Algorithms #8
Hash map


What is hash map ?
HASH + MAP
"Hello world" => 5812101923
Hash code is a numeric value which helps in identification of an object during equality testing and also can serve as an index for the object.
| Key Hash | Value |
|---|---|
| 7216428 | "value1" |
| 5995050 | "value2" |
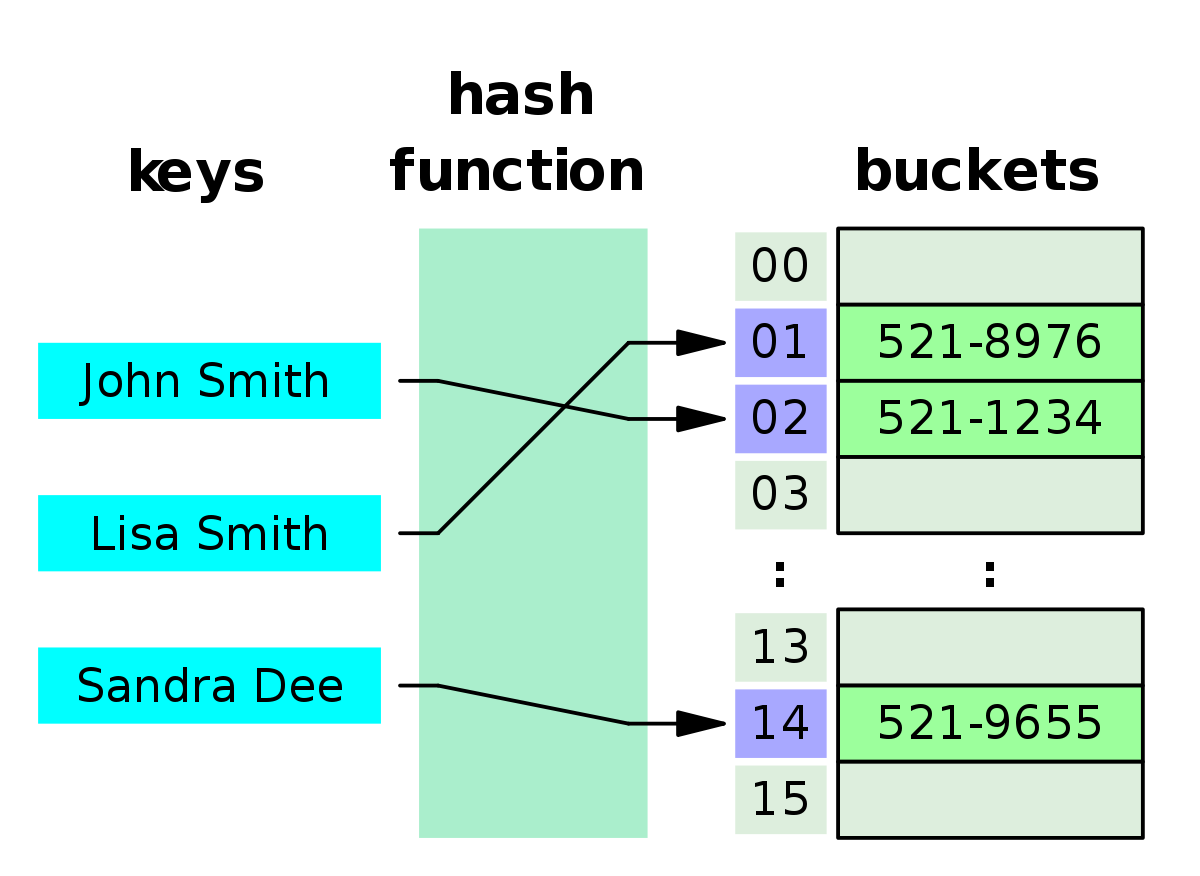
A hash table (hash map) is a data structure that is used to store keys/value pairs. It uses a hash function to compute an index into an array in which an element will be inserted or searched. By using a good hash function, hashing can work well
JavaScript object is already a hash table with built in hash function!
const map = {};
map['test abc'] = 1; // set
map['test abc'] = 2; // set overwrite
map['test abc'] // get -> 2
Object.keys(map).forEach(key => /* ... */ );
for(let key of map) {
// ...
}JS built in Map class
const myMap = new Map();
const keyString = 'a string',
keyObj = {},
keyFunc = function() {};
// setting the values
myMap.set(keyString, "value associated with 'a string'");
myMap.set(keyObj, 'value associated with keyObj');
myMap.set(keyFunc, 'value associated with keyFunc');
myMap.size; // 3
// getting the values
myMap.get(keyString); // "value associated with 'a string'"
myMap.get(keyObj); // "value associated with keyObj"
myMap.get(keyFunc); // "value associated with keyFunc"
myMap.get('a string'); // "value associated with 'a string'"
// because keyString === 'a string'
myMap.get({}); // undefined, because keyObj !== {}
myMap.get(function() {}); // undefined, because keyFunc !== function () {}Map vs objects
- The key difference is that Objects only support string keys where as Maps support more or less any key type.
