VINCENT OGLOBLINSKY


@vogloblinsky


Vincent Ogloblinsky
Frontend software architect

SII Ouest - France
@vogloblinsky

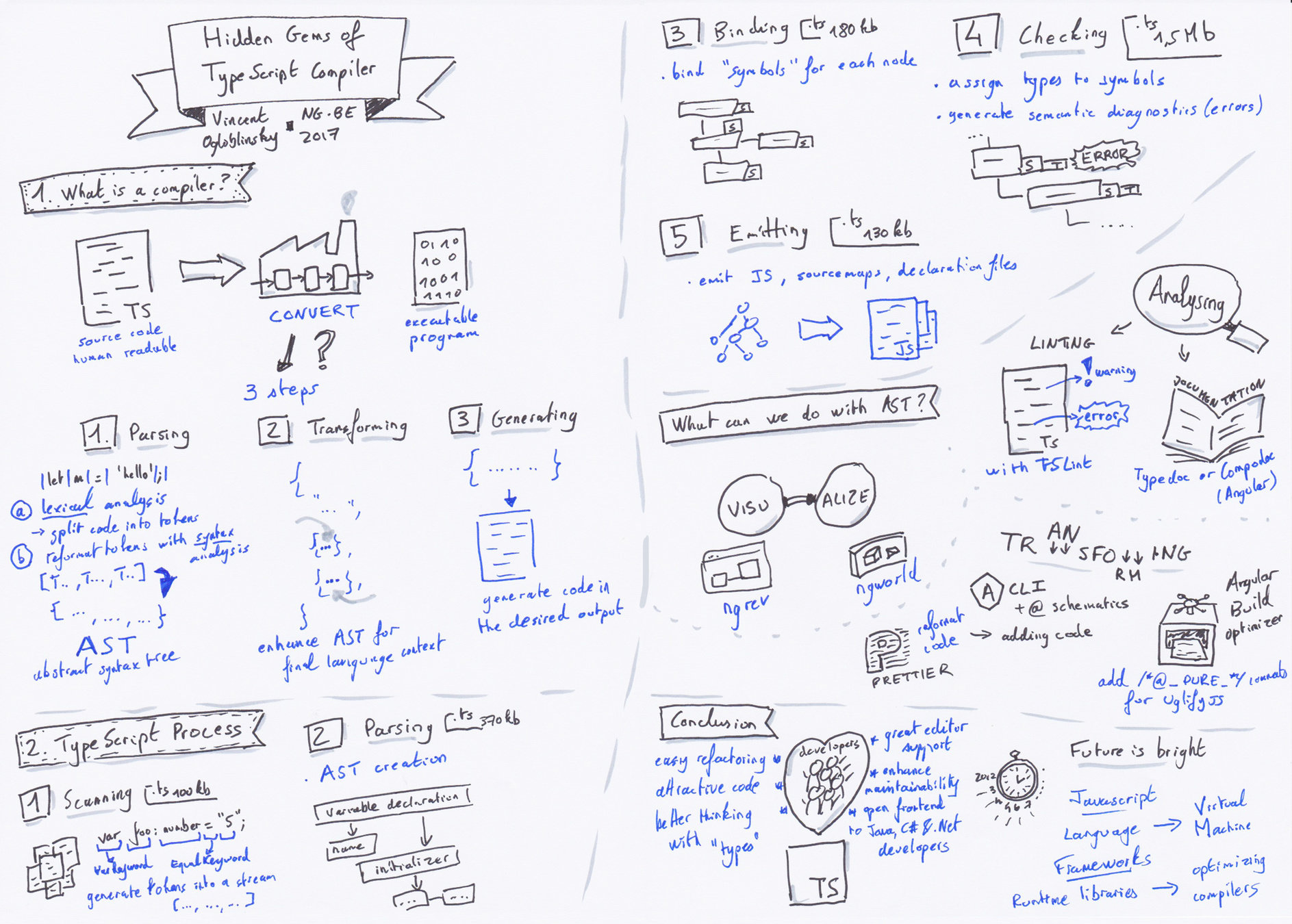
Agenda
What is a compiler?
TypeScript compiler
What can we do with AST?
Have fun with AST?
TypeScript

" TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript. "
JavaScript that SCALES




TypeScript
ES5
ES6
ES7, ESNext
TypeScript
What is a compiler?
What is a compiler?
A compiler is a computer program that transforms source code written in a programming language into another computer language [...] The most common reason for converting source code is to create an executable program.

human readable code
high level
computer readable code
low level
class Greeter {
greeting: string;
constructor(message: string) {
this.greeting = message;
}
greet() {
return "Hello, " + this.greeting;
}
}
let greeter = new Greeter("world");
let button = document.createElement('button');
button.textContent = "Say Hello";
button.onclick = function() {
alert(greeter.greet());
}
document.body.appendChild(button);
class Greeter {
greeting: string;
constructor(message: string) {
this.greeting = message;
}
greet() {
return "Hello, " + this.greeting;
}
}
let greeter = new Greeter("world");
let button = document.createElement('button');
button.textContent = "Say Hello";
button.onclick = function() {
alert(greeter.greet());
}
document.body.appendChild(button);Transpiling is different
var Greeter = /** @class */ (function () {
function Greeter(message) {
this.greeting = message;
}
Greeter.prototype.greet = function () {
return "Hello, " + this.greeting;
};
return Greeter;
}());
var greeter = new Greeter("world");
var button = document.createElement('button');
button.textContent = "Say Hello";
button.onclick = function () {
alert(greeter.greet());
};
document.body.appendChild(button);
same level of abstraction
What is the process of a general compilation?
