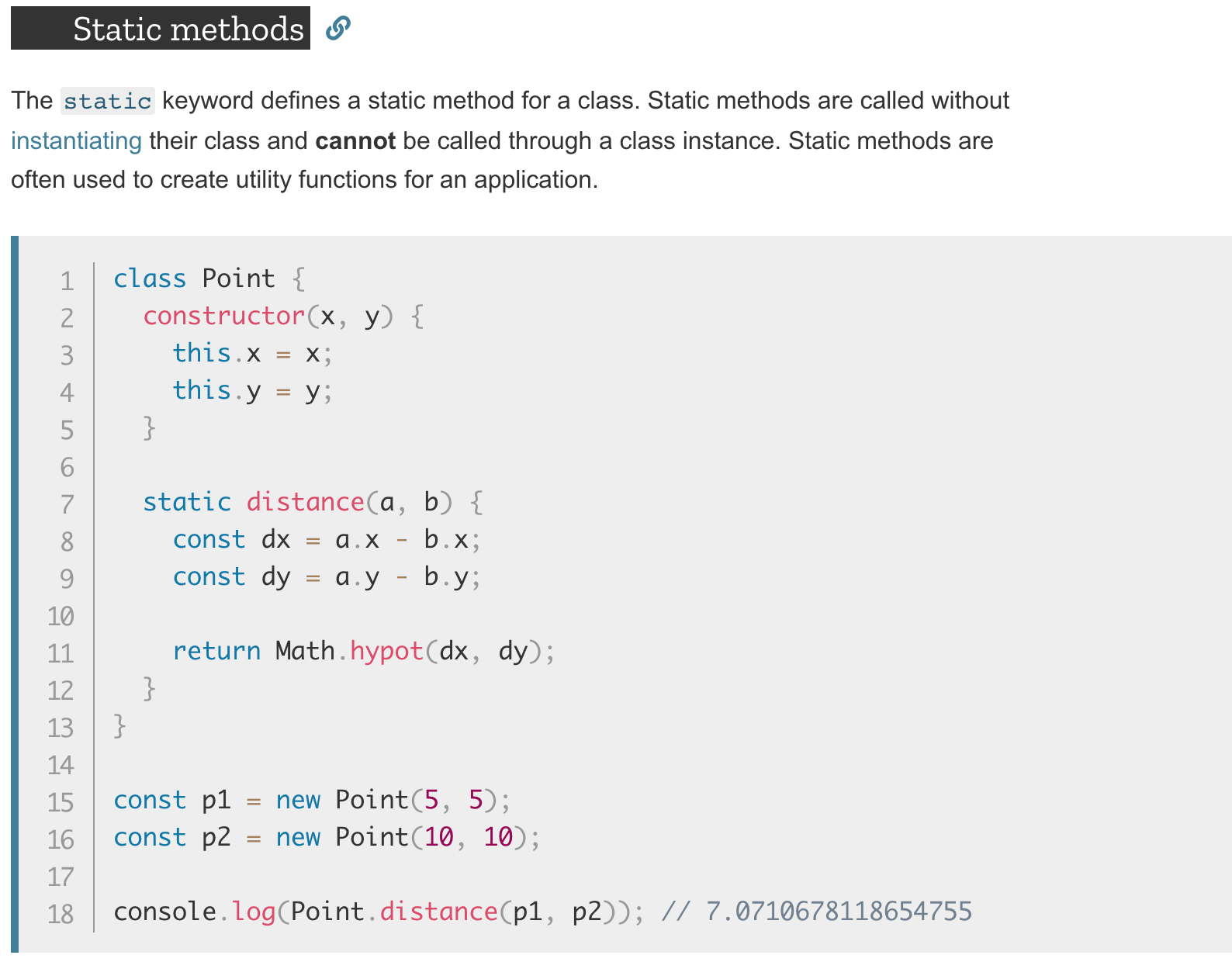
Text




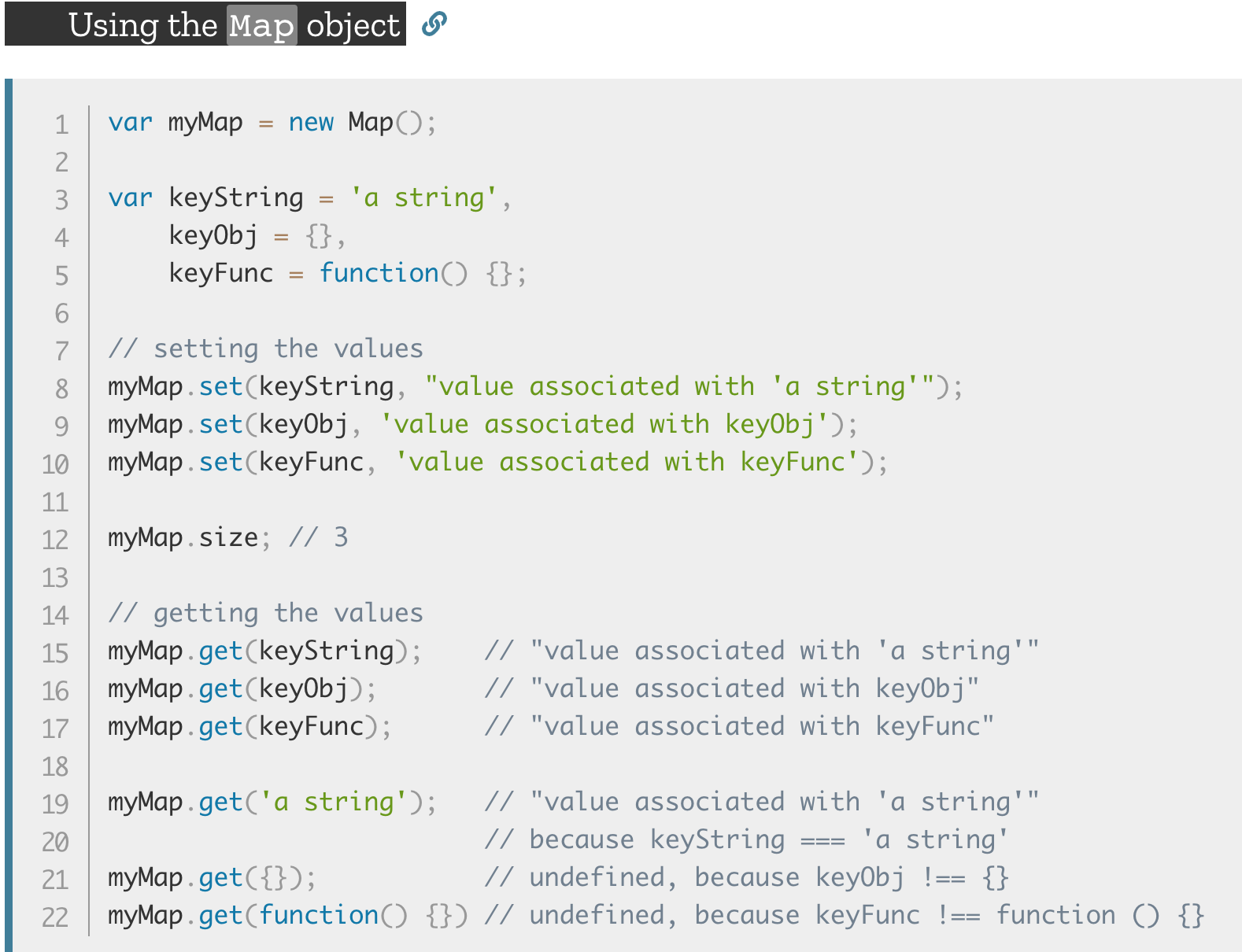