- A Map object can iterate its elements in insertion order

Map vs objects
Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from HashMap in that it maintains a doubly-linked list running through all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map (insertion-order).
JS new Map() is actually LinkedHashMap datastructure
Hash Map time complexity
Average:
get/put O(1)
Worst case:
get/put O(n)
Hash function
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, digests, or simply hashes. The values are used to index a fixed-size table called a hash table. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called hashing or scatter storage addressing.
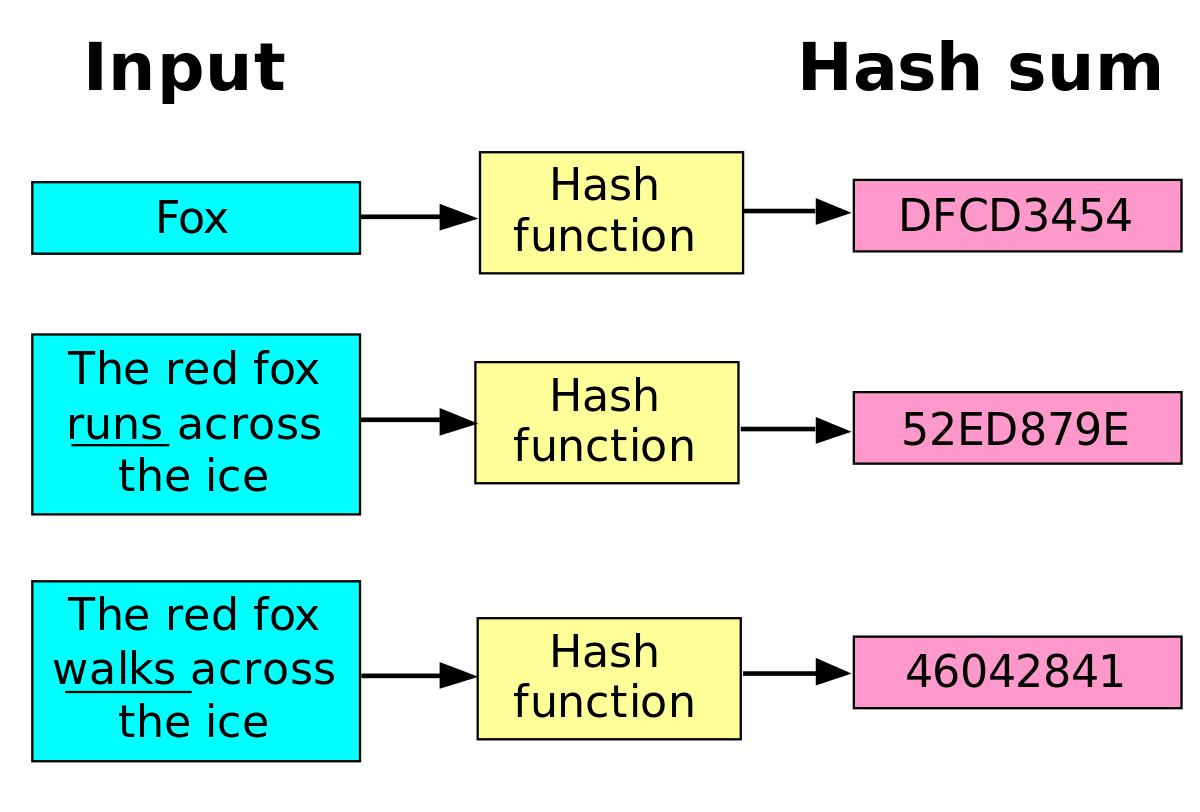
Hash function example
function hashCode(str) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
const chr = str.charCodeAt(i);
hash = ((hash << 5) - hash) + chr;
hash |= 0; // Convert to 32bit integer
}
return hash;
}
// The hash << 5 - hash is the same as hash * 31 + char but a LOT fasterTypes of Hashing
MD5 - An MD5 hash function encodes a string of information and encodes it into a 128-bit fingerprint. MD5 is often used as a checksum to verify data integrity. However, due to its age, MD5 is also known to suffer from extensive hash collision vulnerabilities, but it’s still one of the most widely used algorithms in the world.
SHA-2 – SHA-2, developed by the National Security Agency (NSA), is a cryptographic hash function. SHA-2 includes significant changes from its predecessor, SHA-1. The SHA-2 family consists of six hash functions with digests (hash values) that are 224, 256, 384 or 512 bits: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256.
CRC32 – A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is an error-detecting code often used for detection of accidental changes to data. Encoding the same data string using CRC32 will always result in the same hash output, thus CRC32 is sometimes used as a hash algorithm for file integrity checks. These days, CRC32 is rarely used outside of Zip files.
What are the benefits of Hashing?
- Uses in data-structures like HashMap, HashSet
- One main use of hashing is to compare two files for equality. Without opening two document files to compare them word-for-word, the calculated hash values of these files will allow the owner to know immediately if they are different.
