Continuous Control with Deep RL
Timothy P. Lillicrap, Jonathan J. Hunt, Alexander Pritzel, Nicolas Heess, Tom Erez, Yuval Tassa, David Silver & Daan Wierstra Google Deepmind London, UK
Presented by: Tyler Becker
Motivation
Even extremely coarse discretization: rotate CCW, rotate CW, no rotation $$|\mathcal{A}| = 3^6 = 729$$
Problem: Large Action Space

Even extremely coarse discretization: rotate CCW, rotate CW, no rotation $$|\mathcal{A}| = 3^6 = 729$$
Problem: Large Action Space





Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D. et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518, 529–533 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14236
Problem: Complex State Value Function
Motivation
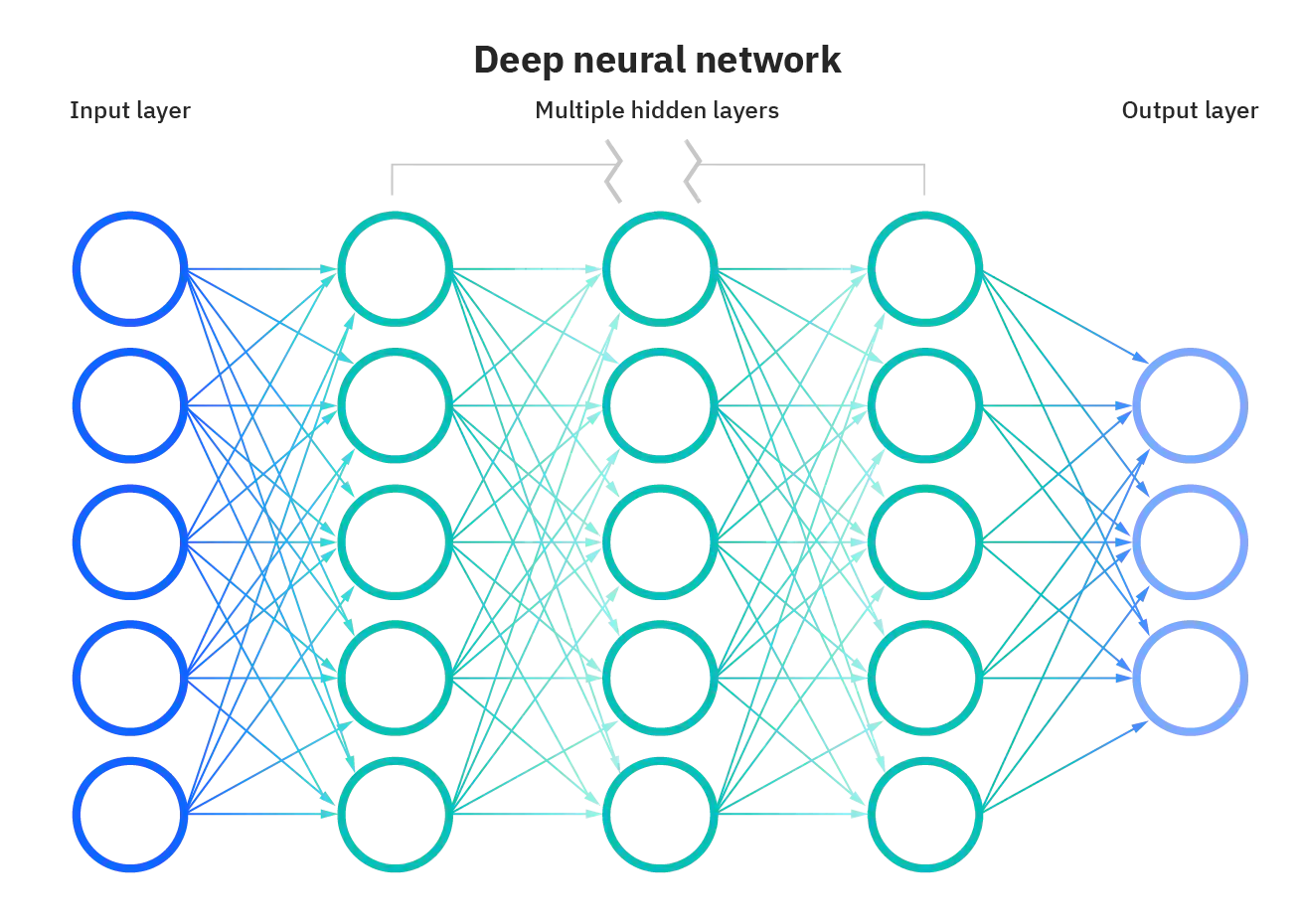
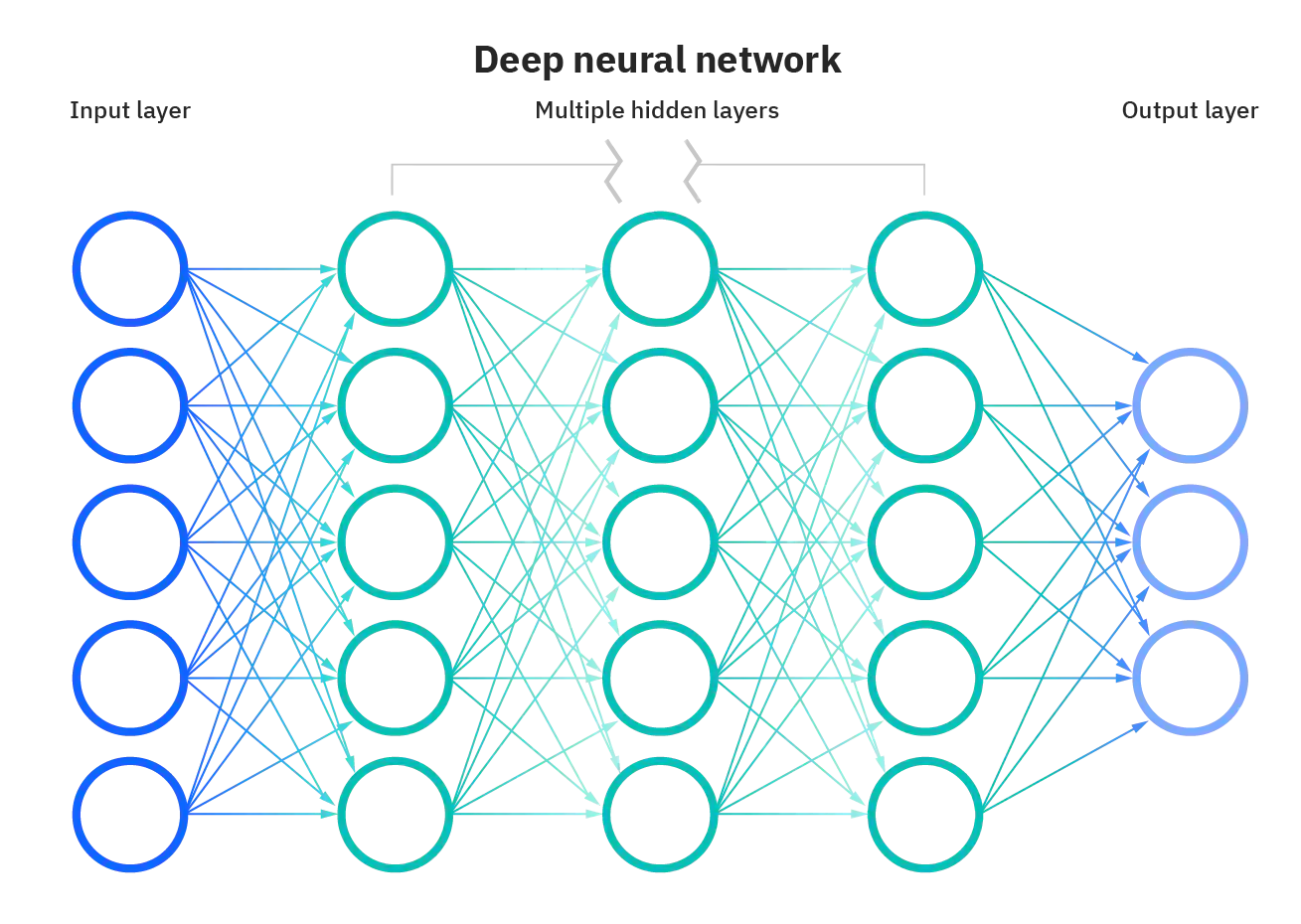
Want continuous \(\mathcal{A}\) compatibility as well as the general applicability provided by the Universal Approximation Theorem
"standard multilayer feedforward networks are capable of approximating any measurable function to any desired degree of accuracy, in a very specific and satisfying sense"
-
Hornik, Kurt, et al. “Multilayer Feedforward Networks Are Universal Approximators.” Neural Networks, vol. 2, no. 5, Jan. 1989, pp. 359–66. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8.