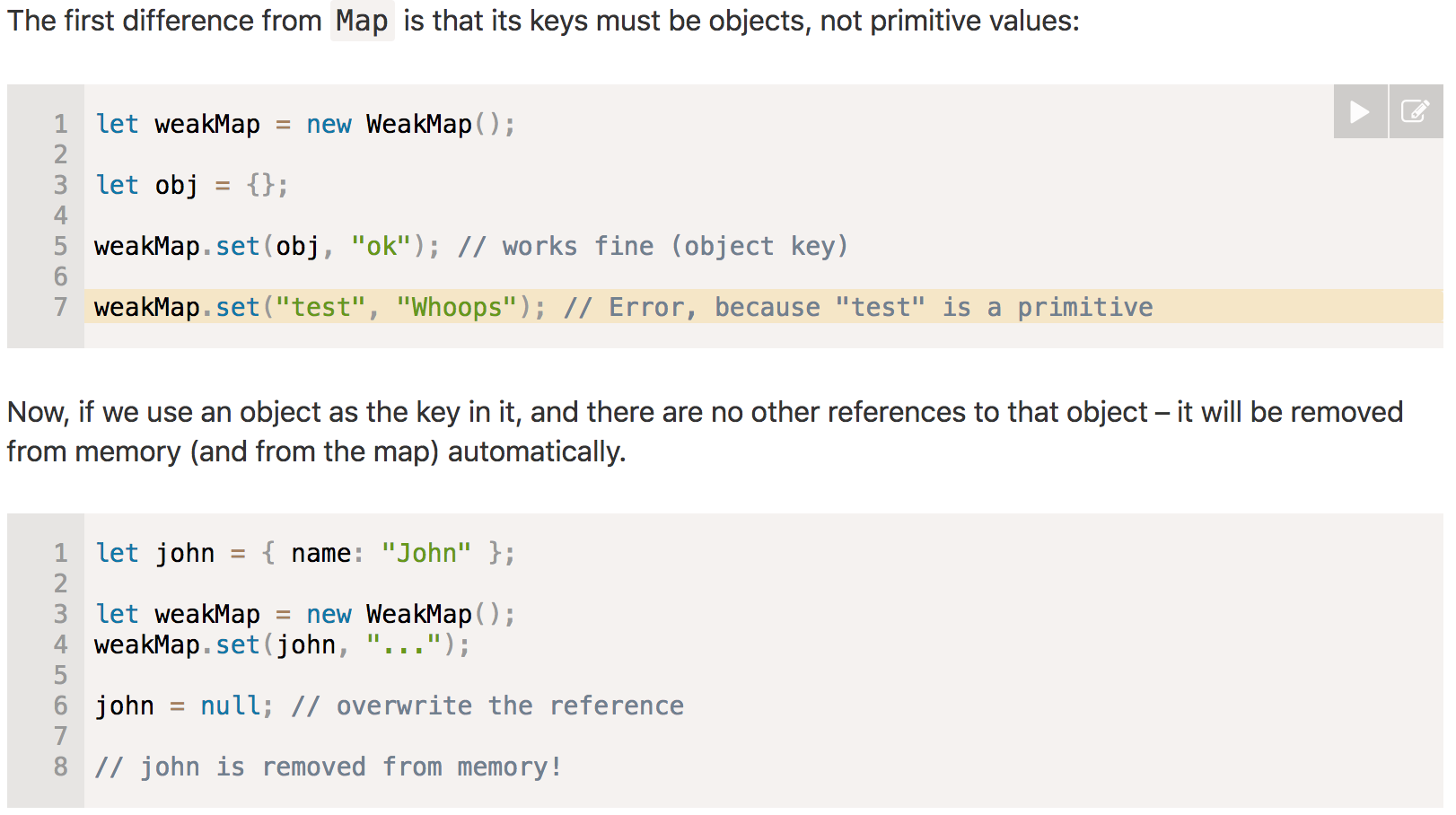
Weak Map
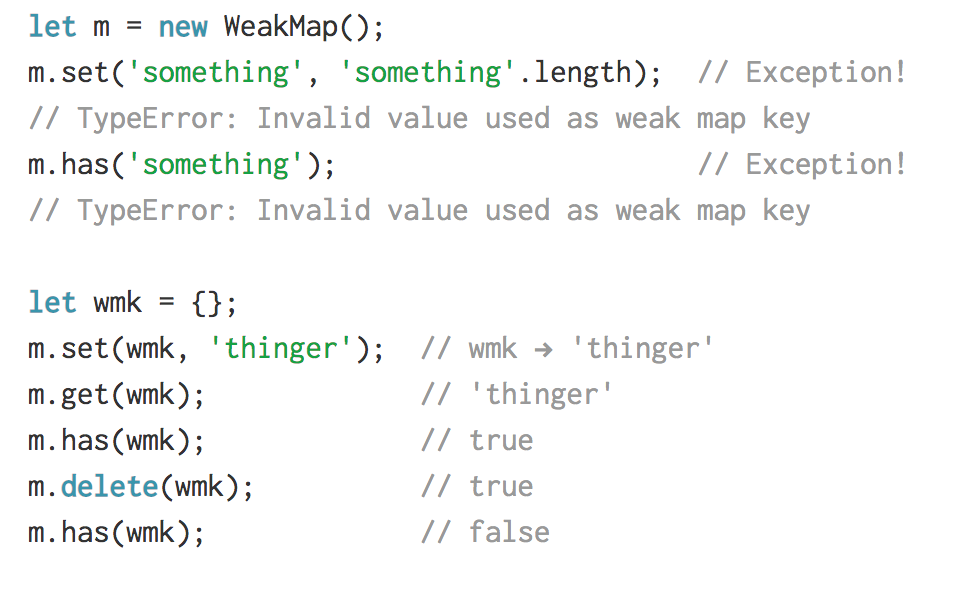
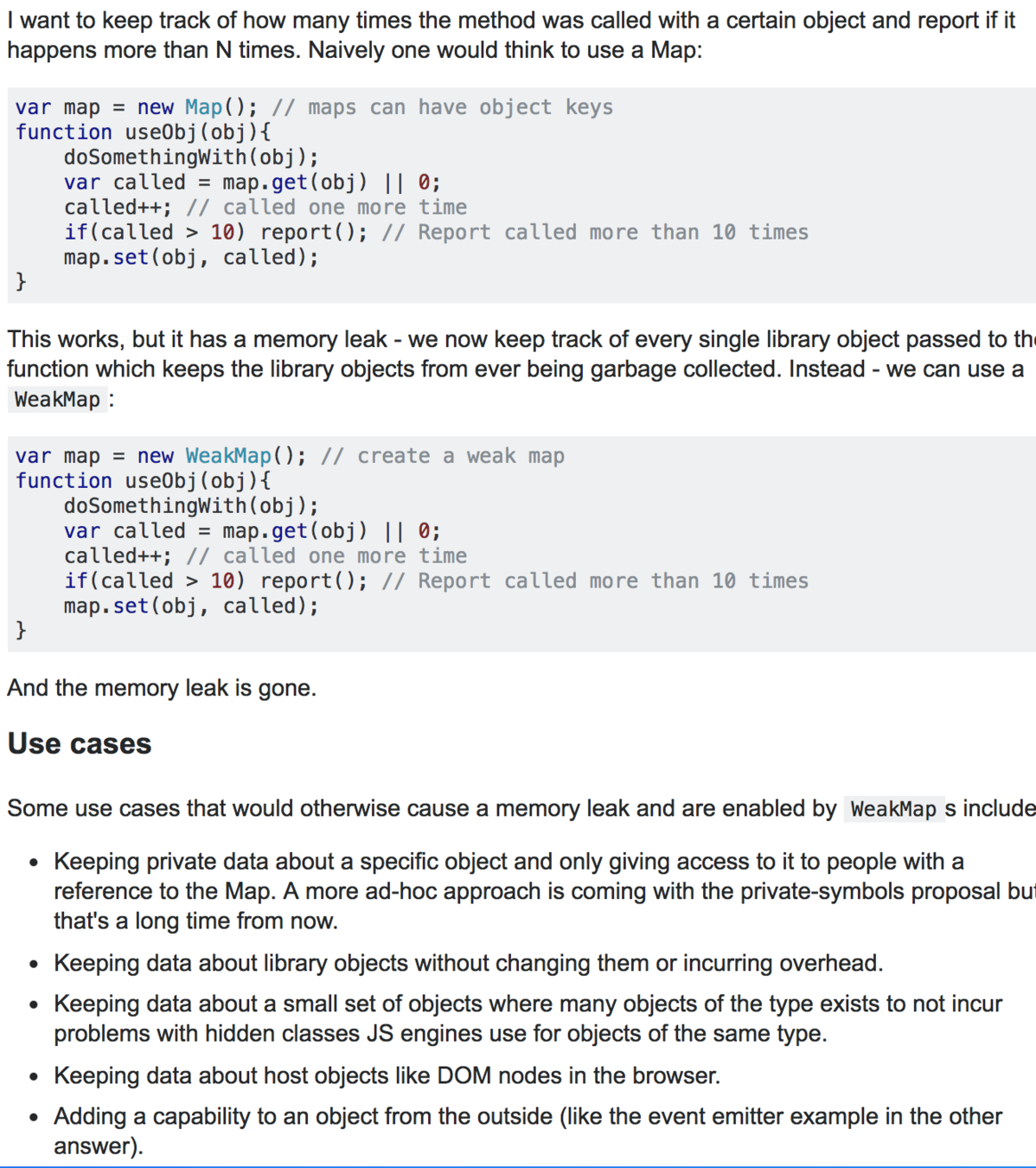
WeakMaps help developers avoid memory leaks by holding references to their properties weakly, meaning that if a WeakMap is the only object with a reference to another object, the GC may collect the referenced object.
