Events: Make It Happen
Events
Events make web pages more interactive. It occurs when the browser does something or when the user engages the web page.
It's the browser's way of saying, "Hey, this just happened."
HTML Events
HTML allows event handlers to be added to HTML elements to make it interactive. Events are normally used in combination with functions and will be triggered when the event occurs.
HTML
<element onclick="function name()"></element>
Javascript
function name(){
//instructions
}
HTML Events
Mouse
onclick
ondblclick
onmousedown
onmouseup
onmousemove
onmouseover
onmouseout
Form
onblur
onfocus
onfocusin
onfocusout
Drag
ondrag
ondragend
ondragover
ondragleave
Keyboard
onkeydown
onkeypress
onkeyup
Some examples...
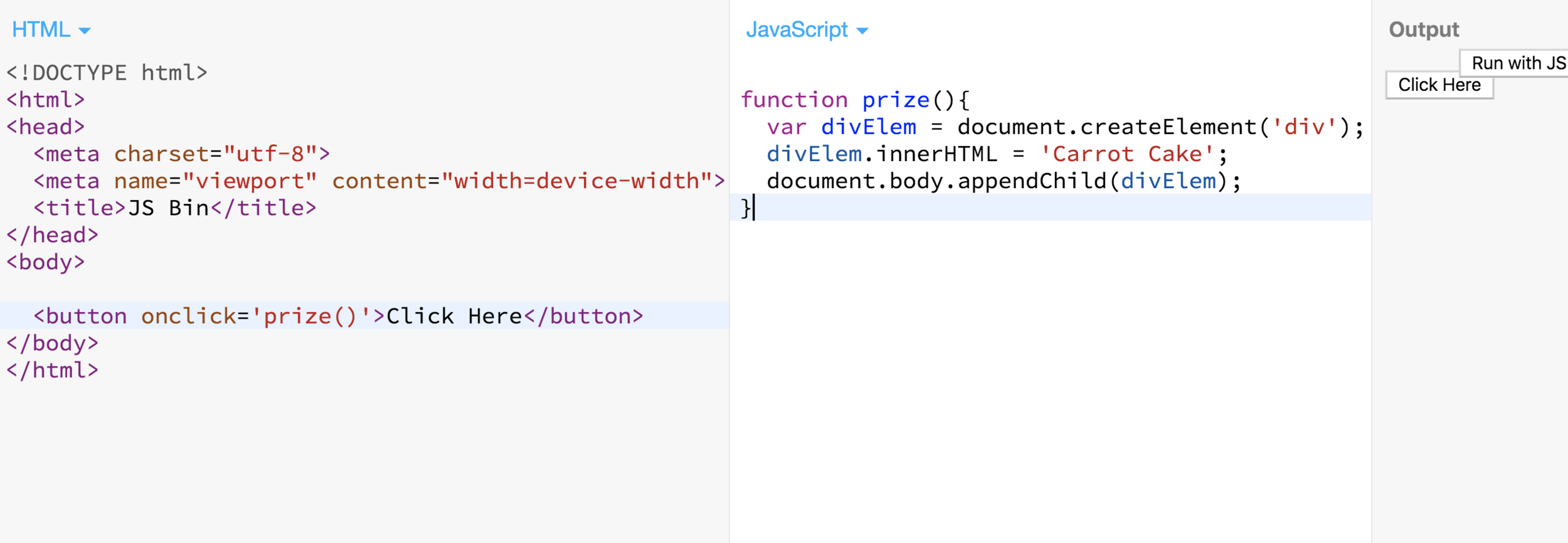
Let's Try One Together
Adding an event to the button element
Event Listeners
Adding Event Listeners is the favored way of handling events and separates Javascript from the HTML, which allows for:
- Better readability
- Can add many event handlers to one element
- Add event listeners when you have no control over the HTML mark-up
How Events Trigger Javascript
Event handling : The steps that are involved to trigger the Javascript code.
Step 1: Select the Element
Select the element node(s) in HTML you want the script to respond to
Step 2: Specify Event
Indicate which event on the selected node(s) will trigger the response (binding an event to a DOM node)
Step 3: Call Code
State the code you want to run when the event occurs