Contributions
Deep Q-Learning
Deterministic Policy Gradients
Deep Deterministic Policy Gradients
- Separate target networks
- Batch learning
- NN function approximation
- continuous \(\mathcal{A}\)
- Actor-critic sample efficiency
Background
DPG
DQN
DPG
Deterministic Policy Gradient
Previously for RL, we had:
\(\pi : \mathcal{S} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{|\mathcal{A}|}\)
$$\pi_\theta(a|s;\theta) = \mathbb{P}[a|s;\theta]$$
What if \(\mathcal{A} = \mathbb{R}^N \)?
Instead, have the policy be deterministic
\(\pi : \mathcal{S} \rightarrow \mathcal{A}\)
$$\pi_\theta(s|\theta) = a$$
DPG
\(\pi : \mathcal{S} \rightarrow \mathcal{A}\)
$$\pi_\theta(s|\theta) = a$$
How do we optimize \(\theta\) for \(\pi_\theta\)?
Want \(\pi_\theta(s) = \argmax_a\left\{Q(s,a)\right\}\)
New unknown variable that comes back despite getting rid of it with determinization:
$$\pi_\theta(a|s;\theta) = \mathbb{P}[a|s;\theta] \rightarrow \pi_\theta(s|\theta) = a$$
DPG
How do we optimize \(\theta\) for \(\pi_\theta\)?
Want \(\pi_\theta(s) = \argmax_a\left\{Q(s,a)\right\}\)
Actor \(\pi_\theta(s)\)
Critic \(Q_\phi(s,a)\)
Climb Q gradient
