Introduction to JavaScript
Vladimir de Turckheim
Lead Node.js engineer @ Sqreen (ex. Steamulo, Secway)




A bit of history
Timeline
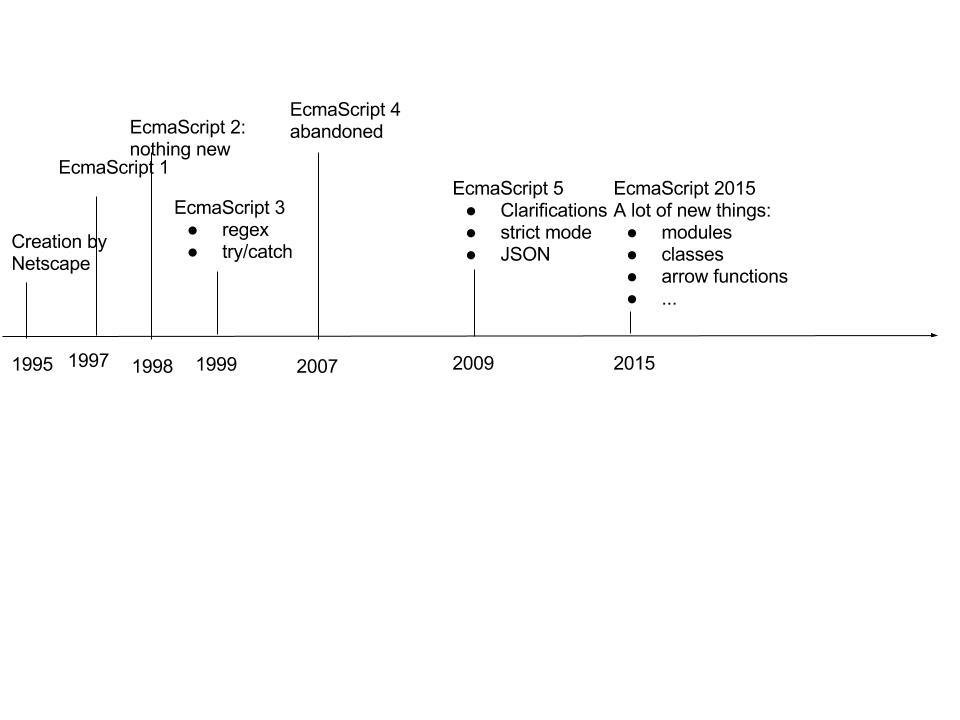
Key dates
- 2006: JQuery
- 2009: Node.js
- 2009: AngularJS
- 2013: React
- 2016: Angular 2
Weird stuff
- ActionScript
- TypeScript
- CoffeeScript
JavaScript is a multi-paradigm programming language which syntax inherits from C with weak duck typing.
This should be enough for you to write JavaScript actually.
Paradigms
- Imperative
- Object oriented (prototypes)
- functionnal
Where to run JavaScript
In the browser
Console
- Press F12
- Find the Console
- Write JS
In a file
<html>
<body>
<script> // write code here </script>
</body>
</html>All browser do not support all versions of JS...
On your computer
Install Node.js
DOC
The best Fr/En doc is the mozzilla one:
https://developer.mozilla.org/fr/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference
Browser support is also indicated there.
Basics
Hello world
// Hello World
alert('hello World');
// in console
console.log('hello world');Comments
// This is a one line comment
/*
this
is
a
multi
line
comment
*/variable declaration and types
var a; // a has the undefined value here.
// undefined is a special value in js that means, that what your are looking for is not here.
var b = 1; // b is a number
var c = 1.1; // c is a number
var d = "hello"; // d is a string
var e = 'hello'; // e is a string
var f = function () {}; // f is a function
var g = {}; // g is an object
var h = null; // h is the null object
var i = NaN; // i is the Not a Number value which is a number
var j = []; // j is an array
var k = true; // k i a boolean
const X = 1; // I am a constant
let y = 2; // I can be changed
Pleas place semicolons (;) even if they are optional// The typeof keyword is used to check the type of a variable
> typeof a
undefined
> typeof b
'number'
'>' means I write this in the js console, the next line is the output of the commandBoolean manipulation
// Equality
var x = 1;
var y = '1';
x == y // true
x === y // false
// when using the ==, a type casting is made.
// Comparison:
var a = true;
var b = false;
a || b // true: a OR b
a && b // false: a AND b
// Negation
!true === falseBoolean manipulation
// falsy values
// The following values are casted as false in boolean equations:
false
''
""
NaN
null
undefined
0
// all other value resolve to true.
