GRAPHS
+
SEARCH
OBJECTIVES
- Use Graph Theory vocabulary and notation
- Discuss different types of search and benefits of each
GRAPHS
GRAPH THEORY VOCAB
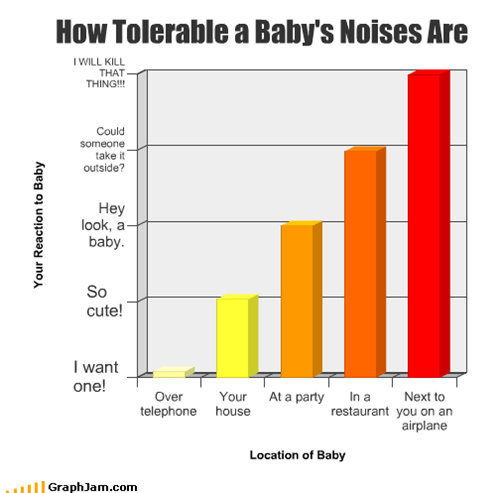
Graph
- Graphs are a very common nonlinear data structure in computer science.
- Graphs are common because it's very easy to describe a lot of real world problems in the language of Graph Theory.
GRAPH THEORY VOCAB
G = (V, E)
- Vertice (node): circles on the graph, represents any form of data
- Edge: the paths that connect that data

GRAPH THEORY VOCAB
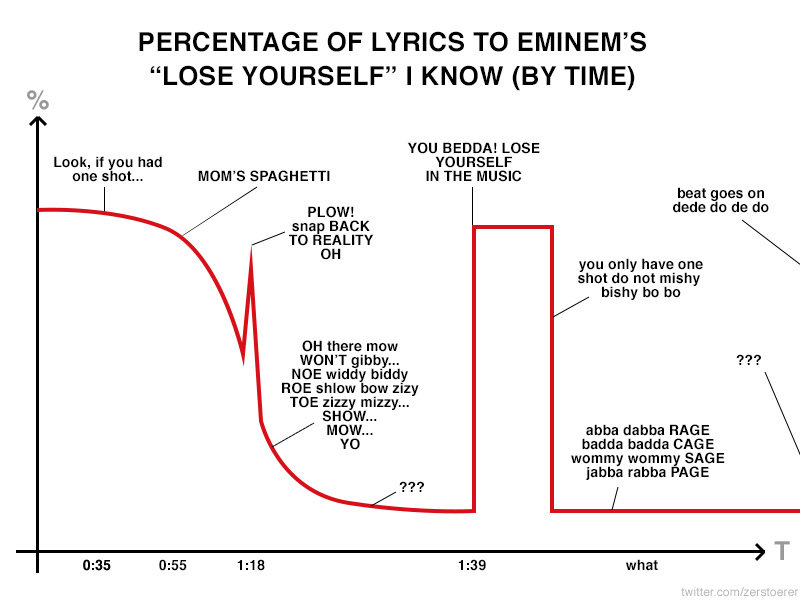
Undirected Graph

Directed Graph

GRAPH THEORY VOCAB
Acyclic Graph
Cyclic Graph




GRAPH THEORY VOCAB
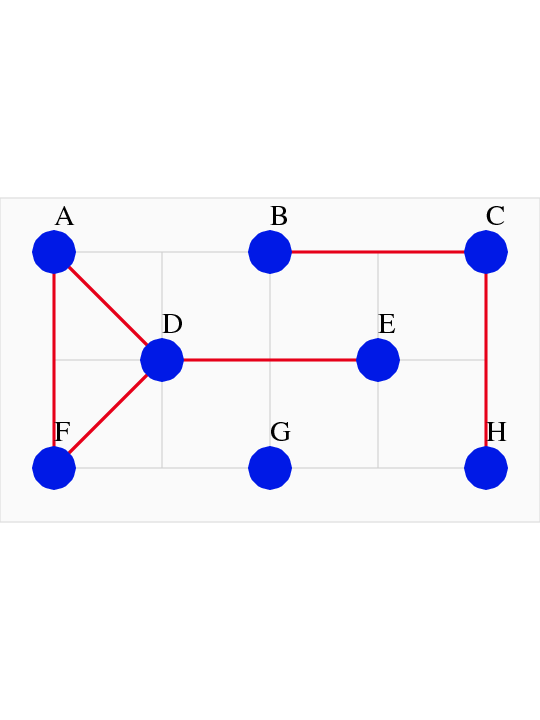
Disconnected Graph
Connected