Descend TD MSE gradient

DQN
Deep Q-Network
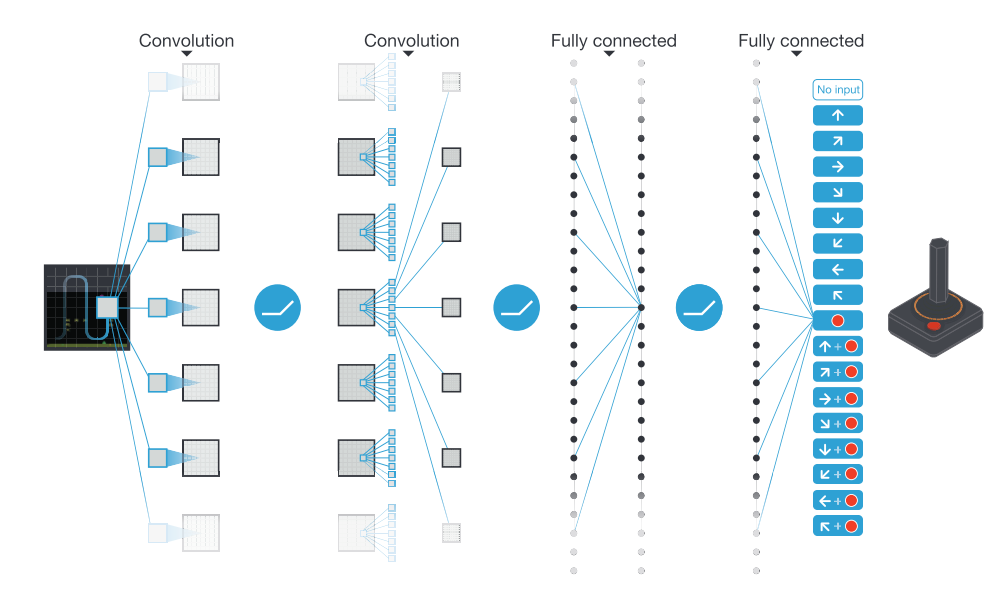
DQN
Vanilla Q-learning
Samples \((s,a,r,s')\) highly correlated
Batches consist of 1 sample
Moving Targets
Changing \(\theta\) to move \(Q_\theta(s,a)\) towards target
(\(r + \gamma\max_{a'}Q_\theta(s',a')\)) also changes target in the process
Maintain an experience buffer to sample from randomly
Maintain a separate target network \(Q_\phi(s',a')\) that is frozen intermittently to prevent target values from varying wildly with current \(Q\) estimates
Problems
Solutions
Problem Setting
Have DQN which works well for discrete actions spaces and can approximate complex Q functions
Have DPG which works with continuous \(\mathcal{A}\), but complexity of Q function that we are able to approximate is dependent on the complexity of the parametric model that we choose
Problem Setting
In combining DQN and DPG, we are now given more freedom in the state/action space complexity of the problems we wish to solve


Given direct state information:
DNN taking body position/velocity
Given direct pixel data to be processed by CNN
Context In Literature
- DQN
- Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D. et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518, 529–533 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14236
- DPG
- Silver, D., Lever, G., Heess, N., Degris, T., Wierstra, D., & Riedmiller, M. (2014). Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 387–395). PMLR.
- TRPO - Solves continuous action space RL without actor-critic architecture
- Lower sample efficiency than DDPG but more stable
- John Schulman, Sergey Levine, Philipp Moritz, Michael I. Jordan, & Pieter Abbeel. (2015). Trust Region Policy Optimization.
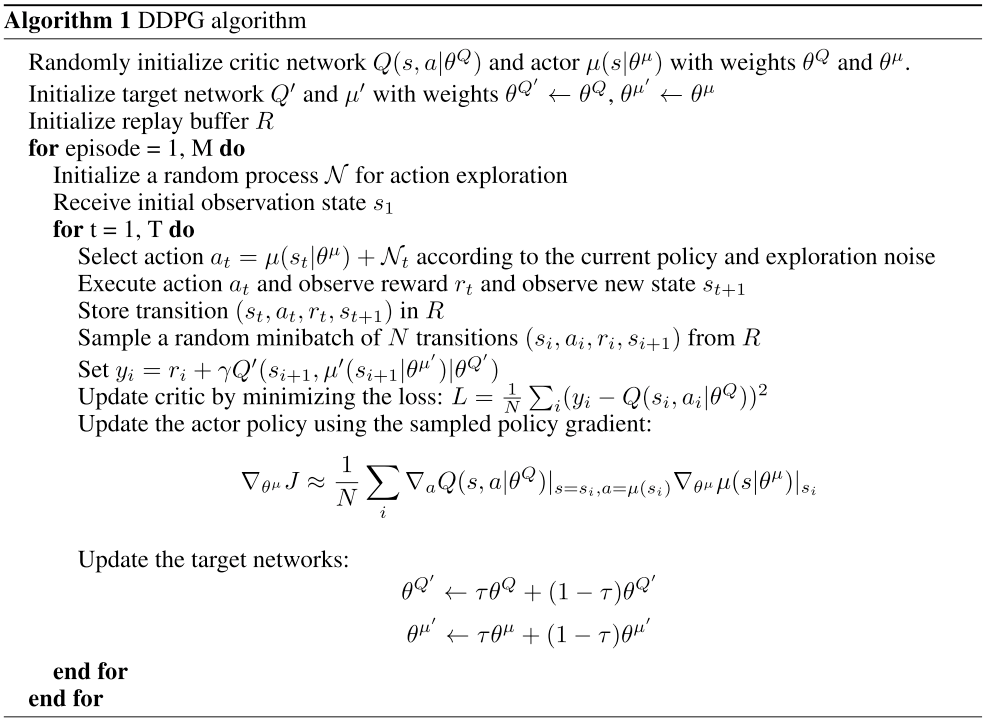
Approach
- Deterministic Actor Network: \(\mu(s|\theta^\mu)\)
- Critic Network: \(Q(s,a|\theta^Q)\)
- Target Networks: \(\mu(s|\theta^{\mu'}),Q(s,a|\theta^{Q'})\)
Exploration:
Softmax sample from \(a\in\mathcal{A}\) via \(Q(s,a)\)
No explicitly listed \(a\in \mathcal{A}\) to choose from
Approach
For critic: want to minimize TD MSE
For actor: want to climb Q gradient
For target networks: want steady/stable convergence
Approach
Experiments
Batch Normalization
Target Network
Target Network + Batch Normalization
Pixel-only inputs