Compilation process
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
take raw code
and turns it into
a more abstract representation
2 steps:
lexical analysis
syntax analysis
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
Lexical analysis
let message = 'hello'split code into tokens
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
Syntax analysis
reformat tokens into a representation describing each part of the syntax and their relations
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
Syntax analysis
"tokens": [
{
"type": "Keyword",
"value": "let"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "message"
},
{
"type": "Punctuator",
"value": "="
},
{
"type": "String",
"value": "\"hello DEVOXX\""
}
]{
"type": "Program",
"body": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "message"
},
"init": {
"type": "Literal",
"value": "hello DEVOXX",
}
}
],
"kind": "let"
}
]
}AST
Abstract Syntax Tree
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
take the AST
and make transformations for each nodes into final language context
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
Generation of code in the desired output
Stringify each nodes
Knows how to print them
Parsing
Transforming
Generating
TypeScript
compiler

Same process
enhanced
with "Type" checking
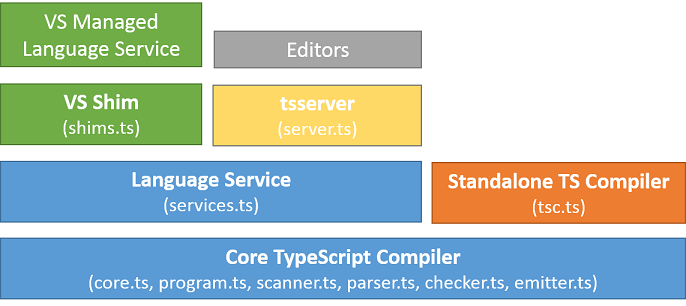
Architectural overview
Scanner
Parser
Checker
The scanner is driven by the parser
First internal part of "parsing"
Creates a tokens stream
Binder
Emitter
Parser
Checker
Binder
Emitter
const ts = require('typescript')
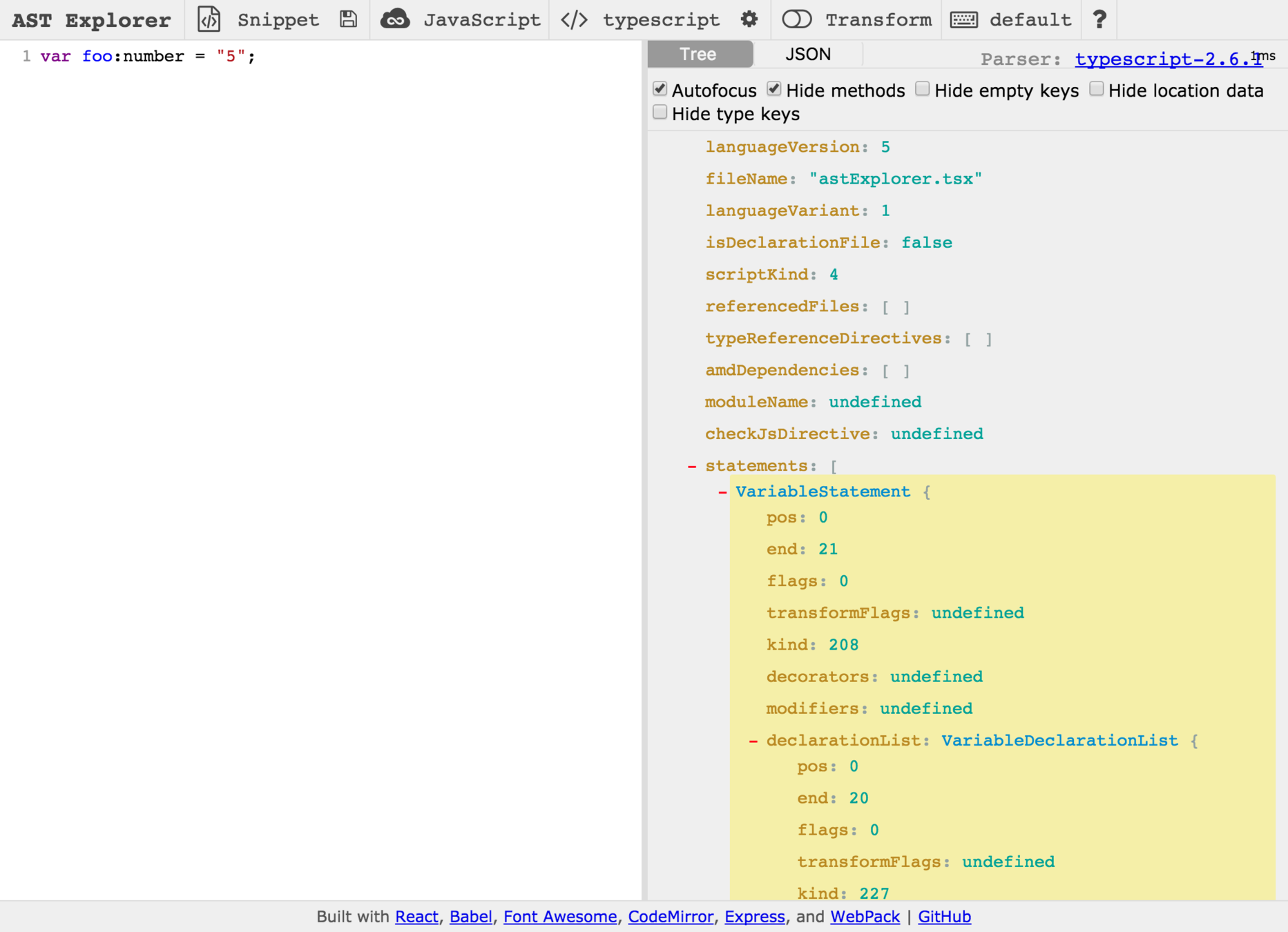
const scanner = ts.createScanner(ts.ScriptTarget.Latest, true);
let sourceCode = `var foo:number = "5";`
function initializeState(text) {
scanner.setText(text);
scanner.setOnError((message) => {console.error(message);});
scanner.setScriptTarget(ts.ScriptTarget.ES5);
scanner.setLanguageVariant(ts.LanguageVariant.Standard);
}
function syntaxKindToName(kind) {
return ts.SyntaxKind[kind];
}
initializeState(sourceCode);
