Advanced JavaScript
What we're Covering
- Scope
- Objects and this
- call, apply, bind
- JavaScript Design Patterns
Scope
Scope
Scope is the set of rules that determines where and how a variable (identifier) can be looked up.
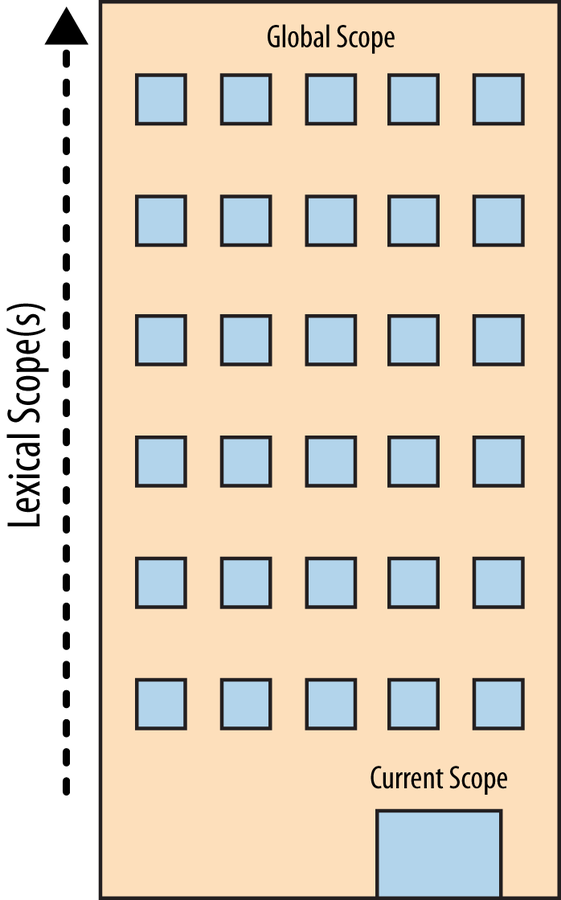
https://github.com/getify/You-Dont-Know-JS
function foo(a) {
console.log( a );
}
foo( 2 );2 was "implicitly" assigned to a
function foo(a) {
console.log( a + b );
}
var b = 2;
foo( 2 );- When searching scope of "foo", b is not found.
- Search in next scope, which is global scope
function foo(a) {
console.log( a + b );
b = a;
}
foo( 2 );- When searching scope of "foo", b is not found.
- Search in next scope, which is global scope
- Not found ---> error
function foo(a) {
b = 17;
console.log(a);
}
foo( 2 );Error or Not?
function foo(a) {
b = 17;
console.log(a);
}
foo( 2 );Error or Not?
Nope! a global variable "b" is created here
'use strict';
function foo(a) {
b = 17;
console.log(a);
}
foo( 2 );Error or Not?
strict mode is a way to opt in to a restricted variant of JavaScript.
** strict mode eliminates some JavaScript silent errors by changing them to throw errors.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Strict_mode
(Lexical) Scope
vs.
Dynamic Scope
(Lexical) Scope
- is the set of rules about how the Engine can look-up a variable and where it will find it
- it is defined at write-time
(Lexical) Scope
function foo() {
console.log( a ); // ??