// Special usage of boolean operators:
var a = 1;
var b = 0;
var c = b || 1; // c is 1;
// casting to a boolean
var d = 1;
!!d === true;
// checking the existence of something
if(something) {
}if, for, while
if (test) {
// do stuff
} else if(other test) {
// do other stuff
} else {
// to other other stuff
}
for(var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// do stuff
}
// variables are not scoped, i exists here too
> i
1000
while (test) {
// ditto
}Objects
In JS, all objects are dicts:
var a = {
key: 'value',
key2: 2
};
a.key === 'value';
a['key2'] === 2;
// you can add claims to the object
a.key3 = 10;
a['key4 weird'] = { a: 1};
> a
{ key: 'value', key2: 2, key3: 10, 'key4 weird': { a: 1} }
> a.pony
undefinedArrays
// Arrays are created with the [] symbols
var a = [1, 'a', {}];
> a[0]
1
a[5] = 10
> a
[ 1, 'a', {}, , , 10 ]
> a[4]
undefined
// get length:
> a.length
6
// add something at the end of an array
var b = [];
b.push(1) // b === [1]
var x = b.pop(); // x === 1; b is []
// concat: it returns a new array;
var c = ['c'];
var d = ['d'];
var e = c.concat(d); // c is ['c']; d is']; is ['c','d'];Functions
// Functions are declared with the `function` keyword
function f (a) { // the name of the function is f
return a + 1;
}
// or
var g = function (a) {
return a + 1;
}
// the function held in the g variable does not have any name,
// it is said to be anonymous
f(1) === 2;
f('a') === 'a1';
// Arrow functions
g = (x) => x + 1;Functions (callbacks)
// Some methods in javascript take a function as parameter
// the method 'map' on arrays:
var a = [1, 2, 3, '4'];
var b = a.map(function (item) { return item + 1; });
> a
[ 1, 2, 3, '4' ]
> b
[ 2, 3, 4, '41' ]
// the anonymous function passed as argument to map
// has been called on all items of a and a new array has been createdMethods on arrays
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array
Can you:
- sort an array
- find an element in an array
- filter an array
- ... ?
Classes
// this function is called a constructor
class Person {
constructor (name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sayHello() {
return 'Hello, my name is ' + this.name;
}
}
var john = new Person('john', 20);
> john.sayHello()
'Hello, my name is john'
> john instanceof Person
trueDOC
The best Fr/En doc is the mozzilla one:
https://developer.mozilla.org/fr/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference
Browser support is also indicated there.
GOOGLE:
"mdn tri liste" :
first result: Array.prototype.sort()
JSON
JSON is a format used to exchange data
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation

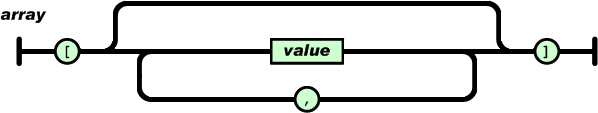
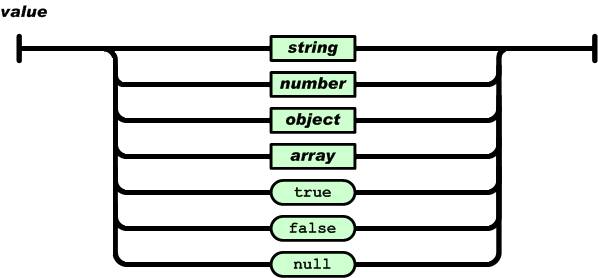
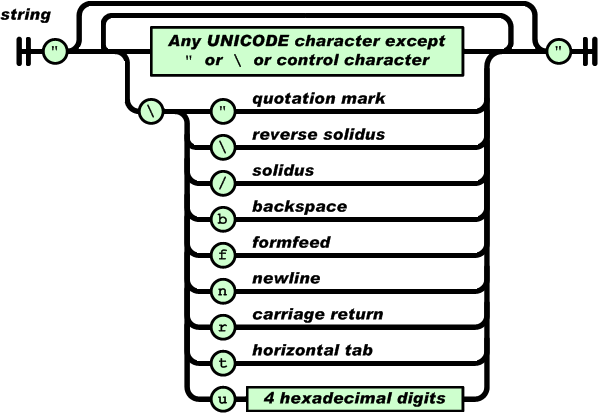
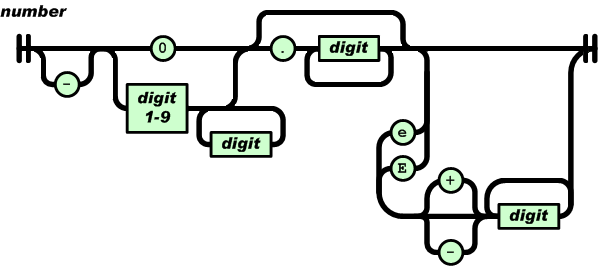
In the real world
{
"key": "value",
"key2": { ... }
}
OR
[1, 2, { ... }]
{...} means any JSON object.
// In js:
var a = { a: 1, b: { c: "c" } };
var aJson = JSON.stringify(a);
var b = JSON.parse(aJson);
> a
{ a: 1, b: { c: 'c' } }
> aJson
'{"a":1,"b":{"c":"c"}}' // this is a string !
> b
{ a: 1, b: { c: 'c' } }
> a == b
falseJQuery & DOM manipulation
JQuery is a JS library that provides an uniform api on all browser and make HTML (DOM) manipulation easier
Code: http://bit.ly/2d37JZT
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main">
<p>hello World</p>
</div>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>- JQuery is imported in the headers
- Our script is imported in body
Ugly part: in our script the $ contains JQuery...