let token = scanner.scan();
while (token != ts.SyntaxKind.EndOfFileToken) {
console.log(token, syntaxKindToName(token));
token = scanner.scan();
}104 'VarKeyword'
71 'Identifier'
56 'ColonToken'
133 'NumberKeyword'
58 'FirstAssignment'
9 'StringLiteral'
25 'SemicolonToken'Scanner
Parser
Checker
The parser is driven by a program
AST is generated here
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Parser
Checker
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
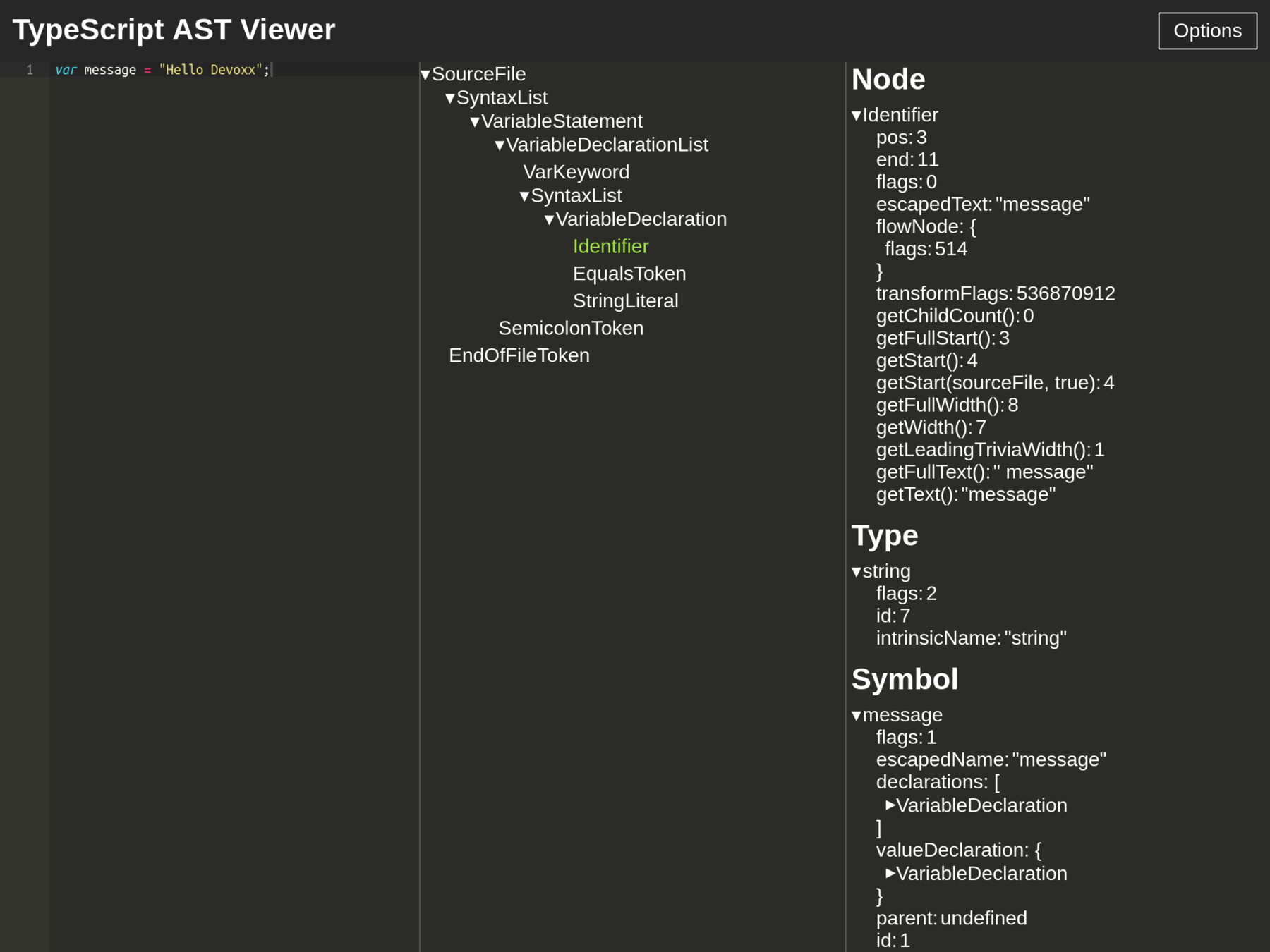
let parsedSourceFile =
ts.createSourceFile(
'file.ts',
sourceCode,
ts.ScriptTarget.ES5,
true
);SourceFileObject {
pos: 0,
end: 21,
flags: 0,
transformFlags: undefined,
parent: undefined,
kind: 265,
text: 'var foo:number = "5";',
bindDiagnostics: [],
languageVersion: 1,
fileName: 'foo.ts',
languageVariant: 0,
isDeclarationFile: false,
scriptKind: 3,
referencedFiles: [],
typeReferenceDirectives: [],
amdDependencies: [],
moduleName: undefined,
checkJsDirective: undefined,
statements:
[ NodeObject {
pos: 0,
end: 21,
flags: 0,
transformFlags: undefined,
parent: [Circular],
kind: 208,
decorators: undefined,
modifiers: undefined,
declarationList: [Object],
modifierFlagsCache: 536870912 },
pos: 0,
end: 21 ],
endOfFileToken: TokenObject { pos: 21, end: 21, flags: 0, parent: [Circular], kind: 1 },
externalModuleIndicator: undefined,
nodeCount: 8,
identifierCount: 1,
identifiers: Map { 'foo' => 'foo' },
parseDiagnostics: [] }Parser
Checker
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Parser
Checker
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Parser
Checker
The binder connects parts into coherent type system
Creates symbols
1st semantic pass
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Parser
Checker
Symbols
connect declaration nodes in the AST to other declarations contributing to the same entity
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Checker
Emitter
Scanner
ts.bindSourceFile(parsedSourceFile, {
target: ts.ScriptTarget.ES5,
module: ts.ModuleKind.CommonJS
});...
