Distributed Node #2
Databases

It's an organized collection of structured information, or data, typically stored electronically in a computer system.
What is a database?
Modern Three-Tier Architecture
Classic representation
Presentation Tier
Business Tier
Data Tier
JSP
EJB
Oracle
What about scaling?

Electron
Business Tier
Data Tier
Business Tier
Data Tier
Business Tier
Data Tier
ROUTER
View
View
Java
SQL based DB
View
Presentation Tier
React
React
React
React
Scaled static server/ CDN
Node
Node
Node
Node
ELB
Business Tier
Scaled Node.js services
Data Tier
Data tier
Scalable DB?
Database challenges
Significant increases in data volume
Data security
Managing and maintaining the database and infrastructure
Removing limits on scalability
- Absorbing significant increases in data volume. The explosion of data coming in from sensors, connected machines, and dozens of other sources keeps database administrators scrambling to manage and organize their companies’ data efficiently.
- Ensuring data security. Data breaches are happening everywhere these days, and hackers are getting more inventive. It’s more important than ever to ensure that data is secure but also easily accessible to users.
- Keeping up with demand. In today’s fast-moving business environment, companies need real-time access to their data to support timely decision-making and to take advantage of new opportunities.
- Managing and maintaining the database and infrastructure. Database administrators must continually watch the database for problems and perform preventative maintenance, as well as apply software upgrades and patches. As databases become more complex and data volumes grow, companies are faced with the expense of hiring additional talent to monitor and tune their databases.
- Removing limits on scalability. A business needs to grow if it’s going to survive, and its data management must grow along with it. But it’s very difficult for database administrators to predict how much capacity the company will need, particularly with on-premises databases.
CAP theorem

CAP theorem, also named Brewer's theorem after computer scientist Eric Brewer, states that it is impossible for a distributed data store to simultaneously provide more than two out of the following three guarantees:
- Consistency: Every read receives the most recent write or an error
- Availability: Every request receives a (non-error) response, without the guarantee that it contains the most recent write
- Partition tolerance: The system continues to operate despite an arbitrary number of messages being dropped (or delayed) by the network between nodes

Slack
Strong Consistency offers up-to-date data but at the cost of high latency
WAIT FOR THE INTERNET TO START WORKING AGAIN
Eventual consistency offers low latency but may reply to read requests with stale data since all nodes of the database may not have the updated data.
Anser based on available data
Available
Not available