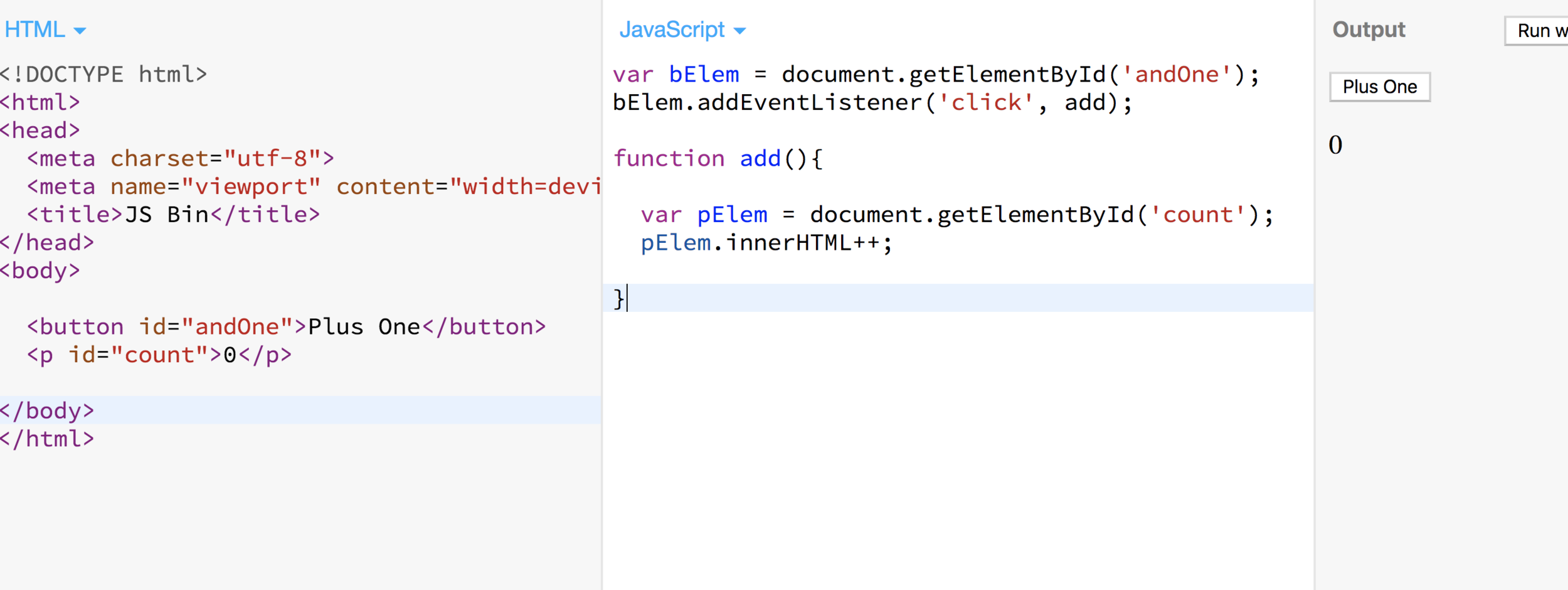
Event Listeners
The syntax goes like this:
element.addEventListener('event', functionName);
select DOM element node to target
Event to bind nodes in quote marks (i.e. "click")
Name of function to call
Event Types
Here are a few events that occur in the browser:
UI
load
unload
error
resize
scroll
Keyboard
keydown
keyup
keypress
Mouse
click
dblclick
mousedown
mouseup
mousemove
mouseover
mouseout
Form
input
change
submit
reset
cut
copy
paste
select
Focus
focus / focusin
blur / focusout
Let's Do an Example
Adding an event listener to a button element
Remember DOM Methods?
You'll be using most of these again...
- getElementById()
- getElementsByClassName()
- getElementsByTagName()
- createElement()
- appendChild()
- innerHTML
- addEventListener()
- querySelector()
- querySelectorAll()
- style
"This" Keyword
The "this" keyword refers to the element that the event is on.
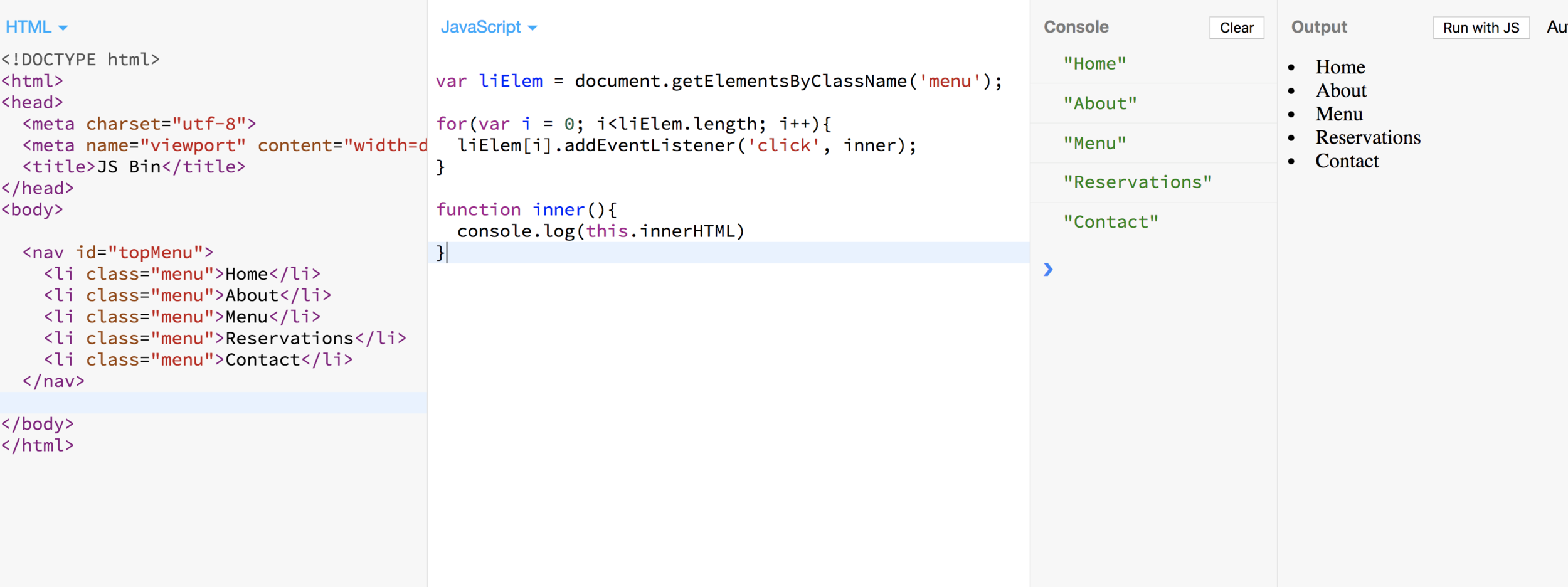
Selecting Elements Using CSS Selector
querySelector() returns the first element node that matches the CSS style selector
querySelectorAll() returns a node list (all elements) that matches a specified CSS selector
Additional Resources
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/EventTarget/addEventListener
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/EventListener
- http://www.w3schools.com/js/js_htmldom_eventlistener.asp
- http://idratherbewriting.com/events-and-listeners-javascript/
- Javascript & JQuery By Jon Duckett