}
function bar() {
var a = 3;
foo();
}
var a = 2;
bar();(Lexical) Scope
(Lexical) Scope
function foo() {
console.log( a ); // 2
}
function bar() {
var a = 3;
foo();
}
var a = 2;
bar();(Lexical) Scope
(Lexical) Scope
function foo() {
console.log( a ); // 3
}
function bar() {
var a = 3;
foo();
}
var a = 2;
bar();(Dynamic) Scope
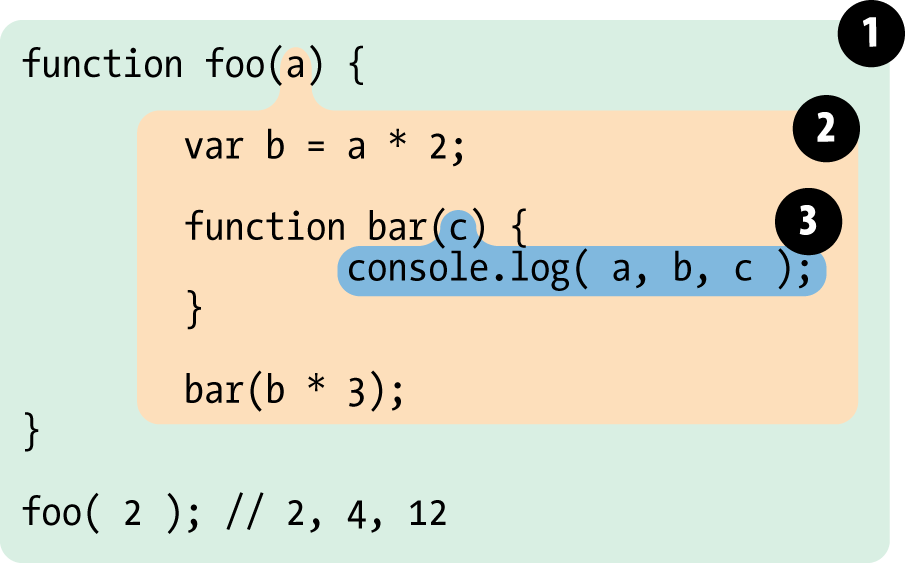
(1) global scope, 1 identifier: foo
(2) scope of foo, 3 identifiers: a, bar, b
(3) scope of bar, 1 identifier: c
Function Scope
function foo(a) {
var b = 2;
// some code
function bar() {
// ...
}
// more code
var c = 3;
}Because a, b, c, and bar all belong to the scope bubble of foo(..), they are not accessible outside of foo(..)
function foo(a) {
var b = 2;
// some code
function bar() {
// ...
}
// more code
var c = 3;
}However, all these identifiers (a, b, c, foo, and bar) are accessible inside of foo(..), and indeed also available inside of bar(..)
// write a function, given "seconds", return a string
// in the format '2:30' (2 minutes, 30 seconds)
function minToSec(totalSeconds) {
var secInMin = 60;
function getMinutes() {
return Math.floor(totalSeconds / secInMin);
}
function getSeconds() {
return Math.floor(totalSeconds % secInMin);
}
return getMinutes() + ':' + getSeconds();
}
formatTime(150);Functions as Scopes
Some Problems
var a = 2;
function foo() { // <-- insert this
var a = 3;
console.log( a ); // 3
} // <-- and this
foo(); // <-- and thispolluting the global scope, a, foo
Polluting global scope
// file: app.js
var submitBtn = document.querySelector('#submit');
submitBtn.addEventLisneter('click', function(event) {
// code here
});IIFE: Inmediately Invoked Function Expression
(function() {
var submitBtn = document.querySelector('#submit');
submitBtn.addEventLisneter('click', function(event) {
// code here
});
})();function is not bound in the enclosing scope, but instead is bound only inside of its own function.
IIFE: Conventions
(function(global, document) {
var submitBtn = document.querySelector('#submit');
submitBtn.addEventLisneter('click', function(event) {
// code here
});
})(window, document);function is not bound in the enclosing scope, but instead is bound only inside of its own function.
IIFE: Variations
(function(global, document) {
})(window, document);
// vs.
(function(global, document) {
}(window, document));function is not bound in the enclosing scope, but instead is bound only inside of its own function.
Blocks as Scopes
for (var i=0; i<10; i++) {
console.log( i );
}
console.log(i); // 9- where we declare variables is not relevant when using var, because they will always belong to the enclosing scope.
- This snippet is essentially "fake" block-scoping, for stylistic reasons, and relying on self-enforcement not to accidentally use i in another place in that scope.
let
for (let i=0; i<10; i++) {
console.log( i );
}
console.log( i ); // ReferenceErrorES6 awesomeness, covered in upcoming workshop!
Hoisting
Hoisting
a = 2;
var a;
console.log( a ); // ????Hoisting
a = 2;
var a;
console.log( a ); // 2Hoisting
a = 2;
var a;
console.log( a ); // 2var a;a = 2;
console.log( a ); // 2variable and function declarations are "moved" from where they appear in the flow of the code to the top of the code
Closures!
Closures
What I didn't know back then, what took me years to understand, and what I hope to impart to you presently, is this secret: closure is all around you in JavaScript, you just have to recognize and embrace it."
- Kyle Smith

Closure
Closure is when a function is able to remember and access its lexical scope even when that function is executing outside its lexical scope.