SQL NoSQL



Hollywar!
1
2
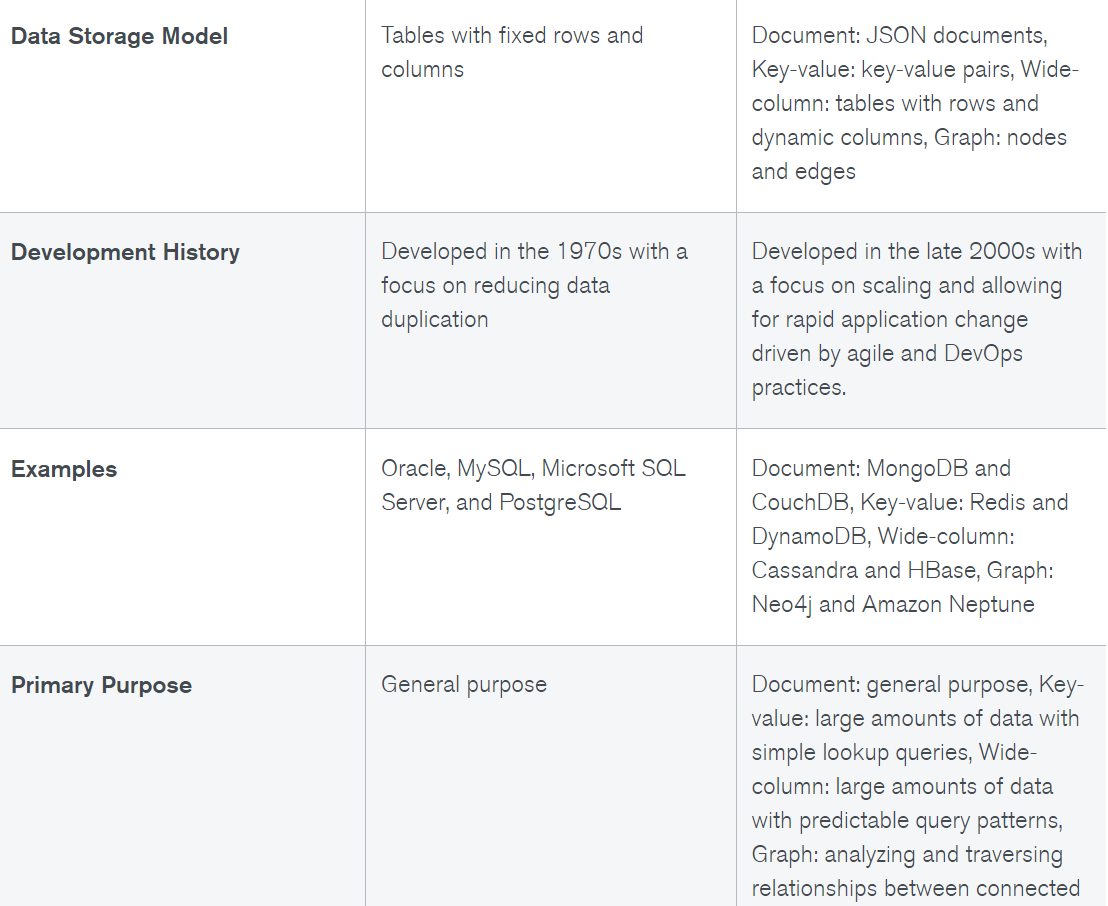
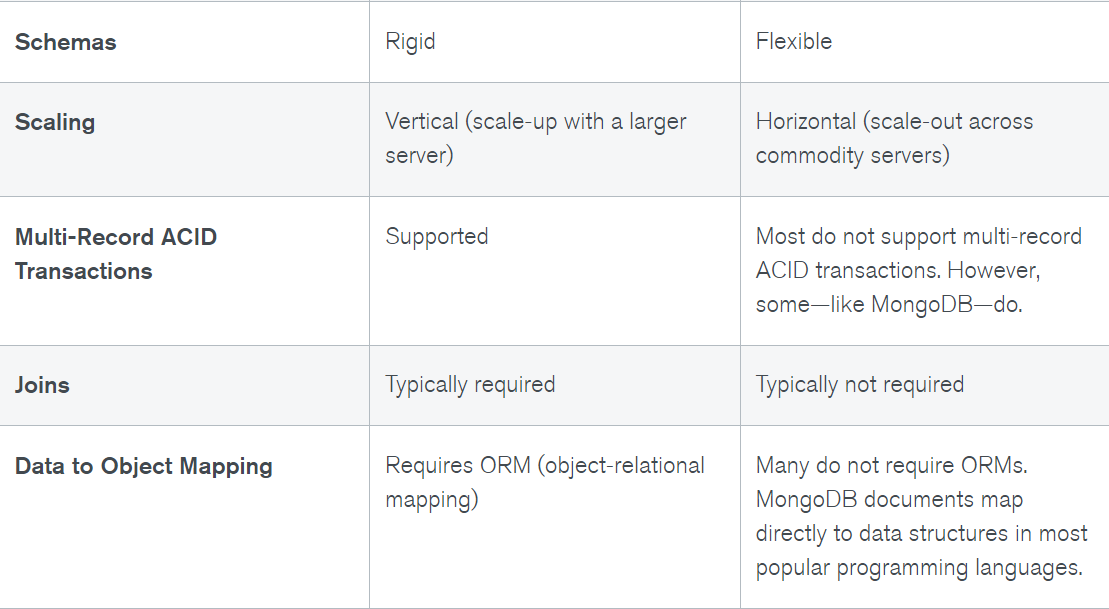
SQL Databases
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL is better/worse than SQL ?
Databases performance
Transactions
Generally speaking, NoSQL solutions have lighter weight transactional semantics than relational databases, but still have facilities for atomic operations at some level.
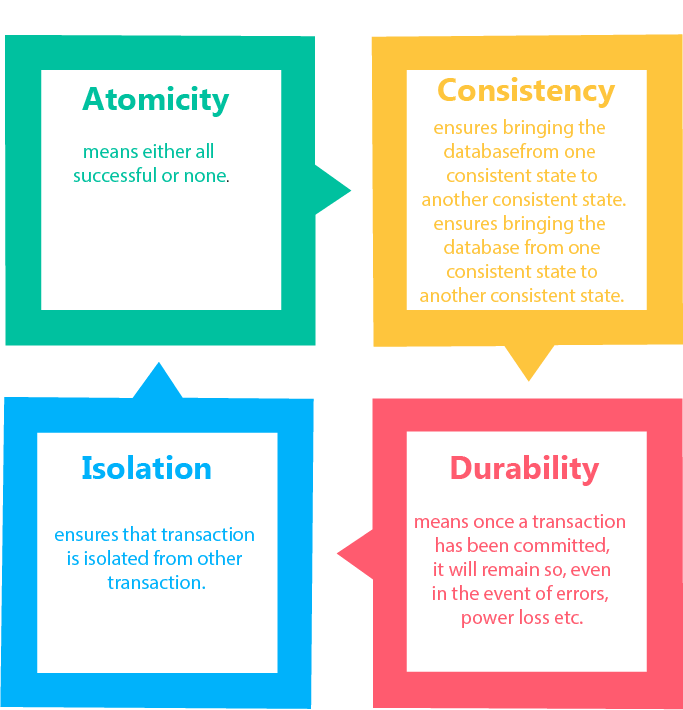
Choose ACID when there is a need for strong consistency in transactions and the schema is fixed.