Weak set
By definition, WeakSet has only three key functionalities
- Weakly link an object into the set
- Remove a link to an object from the set
- Check if an object has already been linked to the set
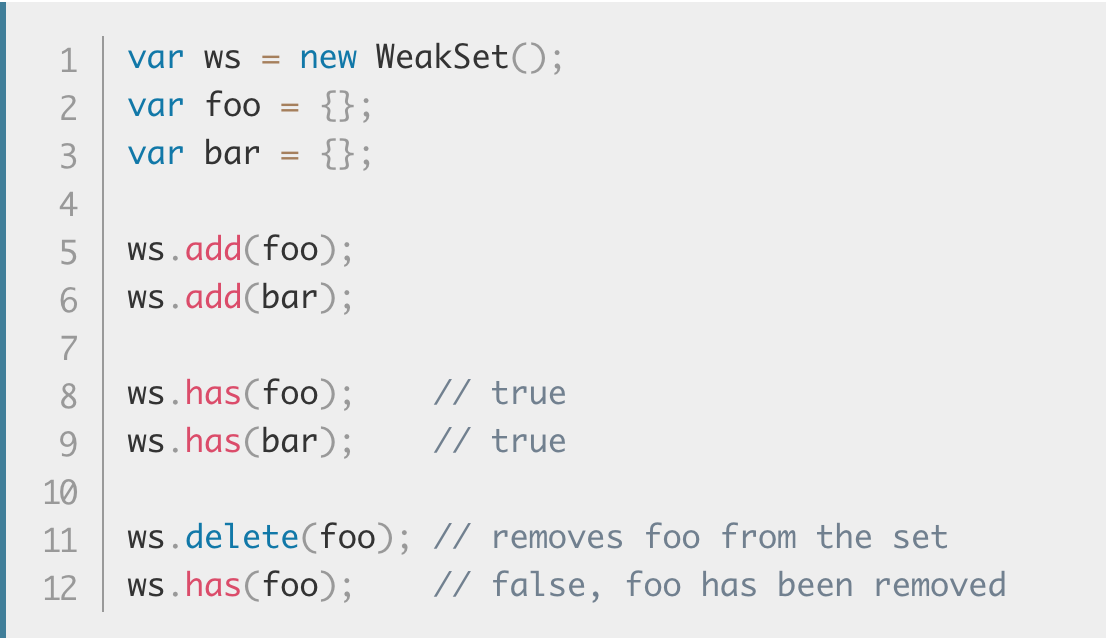
WeakSet objects are collections of objects. An object in the WeakSet may occur only once; it is unique in the WeakSet's collection.
The main differences to the Set object are:
- In contrast to Sets, WeakSets are collections of objects only and not of arbitrary values of any type.
- The WeakSet is weak: References to objects in the collection are held weakly. If there is no other reference to an object stored in the WeakSet, they can be garbage collected. That also means that there is no list of current objects stored in the collection. WeakSetsare not enumerable.
Map, forEach
arr.forEach((num, index) => {
return arr[index] = num * 2;
});// arr = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
let doubled = arr.map(num => {
return num * 2;
});
// doubled = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]filter

find, findIndex
let arr = ['a','b','c'];
arr.findIndex(k => k=='b');
// 1arr.findIndex(k => k=='z');
// -1
if(arr.findIndex(k => k=='z') > 0)
let arr = [2, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12];
function isOdd(i) {
return i % 2 !== 0;
}
arr.findIndex(isOdd);
// 4let arr = ['a','b','c'];
arr.find(k => k=='b');
// 'b'function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
var result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
// expected output: 'resolved'
}
asyncCall();
Promises, async

Bind

- https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-class-example-map
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-class-example-find
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-class-example-filter
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-class-example-foreach
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-class-example-object-destructing
- https://stackblitz.com/edit/react-class-example-object-entries