HelloJS
ReactJS Basic
Zet @ TrunkStudio
2017.08.10
About me
- 周昱安(Zet)
- 國立中央大學資工所 – Web 智慧與資料探勘實驗室
- EXMA-Square 實習工程師
- 熱衷於前端技術開發與學習
- 主要使用 React 社群的相關解決方案

Slides & Project
-
Slides:goo.gl/aSdwai
- Demo Project:goo.gl/pGDzpC
- Practice Project:goo.gl/Tzm4Sx
React
React 捨棄了傳統使用 HTML 的開發方式,
改成完全由 JavaScript 程式來代管 DOM 的產生與操作,
實現 100% 純粹的 Client-Side Rendering。
僅僅是 UI
-
React 本身並不是一個完整的前端框架,而是一個只處理 View 的函式庫,也就是負責定義 UI 並自動管理 DOM 的產生與操作
-
React 是一個中間媒介,連結了 UI 的定義層面與 DOM 的實體層面
Reconciler & Renderer
React 的工作分為兩個部分:
-
Reconciler(react):將你定義的 UI 組合出一個虛擬的畫面結構
-
Renderer(react-dom):以這個虛擬結構作為依據,產生出對應的實際 DOM
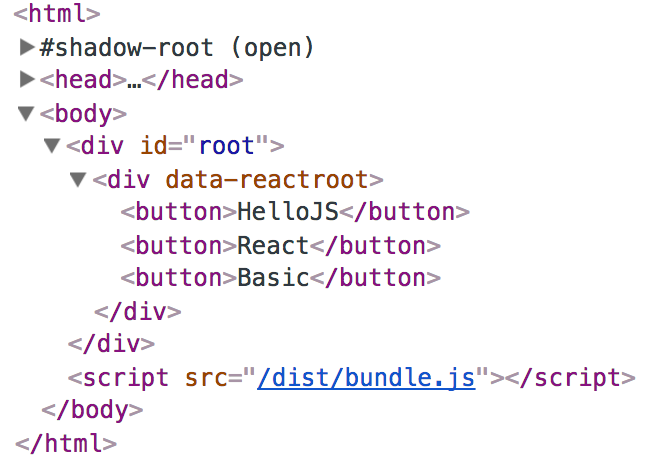
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="/dist/bundle.js"></script>
</html>import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
const reactElement = (
React.createElement('div', { className: 'box' },
React.createElement('button', { onClick: () => alert('clicked') }, 'click me')
)
);
ReactDOM.render(reactElement, document.getElementById('root'));JSX
-
JSX 是 React 在使用的一種特殊 JavaScript 語法糖
-
能夠讓你以可讀性較高的語法來定義 React UI 結構
-
語法長得很像 HTML,但本質上完全不是 HTML
-
瀏覽器看不懂,需要翻譯成原本的 React.createElement 語法才能正常的在瀏覽器上執行
<div className="box">
<button onClick={() => alert('clicked')}>click me</button>
</div>React.createElement("div", {"className": "box"},
React.createElement("button", {"onClick": () => alert("clicked")}, "click me")
)Babel Compile
React Basic Outline
-
Concept
- Component
- Virtual DOM(Reconciler)
-
API
- JSX
- Props
- State
- Event Binding
- Input Data Flow
- Lifecycle
Component
聲明式定義 Component
-
React 允許自定義組件藍圖 ( Component Class ),並抽象化資料傳遞接口
-
可以嵌套或組合,讓前端 UI 程式有更好的可組合性與可重用性
-
Component 本身足以完整的自我表達其可能的顯示變化和擁有的行為
-
每個 Component 結構的第一層,只能有一個根節點元素
-
Component Class 名稱首字母必須大寫
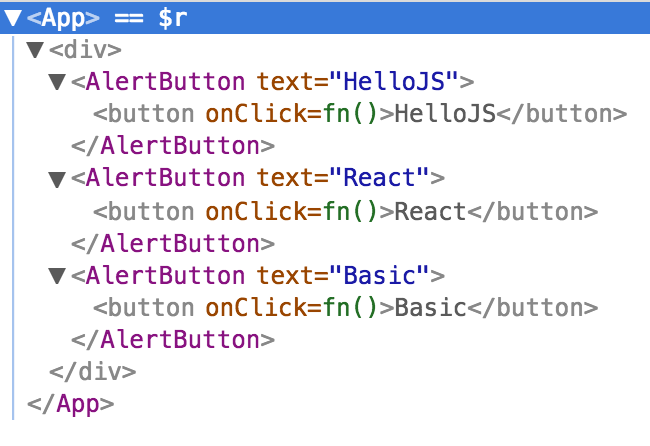
import React from 'react'
class AlertButton extends React.Component {