initializer:
TokenObject {
pos: 16,
end: 20,
flags: 0,
parent: [Circular],
kind: 9,
text: '5',
transformFlags: 536870912 },
symbol:
SymbolObject {
flags: 1,
escapedName: 'foo',
declarations: [ [Circular] ],
valueDeclaration: [Circular],
parent: undefined }Parser
Binder
Parser
Checker
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
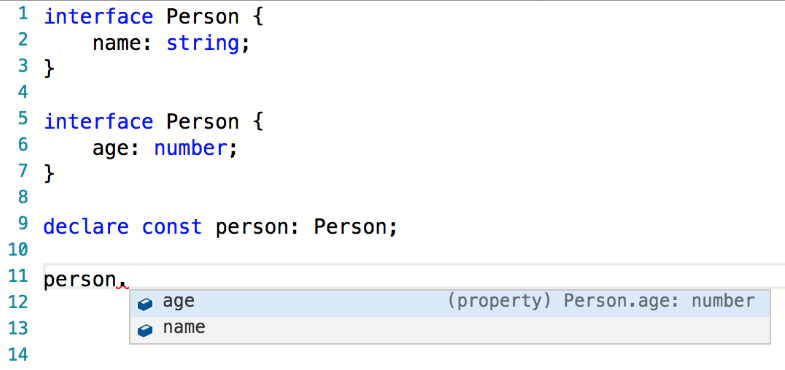
Parser
Checker
The checker driven by a program
2nd semantic pass
- figure out relationships between symbols
- assign types to symbols
- generate semantic diagnostics (errors)
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Emitter
Scanner
const fileName = './src/code.ts';
const program = ts.createProgram([fileName], {
noEmitOnError: true,
noImplicitAny: true,
target: ts.ScriptTarget.ES5,
module: ts.ModuleKind.CommonJS,
outDir: 'dist'
});
const diagnostics = ts.getPreEmitDiagnostics(program);
console.log(diagnostics);[ { file:
SourceFileObject {...},
start: 146,
length: 14,
code: 2322,
category: 1,
messageText: 'Type \'number\' is not assignable to type \'string\'.' } ]Parser
Checker
Binder
Parser
Checker
The emitter generate the desired output :
