OpenSSHがSHA-1を使用したRSA署名を廃止
BacklogのGitで発生した問題と解決にいたるまでの道のり
NuCon '21 in ONLINE
Yuichi Watanabe at Nulab Inc.
Profile
me := Profile{
Name: "Yuichi Watanabe",
Org: "Nulab Inc.",
Product: "Backlog",
Job: "SRE/Backend",
Lang: "Go",
Twitter: "https://twitter.com/vvvatanabe",
GitHub: "https://github.com/vvatanabe",
Slides: "https://slides.com/vvatanabe",
Lives: "Fukuoka",
}
-
問題の発覚
-
問題の調査
-
恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
恒久的な対応の実施
-
反省と今後の改善
Agenda
TypetalkのBacklog開発者のトピックでフィードバックが投稿される
BacklogのGitへSSHでアクセスできない

OpenSSH 8.8へアップグレードすると、BacklogのGitへSSHアクセスできない!?
# 問題の発覚
-
問題の発覚
-
問題の調査
-
恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
恒久的な対応の実施
-
反省と今後の改善
Agenda
SSHプロトコルの接続確立の流れ
Inside SSH protocol v2
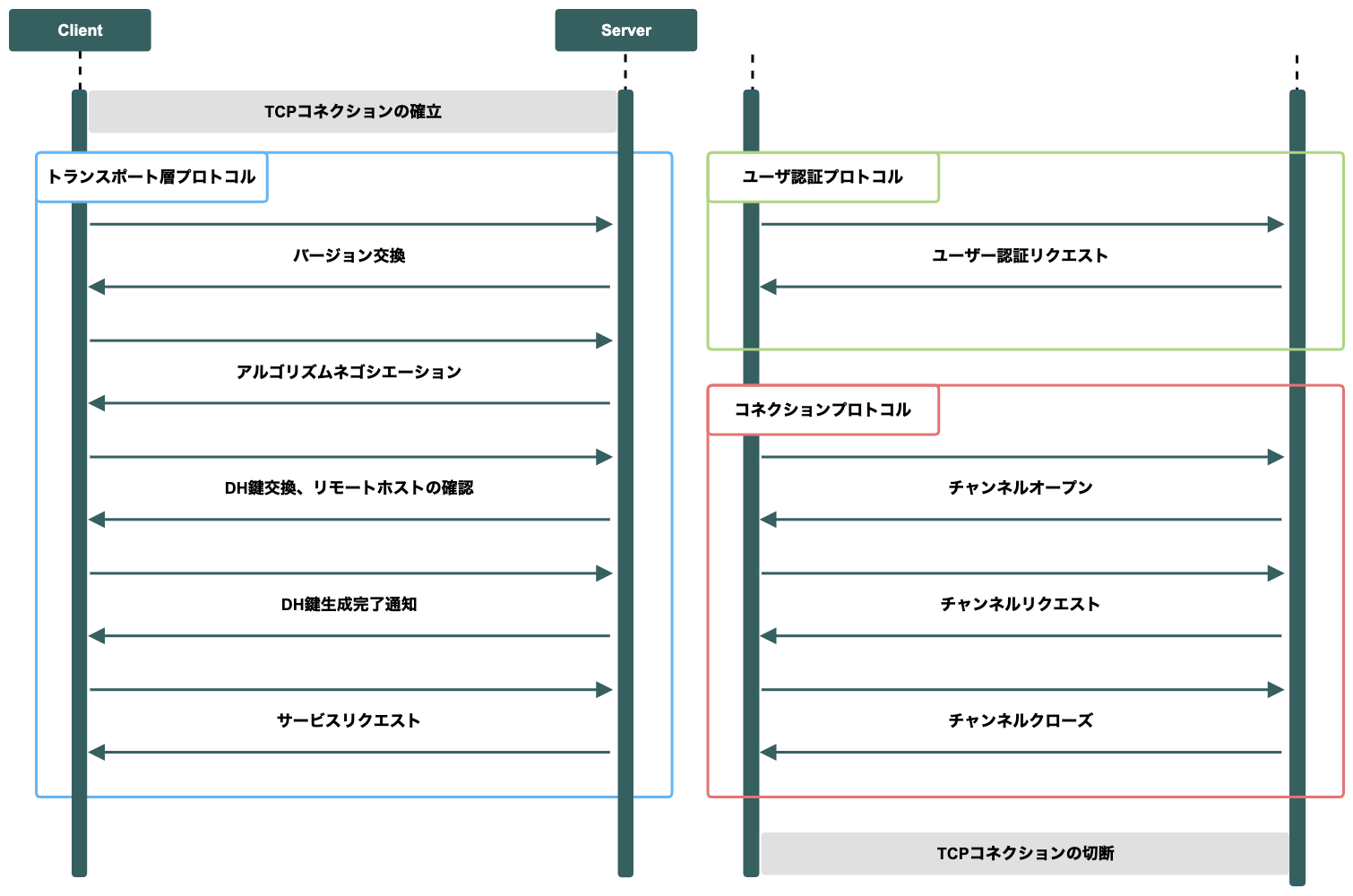
# 問題の調査
SSHプロトコルは4つの独立したプロトコルに分けられる
-
トランスポート層プロトコル
-
ユーザー認証プロトコル
-
コネクションプロトコル
-
ファイル転送プロコトル
# 問題の調査
Inside SSH protocol v2

