Algorithms #6

Datastructures

Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs
What
Is
Datastructure
Anyway
?
?
Data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
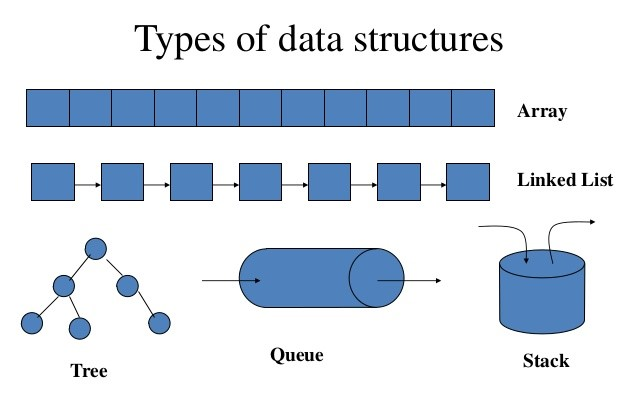
Data Structures
Linked List
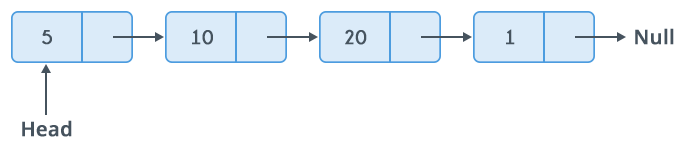
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements, whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence.
Tail
Linked lists are among the simplest and most common data structures.
Applications of linked list
- Implementation of stacks and queues
- Implementation of graphs : Adjacency list representation of graphs is most popular which is uses linked list to store adjacent vertices.
- Dynamic memory allocation : We use linked list of free blocks.
- Image viewer – Previous and next images are linked, hence can be accessed by next and previous button.
- Previous and next page in web browser – We can access previous and next url searched in web browser by pressing back and next button since, they are linked as linked list.
- Music Player – Songs in music player are linked to previous and next song. you can play songs either from starting or ending of the list.

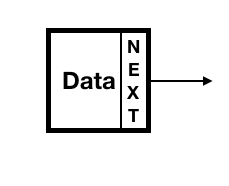
Node
One piece of data


class Node {
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}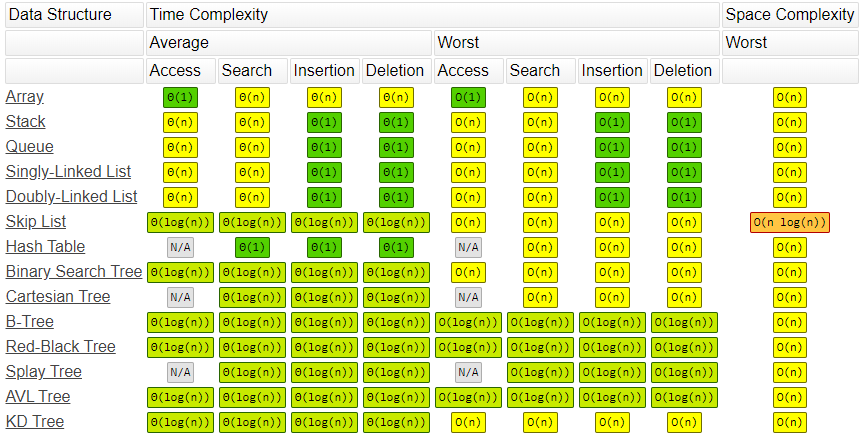
Common Data Structure Operations
Difference between Singly linked list and Doubly linked list
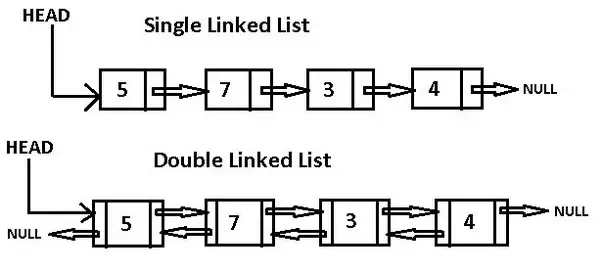
1-way or singly linked list is the simple one in which there is one head node and other nodes are connected in forward manner. i.e, you cannot traverse backwards as there is no back pointer.
2-way or doubly linked list is more advanced one in which each node contains one more link which points to the previous element/node. You can traverse forward as well as backwards in this Data structure.

Problem #1
Create class OneWayLinkedList, create construnctor with Head and Tail nodes. Implement push(data) method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.length // 3
list.head.next.next.data // 3Problem #2
Implement toArray() method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.toArray(); // [1,2,3]Problem #3
Implement pop() method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.toArray(); // [1,2,3]
const a = list.pop(); // 3
const b = list.pop(); // 2

Problem #4
Implement getNode and get method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
get(0) //1
get(2) //3
getNode(2) // { value: 3, next: null }

Problem #5
Implement insert and remove method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.remove(1)
list.length // 2
getNode(1) // { value: 3, next: null }
list.insert(100, 1);
list.length // 3
getNode(1) // { value: 100, next <NODE> }Problem #6
Implement shift and unshift methods
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.shift() // 1
list.unshift(100);
getNode(0) // { value: 100, next: <NODE> }
Problem #7
Implement reverse method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.reverse()
.toArray() // [3,2,1]

Problem #8
Implement mid method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.push(4);
list.push(5);
// [1,2,3,4,5]
list.mid() // 3

Problem #9
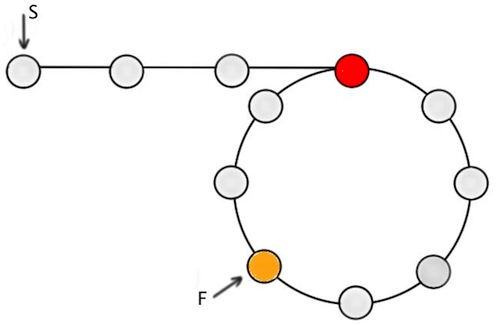
Implement hasLoop method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.push(4);
list.push(5);
// [1,2,3,4,5]
list.tail.next = list.head
list.hasLoop() // true

Problem #10
Implement rotate method
const list = new OneWayLinkedList();
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.push(4);
list.push(5);
// [1,2,3,4,5]
list.rotate(2)
.toArray() // [3,4,5,1,2]
list.rotate(-2)
.toArray() // [1,2,3,4,5]
Thank you!