$('#main').click(function () {
$('.second').text('hello');
// we select all items whose class is 'second' (the . means class) and change their
// text to 'hello';
$('#main').css('background-color', 'yellow');
// we change the color of the element whos id is 'main' (the # means id)
});
// AJAX call
var settings = {
"async": true,
"crossDomain": true,
"url": "http://petstore.swagger.io/v2/pet/findByStatus?status=available",
"method": "GET",
"headers": {
"accept": "application/json"
}
}
$.ajax(settings).done(function (response) {
console.log(response);
});index.js
RTFM
LMGTFY
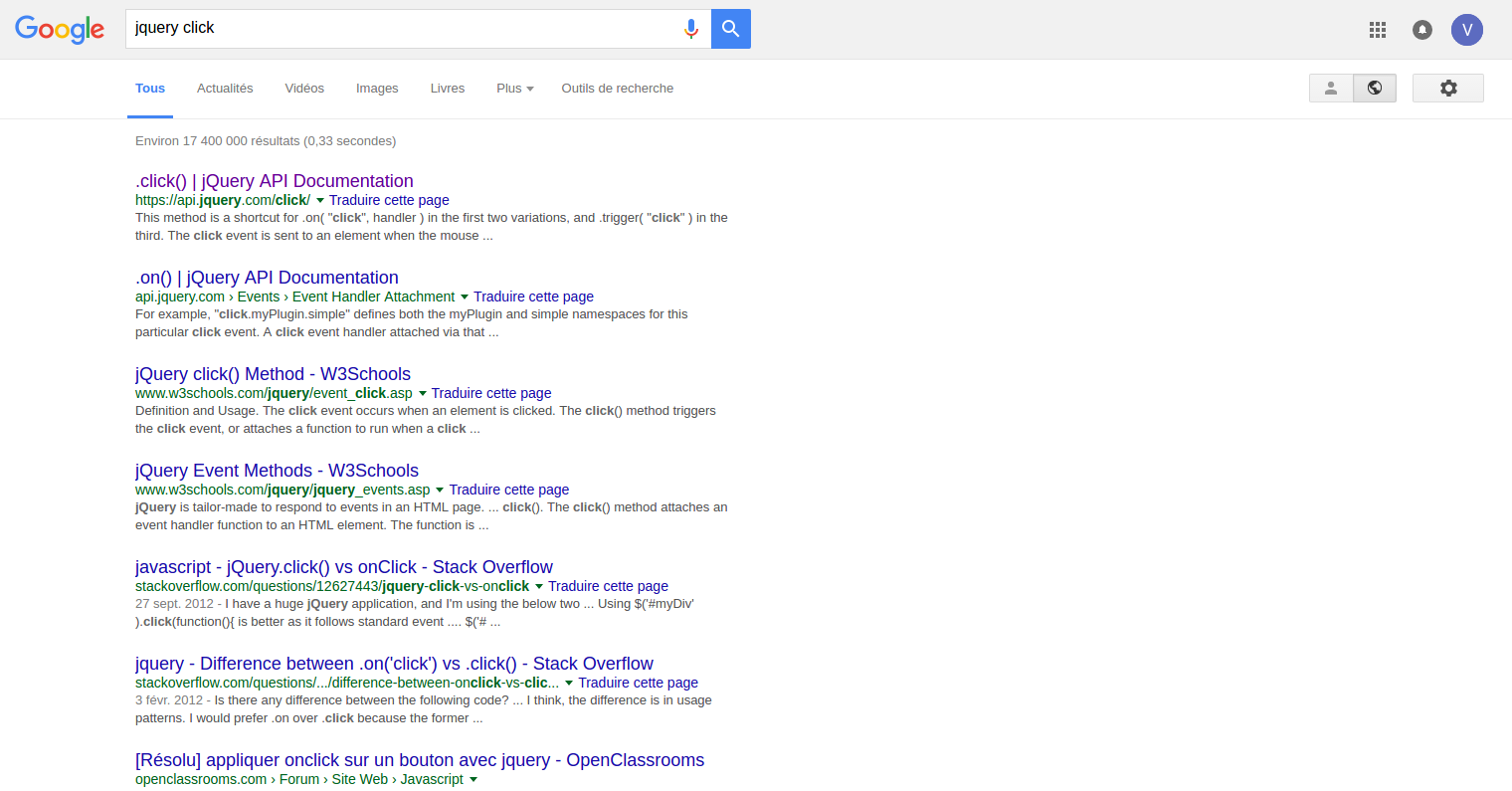
Good places to find help
- StackOverflow
- Github issues
Please do not open an issue unless you have googled your problem for at least 2 hours !!
Workshop
- Get the base project (previously on this pres)
- Start it and reproduce what we did in the slides
- Go to http://petstore.swagger.io/#!/pet/findPetsByStatus
- From the starter project and with the help of the online documentation create a page with:
- 3 buttons: "available", "pending", "sold"
- When we click on them, it displays the list of pets by status