TCP接続が確立された後、サーバとクライアントの間でSSHバージョン文字列を交換する
(サーバーとクライアント間で使用するSSHプロトコルのバージョンを決定する)
# 問題の調査
Inside SSH protocol v2

クライアントとサーバー間の暗号通信で用いる各アルゴリズムのネゴシエーション(使用可能な暗号アルゴリズムの交換)を行う
-
Kex algorithms
-
Server host key algorithms
-
Encryption algorithms a.k.a Cipher
-
MAC algorithms
-
Compression algorithms
# 問題の調査
Inside SSH protocol v2

# 問題の調査
Inside SSH protocol v2
-
Diffie-Hellman鍵交換方式で暗号通信で使う共通鍵を交換する
-
中間者攻撃を防ぐためにホスト認証を行う。
-
サーバーが持つホスト公開鍵と、クライアントのknown_hostsに保持しているホスト公開鍵の照合
-

-
OpenSSH 8.8で動作検証する
SSHクライアントのdebugログを読む
# 問題の調査
$ ssh -V
OpenSSH_8.8p1, OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
$ git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv -F /dev/null" clone \ foo@foo.git.backlog.com:/BAR/baz.git
〜 省略 〜
debug2: peer server KEXINIT proposal
debug2: KEX algorithms: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
debug2: host key algorithms: ssh-rsa
〜 省略 〜
debug1: kex: algorithm: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
debug1: kex: host key algorithm: (no match)
Unable to negotiate with 54.258.105.89 port 22: no matching host key type found. Their offer: ssh-rsa
fatal: Could not read from remote repository.
Please make sure you have the correct access rights
and the repository exists.
-
OpenSSH 8.8で動作検証する
-
SSHクライアントのdebugログを出力する
-
git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv"
-
SSHクライアントのdebugログを読む
# 問題の調査
$ ssh -V
OpenSSH_8.8p1, OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
$ git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv -F /dev/null" clone \ foo@foo.git.backlog.com:/BAR/baz.git
〜 省略 〜
debug2: peer server KEXINIT proposal
debug2: KEX algorithms: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
debug2: host key algorithms: ssh-rsa
〜 省略 〜
debug1: kex: algorithm: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
debug1: kex: host key algorithm: (no match)
Unable to negotiate with 54.258.105.89 port 22: no matching host key type found. Their offer: ssh-rsa
fatal: Could not read from remote repository.
Please make sure you have the correct access rights
and the repository exists.
-
OpenSSH 8.8で動作検証する
-
SSHクライアントのdebugログを出力する
-
git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv"
-
-
ホスト鍵のアルゴリズムはssh-rsaが選択されているように見受けられる
SSHクライアントのdebugログを読む
# 問題の調査
$ ssh -V
OpenSSH_8.8p1, OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
$ git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv -F /dev/null" clone \ foo@foo.git.backlog.com:/BAR/baz.git
〜 省略 〜
debug2: peer server KEXINIT proposal
debug2: KEX algorithms: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
debug2: host key algorithms: ssh-rsa
〜 省略 〜
debug1: kex: algorithm: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
debug1: kex: host key algorithm: (no match)
Unable to negotiate with 54.258.105.89 port 22: no matching host key type found. Their offer: ssh-rsa
fatal: Could not read from remote repository.
Please make sure you have the correct access rights
and the repository exists.
-
OpenSSH 8.8で動作検証する
-
SSHクライアントのdebugログを出力する
-
git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv"
-
-
ホスト鍵のアルゴリズムはssh-rsaが選択されているように見受けられる
-
一致するホスト鍵タイプが見つからない?と言われている
SSHクライアントのdebugログを読む
# 問題の調査
$ ssh -V
OpenSSH_8.8p1, OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020
$ git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv -F /dev/null" clone \ foo@foo.git.backlog.com:/BAR/baz.git
〜 省略 〜
debug2: peer server KEXINIT proposal
debug2: KEX algorithms: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
debug2: host key algorithms: ssh-rsa
〜 省略 〜
debug1: kex: algorithm: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
debug1: kex: host key algorithm: (no match)
Unable to negotiate with 54.258.105.89 port 22: no matching host key type found. Their offer: ssh-rsa
fatal: Could not read from remote repository.
Please make sure you have the correct access rights
and the repository exists.
-
サーバー側のログに関連しそうなエラーが出力されている
-
ホスト鍵の共通アルゴリズムがない?と読み取れる
SSHサーバーのerrorログを読む
ssh: no common algorithm for host key;
client offered: [rsa-sha2-512-cert-v01@openssh.com rsa-sha2-256-cert-v01@openssh.com rsa-sha2-512 rsa-sha2-256 ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp384-cert-v01@openssh.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp521-cert-v01@openssh.com sk-ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com ssh-ed25519 ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 ecdsa-sha2-nistp384 ecdsa-sha2-nistp521 sk-ssh-ed25519@openssh.com sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256@openssh.com],
server offered: [ssh-rsa]-
エラーログを出力している該当のコードは?
-
BacklogのGit SSHサーバー
-
Goで実装している
-
-
SSHプロトコルの実装
-
golang.org/x/cryptoのsshパッケージ(以下、crypto/sshと呼ぶ)を使用している
-
-
# 問題の調査

