Rust in VLC
Alexandre Janniaux - Juin 2025
2022: Integration of rav1e, first contrib in rust (and only one built in contrib)
2021: Integration of rav1e, first contrib in rust (and only one built in contrib)
2023: Bindings from Loïc and integration in buildsystem, rework of the stream_t API
2024: Rework of the module API, integration of telegraf-rs tracer
2025: Static plugin support, first 100% safe bindings for tracer and start logger capabilities
/* Current trait for implementing tracers */
pub trait TracerCapability: Sync {
fn open(obj: &mut Object)
-> Option<impl TracerCapability>
where
Self: Sized;
fn trace(&self, tick: Tick, trace: &Trace);
}
/* Fails to compile, MT issue! */
use std::cell::Cell;
use vlcrs_core::object::Object;
use vlcrs_core::tracer::{Tick, TracerCapability, Trace};
struct Module { last_trace_tick: Cell<Tick>, }
impl TracerCapability for Module {
fn open(obj: &mut Object)
-> Option<impl TracerCapability> {
Some(Self{
last_trace_tick: Cell::from(Tick(0))
})
}
fn trace(&self, tick: Tick, trace: &Trace) {
let mut state = self.last_trace_tick.get_mut();
*state = tick;
}
}- Enforce strong typing
- Enforce threading
- No fiddling with p_sys
- Integration in documentation makes it very comfortable
pub struct TracerModuleLoader;
impl<T> ModuleProtocol<T> for TracerModuleLoader
where
T: TracerCapability,
{
type Activate = TracerCapabilityActivate;
fn activate_function() -> Self::Activate {
activate_tracer::<T>
}
}
const TRACER_OPERATIONS:
sys::vlc_tracer_operations =
sys::vlc_tracer_operations {
trace: tracer_trace,
destroy: tracer_destroy,
};
extern "C" fn activate_tracer<T: TracerCapability>(
obj: &mut Object,
opaque: &mut MaybeUninit<*mut c_void>,
) -> Option<&'static sys::vlc_tracer_operations> {
if let Some(instance) = T::open(obj) {
let wrapper: Box<dyn TracerCapability> =
Box::try_new(instance).ok()?;
let sys = Box::into_raw(
Box::try_new(wrapper).ok()?);
opaque.write(sys as *mut _);
return Some(&TRACER_OPERATIONS);
}
None
}
- Can enforce matching capability strings
- Implement the core API
- Generate everything VLC needs to probe
- Hide the complexity for module developers
/* Those slides are definitively too small */
struct TelegrafTracer {
endpoint: Mutex<UnsafeCell<telegraf::Client>>,
}
impl TracerCapability for TelegrafTracer {
fn open(_obj: &mut vlcrs_core::object::Object)
-> Option<impl TracerCapability>
where
Self: Sized,
{
let endpoint_address =
std::env::var("VLC_TELEGRAF_ENDPOINT")
.unwrap_or(String::from("tcp://localhost:8094"));
let endpoint = Client::new(&endpoint_address)
.map(UnsafeCell::new)
.map(Mutex::new)
.unwrap();
Some(Self { endpoint })
}
/* ... */
}
/* Implementation in telegraf-rs module */
module! {
type: TelegrafTracer (TracerModuleLoader),
capability: "tracer" @ 0,
category: ADVANCED_MISC,
description: "Tracer module forwarding the traces\
to a Telegraf endpoint",
shortname: "Telegraf tracer",
shortcuts: ["telegraf"],
}