handleClick = () => {
alert(this.props.text);
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>{this.props.text}</button>
);
}
}組合併重用 Component
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<AlertButton text="HelloJS"/>
<AlertButton text="React"/>
<AlertButton text="Basic"/>
</div>
);
}
}
Virtual DOM
(Reconciler)
Virtual DOM(Reconciler)
-
Virtual DOM 是一份純資料的 Tree 物件結構,映射對應到實際的 DOM
-
使用 React.createElement 函數來產生 Tree 節點(React Element)
-
Virtual DOM 為自定義 Component 提供了中介的虛擬層,讓開發者能以聲明式的方式定義 UI 的顯示邏輯與行為
-
我們透過定義 Component 來表達「UI 什麼情況該如何呈現」,而「要用什麼手段來達到這個畫面改變(如何產生和操作 DOM)」 ,React 則會自動幫你完成 (react-dom 這個 Renderer 的工作)
React.createElement('div', null,
React.createElement(AlertButton, { text: 'HelloJS' }),
React.createElement(AlertButton, { text: 'React' }),
React.createElement(AlertButton, { text: 'Basic' })
)Why Virtual DOM ?
-
UI 開發最大的兩個問題與挑戰就是「可重用性」與「反應變化」
-
然而 Web 中建構 UI 的媒介 – DOM,並沒有直接滿足以下需求的能力:
-
自定義資料抽象化
-
複雜情形的組合與重用
-
綁定資料來源以自動反應顯示結果與變化
-
-
因此 React 建立了一個虛擬結構層,來間接實現這些對於 UI 開發來說相當重要的能力
-
我們對於 Virtual DOM 這個虛擬結構層以 Component 的形式定義想要的 UI 呈現結構,而 Renderer 則會幫我們將其自動轉換成對應的實際 DOM 結果
One-way Data Flow
-
One-way Data Flow(單向資料流)
- UI 是你的應用程式的資料去延伸的顯示結果
-
只有因為資料改變,才能導致 UI 的顯示結果自動跟著改變
-
這個因果關係永遠不能逆向
-
UI 只能被動的隨資料而反應變化
-
UI 不能反過來主動直接修改資料或是修改 UI 自己的顯示結果
-
Always Redraw
-
React 如何實現單向資料流:當 UI 的來源資料有變化時
-
不需要關心整份資料中具體是變化了哪些部分
-
先把 UI 畫面全部洗掉,然後再依據完整的最新資料全部重新產生 UI 畫面,通常可以保證顯示結果一定是正確的
-
-
然而每次都重繪全部的實體 DOM 顯然在效能考量之下是不可行的,但是重繪 Virtual DOM 則成本相對降低許多,因此 React 實作了一套 Reconciliation 演算法來實現這個概念與流程
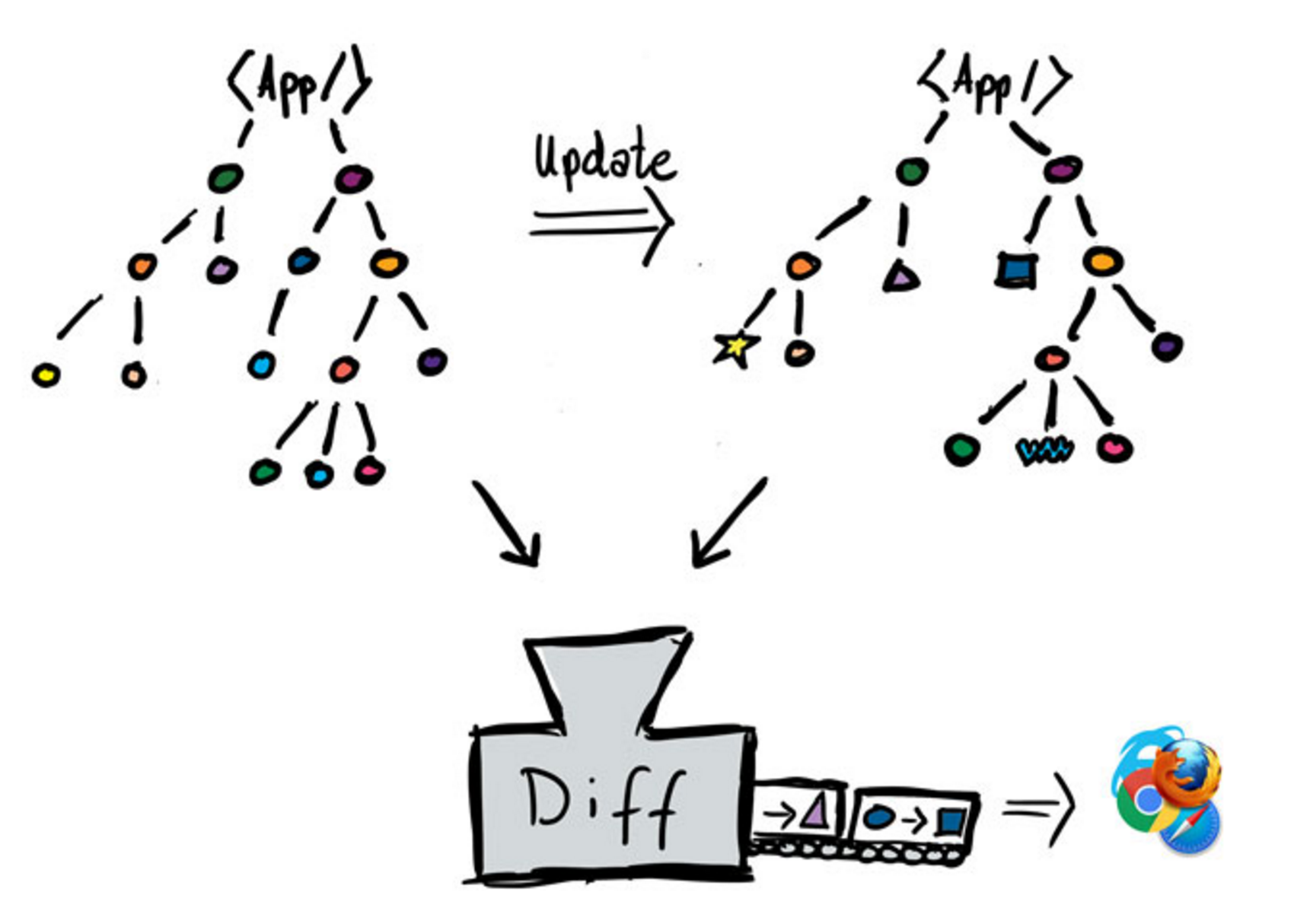
Reconciliation(Diff 演算法)
當畫面需要改變時,根據最新的資料重繪出新的 Virtual DOM Tree,
並與改變前的舊 Virtual DOM Tree 進行全面式的比較與計算,
其中被發現新舊差異的地方,才真的會在實際的 DOM 上發生操作改變
JSX
(React.createElement)
JSX 語法
-
JSX 是 React.createElement 函數的語法糖,用來建立 Virtual DOM 節點結構
-
支援原生 HTML DOM 有的標籤以及自訂的 Component Class 標籤
-
嚴格標籤閉合
-
與 HTML 重要的語法差異
-
class → className