golang.org/x/cryptoを読む
func (t *handshakeTransport) enterKeyExchange(otherInitPacket []byte) error {
〜 省略 〜
var err error
t.algorithms, err = findAgreedAlgorithms(isClient, clientInit, serverInit)
if err != nil {
return err
}
〜 省略 〜
# 問題の調査
-
handshakeTransport struct
-
トランスポート層プロトコルの実装
-
-
enterKeyExchange method
-
暗号アルゴリズムのネゴシエーション
-
findAgreedAlgorithms関数へ三GO
-

func findAgreedAlgorithms(isClient bool, clientKexInit, serverKexInit *kexInitMsg) (algs *algorithms, err error) {
result := &algorithms{}
〜 省略 〜
result.kex, err = findCommon("key exchange", clientKexInit.KexAlgos, serverKexInit.KexAlgos)
if err != nil {
return
}
result.hostKey, err = findCommon("host key", clientKexInit.ServerHostKeyAlgos, serverKexInit.ServerHostKeyAlgos)
if err != nil {
return
}
〜 省略 〜 golang.org/x/cryptoを読む
# 問題の調査
-
サーバーとクライアント間で共通のアルゴリズムを探す(Kex, host key, Cipher, MAC, Compression)
-
findCommon関数で実際に一致するものを判定している
-

-
共通のアルゴリズムが見つかった場合
-
一致したアルゴリズムの文字列が返却される
-
-
共通のアルゴリズムが見つからなかった場合
-
対象の文言のエラーが返却される
-
func findCommon(what string, client []string, server []string) (common string, err error) {
for _, c := range client {
for _, s := range server {
if c == s {
return c, nil
}
}
}
return "", fmt.Errorf("ssh: no common algorithm for %s; client offered: %v, server offered: %v", what, client, server)
}golang.org/x/cryptoを読む
# 問題の調査
ssh: no common algorithm for host key;
client offered: [rsa-sha2-512-cert-v01@openssh.com rsa-sha2-256-cert-v01@openssh.com rsa-sha2-512 rsa-sha2-256 ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp384-cert-v01@openssh.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp521-cert-v01@openssh.com sk-ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com ssh-ed25519 ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 ecdsa-sha2-nistp384 ecdsa-sha2-nistp521 sk-ssh-ed25519@openssh.com sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256@openssh.com],
server offered: [ssh-rsa]-
トランスポート層プロトコルのアルゴリズムネゴシエーションの段階で失敗している
-
サーバーとクライアント間でホスト鍵のアルゴリズムの合意を得れない状況
-
共通のアルゴリズムを検索しているが一致するものが存在しない
-
golang.org/x/cryptoを読む
# 問題の調査
OpenSSH 8.8からSHA-1ハッシュアルゴリズムを使ったRSA署名が廃止されていた