.js, .d.ts, or .js.map
use .emit of a program
internally use a transformer
print the final code
Binder
Emitter
Scanner
Scanner
const fileName = './src/code.ts'; // var foo:number = '5';
const program = ts.createProgram([fileName],
{
noEmitOnError: true,
noImplicitAny: true,
target: ts.ScriptTarget.ES5,
module: ts.ModuleKind.CommonJS,
outDir: 'dist'
});
let emitResult = program.emit();
console.log(emitResult);{ diagnostics:
[ { file: [Object],
messageText: 'Type \'"5"\' is not assignable to type \'number\'.' } ],
sourceMaps: undefined,
emittedFiles: undefined,
emitSkipped: true }Parser
Binder
Checker
Emitter
Scanner
const fileName = './src/code.ts'; // var foo:number = 5;
const program = ts.createProgram([fileName],
{
noEmitOnError: true,
noImplicitAny: true,
target: ts.ScriptTarget.ES5,
module: ts.ModuleKind.CommonJS,
outDir: 'dist'
});
let emitResult = program.emit();
console.log(emitResult);{ emitSkipped: false,
diagnostics: [],
emittedFiles: undefined,
sourceMaps: undefined }Parser
Binder
Checker
Emitter
What can we do with AST?
Analysing
-
linting
-
analysing complexity
-
documentation
-
API conformance
-
statistics
Linting with TSLint
