Building Rails RESTful API with Trailblazer



Vladislav Trotsenko
software engineer at RubyGarage
@bestwebua
What is Trailblazer?
It's an advanced business logic framework

Benefits
- Provides new high-level abstractions extending basic MVC pattern
- Enforces an intuitive code structure
- Lets you focus on your application code, minimize bugs and improve the maintainability
What problems does solve Trailblazer?
- Bloated models
- Bloated controllers
- Unstructured services
- Cumbersome error handling
Trailblazer downsides
- Composition over inheritance
- Often more code
- Low code quality of Tralblazer itself
- No upgrade docs between major versions
- A lot of old dry-stack dependencies

Basic Trailblazer layers
for API
OPERATION
CONTRACT
REPRESENTER
serializer
ENDPOINT
service object
form object
generic http handler for operation results
POLICY
auth for operation
Code structure
To avoid constants naming collision with your active_record models it’s better to name your concepts using plurals nouns.
├── app
│ ├── concepts
│ │ ├── api
│ │ │ ├── v1
│ │ │ │ ├── projects
│ │ │ │ │ ├── contract
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── create.rb
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── index.rb
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── show.rb
│ │ │ │ │ ├── operation
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── create.rb
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── index.rb
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── show.rb
│ │ │ │ │ ├── serializer
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── create.rb
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── index.rb
│ │ │ │ │ │ ├── show.rb
│ │ │ │ │ ├── policy
│ │ │ │ │ ├── worker
│ │ ├── application_contract.rb
│ │ ├── application_decorator.rb
│ │ ├── application_operation.rb
│ │ ├── application_serializer.rb
│ │ ├── application_worker.rb
│ ├── endpoints
│ │ ├── application_endpoint.rb── lib
├── contract
├── decorator
├── operation
├── query
├── serializer
├── service
├── step
├── workerTrailblazer’s code structure organizes by concept, and then by technology.
app/controllers/v1/projects_controller.rbEndpoint
Concept, benefits, use cases
CONTROLLER
OPERATION
ENDPOINT
params
params
result
match result condition with http status
result matcher
request
render result with http status
response
# app/controllers/api/v1/users/registrations_controller.rb
module Api::V1::Users
class RegistrationsController < ApiController
def create
run Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Operation::Create
if result.success?
render json: UserSerializer.new(@model).serialized_json
elsif @model.blank?
head :not_found
elsif result['result.policy.default'].failure?
head :forbidden
else
render json: ErrorSerializer.new(@form).serialized_json,
status: :unprocessable_entity
end
end
end
end# app/controllers/api/v1/users/registrations_controller.rb
module Api::V1::Users
class RegistrationsController < ApiController
def create
endpoint Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Operation::Create
end
end
endOldschool action with operation
vs
action with endpoint layer
# app/controllers/api/v1/users/registrations_controller.rb
module Api::V1::Users
class RegistrationsController < ApiController
def create
endpoint Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Operation::Create
end
end
end
# app/controllers/concerns/default_endpoint.rb
module DefaultEndpoint
def default_handler
lambda do |match|
match.created { |result| render(result, :created) }
end
end
def endpoint(operation, options: {}, &block)
ApplicationEndpoint.call(operation, default_handler,
{ params: params.to_unsafe_hash, **operation_options(options) }, &block
)
end
end
# app/endpoints/application_endpoint.rb
class ApplicationEndpoint < Trailblazer::Endpoint
MATCHER = Dry::Matcher.new(
created: Dry::Matcher::Case.new(
match: ->(result) { result.success? && result[:semantic_success].eql?(:created) }
)
)
def matcher; ApplicationEndpoint::MATCHER; end
endOperation
Concept, benefits, use cases
An operation is a service object
The flow pipetree is a mix of the Either monad and Railway-oriented programming
An operation is not a monolithic god object, but a composition of many stakeholders.