- これは既にOpenSSH 8.3のリリース時にアナウンスされていたこと
OpenSSH 8.8のリリースノートを読む
# 問題の調査
-
認知はしていが業務のタスクとして起票できていなかったため、事前に対応できてなかった
-
問題の発覚
-
問題の調査
-
恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
恒久的な対応の実施
-
反省と今後の改善
Agenda

-
RSAの署名方式であるハッシュアルゴリズムのSHA-1を指す
-
鍵の形式のRSAそのものが廃止されたわけではない
-
-
OpenSSH 7.2からRFC8332に従ってハッシュアルゴリズムのSHA-256/512をサポートしている
-
クライアントの鍵の形式がssh-rsaであっても、クライアントは意識せずそのまま使用できるはず
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
OpenSSH 8.8で廃止されたssh-rsaとは?
-
BacklogのGit SSHサーバーが使用しているホスト鍵
-
ssh-rsa
-
-
RFCで定義されているRSAに対応する署名方式のハッシュアルゴリズム
-
ssh-rsa (SHA-1)
-
rsa-sha2-256 (SHA-256)
-
rsa-sha2-512 (SHA-512)
-
-
SSHクライアント側でssh-rsaが無効になっていても、rsa-sha2-256、rsa-sha2-512をクライアントとサーバーの双方がサポートしていれば、アルゴリズムのネゴシエーションは完了するはず
-
OpenSSH 7.2からrsa-sha2-256、rsa-sha2-521をサポートしている
-
golang.org/x/cryptoにおけるRSA署名を調査する
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
$ git -c core.sshCommand="ssh -vvv -F /dev/null" clone \ foo@foo.git.backlog.com:/BAR/baz.git
...
debug2: peer server KEXINIT proposal
debug2: KEX algorithms: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
debug2: host key algorithms: ssh-rsa
...
debug1: kex: algorithm: curve25519-sha256@libssh.org
debug1: kex: host key algorithm: (no match)
Unable to negotiate with 54.258.105.89 port 22: no matching host key type found. Their offer: ssh-rsa
fatal: Could not read from remote repository.
Please make sure you have the correct access rights
and the repository exists.
-
しかし、SSHサーバーは使用可能なホスト鍵アルゴリズムとしてssh-rsaのみ返している
-
サーバー側のコードを確認する三GO
-
crypto/ssh
-
golang.org/x/cryptoにおけるRSA署名を調査する
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
func (t *handshakeTransport) sendKexInit() error {
// 〜 省略 〜
msg := &kexInitMsg{
KexAlgos: t.config.KeyExchanges,
// 〜 省略 〜
}
if len(t.hostKeys) > 0 {
for _, k := range t.hostKeys {
msg.ServerHostKeyAlgos = append(
msg.ServerHostKeyAlgos, k.PublicKey().Type())
}
} else {
msg.ServerHostKeyAlgos = t.hostKeyAlgorithms
}
// 〜 省略 〜
if err := t.pushPacket(packetCopy); err != nil {
return err
}
// 〜 省略 〜 golang.org/x/cryptoにおけるRSA署名を調査する
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
handshakeTransport struct
-
トランスポート層プロトコルの実装
-
-
sendKexInit method
-
SSH_KEX_INITメッセージをSSHクライアントへ送信
-
-
SSH_KEX_INITメッセージ
-
受け入れ可能な各暗号アルゴリズム
-
-
各ホスト鍵のアルゴリズムをPublicKey().Type()で取得している
-
ホスト鍵がRSAの場合のPublicKeyインターフェイスの実装は?
-
type rsaPublicKey rsa.PublicKey
func (r *rsaPublicKey) Type() string {
return "ssh-rsa"
}golang.org/x/cryptoにおけるRSA署名を調査する
-
rsaPublicKey
-
ホスト鍵がRSAの場合の実装
-
Type名(アルゴリズム名)はssh-rsaとなる
-
-
ホスト鍵アルゴリズムのrsa-sha2-256、rsa-sha2-512はRSAのホスト鍵に対してデフォルトでは適用されない
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
他の暗号タイプのホスト鍵を差し替えを検討