Closure
function foo() {
var a = 2;
function bar() {
console.log( a );
}
return bar;
}
var baz = foo();
baz(); // 2 -- Whoa, closure was just observed, man.bar() closes over that inner scope of foo(), which keeps that scope alive for bar() to reference at any later time.
Closure lets the function continue to access the lexical scope it was defined in at author-time.
Closure
for (var i=1; i<=5; i++) {
setTimeout( function timer(){
console.log( i );
}, i*1000 );
}
// what does that output?Closure
for (var i=1; i<=4; i++) {
setTimeout( function timer(){
console.log( i );
}, i*1000 );
}
// what does that output?
5
5
5
5
- Why "5": setTimeout executes well after the for-loop condition terminates, after that i = 5
- we are trying to imply that each iteration of the loop "captures" its own copy of i
- all 5 functions are closed over the same shared global scope, which has, in fact, only one i in it
IIFE Creates a Scope
for (var i=1; i<=5; i++) {
(function(j){
setTimeout( function timer(){
console.log( j );
}, j*1000 );
})( i );
}ES6 Awesomeness
for (let i=1; i<=5; i++) {
setTimeout( function timer(){
console.log( i );
}, i*1000 );
}
// vs.
for (var i=1; i<=5; i++) {
(function(j){
setTimeout( function timer(){
console.log( j );
}, j*1000 );
})( i );
}Objects and this
this in Functions
function foo(num) {
console.log('foo: ' + num);
// keep track of how many times 'foo' is called
this.count++;
}
foo.count = 0;
var i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
foo(i);
}
// foo: 0
// foo: 1
// foo: 2
// foo: 3
// how many times was 'foo' called?
console.log(foo.count) // ???this in Functions
function foo(num) {
console.log('foo: ' + num);
// keep track of how many times 'foo' is called
this.count++;
}
foo.count = 0;
var i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
foo(i);
}
// foo: 0
// foo: 1
// foo: 2
// foo: 3
// how many times was 'foo' called?
console.log(foo.count) // 0 - say what?default this binding
- this is not an author-time binding, but a runtime binding
- contextually based on the condition of the function's invocation
- has everything to do with the manner in which the function was called
function foo(num) {
console.log('foo: ' + num);
// this here refers to the global object (window)
this.count++;
}
// count property added to foo() function object
foo.count = 0;
foo(); // default bindingthis (implicit binding)
var coolShirt = {
name: 'Angular T-Shirt',
price: 19.99,
quantity: 10,
calculateTax: function() {
return this.price * 0.08
}
};
// function is called with context (owning, containing object)
console.log(coolShirt.calculateTax());if function is object property, it has a containing object
this (explicit binding)
var coolShirt = {
name: 'Angular T-Shirt',
price: 19.99,
quantity: 10,
};
function calculateTax() {
return this.price * 0.08;
}
// "call" the calculateTax function, where the context
// is the object "coolShirt"
var tax = calculateTax.call(coolShirt);
this (new binding)
function StoreItem(name, price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = 10;
}
var awesomeShirt = new StoreItem('Angular T-Shirt', 19.99);
var coolShirt = new StoreItem('ES6 T-Shirt', 18.99);
console.log(awesomeShirt.name); // 'Angular T-Shirt'
console.log(coolShirt.name); // 'ES6 T-Shirt'if function called with new (new binding), this is the newly constructed object
this gotcha
function StoreItem(name, price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = 10;
this.tax = calculateTax();
function calculateTax() {
return this.price * 0.08;
}
}
var awesomeShirt = new StoreItem('Angular T-Shirt', 19.99);
console.log(awesomeShirt.name); // 'Angular T-Shirt'
console.log(awesomeShirt.tax); // NaNwhen you define one function inside another this automatically gets set to the global scop
this gotcha
function StoreItem(name, price) {
var self = this;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = 10;
this.tax = calculateTax();
function calculateTax() {
return self.price * 0.08;
}
}
var awesomeShirt = new StoreItem('Angular T-Shirt', 19.99);
console.log(awesomeShirt.name); // 'Angular T-Shirt'
console.log(awesomeShirt.tax); // 1.5992when you define one function inside another "this" automatically gets set to the global scope
call, apply, bind
.call()
The call() method calls a function with a given this value and arguments provided individually.
fun.call(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]]).call()
function Product(name, price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
if (price < 0) {
throw RangeError('Cannot create product ' +
this.name + ' with a negative price');
}
}
function Food(name, price) {
Product.call(this, name, price);
this.category = 'food';
}
var cheese = new Food('feta', 5);
// cheese.name
// cheese.price.apply()
The apply() method calls a function with a given this value and arguments provided as an array
fun.apply(thisArg, [argsArray]).apply()
// Math.max takes in n numbers and gets the max
// what about if you have array like this:
var numbers = [5, 6, 2, 3, 7, 0, 4, 6, 8];
// ???
var max = Math.max(numbers[0], numbers[1], ....)