NoSQL with ACID?

Choosing the right DB
Answer following questions
Integration consideration

Scaling requirements

Support expertise

Service costing

CAP

Simplicity

Test!
You are building an internal "Timesheet" app for the company with 1000 employees
Scale: may not be needed
Consistency: eventual is fine
Availability: not critical
You are building a google advertising app that analyses user's search requests and shows ads
Scale: critical
Consistency: eventual is fine
Availability: critical
You are building a banking application where the user may send money to multiple groups of users updating several tables
Scale: critical
Consistency: Strong
Availability: less important
ACID: yes
You are building a massive trading system with lots of data. You care about professional support and you have money
Scale: critical
Consistency: strong
Availability: still important
MongoDB
The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy
What is MongoDB?
Mongo-DB is a document database which provides high performance, high availability and easy scalability.
How is MongoDB better than other SQL databases?
MongoDB allows a highly flexible and scalable document structure. For e.g. one data document in MongoDB can have five columns and the other one in the same collection can have ten columns. Also, MongoDB database are faster as compared to SQL databases due to efficient indexing and storage techniques.
Does MongoDB support foreign key constraints?
No. MongoDB does not support such relationships.
Does MongoDB support ACID transaction management and locking functionalities?
MongoDB, has always supported ACID transactions in a single document and, when leveraging the document model appropriately, many applications don't need ACID guarantees across multiple documents
How can you achieve transaction and locking in MongoDB?
To achieve concepts of transaction and locking in MongoDB, we can use the nesting of documents, also called embedded documents. MongoDB supports atomic operations within a single document.
When to use MongoDB?