if "type-checking" enabled
lint & do semantic ruling
if not
lint with rules using internal walker
if fix enabled
apply patch using normal string APIs
Managing AST
ts-simple-ast by David Sherret
Managing AST
tsquery by Graig Spence
Documentation
Typedoc

Documentation
Compodoc
Compodoc
One big challenge
deals with dynamic imports of routes metadatas
// home-paths.ts
export const PATHS = {
home: 'homeimported'
};
// home-routing.module.ts
import { PATHS } from './home-paths';
const HOME_ROUTES: Routes = [
{
path: PATHS.home,
component: HomeComponent
}
];PropertyAccessExpression
StringLiteral
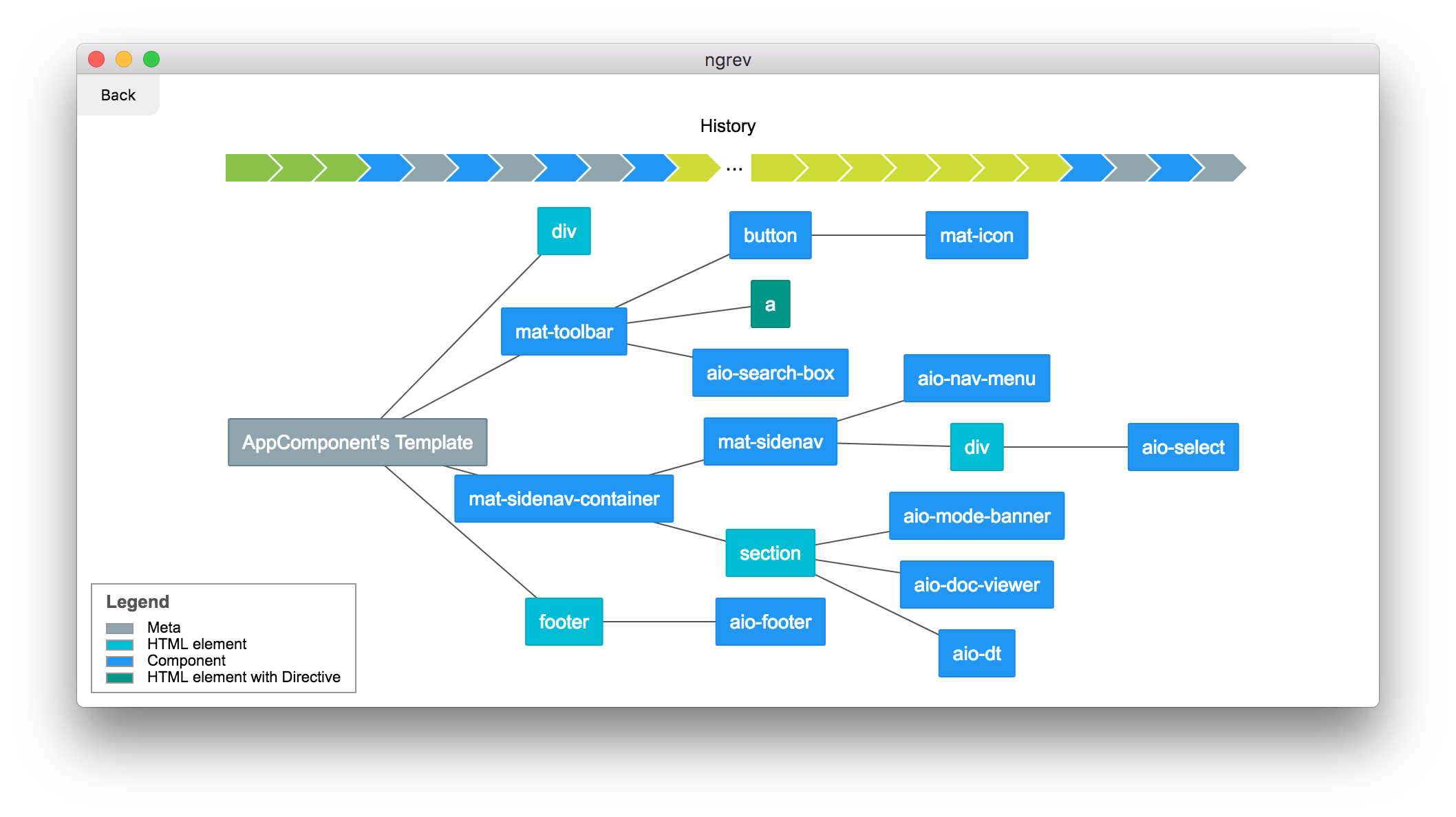
Compodoc
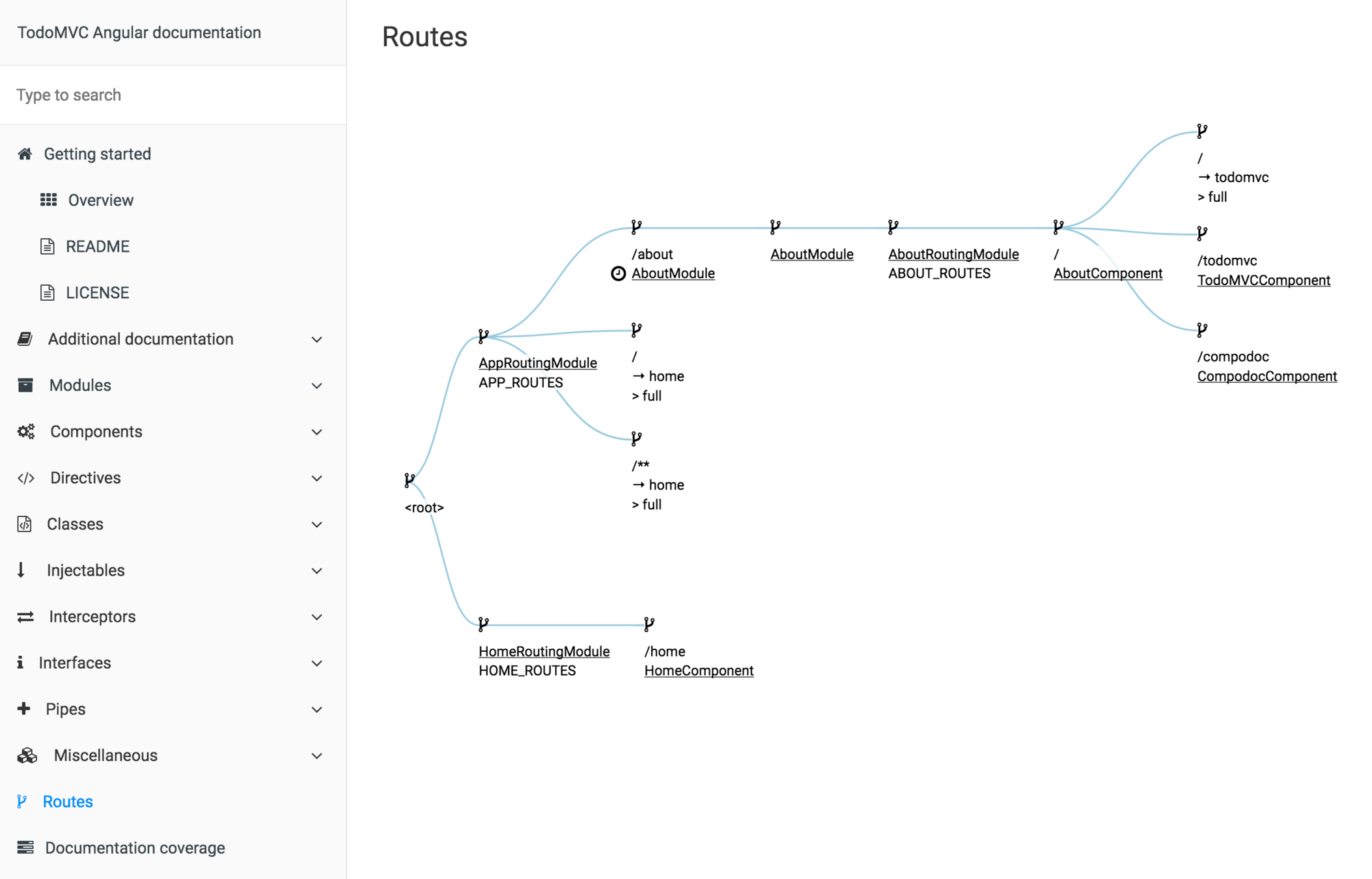
Visualize
Statistics
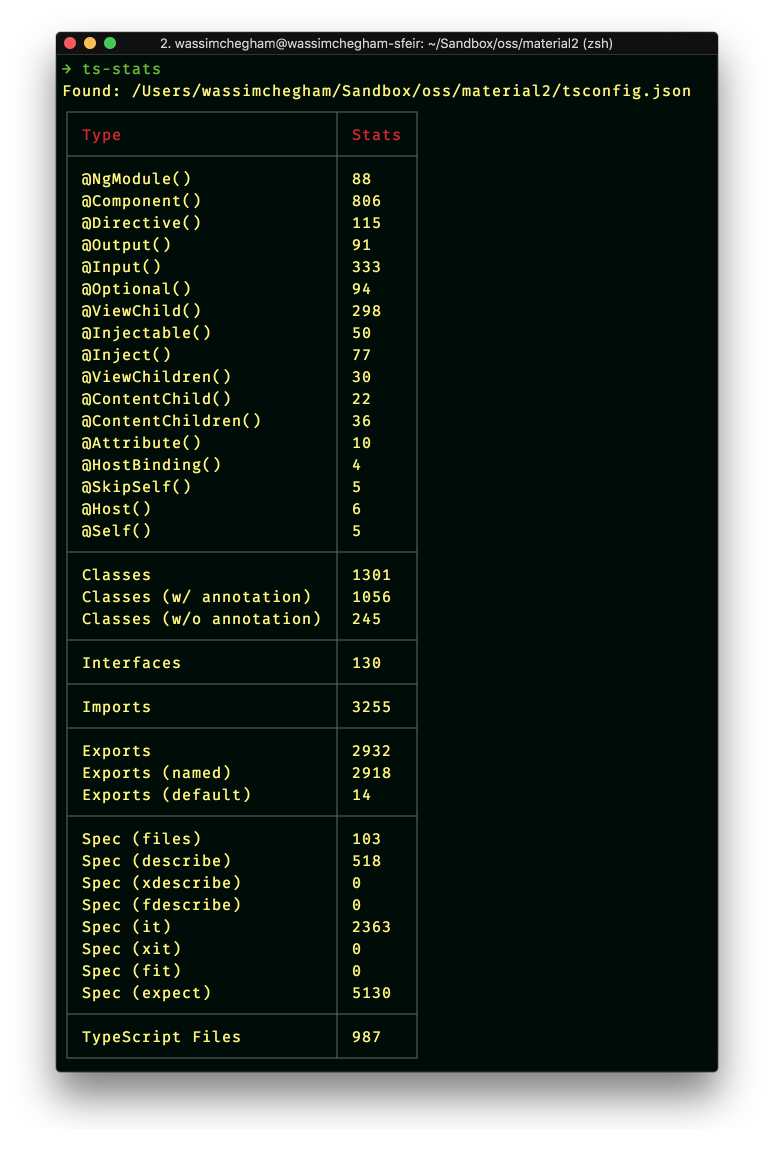
Transforming
- edit code
- transpile code
- generate code
- preprocess
- reformat
Edit code
@schematics
exemple: adding declaration in a module
CLI
Transforming

Refactoring
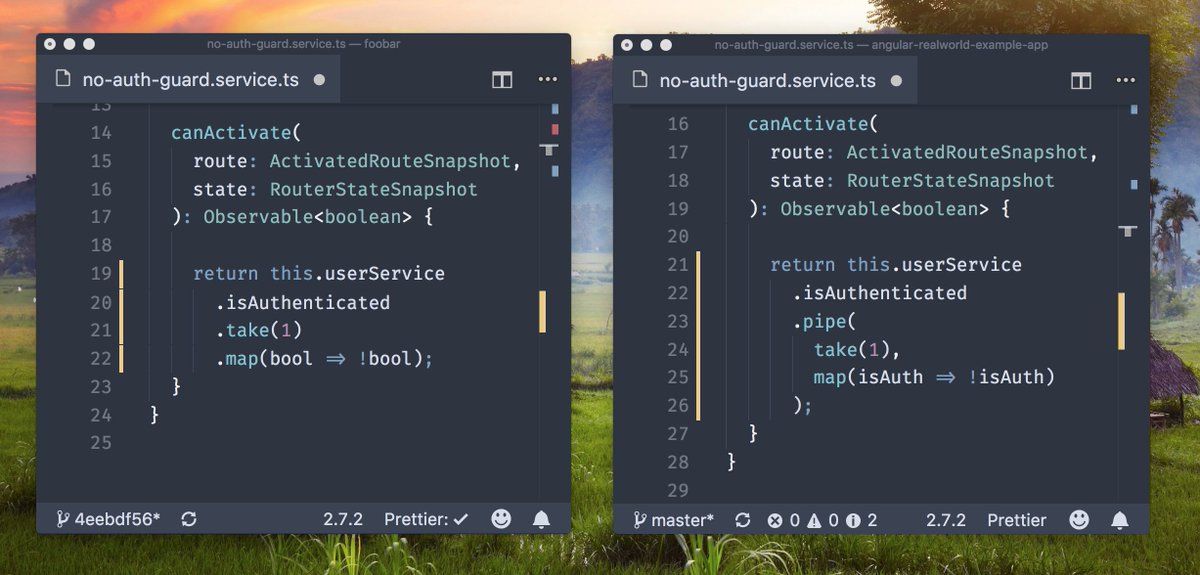
Automatically add missing types
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
add(5, 6);function add(a: number, b: number) {
return a + b;
}
add(5, 6);Have fun
with AST?