// what if we don't know the size of the numbers?.apply()
var numbers = [5, 6, 2, 3, 7, 0, 4, 6, 8];
var max = Math.max.apply(null, numbers); // done. cool, right?.bind()
The bind() method creates a new function that, when called, has its this keyword set to the provided value, with a given sequence of arguments preceding any provided when the new function is called.
fun.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]]).bind()
var myObj = {
specialFunction: function () {
},
anotherSpecialFunction: function () {
},
getAsyncData: function (cb) {
cb();
},
render: function () {
var that = this;
this.getAsyncData(function () {
that.specialFunction();
that.anotherSpecialFunction();
});
}
};
myObj.render();.bind()
var myObj = {
specialFunction: function () {
},
anotherSpecialFunction: function () {
},
getAsyncData: function (cb) {
cb();
},
render: function () {
this.getAsyncData(function () {
this.specialFunction();
this.anotherSpecialFunction();
}).bind(this);
}
};
myObj.render();.bind()
Function.prototype.bind = function (scope) {
var fn = this;
return function () {
return fn.apply(scope);
};
}JavaScript Design Patterns
Constructor Pattern
By simply prefixing a call to a constructor function with the keyword "new", we can tell JavaScript we would like the function to behave like a constructor and instantiate a new object with the members defined by that function.
function Listing(address, sqFootage, price) {
this.address = address;
this.sqFootage = sqFootage;
this.price = price;
this.toString() = function() {
return this.address + ',' + this.sqFootage + 'sq, $' + this.price;
}
}
// usage
var listing1 = new Listing('123 main City, CA', 2500, 500000);
console.log(listing1.toString());Constructor Pattern
function Listing(address, sqFootage, price) {
this.address = address;
this.sqFootage = sqFootage;
this.price = price;
this.toString() = function() {
return this.address + ',' + this.sqFootage + 'sq, $' + this.price;
}
}
// usage
var listing1 = new Listing('123 main City, CA', 2500, 500000);
console.log(listing1.toString());Problem: functions such as toString() are redefined for each of the new objects created using the Listing constructor
Not optimal: the function should be shared between all of the instances of the Listing type
Constructors with Prototypes
function Listing(address, sqFootage, price) {
this.address = address;
this.sqFootage = sqFootage;
this.price = price;
}
Listing.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.address + ',' + this.sqFootage + 'sq, $' + this.price;
}
// usage
var listing1 = new Listing('123 main City, CA', 2500, 500000);
var listing2 = new Listing('456 main City, CA', 2500, 600000);
// ...
console.log(listing1.toString());- Functions (like objects in JS, contain a "prototype" object)
- when we call a JS constructor to create an object, all the properties of the constructor's prototype are then made available to the new object
- Multiple "Listing" objects can be created which access the same prototype.
Object Prototypes
Object Prototypes
function StoreItem(name, price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.quantity = 10;
}
StoreItem.prototype.calculateTax = function() {
return this.price * 0.08;
}
var awesomeShirt = new StoreItem('Angular T-Shirt', 19.99);
console.log(awesomeShirt.calculateTax()); // 1.5992functions that will be used by all "StoreItem" objects should just be placed on the prototype
What is the Prototype?
What is the prototype?
- Every object within JavaScript has a "secret" property
- Each object has an internal link to another object called its prototype
var str = 'JavaScript is awesome! ';
console.log(str.__proto__); // don't mess with __ proto__String Prototype
- All String instances inherit from String.prototype
var str = 'JavaScript is awesome! ';
str.replace('JavaScript', 'Angular');
// .trim() is only available on IE9+
// we can add a trim function to the String prototype,
// thus available on ALL String instances
if(!String.prototype.trim) {
String.prototype.trim = function() {
return this.replace(/^\s+|\s+$/g, ‘’);
};
}
var trimmed = str.trim(); // 'JavaScript is awesome!';https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/String/prototype
Object.create()
- creates a new object with the specified prototype object and properties.