Is MongoDB really a “schemaless” database?
And that’s true. But it doesn’t mean that there is no schema.
db.createCollection("students", {
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: "object",
required: [ "name", "year", "major", "address" ],
properties: {
name: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required"
},
year: {
bsonType: "int",
minimum: 2017,
maximum: 3017,
description: "must be an integer in [ 2017, 3017 ] and is required"
},
major: {
enum: [ "Math", "English", "Computer Science", "History", null ],
description: "can only be one of the enum values and is required"
},
gpa: {
bsonType: [ "double" ],
description: "must be a double if the field exists"
},
address: {
bsonType: "object",
required: [ "city" ],
properties: {
street: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string if the field exists"
},
city: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required"
}
}
}
}
}
}
})
db.students.insert({
name: "Alice",
year: NumberInt(2019),
major: "History",
gpa: 3.0,
address: {
city: "NYC",
street: "33rd Street"
}
})Issue the following command to add a validator to the contacts collection:
db.runCommand( {
collMod: "contacts",
validator: { $jsonSchema: {
bsonType: "object",
required: [ "phone", "name" ],
properties: {
phone: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required"
},
name: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required"
}
}
} },
validationLevel: "moderate"
} )What is the syntax to create a collection and to drop a collection in MongoDB?
- Syntax to create collection in MongoDB is db.createCollection(name,options)
- Syntax to drop collection in MongoDB is db.collection.drop()
What are indexes in MongoDB?
Indexes are special structures in MongoDB, which stores a small portion of the data set in an easy to traverse form. Ordered by the value of the field specified in the index, the index stores the value of a specific field or set of fields.
ODM and ORM?
Disadvantages
Loss in developer productivity whilst they learn to program with ORM.
Developers lose understanding of what the code is actually doing - the developer is more in control using SQL
ORM has a tendency to be slow
ORM fail to compete against SQL queries for complex queries.
Mongoose vs TypeORM
which one to use?
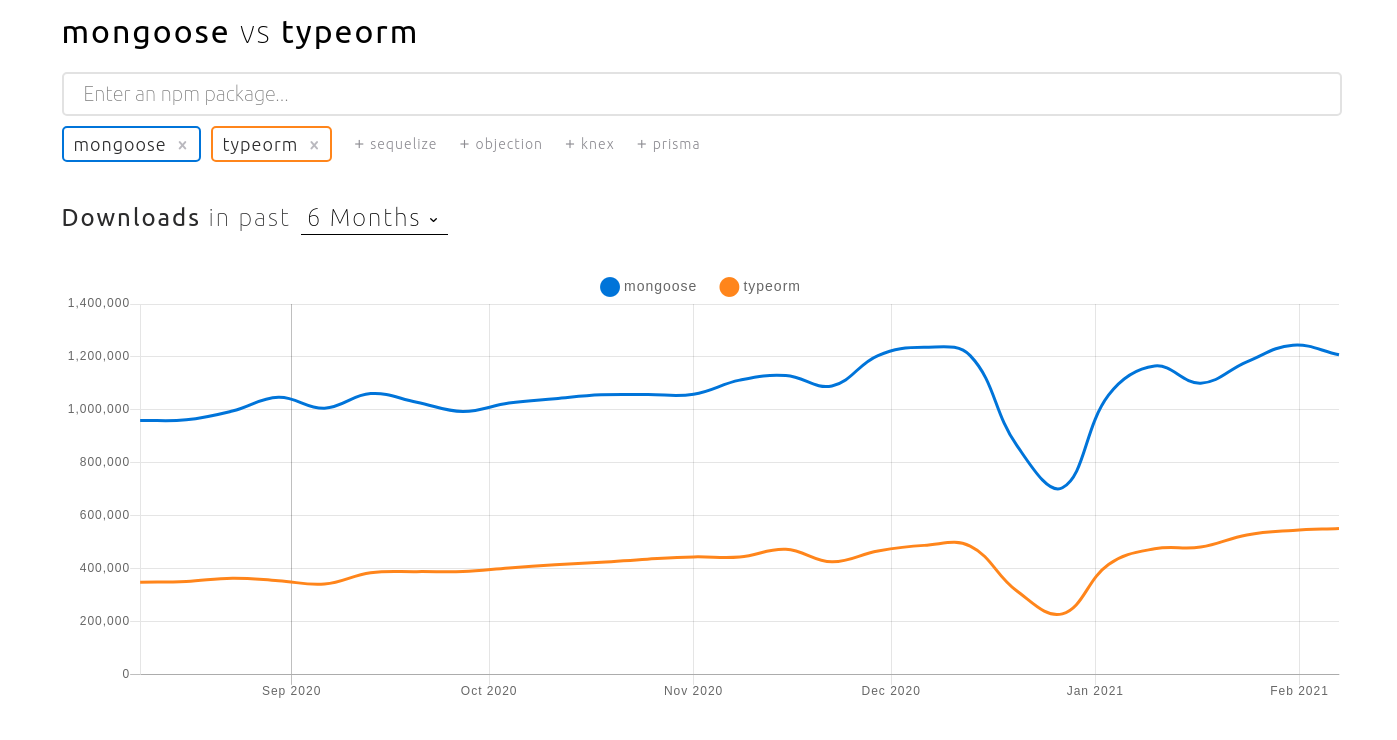
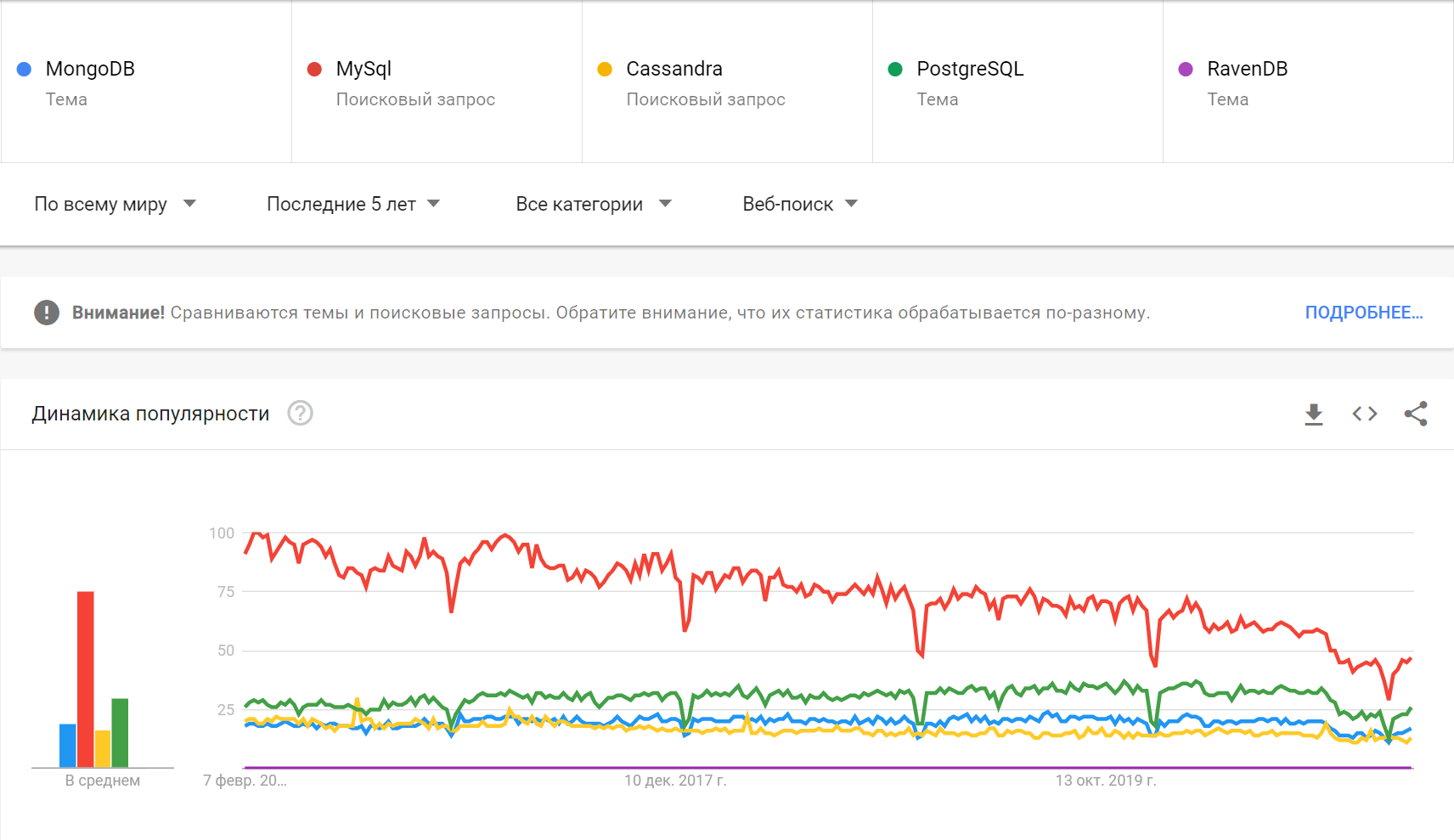
Trends
TypeORM has *basic* MongoDB support
Play with MongoDB