Operation possible steps
SomeOperation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :step_method # method
step Api::V1::Lib::Step::SharedStep # shared step
step StepMacros(:param_1, :param_2) # macros
def step_method(ctx, **) # context of 'step-method'
ctx[:thing] = :thing # should be inside operation
end
endDefining steps in operation
# app/concepts/api/v1/lib/step/shared_step.rb
module Api::V1::Lib::Step
class SharedStep
def self.call(ctx, **)
ctx[:thing] = :thing
end
end
end
Defining shared step
No need use extend Uber::Callable
Macros
Trailblazer provides predefined macroses for most cases of business logic
- Contract
- Subprocess(Nested)
- Wrap
- Rescue
- Policy
- Model
step containers that help with transactional features for a group
of steps per operation
permissions users handler
create and find models based on input
validation and persisting verified data
What about own macros?
# app/concepts/application_decorator.rb
class ApplicationDecorator < Draper::Decorator; end
# lib/macro/model_decorator.rb
module Macro
def self.ModelDecorator(decorator:, **)
step = ->(ctx, **) {
model = ctx[:model]
ctx[:model] = decorator.public_send(
(model.is_a?(Enumerable) ? :decorate_collection : :decorate), model
)
}
task = Trailblazer::Activity::TaskBuilder::Binary(step)
{ task: task, id: "model_decorator_id#{task.object_id}" }
end
end
# calling macros from operation
SomeOperation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step Macro::ModelDecorator(decorator: SomeDecorator)
endModelDecorator example
| SHARED STEP | MACROS | |
|---|---|---|
| Accepts params | - | + |
| Concept scope | + | - |
| Readability | + | - |
SomeOperation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step Api::V1::Lib::Step::SharedStep
step Macro::StepMacros(:param_1, :param_2)
endShared step vs Macros
Basic operation
implementation
# app/concepts/api/v1/users/registrations/operation/create.rb
module Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Operation
class Create < Trailblazer::Operation
extend Contract::DSL
feature Reform::Form::Dry
contract do
property :email
property :password
property :password_confirmation, virtual: true
validation :default do
configure { config.namespace = :user_password }
required(:email).filled(:str?)
...
end
end
pass Model(Account, :new)
step Contract::Build()
step Contract::Validate()
step Contract::Persist()
pass :set_semantic
pass :set_email_token
pass :send_confirmation_link
pass :renderer
def set_semantic(ctx, **); ctx[:semantic_success] = :created; end
def set_email_token(ctx, model:, **); end
def send_confirmation_link(_ctx, model:, email_token:, **); end
def renderer(ctx, **); ctx[:renderer] = { serializer: SerializerClass }; end
end
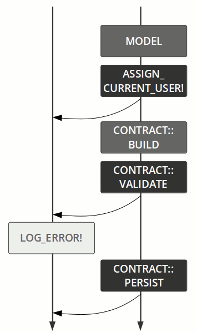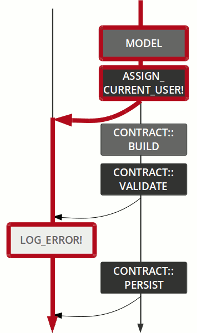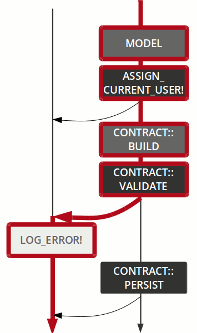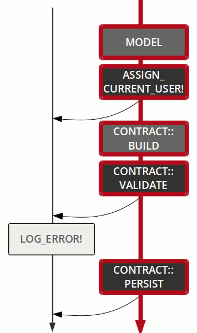
endOperation
flow
control
Model
Contract::Build
Contract::Validate
Contract::Persist
set_email_token
send_confirmation
renderer
log error
Left
track
Right
track
set_semantic
step
pass
fail
failure
# app/concepts/api/v1/users/registrations/operation/create.rb
module Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Operation
class Create < ApplicationOperation
step Model(Account, :new)
step Contract::Build(constant: Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Contract::Create)
step Contract::Validate()
step Contract::Persist()
pass Macro::Semantic(success: :created)
pass :set_email_token
pass :send_confirmation_link
pass Macro::Renderer(serializer: Api::V1::Lib::Serializer::Account)
def set_email_token(ctx, model:, **); end
def send_confirmation_link(_ctx, model:, email_token:, **); end
end
end
# app/concepts/application_contract.rb
class ApplicationContract < Reform::Form; feature Reform::Form::Dry; end
# app/concepts/api/v1/users/registrations/contract/create.rb
module Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Contract
class Create < ApplicationContract
property :email
validation :default do
configure { config.namespace = :user_password }
required(:email).filled(:str?)