// Shape - superclass
function Shape() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
// superclass method
Shape.prototype.move = function(x, y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
console.info('Shape moved.');
};
// Rectangle - subclass
function Rectangle() {
Shape.call(this); // call super constructor.
}
// subclass extends superclass
Rectangle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Rectangle.prototype.constructor = Rectangle;
var rect = new Rectangle();
console.log('Is rect an instance of Rectangle?', rect instanceof Rectangle);// true
console.log('Is rect an instance of Shape?', rect instanceof Shape);// true
rect.move(1, 1); // Outputs, 'Shape moved.'General Pattern for Object Modeling
- creates a new object with the specified prototype object and properties.
function PieChart(el, data) {
this.el = el;
this.data = data;
this.render();
}
PieChart.prototype.render = function () {
this.svg();
this.visualize();
};
PieChart.prototype.svg = function () {
// ...
};
PieChart.prototype.visualize = function () {
// ...
};var stats = new PieChart('.stats', data);The Module Pattern
-
Modules are integral piece of any robust application's architecture
-
help in keeping units of code separated and cleanly organized
Object Literals
var myObjectLiteral = {
variableKey: variableValue,
functionKey: function () {
// ...
}
};Object literals don't require instantiation using the new operator.
Object Literals
var myModule = {
myProperty: "someValue",
// object literals can contain properties and methods.
// e.g we can define a further object for module configuration:
myConfig: {
useCaching: true,
language: "en"
},
// a very basic method
saySomething: function () {
console.log( "Where in the world is Paul Irish today?" );
},
// output a value based on the current configuration
reportMyConfig: function () {
console.log( "Caching is: " + ( this.myConfig.useCaching ? "enabled" : "disabled") );
},
// override the current configuration
updateMyConfig: function( newConfig ) {
if ( typeof newConfig === "object" ) {
this.myConfig = newConfig;
console.log( this.myConfig.language );
}
}
};
// Outputs: Where in the world is Paul Irish today?
myModule.saySomething();
// Outputs: Caching is: enabled
myModule.reportMyConfig();
// Outputs: fr
myModule.updateMyConfig({
language: "fr",
useCaching: false
});
// Outputs: Caching is: disabled
myModule.reportMyConfig();The Module pattern was originally defined as a way to provide both private and public encapsulation for classes in conventional software engineering.
var testModule = (function () {
var counter = 0;
return {
incrementCounter: function () {
return counter++;
},
resetCounter: function () {
console.log( "counter value prior to reset: " + counter );
counter = 0;
}
};
})();
// Usage:
// Increment our counter
testModule.incrementCounter();
// Check the counter value and reset
// Outputs: counter value prior to reset: 1
testModule.resetCounter();var myModule = (function () {
var myPrivateVar, myPrivateMethod;
// A private counter variable
myPrivateVar = 0;
// A private function which logs any arguments
myPrivateMethod = function( foo ) {
console.log( foo );
};
return {
// A public variable
myPublicVar: "foo",
// A public function utilizing privates
myPublicFunction: function( bar ) {
// Increment our private counter
myPrivateVar++;
// Call our private method using bar
myPrivateMethod( bar );
}
};
})();var Listing = (function() {
function Listing(address, sqFootage, price) {
this.address = address;
this.sqFootage = sqFootage;
this.price = price;
}
Listing.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.address + ',' + this.sqFootage + 'sq, $' + this.price;
};
return Listing;
})();Module to implement re-usable model
Exercise: implement a ShoppingCartModule
- "private" shopping cart array
- should have exposed API methods: addItem(), getItemCount(), getTotal()
- addItem() takes in ShoppingItem items
- use IIFE constructs
Exercise: implement a ShoppingItem model
- constructor function should take in name, price, and sku
- should have exposed API methods: toString(), calculateTax()
- "private" taxPercentage (0.8)
- use IIFE constructs
Solution:
Modern JavaScript Development with ES6
Gulp, ES6, Webpack
Saturday, April 16, 2016
Mailing List: http://eepurl.com/bzsn7r


Modern JavaScript Development with ES6
Mailing List: http://eepurl.com/bzsn7r