- Hashing is also used to verify the integrity of a file after it has been transferred from one place to another, typically in a file backup program like SyncBack. To ensure the transferred file is not corrupted, a user can compare the hash value of both files. If they are the same, then the transferred file is an identical copy.
- In some situations, an encrypted file may be designed to never change the file size nor the last modification date and time (for example, virtual drive container files). In such cases, it would be impossible to tell at a glance if two similar files are different or not, but the hash values would easily tell these files apart if they are different.
Hash maps in the enterprise?
Each redis database instance ( databases are indexed from 0 to max configured ) has a key space associated with it which is nothing but a wrapper on hash table implementation. Whatever data redis stores be it string, redis set or redis hash, everything is saved inside the hash tables

How does hash map works ?
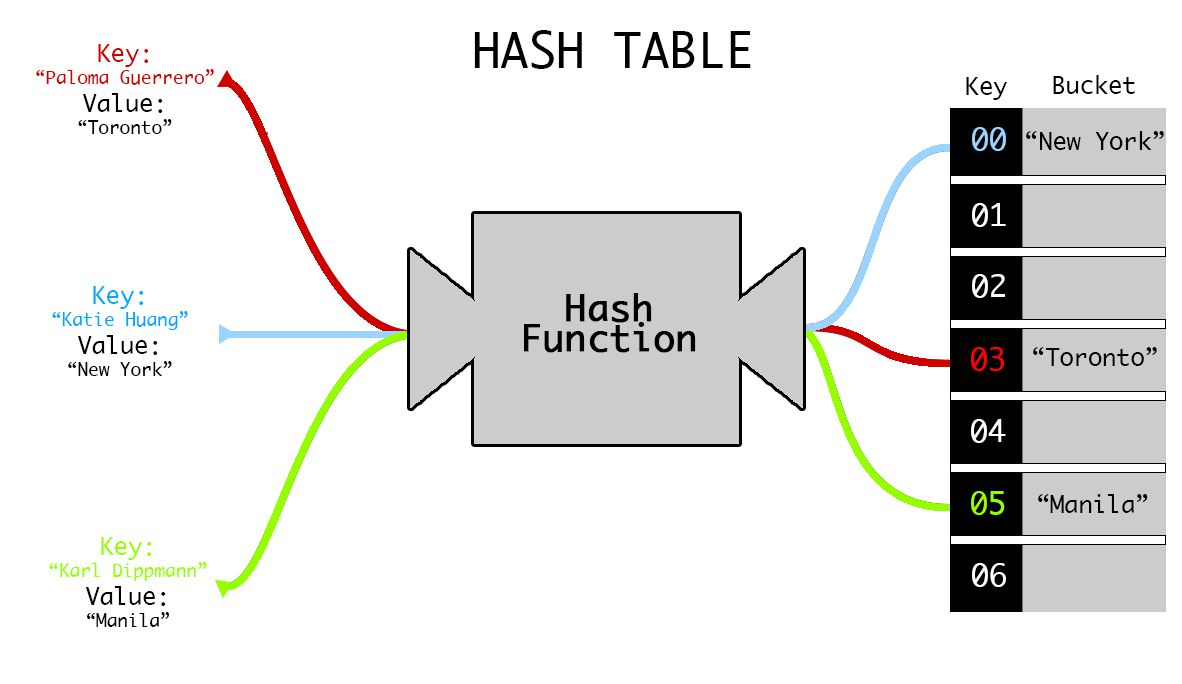
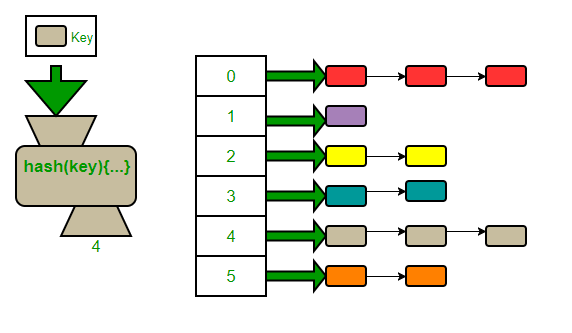
But what if hash code is the same ?
hash map entry become a linked list!
Try to implement HashMap using array!
class HashTable {
constructor() {
/* implement this */
}
set(key, value) {
/* implement this */
}
get(key) {
/* implement this */
}
keys() {
/* implement this */
}
}
const test = new HashTable();
test.set('black', '#000');
test.set('white', '#fff');
test.set('red', '#f00');
test.set('blue', '#00f');
test.set('green', '#0f0');
console.log(test);
console.log(test.get('green'));
console.log(test.get('black'));
console.log(test.get('red'));
console.log(test.get('white'));
console.log(test.keys());// сделаем объект range итерируемым
range[Symbol.iterator] = function() {
let current = this.from;
let last = this.to;
// метод должен вернуть объект с методом next()
return {
next() {
if (current <= last) {
return {
done: false,
value: current++
};
} else {
return {
done: true
};
}
}
}
};
for (let num of range) {
alert(num); // 1, затем 2, 3, 4, 5
}Problem #2
design a hash set!
Thank you!