docker run -d mongo
docker ps
docker inspect 835af70ea08a # mongo idMongo setup
"Networks": {
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "e9acd2b3a9fa0abe80af842b20860f546bd557644b75c25f35476c0bc849b09c",
"EndpointID": "f887ce1095db8138e5159dd87200789b9e52b13f1f2bf378a07195aeb8bec8de",
"Gateway": "10.10.1.1",
"IPAddress": "10.10.1.3", <--------------------
"IPPrefixLen": 24,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:0a:0a:01:03",
"DriverOpts": null
}
}
}
Search for the mongo IP
mongo --host 10.10.1.3
> show dbs
> use TestDB
> db.dropDatabase()
> use users
> db.users.insert([{...}])
> show collections
> db.find().pretty()
> db.users.findOne()Mongo quick reminder
[
'{{repeat(15, 17)}}',
{
_id: '{{objectId()}}',
isActive: '{{bool()}}',
age: '{{integer(20, 40)}}',
username: '{{firstName()}}',
email: '{{email()}}',
claims: ['asd']
}
]Generate some data https://www.json-generator.com/
db.users.deleteOne( {"_id": ObjectId("4d512b45cc9374271b02ec4f")});
db.users.update(
{ _id: 1 },
{
$inc: { age: 5 },
$set: {
item: "ABC123",
"info.publisher": "2222",
tags: [ "software" ],
"ratings.1": { by: "xyz", rating: 3 }
}
}
)Update & delete
db.users.find(
{
"$or": [
{ "age": { "$gte": 20 } }
{ "active": true }
]
},
{
"username": 1,
"_id": 0
}
).limit(3).explain("executionStats")
db.users.ensureIndex({ "age": 1 })
db.users.getIndexes()
db.users.dropIndex({ "age": 1 })Find query & indexes
db.sales.insertMany([
{ '_id' : 1, 'item' : 'abc', 'price' : 10, 'quantity' : 2, 'date' : new Date('2014-03-01T08:00:00Z') },
{ '_id' : 2, 'item' : 'jkl', 'price' : 20, 'quantity' : 1, 'date' : new Date('2014-03-01T09:00:00Z') },
{ '_id' : 3, 'item' : 'xyz', 'price' : 5, 'quantity' : 10, 'date' : new Date('2014-03-15T09:00:00Z') },
{ '_id' : 4, 'item' : 'xyz', 'price' : 5, 'quantity' : 20, 'date' : new Date('2014-04-04T11:21:39.736Z') },
{ '_id' : 5, 'item' : 'abc', 'price' : 10, 'quantity' : 10, 'date' : new Date('2014-04-04T21:23:13.331Z') },
{ '_id' : 6, 'item' : 'def', 'price' : 7.5, 'quantity': 5, 'date' : new Date('2015-06-04T05:08:13Z') },
{ '_id' : 7, 'item' : 'def', 'price' : 7.5, 'quantity': 10, 'date' : new Date('2015-09-10T08:43:00Z') },
{ '_id' : 8, 'item' : 'abc', 'price' : 10, 'quantity' : 5, 'date' : new Date('2016-02-06T20:20:13Z') },
]);
const aggregation = [
{ $match: { quantity: { $gte: 10 } } },
{ $group: { _id : null, avg: { $avg: '$price' } } }
];
db.sales.aggregate(aggregation);Aggregation
Setup Mongoose and Nest.js