GRAPH THEORY VOCAB
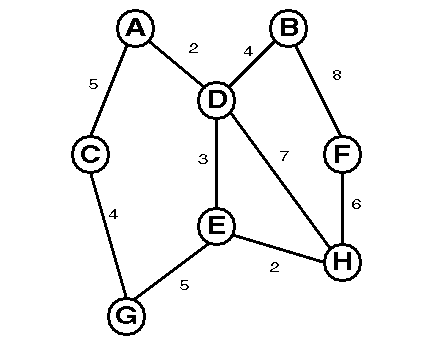
Weighted Graphs
Weight: value assigned to graph edges, typically representing the cost of traveling between two vertices
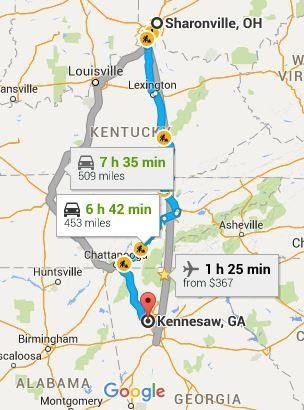
REVIEW!

REVIEW!

REVIEW!

REVIEW!

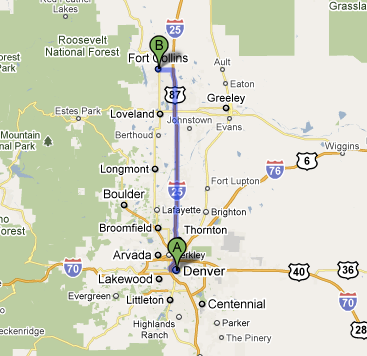
B >>>>>>>> H
REVIEW!
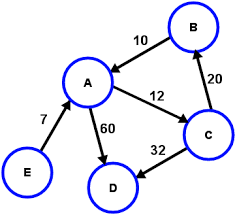
REVIEW!
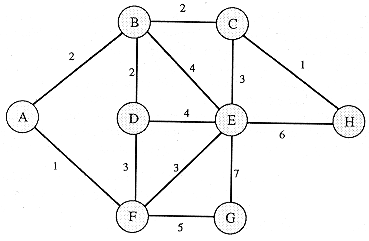
Best path from B to G
11
2
6
3
V
GRAPH THEORY NOTATION
Ordered Pairs
(A, V)
(A, V) != (V, A)
What kind of graph would have this notation?
GRAPH THEORY NOTATION
Unordered Pairs
{B, X}
{B, X} = {B, X}
What kind of graph would have this notation?
GRAPH THEORY NOTATION
VERTEX SET
Listing Vertices
{R, O, Y, G, B, P}
GRAPH THEORY NOTATION
/ Edge Set / Adjacency List /
Listing Edges
{{a, b}, {b, c}, {b, d}, {c, d}, {d, e}, {e, f}}
REVIEW!

REVIEW!
(Y, A)
(A, Y)
!=
REVIEW!
{C, S}
{S, C}
=
REVIEW!
(B, L)
{L, P}
GRAPH THEORY RESOURCES
SEARCH

SEARCH
Linear Data
Nonlinear Data
- Linear Search
- Binary Search
- Breadth First Search (BFS)
- Depth First Search (DFS)