Browsing files inside a project can be very complicated
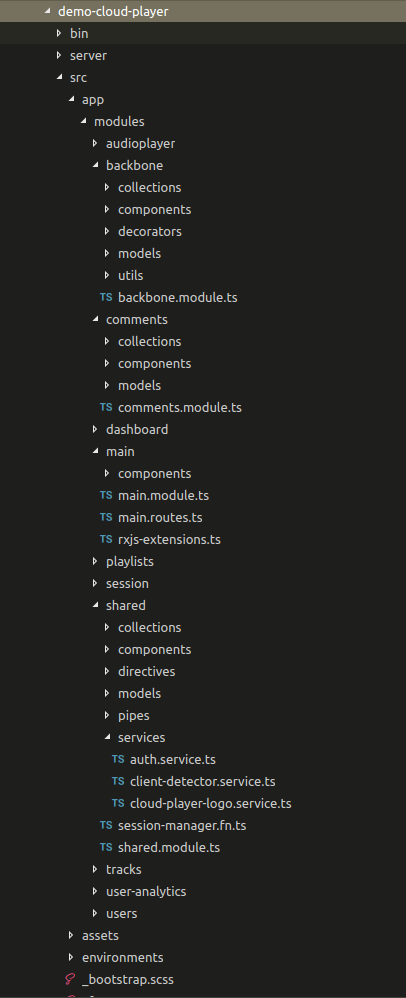
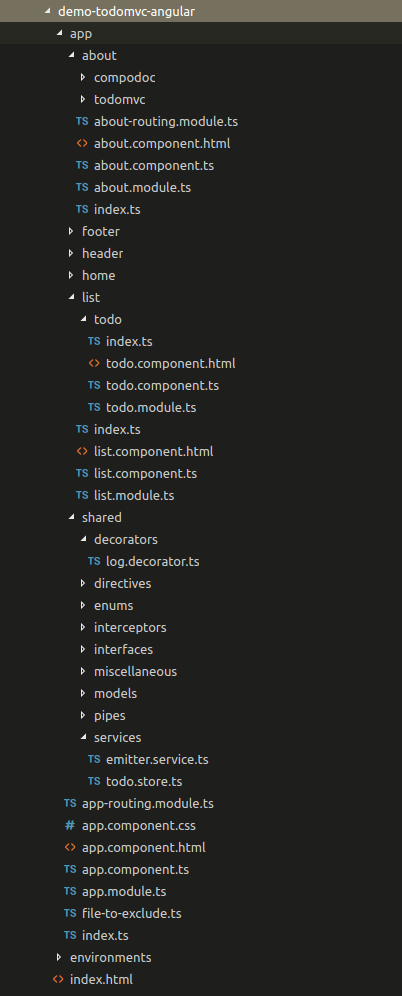
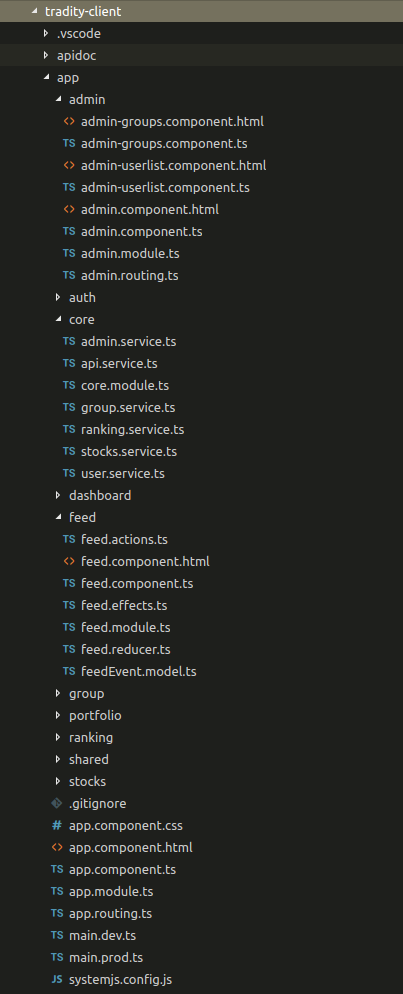
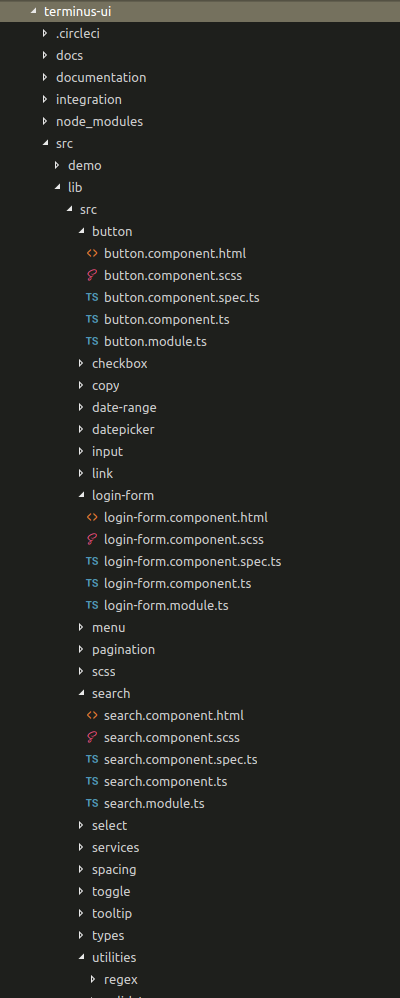
Let's answering the question:
What are the relations between my files?