-
ecdsa(ecdsa-sha2-nistp256/384/512)
-
ed25519(ssh-ed25519)
-
-
クライアントのknown_hostsに記録している公開鍵と一致しなくなる
-
クライアント側で中間者攻撃を疑われて接続が中断される
-
事前にホスト鍵を変更するといったユーザーへのアナウンスが必須
-
-
このアプローチは影響範囲が大きいのでいったん保留に
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
@ WARNING: REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED! @
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
IT IS POSSIBLE THAT SOMEONE IS DOING SOMETHING NASTY!
Someone could be eavesdropping on you right now (man-in-the-middle attack)!
It is also possible that a host key has just been changed.ホスト鍵の差し替えを検討する
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
UpdateHostKeyとは?
-
SSHプロ卜コルの拡張機能の一つ
-
サーバーが持つすべてのホスト鍵をクライアントへ通知する仕組み
-
クライアントは、受け取ったホスト鍵のうちどれがknown_hostsに存在するか確認する
-
クライアントは、接続先のそれまでに認知していないホスト鍵を知ることができ、known_hostsをより良い暗号タイプの公開鍵へグレイスフルに更新できるようにな
-
SSHのGlobal Requestを使って、hostkeys-00@openssh.com、hostkeys-prove-00@openssh.comと呼ばれるメッセージをやり取りすることで実現する
-
-
このプロトコルはクライアントのUpdateHostKeysを有効にすることで動作する
-
OpenSSH 8.5からデフォルトで有効になっている
-
UpdateHostKeyの活用を検討する
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
しかし、これはユーザー認証後、つまりアルゴリズムのネゴシエーションが正常に完了してから開始される
-
今回のケースでは、もとのホスト鍵はRSAなのでトランスポート層プロトコルのアルゴリズムネゴシエーションで失敗する
UpdateHostKeyの活用を検討する
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
ここまでの調査結果から、crypto/sshでホスト鍵のアルゴリズムとしてrsa-sha2-256、rsa-sha2-512をサポートするアプローチを選択した。
-
crypto/sshを改修する三GO
[結論] rsa-sha2-256、rsa-sha2-512をサポートする
# 恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
問題の発覚
-
問題の調査
-
恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
恒久的な対応の実施
-
反省と今後の改善
Agenda
-
GoのIssueを検索すると、案の定SHA-2のサポートを求める複数のIssueが上がっていた
golang.org/x/cryptoのIssueを調査する
# 恒久的な対応の実施
-
両者異なるアプローチでPull Requestを作成していた
-
ssh: support RSA SHA-2 (RFC8332) signatures [#37278]
- ホスト鍵がRSAの場合に、SHA-1、SHA-256、SHA-512を受け入れ可能なアルゴリズムとしてデフォルトでSSH_KEX_INITメッセージに含める
- ssh: allow the client public key auth method to use custom algorithms during the ssh handshake [#39885]
- 特定の署名ハッシュアルゴリズムを指定可能な構造体(ホスト鍵を表す)を提供する
- デフォルトはssh-rsa(SHA-1)だが、外からカスタムしてSHA-256、SHA-512を指定できる
- 特定の署名ハッシュアルゴリズムを指定可能な構造体(ホスト鍵を表す)を提供する
-
ssh: support RSA SHA-2 (RFC8332) signatures [#37278]
-
仕様となるRFC8332を確認して、上記のトピックブランチをローカルで動作検証
-
SSHのテストサーバーを実装
-
既存のPull Requestを検証する
# 恒久的な対応の実施
-
両方のアプローチは、ホスト鍵のアルゴリズムのネゴシエーションは成功したが...
-
その後のユーザー認証に失敗
-
SSHクライアントがユーザー認証リクエストとして送信するメッセージのパラメーター(認証メソッド)に、期待している公開鍵認証の値(publickey)が含まれていない
-
サーバー側はどのユーザー認証方式を適用すればいいのか決定できない状態
既存のPull Requestを検証する
# 恒久的な対応の実施
RFC8332を読み進めると、SSHの拡張ネゴシエーションメカニズムの一つである「server-sig-algs」をサーバー側で実装する必要があることがわかった

RFC8308 server-sig-algsを実装する
# 恒久的な対応の実施
- サーバーが受け入れ可能な署名ハッシュアルゴリズムの一覧を、クライアントへ通知するための仕組み
-
トランスポート層プロトコルのアルゴリズムネゴシエーションを拡張する