SEARCH
Linear Data Searches
Linear Search
To search from left to right.
"Let's use a for loop to find the value we're looking for"
SEARCH
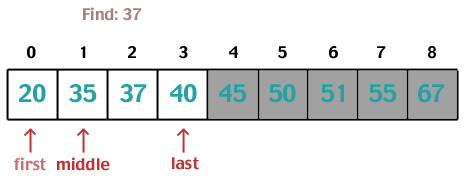
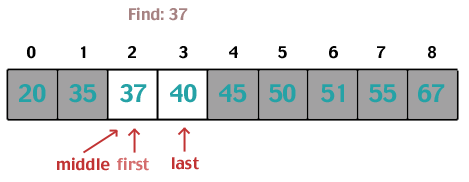
Linear Data Searches
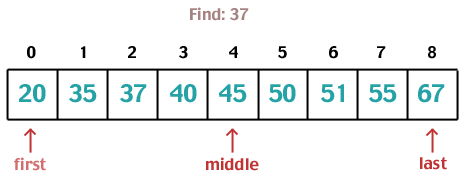
Binary Search
To search by comparing desired value to middle of list. Halving the list and then searching again as needed.
"Let's use a divide and conquer method to find it. This is great as long as the list is sorted!"
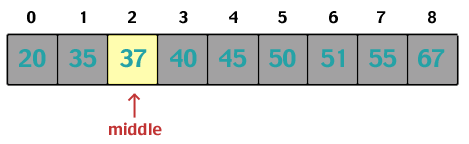
SEARCH
Non-Linear Data Searches
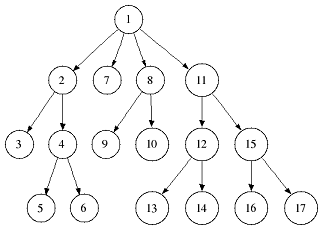
Depth First Search
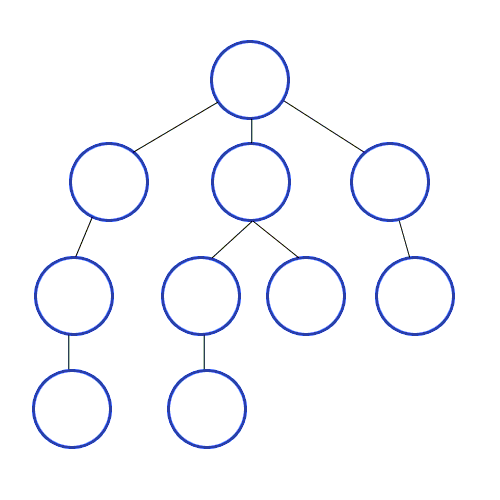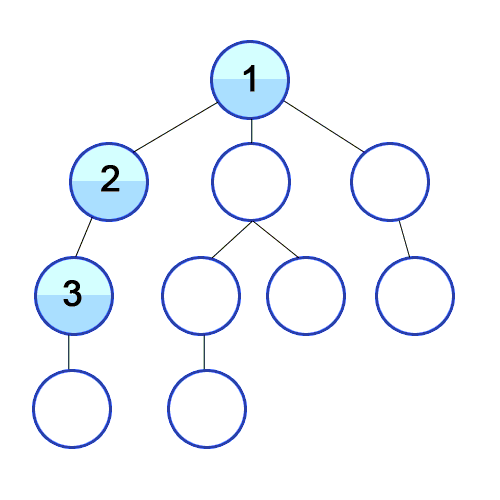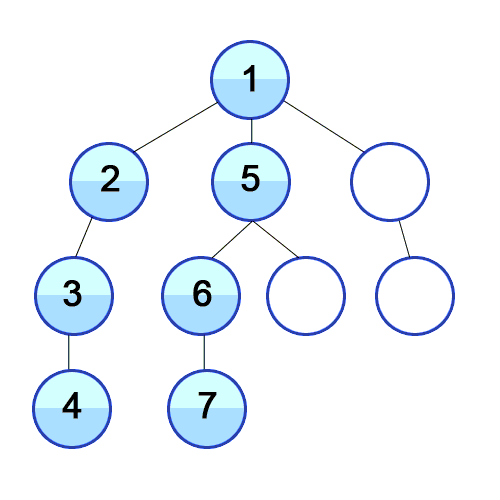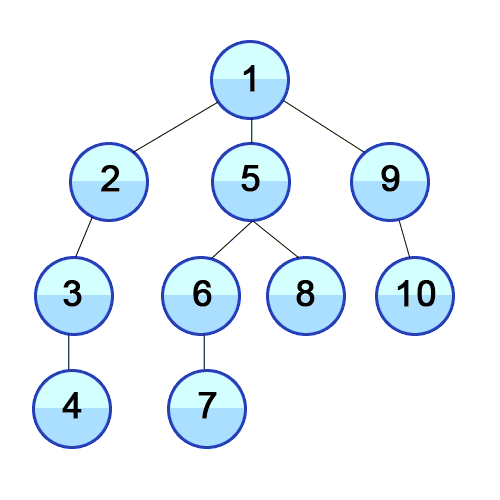
A strategy for searching in a tree in branch order.
When to use
