Women in Technology
Data & information
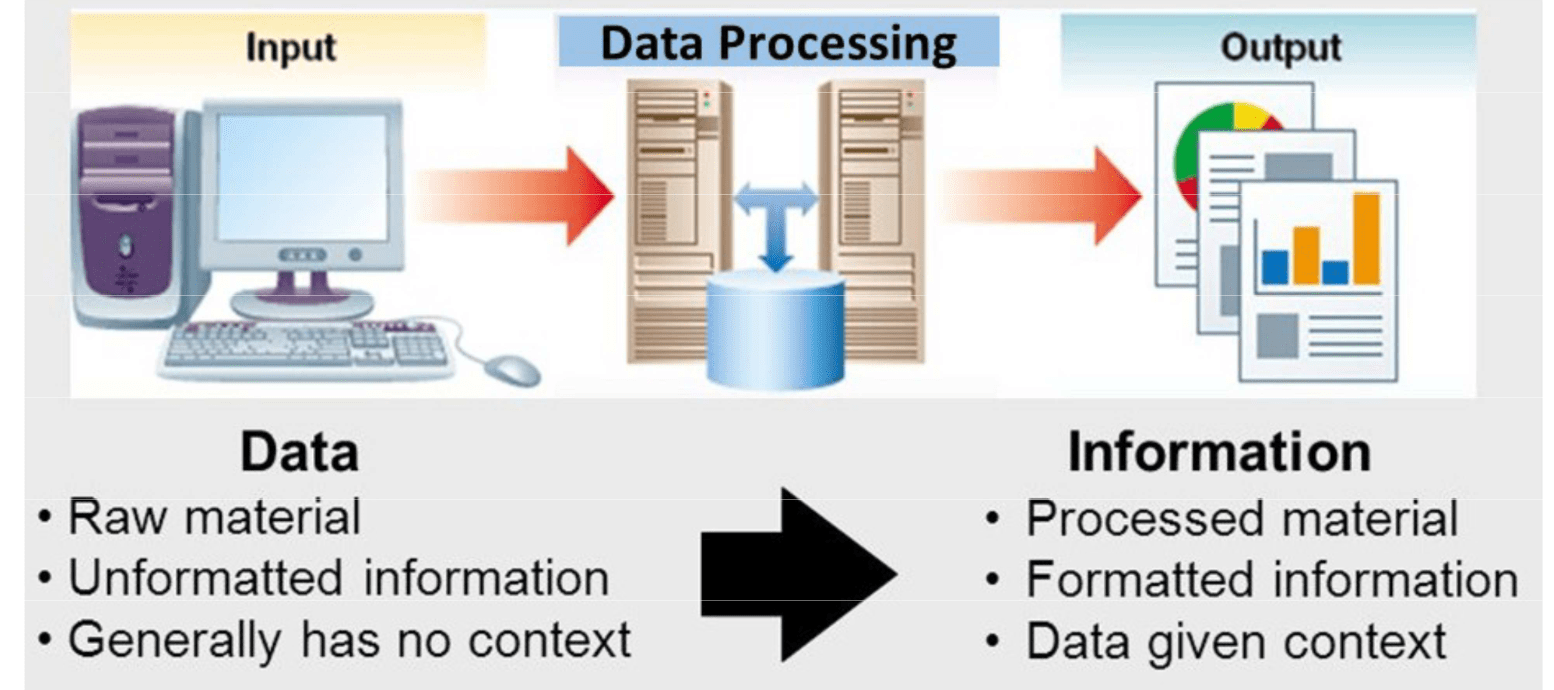
Collection of data
Organization of data
Presentation of data
Analysis of data
Data Analysis
- Data analysis is defined as a process of cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to discover useful information for business decision-making.
- The purpose of Data Analysis is to extract useful information from data and taking the decision based upon the data analysis.
Types
-
Descriptive Analytics:
- Objective: Describes what has happened in the past.
- Focus: Summarizes and provides an overview of historical data.
- Methods: Aggregation, summarization, and data visualization.
- Example: Generating reports on monthly sales, summarizing website traffic, or creating dashboards displaying key performance indicators (KPIs).
-
Diagnostic Analytics:
- Objective: Examines past data to understand why a certain event happened.
- Focus: Identifying patterns, correlations, and relationships.
- Methods: Drill-down, data mining, and correlation analysis.
- Example: Investigating the reasons behind a sudden spike or drop in sales, analyzing the factors contributing to customer churn, or identifying the root causes of production issues.
-
Predictive Analytics:
- Objective: Predicts future outcomes or trends based on historical data.
- Focus: Forecasting and making predictions.
- Methods: Statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and time-series analysis.
- Example: Forecasting future sales based on historical data, predicting equipment failures in a manufacturing plant, or estimating the likelihood of a customer making a purchase.
-
Prescriptive Analytics:
- Objective: Recommends actions to optimize a particular outcome.
- Focus: Providing advice on what actions to take to achieve desired results.
- Methods: Optimization algorithms, simulation, and decision analysis.
- Example: Recommending optimal pricing strategies for products, suggesting personalized marketing approaches for different customer segments, or advising on inventory levels to minimize stockouts.
Methods
Pandas
Numpy
matplotlib
Seaborn
Scikit-learn
Pandasql
Uplifting the gross roots using Foss
Vijayalakshmi
VGLUG Foundation
Sept 14, 2023
DebConf 23, Kochi

Uplifting the gross roots using Foss
Vijayalakshmi
VGLUG Foundation
Sept 14, 2023
DebConf 23, Kochi


VGLUG?
Foss into the Mass
Mass into the Foss
- Meet-ups
- SFD(Software Freedom Day)
- Workshops in colleges
- Hackathons
- conferences
Foss Meet-ups
College Glugs
Foss Technology Trainings
100 Glugs in 100 villages