Introducing madge

Generate a visual graph of your JavaScript module dependencies
Works with TypeScript files too
I love 3D & visualization
Let's extrude these graphics !
Demo time
madge 3D

We all love music
Demo time
TypeScript AST soundtrack
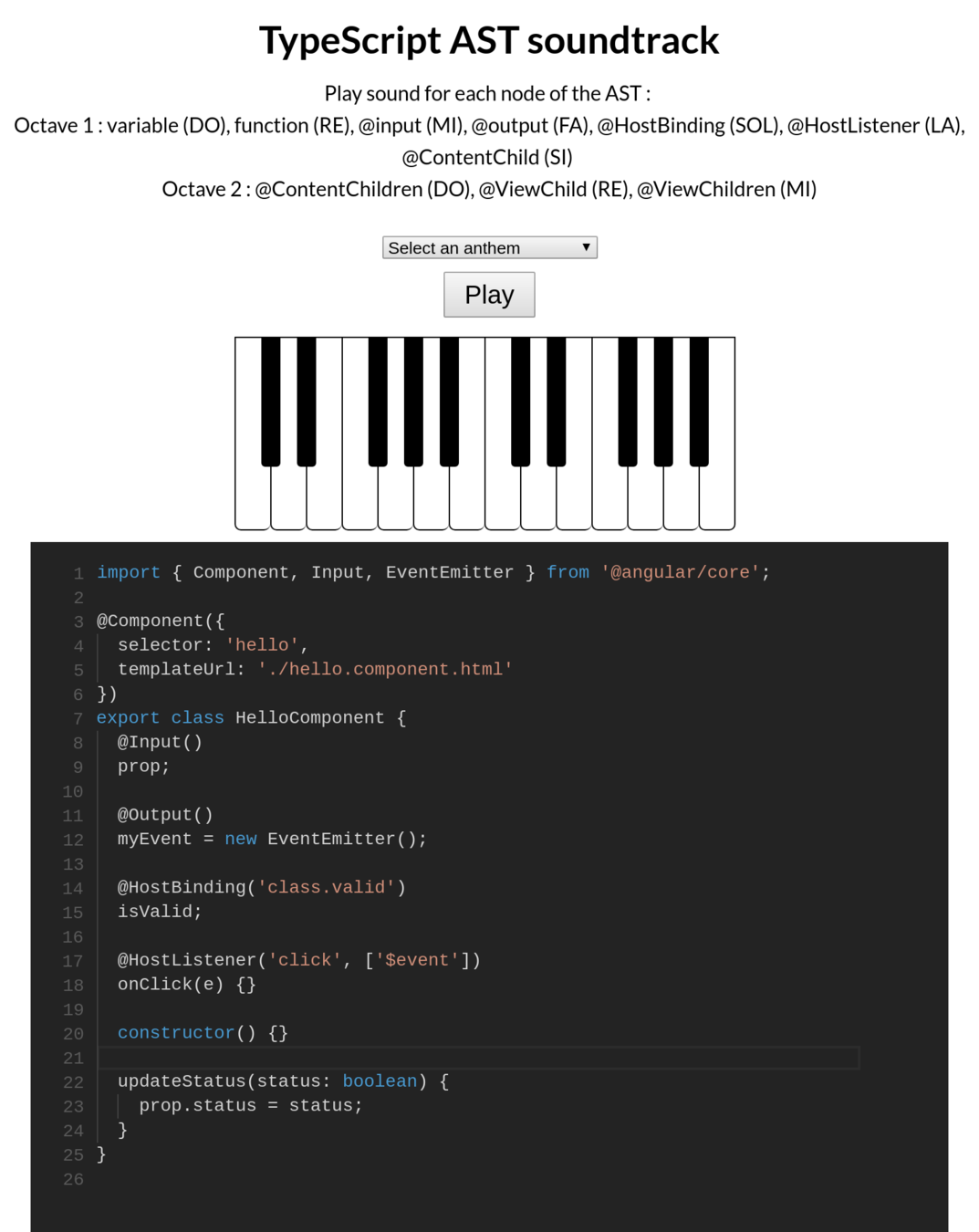
Generate sound with
Angular/TypeScript AST
Conclusion
We
all

Conclusion
Cons from the community
- extra compilation step
- JavaScript libraries integration
- lack of documentation for internal APIs
Conclusion
Pros from the community
- refactoring quickly & safely (thanks to TS language service) & enhance JS codebase gradually
- attractive code
- think with "type", code more "precise"
- enhance "maintainability" and "readability"
- open frontend community to Java, C# or .Net developers
- great editor support / boost productivity
Conclusion
Future is bright
JavaScript will be more a VM than a language
Frameworks move from runtime libraries into optimizing compilers
Resources
How to be* a compiler — make a compiler with JavaScript
https://medium.com/@kosamari/how-to-be-a-compiler-make-a-compiler-with-javascript-4a8a13d473b4
TypeScript Deep Dive
https://basarat.gitbooks.io/typescript/docs/compiler/overview.html
TypeScript - Architectural Overview
https://github.com/Microsoft/TypeScript/wiki/Architectural-Overview
TypeScript - Compiler Internals
https://github.com/Microsoft/TypeScript/wiki/Compiler-Internals
Resources
The Rise of TypeScript?
https://developer.telerik.com/featured/the-rise-of-typescript/
Moving from JavaScript to TypeScript at Slack
https://www.infoq.com/news/2017/04/going-typescript-slack
Compilers are the New Frameworks
https://tomdale.net/2017/09/compilers-are-the-new-frameworks/
The Future of JavaScript Will Be Less JavaScript
https://medium.com/@mrdaniel/the-future-of-javascript-will-be-less-javascript-cea373eb57fd
Thanks for listening !
Ask me anything during the conference
Sketch-notes : bit.ly/2AYVcp7