-
所有 property 名稱改以駝峰式命名,EX:onclick → onClick
-
<div>
<h2 className="title">Title</h2>
<NumberItem number={100}/>
<br/>
</div>表達式的印出顯示
-
使用 { } 語法來填入 JavaScript 表達式(一個值),其中可直接當作顯示內容印出的型別有:
-
React Element:當作子節點插入
-
String:直接印出
-
Number:轉成字串後直接印出
-
Array:攤平成多個表達式後印出(如果 item 的值也是這些可印的型別)
-
Boolean、Null、Undefined:什麼都不印,直接忽略
-
-
可以在 Component 之間用 Props 傳遞,但不能當顯示內容印出的型別有:
-
Object
-
Function
-
條件判斷式
- JSX 中不可以直接寫 if / else,因為實際上是一個 React Element 物件結構
- 使用 && 運算子來達到 if 判斷式的效果
- 使用三元運算子來達到 if / else 判斷式的效果
<div>
{(a > 100) && (
<AlertButton text="HelloJS"/>
)}
<AlertButton text="React"/>
<AlertButton text="Basic"/>
</div><div>
{(a > 100) ? (
<AlertButton text="HelloJS"/>
): (
<AlertButton text="React"/>
)}
<AlertButton text="Basic"/>
</div>Inline Style
-
使用 JavaScript Object 來撰寫,並填入 HTML 類型的 React Element 的 style props 當中
-
CSS Property:名稱改用駝峰式命名
-
CSS Value:數字的預設單位是 px,其他數字單位或非數字的值要使用字串來表示
const styles = {
padding: 15,
backgroundColor: 'yellow',
fontSize: 20
}
<button style={styles}>按鈕</button>迭代輸出顯示內容
- 使用陣列型別的 map 函數批量迭代產生 React Element 或其他顯示內容的陣列
- 當陣列中的 item 是 React Element 時,應該要給予一個唯一的 key,以優化重繪時的 Reconciliation 效率
<div>
{numbers.map((number, key) => (
<button key={key}>{number}</button>
))}
</div>Props
Props
Props 是將資料從 Component 外部傳遞給 Component 內部的媒介
在 Component 內部透過 this.props 取得傳遞進來的 Props 資料物件
當 Props 資料傳遞到 Component 內部後,應是不可再變更的固定值
設計 Component 時抽象化出跟問題相關的 Props,以方便進行重用
JSX 中,若想要傳遞的 Props 的值是字串的話,可以直接使用雙引號,其他型別的值則需要使用 {} 來包住
class TodoList extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<TodoItem title="吃飯" isCompleted={true}/>
<TodoItem title="洗澡" isCompleted={false}/>
<TodoItem title="睡覺" isCompleted={false}/>
</div>
);
}
}class TodoItem extends React.Component {
render() {
const { isCompleted, title } = this.props;
return (
<div>
<input type="checkbox" checked={isCompleted}/>
<span>{title}</span>
</div>
);
}