/* Example with multiple modules */
module! {
type: TestModuleFilter (FilterModuleLoader),
capability: "video_filter" @ 0,
category: VIDEO_VFILTER,
description: "A new module",
shortname: "mynewmodule",
shortcuts: ["mynewmodule_filter"],
submodules: [{
type: TestModuleFilter (TestOtherCapabilityLoader),
capability: "other_capability" @ 0,
category: VIDEO_VFILTER,
description: "Another module",
shortname: "othermodule"
}]
}- Type-safe description
- Strong integration with traits
- Generate everything VLC needs to probe
/* src/module/stream_filter.rs */
/// Stream filter module
pub trait Module {
/// Open function for a stream filter module
fn open<'a>(
_this_stream: ThisStream<'a>,
source: &'a mut Stream,
logger: &'a mut Logger,
args: &mut ModuleArgs,
) -> Result<StreamModule<'a>>;
}
/* src/module/demux.rs */
/// Stream filter module <-- (unseen copypaste typo)
pub trait Module {
/// Open function for a stream filter module
fn open<'a>(
_this_demux: ThisDemux<'a>,
source: &'a mut Stream,
es_out: &'a mut EsOut,
logger: &'a mut Logger,
_args: &mut ModuleArgs,
) -> Result<DemuxModule<'a>>;
}
/* Example */
module! {
type: Inflate,
capability: "stream_filter" @ 331,
category: SUBCAT_INPUT_STREAM_FILTER,
description: "Zlib decompression filter - Built in Rust",
}
- No need for loaders
- Cannot implement custom capabilities
- Cannot split in crates
- See !2738
trait CapabilityTrait {
type Loader = ...;
type Activate = ...;
type Deactivate = ...;
/* Rest of the required implementation
for modules */
}
/* Example of implementation */
unsafe extern "C"
fn activate_filter<T: CapabilityTrait>(
obj: *mut vlc_filter_t,
valid: &mut boo
) -> c_int {
T::open(obj, valid);
0
}
/* BUT, Cannot implement variadic that way: */
fn activate<T: EncoderCapability>(
obj: *mut encoder_t
) {
static ENCODER_OPS : vlc_encoder_operations
= vlc_encoder_operations{
encode_video: encode_video_impl::<T>
};
(*obj).sys = &ENCODER_OPS;
}
- Apparently no need for Loaders
- But cannot work with any state
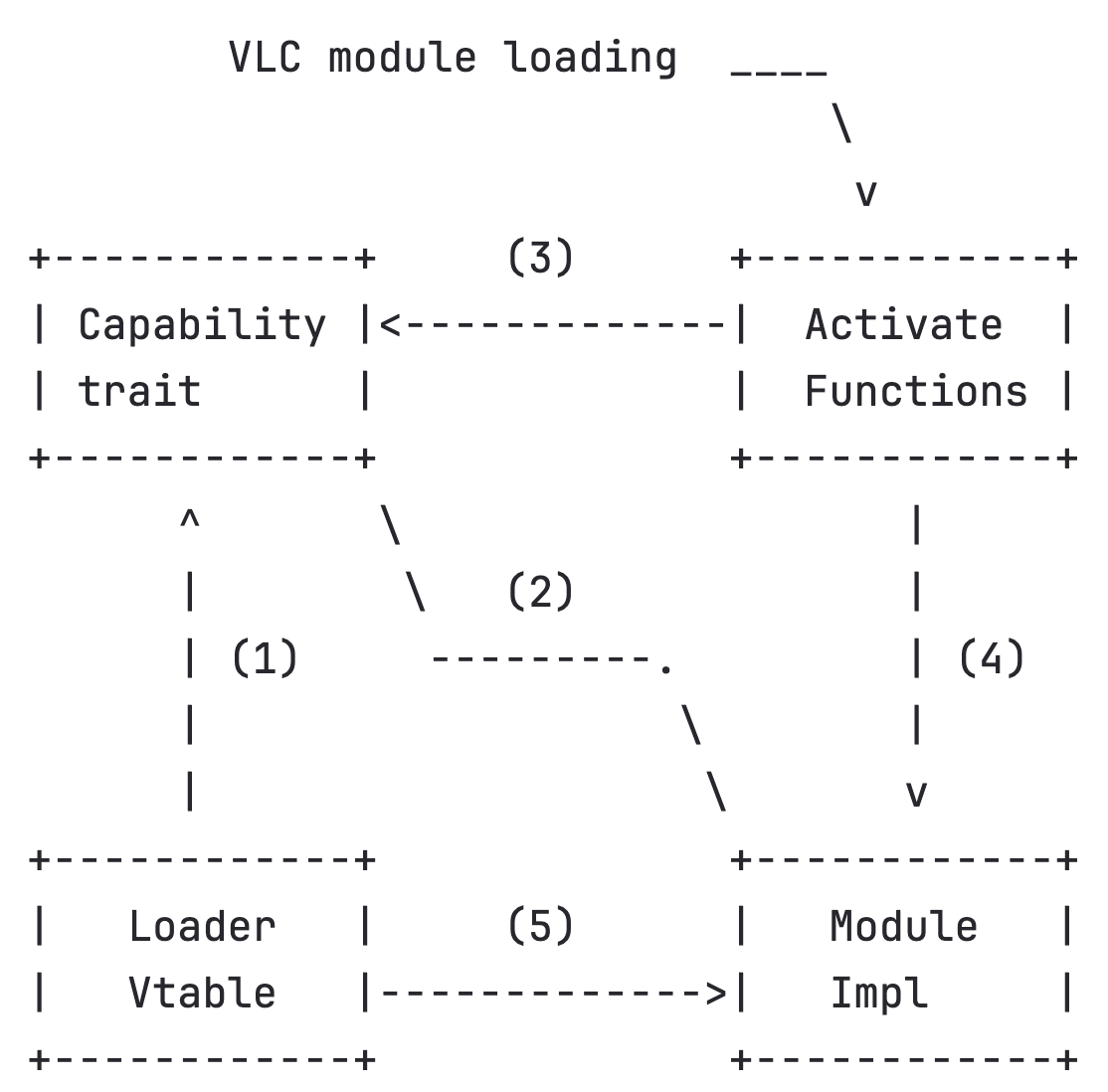
Low budget slide from MR !5726

Pros
- Very strong threading description / typing
- Tests and documentation are improved a lot
- Rust std is great for newcomers
- Enforce proper APIs
Cons
- Need to implement the vtable -> traits compat
- Additional allocation
- Implementing safe bindings on some APIs can be tedious
- Implementing safe extern "C" API need some toughts
Define regular design pattern
- Callback listener for player, playlist, etc.
- Define parsing "standards" for reading formats.
1.
Add missing core features
- VLC variable integration, see prototype from Loïc.
- Define normal modules that are !Sync.
- Add common base types, like Tick (!5604) or fourcc (!4164). ES formats are also missing.
2.
Add production modules
- telegraf-rs is still a module for development, not used by most users.
- wasmer-rs module from GSoC is a promising candidate for this.
- Any demux?
3.
Thanks!
