Experiences with
React Js and Redux
UDE Demo
React Js
Key benefits
- Declarative
- Component-Based (Composable)
- Learn Once, Write Anywhere
var HelloMessage = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return <div>Hello {this.props.name}</div>;
}
});
ReactDOM.render(<HelloMessage name="John" />, mountNode);"use strict";
var HelloMessage = React.createClass({
displayName: "HelloMessage",
render: function render() {
return React.createElement(
"div",
null,
"Hello ",
this.props.name
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(React.createElement(HelloMessage, {
name: "John"
}), mountNode);Component API
setState
replaceState
forceUpdate
isMounted
Life Cycle
Mounting: componentWillMount
Mounting: componentDidMount
Updating: componentWillReceiveProps
Updating: shouldComponentUpdate
Updating: componentWillUpdate
Unmounting: componentWillUnmount
Under the hood
- Turned O(n3) problem into a O(n)
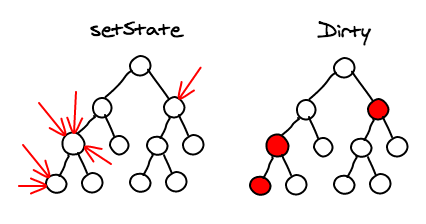
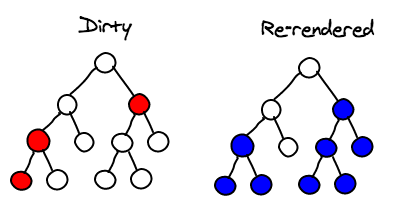
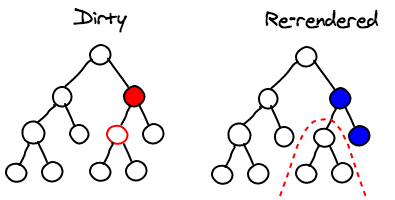
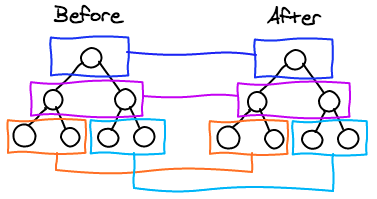
Things not much missed
- Two way data binding
- Inheritence
- Custom event model (e.g. Backbone.Events)
Performance
Redux Basics
Actions
Actions are payloads of information that send data from your application to your store. They are the only source of information for the store. You send them to the store using store.dispatch().
Here’s an example action creator which returns an action to add a new todo item:
const ADD_TODO = 'ADD_TODO';
function addTodo () {
return {
type: ADD_TODO,
text: 'Build my first Redux app'
}
}Reducers
Actions describe the fact that something happened, but don’t specify how the application’s state changes in response. This is the job of a reducer.
const initialState = {
visibilityFilter: VisibilityFilters.SHOW_ALL,
todos: []
}
function todoApp(state = intialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case ADD_TODO:
return Object.assign({}, state, {
todos: [...state.todos, {
text: action.text,
completed: false
}]
});
default:
return state;
}
}Store
The Store is the object that brings them together. The store has the following responsibilities:
- Holds application state;
- Allows access to state via getState();
- Allows state to be updated via dispatch(action);
- Registers listeners via subscribe(listener);
- Handles unregistering of listeners via the function returned by subscribe(listener).
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import todoApp from './reducers'
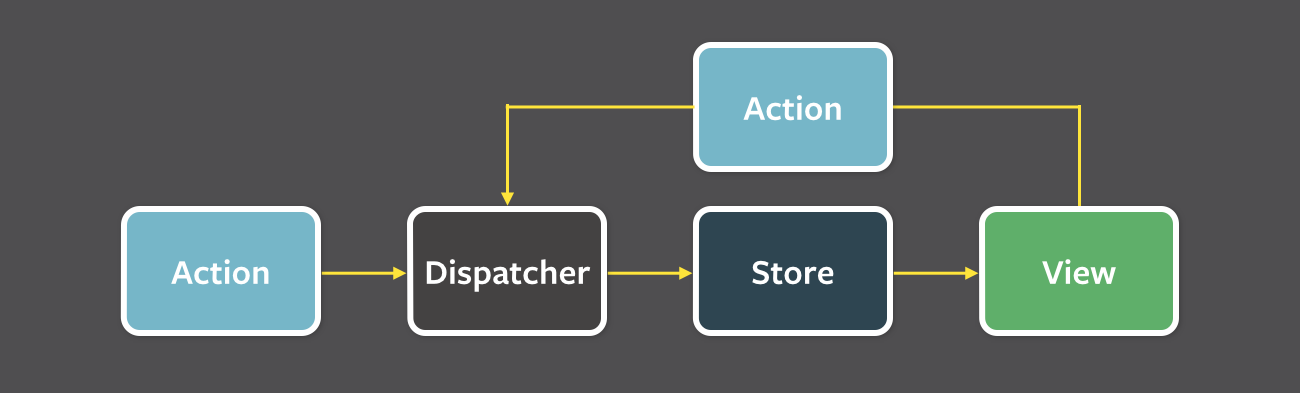
let store = createStore(todoApp);Unidirectional data flow
-
You call action - store.dispatch(action)
-
The Redux store calls the reducer function you gave it.
-
The root reducer may combine the output of multiple reducers into a single state tree.
-
The Redux store saves the complete state tree returned by the root reducer.
Challenges and solutions
State Synchronize
- Synchronize state across tabs.
- Use browser local storage.
- Subset of state store.
- Redux Partial state update to Local Storage.
- No framework fits our application.
- Action based state update.
- Solution: Can subscribe to redux store for changes.
Redux state Subscribe
function handleChange() {
let previousValue = currentValue
currentValue = select(store.getState())
}
let unsubscribe = store.subscribe(handleChange)We know the state but not the action.
Cannot diff for every state change - performance problem
Solution : Use Component and Reducer
export default class LocalStateSync extends Component {
constructor(props) {
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
if(!nextProps.controller.performStateSync){
return;
}
this._sendSession(session, nextProps.controller.stateStoreType, AppConstants.STORE_UPDATE);
nextProps.sessionActions.stateSyncComplete();
}export function stateSyncComplete() {
return {
type: Types.STATE_SYNC_COMPLETE
}
}Action
Reducer
const controller = (state = initialState, action) => {
let finalSession = {};
let finalStoreKey;
if(action.type == Types.STATE_SYNC_COMPLETE) {
return Object.assign({}, state, {
performStateSync: false
});
}
for(let idx in actions){
// If this is action we are looking at .. then update the state.
if(actions[idx] == action.type){
return Object.assign({}, state, {
performStateSync: true,
stateVariables : AppConstants.STATE_STORE_CONFIG[action.type][SESSION_KEYS_INDEX],
stateStoreType : AppConstants.STATE_STORE_CONFIG[action.type][SESSION_STORE_TYPE_INDEX]
});
}
}
return state;
}
STATE_STORE_CONFIG: {
START_MINIMIZE : [['session.minimized'], 'tab'],
START_MAXIMIZE : [['session.minimized','session.unreadMessageCount'],'tab'],
ADD_AGENT_MESSAGE : [['session.unreadMessageCount'], 'tab']
}WEB API
export function endChat(chatEndedBy) {
if (chatEndedBy == AppConstants.CHAT_ENDED_BY.USER) {
WorkFlowProvider.call("leaveChat");
}
return {
type: Types.END_CHAT,
chatEndedBy
};
}Not a Pure function
Pros
- Reusable Components
- Code Structure
- Ease of Debugging
- Unit test cases
- Less Learning Curve
Future
- preact and others
- virtual-dom and others
- reflux, flux and others