Batch Normalization
- NN's sensitive to input distributions
- Input distribution of \(\mathcal{N}(1,1)\) much more likely to train more effectively than input distribution of \(\mathcal{N}(10^6,10)\)
- Input distributions change with environment and training progress
-
Solution: transform minibatch for each layer to \(\mathcal{N}(1,1)\)
- Maintain running avg of \(\mu, \sigma\) for testing
- Consistent inputs across problems & training progress
https://www.jeremyjordan.me/batch-normalization/
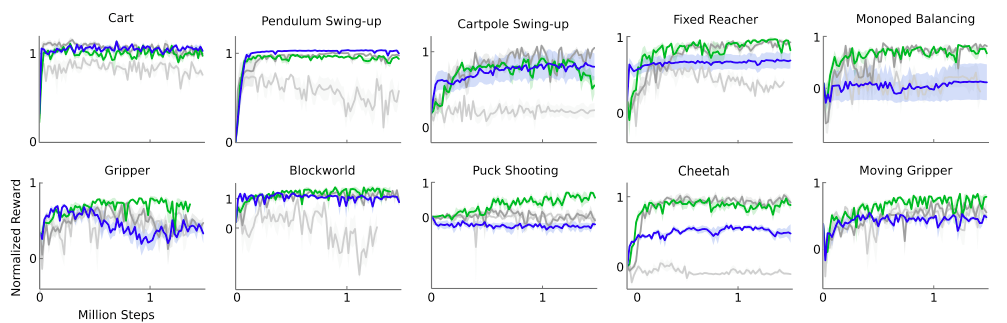
Experiments

Batch Normalization
Target Network
Target Network + Batch Normalization
Pixel-only inputs
Experiments
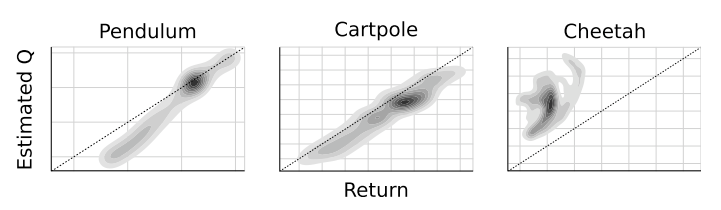
Computational Resources
- Substantially fewer experience steps required for DDPG relative to DQN (~20x)
- Low-dimensional networks with ~130,000 parameters
- High-dimensional networks with ~430,000 parameters
Limitations
Does not work in partially observable environments
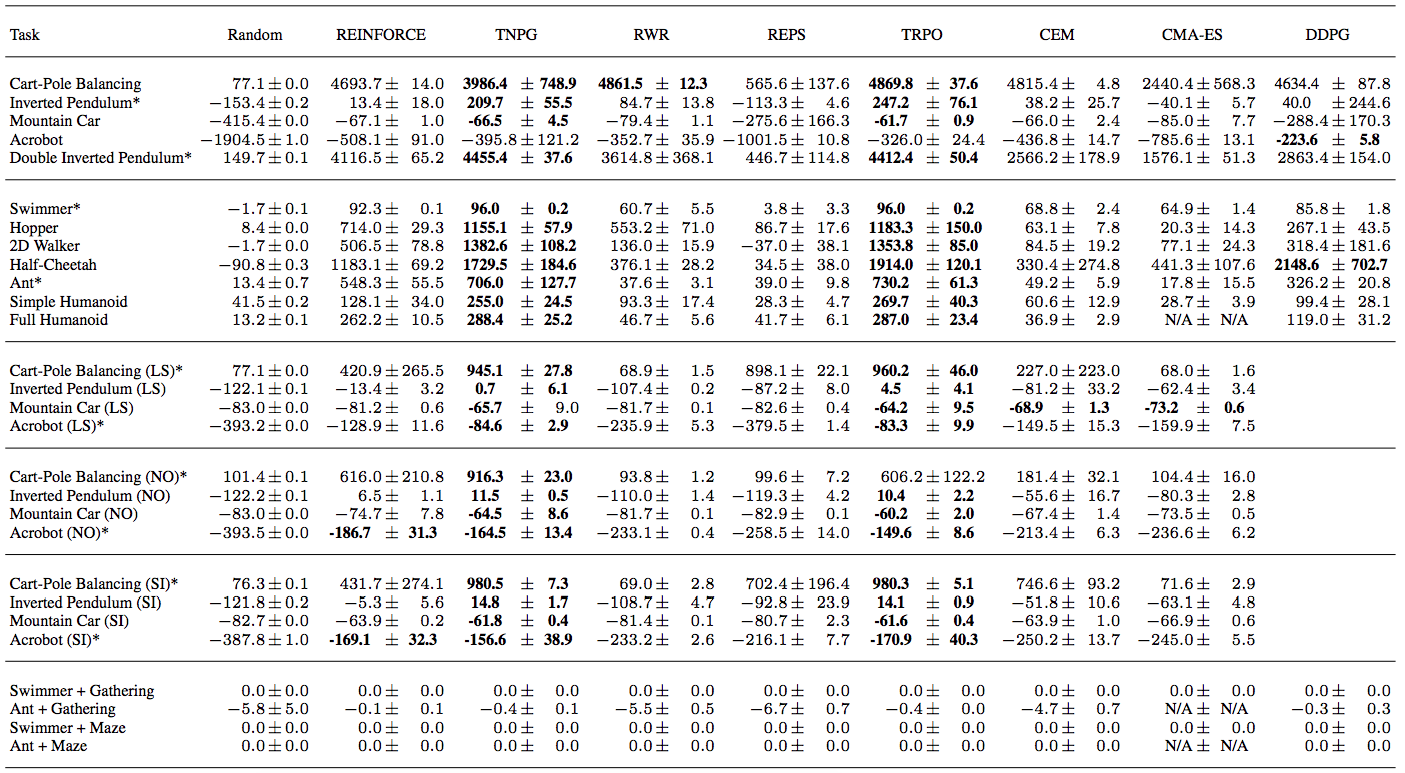
Yan Duan, Xi Chen, Rein Houthooft, John Schulman, & Pieter Abbeel. (2016). Benchmarking Deep Reinforcement Learning for Continuous Control.