}State
State
-
State 是 Component 內部的可變資料的存放載體
-
透過 this.state 取得目前 Component 個體的 State 資料物件
-
使用 this.setState 函數來修改 State 資料物件,並連帶髮起重繪
-
調用 setState 修改資料後,該 Component 以及其包含的所有子孫 Component 都會跟著自動發起重繪,以更新 Virtual DOM Tree
-
因此 setState 方法就是 Virtual DOM 重繪以及 Reconciliation 流程的發起者,從資料變更一直到最後反應出實際 DOM 的變更效果
-
State
class TodoApp extends React.Component {
state = {
todos: [
{ title: '吃飯', isCompleted: true },
{ title: '洗澡', isCompleted: false},
{ title: '睡覺', isCompleted: false}
]
}
handleAddTodo = () => {
this.setState({
todos: [...this.state.todos, {
title: '上課',
isCompleted: true
}]
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Todo App</h2>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}/>
<button onClick={this.handleAddTodo}>add todo</button>
</div>
);
}
}Event Binding
Event Binding
-
Virtual DOM 對於 HTML 實作了幾乎所有的事件的對應接口
-
事件名稱因應 Virtual DOM 與 JSX 的慣例,全部變成駝峰式
-
會將 event 物件以第一個參數傳入你綁定的函數,其中 event.target 可以取得該 React Element 對應的實體 DOM
-
更詳細的 API 說明,可以參考官方文件
class Button extends React.Component {
handleClick(event) {
console.log(event);
console.log(event.target);
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>{this.props.text}</button>
);
}
}Where's "this" in Function
-
若函數有存取原本定義處的 Component 的 this,在函數被傳遞之後將不再能夠正確地找到原本的 this
- 因此我們需要在傳遞前先 bind 好指定的 this,讓函數記住 this 是誰
- 可以使用 Arrow Function 來定義會被傳遞的函數,利用其自動 bind this 的特性來輕鬆優雅的解決這個問題
class Button extends React.Component {
handleClick = () => {
alert(this.props.text);
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>{this.props.text}</button>
);
}
}Input Data flow
- 原生的HTML <input> 元素是自帶資料狀態的
- 在 React 中,有兩種處理方式
- Uncontrolled:依照原來的自帶資料狀態模式
- Controlled:使用單向資料流的模式,獨立地點存放 input 中的資料並綁定 UI
Input Data Flow
Uncontrolled Input
-
input 本身自己管理資料狀態,不與資料來源綁定
-
使用 defaultValue 或 defaultChecked 來設定預設值
-
這種做法代表你不能夠透過修改資料來源來隨意控制現在 Input 的值,也沒有一個集中地點可以取得目前 Input 的值