...
end
end
endAfter refactoring...
✅
✅
✅
Fast Track
You can short-circuit specific tasks using a built-in mechanism called fast track.
How to use pass_fast, fail_fast and fast_track?
Fast Track: pass_fast
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :create_model
step :validate, pass_fast: true
fail :assign_errors
step :index
pass :uuid
step :save
fail :log_errors
end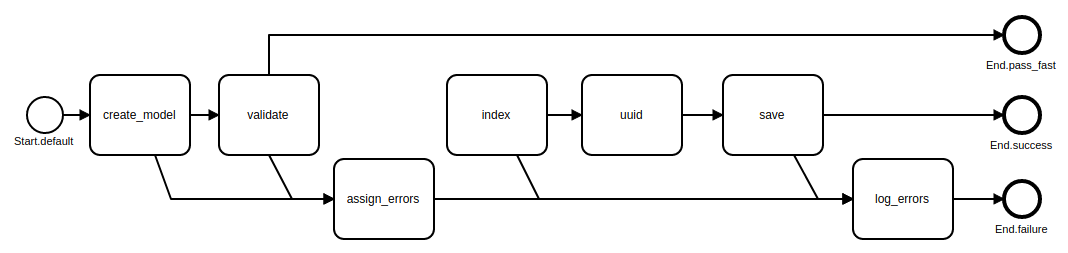
Fast Track: fail_fast
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :create_model
step :validate
fail :assign_errors, fail_fast: true
step :index
pass :uuid
step :save
fail :log_errors
end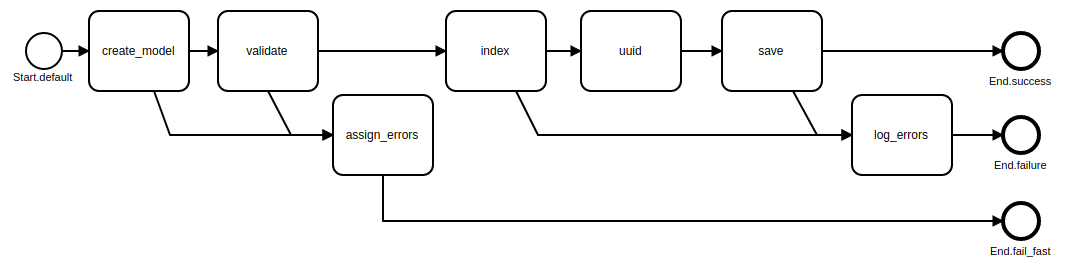
Fast Track: fast_track
OperationWithFailFastPassFast = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :set_payload
fail :log_error, fail_fast: true
step :set_model
fail Macro::Semantic(failure: :not_found)
end
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :tokens_eql?
fail :log_error
end
SomeParentOperation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step Subprocess(OperationWithFailFastPassFast), fast_track: true
step Subprocess(Operation)
end
Connections
You can define custom connection between tasks
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :new?, Output(:failure) => :some_id
fail :validation_error
step :index, id: :some_id
step :other_step
end
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :inclusion_query_param_passed?,
Output(:failure) => End(:success) # instead of 'End.success'
step :other_step
endMagnetic
You can define custom connection between tasks
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :find_model, Output(:failure) => Track(:create_route)
step :update
step :create, magnetic_to: [:create_route]
step :save
end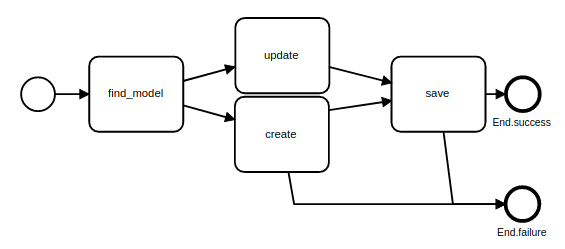
Magnetic
The same result with alternate definition
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :find_model, Output(:failure) => :some_id
step :update
step :create, id: :some_id, magnetic_to: [:create_route]
step :save
end
Operation = Class.new(Trailblazer::Operation) do
step :find_model, Output(:failure) => :create
step :update
step :create, magnetic_to: [:create_route]
step :save
endContract
Concept, benefits, use cases
A contract is an abstraction to handle validation of arbitrary data or object state
The actual validation can be implemented using Reform with ActiveModel::Validation or dry-validation, or a Dry::Schema directly without Reform :)
For params validation use Dry::Validation as contract otherwise use Reform
# app/concepts/application_contract.rb
class ApplicationContract < Reform::Form; feature Reform::Form::Dry; end
# app/concepts/api/v1/users/registrations/contract/create.rb
module Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Contract
class Create < ApplicationContract
property :email
property :password
property :password_confirmation, virtual: true
validation :default do
configure { config.namespace = :user_password }
required(:email).filled(:str?, max_size?: EMAIL_MAXSIZE, format?: EMAIL_REGEX)
required(:password).filled(:str?)
