Computer Hardware Components & Networks
Computer Hardware
- Motherboard
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Hard Disk (HD)
- Data Storage Metrics
Motherboard
The backbone of the computer as it connects all parts of a computer together (CPU, memory, hard drives and all other ports and expansion cards).

Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU processes most of the commands from the computer's other hardware and software. The clock speed of a processor is the number of instructions it can process in any given second.
1 Hz (hertz) can process one piece of instruction every second
1.6GHz (gigahertz) = 1.6 billion instructions each second

Random Access Memory (RAM)
The computer uses RAM to load data because it is much quicker than running the same data off a hard drive. All the data that you are actively using on your computer is temporarily stored in RAM.

Hard Drive (HD)
The hard drive (hard disk drive) is the main storage device in a computer. The operating system, software and other files are stored in the HD

Data Storage Metrics
byte - the amount of storage required to store a single character of text
To convert from one unit to another, multiple 1,024:
8 bits = 1 byte (B)
1,024 bytes = 1 kilobyte (KB)
1,024 kilobytes = 1 megabyte (MB)
1,024 megabytes = 1 gigabyte (GB)
1,024 gigabytes = 1 terabyte (TB)
1,024 terabytes = 1 petabyte (PB)
Gigabyte (GB)
- Can hold almost 300 MP3 songs
- HD Netflix movie is over 4GB
- DVD movie disc holds about 9.4 GB
- Most smartphones store 64 GB or 128GB of data
Terabyte (TB)
- Can hold about 130,000 digital photos
- Monthly ISPs cap monthly data usage to 1 TB
- The Hubble Space Telescope generates about 10 TB of data every year
How much can it hold?
Computer Networking
- Computer Network
- Network Devices
- Protocols
- IP Addresses
- Ports & Sockets
Computer Network
Connection of multiple devices using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data (packets).
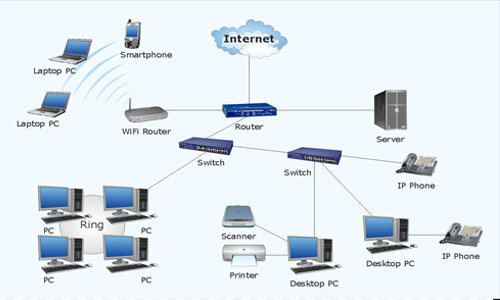
Network Devices
- Router - is responsible for routing traffic from one network to another.
- Hub - is a networking device used to connect multiple network hosts
- Bridge - connects two subnetworks as a part of the same network
- Switch - filters and forwards data packets (smarter way vs a hub)
Protocols
- Protocols are a set of algorithms/rules that defines how devices communicate across the network.
- Most common networks use the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) protocol which is a combination of two protocols that allows computers to communicate with each other through networking ports.
IP (Internet Protocol) Address
- Unique identifier (address) for any device that is on a computer network.
- All communication to and from the device in that network will be done in terms of its IP address.
- When your device sends a request, it tags the request with your IP Address so that the sender knows where to send the response.
$ ifconfigPort & Sockets
- A port an end point which data can be sent and received
- A socket is a unique combination of IP addresses and ports
How a connection is established:
- A computer request to connect to a port
- Once a connection is established, a socket is created
- Data packets are then sent to that socket