Original paper does not compare to other algorithms
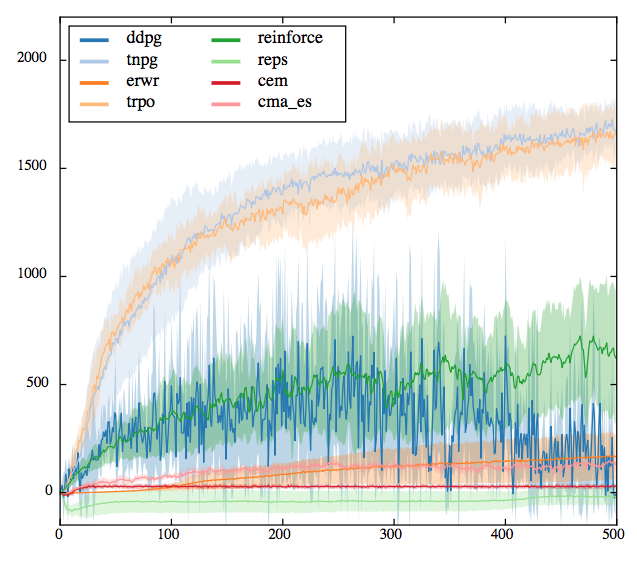
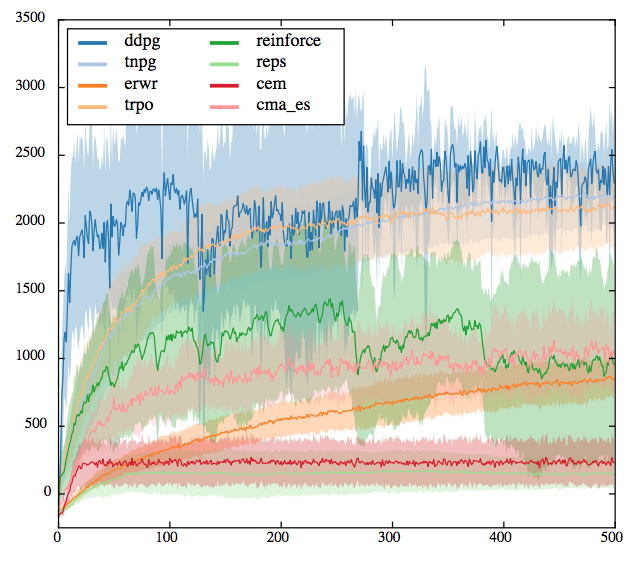
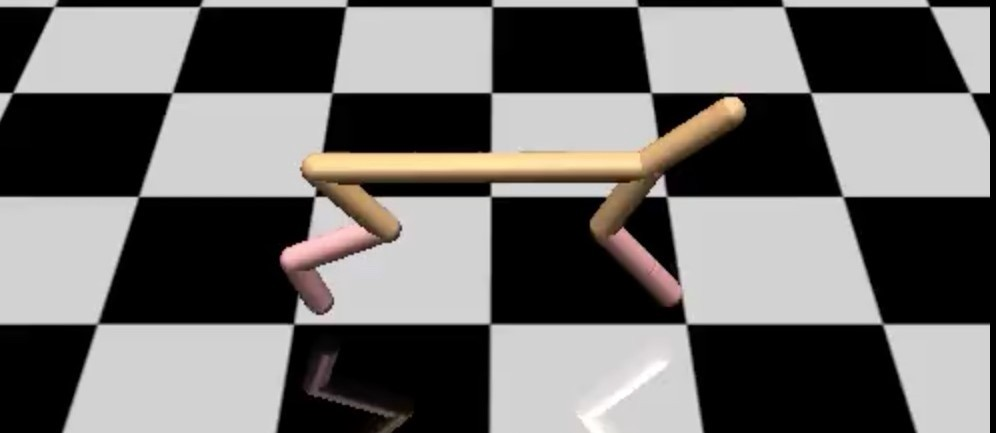
Walker
Half-Cheetah
Impact & Legacy

Inclusion in plenty of RL overviews
Effort to quantify sample efficiency
- Measuring Progress in Deep Reinforcement Learning Sample Efficiency - Dorner
Future Work
- Applying Rainbow DQN concepts
- Asynchronous policy updates with multiple agents
- Deep Reinforcement Learning for Robotic Manipulation with Asynchronous Off-Policy Updates - Gu et al.
Contributions (Recap)
Deep Q-Learning
Deterministic Policy Gradients
Deep Deterministic Policy Gradients
- Separate target networks
- Batch learning
- NN function approximation
- continuous \(\mathcal{A}\)
- Actor-critic sample efficiency