required(:password_confirmation).filled(:str?)
required(:password).filled(
:str?, min_size?: PWD_MINSIZE, format?: PWD_REGEX
).confirmation
end
validation :email, if: :default do
configure do
def email_uniq?(value)
!Account.exists?(email: value)
end
end
required(:email, &:email_uniq?)
end
end
endContract usage: contract class definition
# app/concepts/api/v1/users/registrations/operation/create.rb
module Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Operation
class Create < ApplicationOperation
step Model(Account, :new)
step Contract::Build(constant: Api::V1::Users::Registrations::Contract::Create)
step Contract::Validate() # Contract::Validate(key: :user)
step Contract::Persist()
end
endContract usage: plug the contract
- After run Contract::Build contract will be saved to ctx['contract.default']
The Contract::Build accepts the :name option to change the name from default - By default Contract::Validate will use ctx[:params] as the data to be validated
You can validate a nested hash from the original params structure -
Contract::Persist push validated data from the contract to the model
If you don't want to save data to model just use Contract::Persist(method: sync)
# app/concepts/api/v1/lib/operation/sorting.rb
class Api::V1::Lib::Operation::Sorting < ApplicationOperation
step :sort_params_passed?, Output(:failure) => End(:success)
step Macro::Contract::Schema(Api::V1::Lib::Contract::SortingPreValidation, name: :uri_query)
step Contract::Validate(name: :uri_query)
step :set_validation_dependencies # sets ctx[:available_sortable_columns]
step Macro::Contract::Schema(
Api::V1::Lib::Contract::SortingValidation,
inject: %i[available_sortable_columns],
name: :uri_query
)
step Contract::Validate(name: :uri_query), id: :sorting_validation
step :order_options
end- Custom Macro::Contract::Schema instead of Contract::Build
- You should add uniq id for each one Contract::Validate after first one
HTTP request example:
GET /users?sort=name,-age
Dry::Validation as contract,
JSON API sorting implementation
# app/concepts/api/v1/lib/contract/sorting_pre_validation.rb
module Api::V1::Lib::Contract
SortingPreValidation = Dry::Validation.Schema do
required(:sort).filled(:str?)
end
end
# app/concepts/api/v1/lib/contract/sorting_validation.rb
module Api::V1::Lib::Contract
SortingValidation = Dry::Validation.Schema do
configure do
config.type_specs = true
option :available_sortable_columns
def sort_params_uniq?(jsonapi_sort_params)
jsonapi_sort_params = jsonapi_sort_params.map(&:column)
jsonapi_sort_params.eql?(jsonapi_sort_params.uniq)
end
def sort_params_valid?(jsonapi_sort_params)
jsonapi_sort_params.all? do |jsonapi_sort_parameter|
available_sortable_columns.include?(jsonapi_sort_parameter.column)
end
end
end
required(:sort, Types::JsonApi::Sort) { sort_params_uniq? & sort_params_valid? }
end
endDry::Validation as contract,
JSON API sorting implementation
Summary
- Use naming convention
- Handle all operation results cases in one place
- DRY: use shared steps, shared operation and macroses
- Use Dry::Validation over Reform for validation cases