If the tree is very wide, a BFS might need too much memory, so it might be completely impractical. If solutions are frequent but located deep in the tree, BFS could be impractical.
SEARCH
Non-Linear Data Searches
Breadth First Search
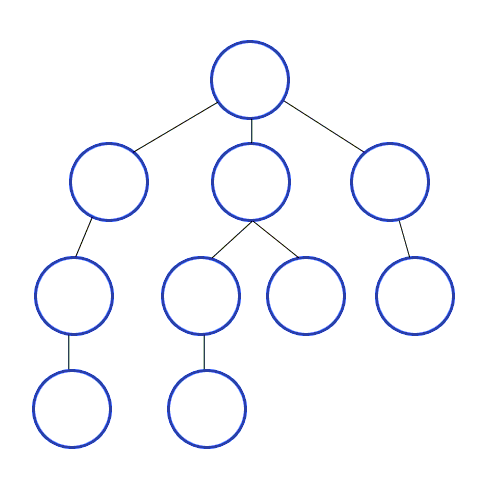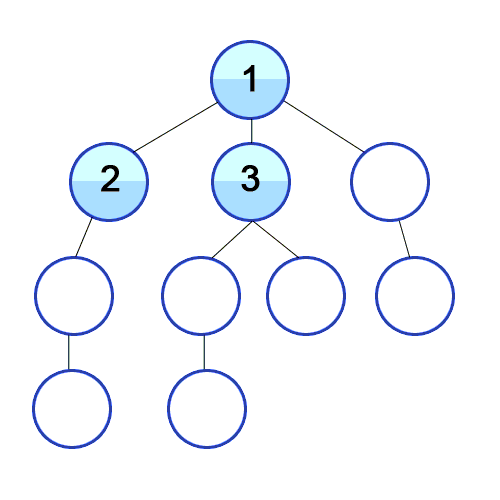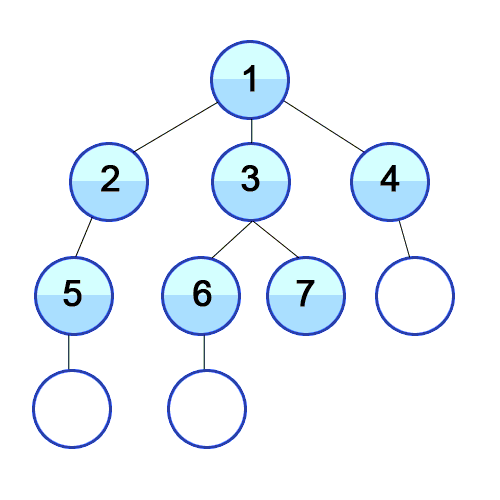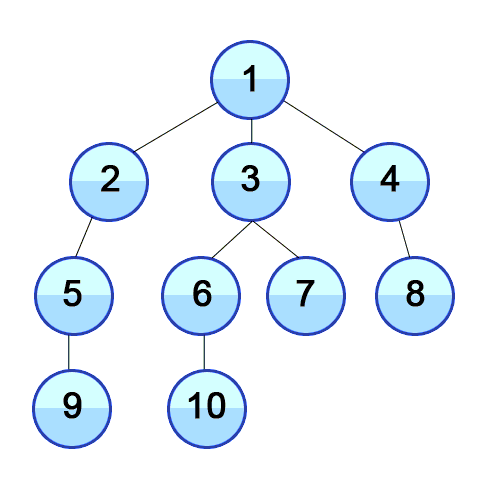
A strategy for searching in a tree in level order.
When to use
If you know a solution is not far from the root of the tree, a breadth first search (BFS) might be better.
If the tree is very deep and solutions are rare, depth first search (DFS) might take an extremely long time, but BFS could be faster.
REVIEW!
SEARCH REVIEW
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11]
SEARCH REVIEW
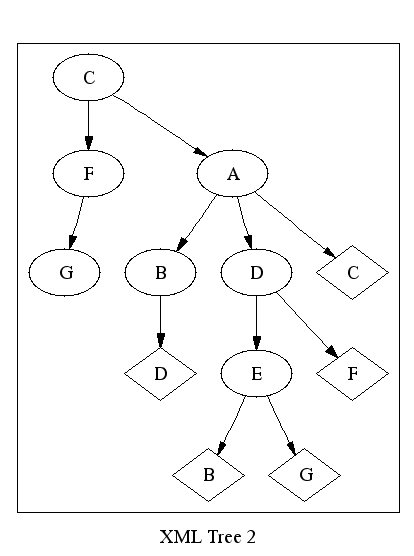
SEARCH REVIEW
["7", 7, 23, true, "& the cow jumped over", null, "down 3%"]
SEARCH REVIEW
WE DID IT!