class UncontrolledInputExample extends React.Component {
handleInputChange = (event) => {
console.log(event.target.value);
}
render() {
return (
<input
type="text"
defaultValue="hello"
onChange={this.handleInputChange}
/>
);
}
}Controlled Input
-
Input 自己本身不存放資料,也不能隨意改變自己顯示的值,與指定的資料來源綁定
-
使用 value 或 checked 來指定綁定的資料來源
-
使用 onChange 來指定接收資料的函數,並且在該函數中呼叫修改資料來源,以達到資料變更後新資料回流到 input 中
class ControlledInputExample extends Component {
state = {
inputText: 'hello'
}
handleInputChange = (event) => {
this.setState({
inputText: event.target.value
});
}
render() {
return (
<input type="text" value={this.state.inputText} onChange={this.handleInputChange}/>
);
}
}Lifecycle
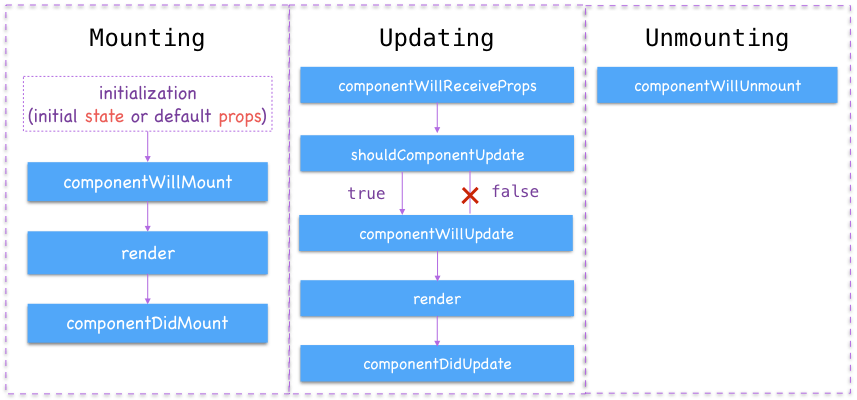
組件的生命週期
render
- 每個 React Component 都必需定義的方法,負責決定要繪製的 UI 之構成(Virtual DOM 節點結構)
- 必須 return 僅一個 React Element,所以 Component 結構第一層才只能有一個節點
- 每次 Component 成功重繪的生命週期中都會被呼叫到並執行
componentDidMount
- 在 Component 初始化並且首次繪製完成並產生對應的實體 DOM 後觸發,重繪時不會觸發
- 在 Component 的實際 DOM 被從畫面中拆除之前,只會發生一次
- 通常一些首次進入畫面後想發生的事情就適合在這裡呼叫,例如發起 AJAX 向後端 API 請求資料
More React
Flux
- React 只負責組織與產生 UI,而不規定你要如何組織與存放你的資料
- 當資料散落在多個 Component 各自的 this.state 時,將會難以自由的相互傳遞與統一管理
- Facebook 提出了 Flux 的概念,建立獨立於 React 之外的 Store 來存放整個應用的資料,但與 React 相互配合與串接,構成更純淨且分工明確的單向資料流
- 而社群中最主流的 Flux-like 函數庫就是 Redux
View
( React )
Store
Action
Reducer
dispatch
資料需要改變
return
newState
資料完成變更
React 發起重繪
Server
Redux
Front-End Routing
- 對於 Single Page Application 來說,View Route 只有一個
- Routing 在前端只是部分畫面的替換,以及網址的假修改
- EX:https://webpack-raeact-boiler.firebaseapp.com/
-
React Router
- 專門搭配 React 使用的 Front-End Routing 解決方案
- 不是由 Facebook 官方開發的,但已成為公認的預設選擇
- 幫我們處理好路由網址比對,以及對應的 Component 切換
More Renderer
- React 的 Renderer 可以替換並由社群貢獻開發,而核心的 Reconciliation 演算法則可以直接共用。這使 React 的虛擬結構組織能力得以在 HTML DOM 以外的媒介或平台實現,讓使用 React 開發各種平台的原生應用程式成為可能
- React Native:Android & iOS
- React Native for Windows
- React Canvas
- React VR