yarn add @nestjs/mongoose mongooseOnce the installation process is complete, we can import the MongooseModule into the root AppModule.
Install needed packages
@Module({
imports: [
UsersModule,
ConfigModule.forRoot(),
MongooseModule.forRoot('mongodb://10.10.1.3/users'),
],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}The forRoot() method accepts the same configuration object as mongoose.connect() from the Mongoose package
Setup root module
import { MongooseModule } from '@nestjs/mongoose';
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UsersService } from './users.service';
import { UsersController } from './users.controller';
import { User, UserSchema } from './schemas/user.schema';
@Module({
imports: [
MongooseModule.forFeature([{ name: User.name, schema: UserSchema }]),
],
controllers: [UsersController],
providers: [
{
provide: 'IUsersService',
useClass: UsersService,
},
],
})
export class UsersModule {}
Inject ODM
Users module
import { Prop, Schema, SchemaFactory } from '@nestjs/mongoose';
import { Document } from 'mongoose';
import { Permissions } from '../enums/Permissions';
@Schema({ timestamps: true })
export class User {
@Prop({ unique: true })
username: string;
@Prop({ unique: true, index: true })
email: string;
@Prop({ default: true })
active: boolean;
@Prop({
enum: Permissions,
type: [String],
default: [Permissions.WRITE_TEXTS],
})
claims: string[];
}
export type UserDocument = User & Document;
export const UserSchema = SchemaFactory.createForClass(User);
Define a schema and document
import { UserDocument } from './../schemas/user.schema';
import { User } from '../schemas/user.schema';
import { CreateUserDto } from '../dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from '../dto/update-user.dto';
export interface IUsersService {
create(createUserDto: CreateUserDto): Promise<User>;
findAll(): Promise<UserDocument[]>;
findOne(id: string): Promise<User>;
update(id: string, updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto): Promise<User>;
remove(id: string): Promise<string>;
}
Update UserService interface
import { User, UserDocument } from './schemas/user.schema';
import { Injectable, Logger, NotFoundException } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
import { IUsersService } from './interfaces/IUserService';
import { v4 as uuid } from 'uuid';
import { InjectModel } from '@nestjs/mongoose';
import { Model } from 'mongoose';
@Injectable()
export class UsersService implements IUsersService {
private readonly logger = new Logger(UsersService.name);
constructor(@InjectModel(User.name) private userModel: Model<UserDocument>) {}
async create(createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
const createdUser = new this.userModel(createUserDto);
return createdUser.save();
}
async findAll() {
return this.userModel.find();
}
async findOne(id: string) {
const user = this.userModel.findById(id);
if (!user) {
this.logger.warn(`User with id ${id} doen't exist`);
this.logger.error(`User with id ${id} doen't exist`);
this.logger.debug(`User with id ${id} doen't exist`);
throw new NotFoundException(`User with id ${id} doen't exist`);
}
return user;
}
async update(id: string, updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto) {
const user = await this.findOne(id);
user.username = updateUserDto.username ?? user.username;
user.email = updateUserDto.email ?? user.email;
return user.save();
}
async remove(id: string) {
const user = await this.findOne(id);
user.remove();
return id;
}
}
Implment methods
Thank You!