RFC8308 server-sig-algsを実装する
# 恒久的な対応の実施
「server-sig-algs」とは?
「server-sig-algs」の処理の流れ
RFC8308 server-sig-algsを実装する
# 恒久的な対応の実施
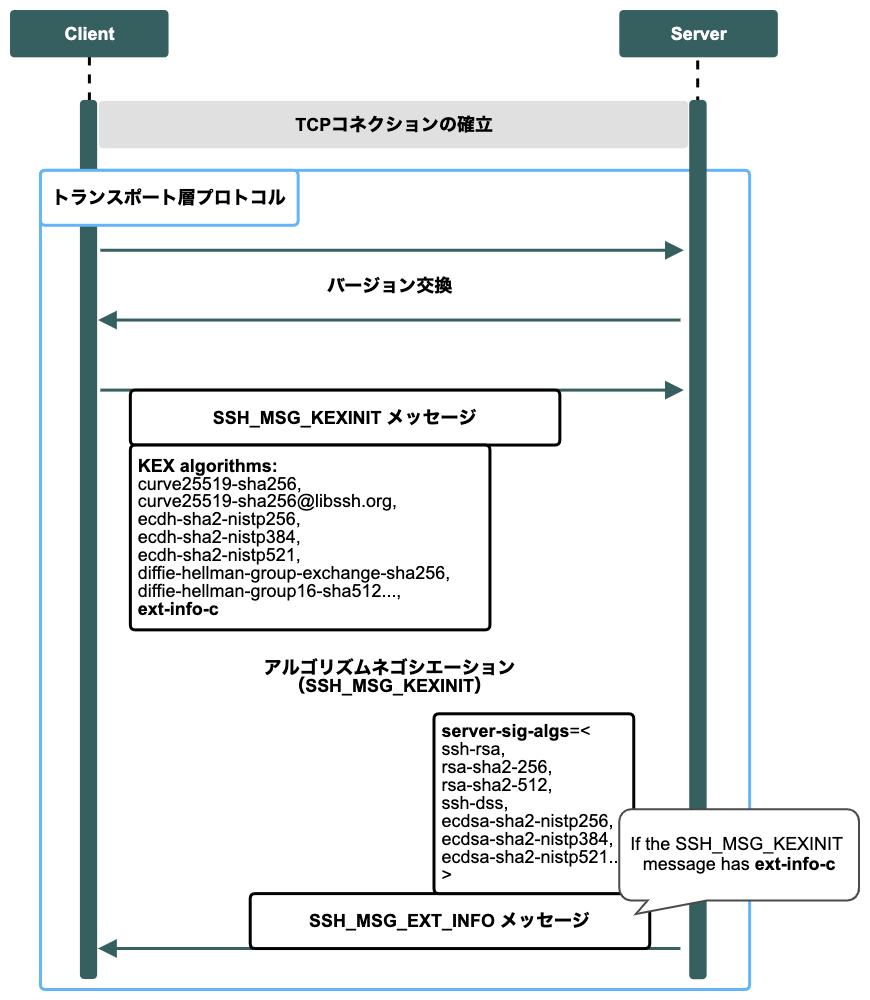
1. サーバーがTCP接続を受け入れたら、SSHプロトコルを開始
2. サーバーとクライアント間でSSHプロトコルのバージョン情報を交換
3. SSH_MSG_KEXINIT(※1)を開始
4. クライアントはSSH_MSG_KEXINITメッセージのパラメーター(※2)にext-info-c文字列を含めて送信
※1クライアントとサーバー間の暗号アルゴリズムのネゴシエーション
※2 kex_algorithmsフィールド
RFC8308 server-sig-algsを実装する
# 恒久的な対応の実施

# SSH_MSG_EXT_INFOのフォーマット
byte SSH_MSG_EXT_INFO (value 7)
uint32 nr-extensions
repeat the following 2 fields "nr-extensions" times:
string extension-name
string extension-value (binary)
# server-sig-algsのフォーマット
string "server-sig-algs"
name-list public-key-algorithms-accepted
「server-sig-algs」の処理の流れ
5. サーバーはSSH_MSG_KEXINITメッセージにext-info-c文字列が含まれているか判定する
6. SSH_MSG_EXT_INFOメッセージにKey-Value形式で受け入れ可能な署名アルゴリズムのリストを含めて、クライアントへ送信する
7. クライアントは、SSH_MSG_EXT_INFOメッセージに含まれる署名アルゴリズムのリストから、適切なアルゴリズムを選択する
-
RFC8332を満たす既存のPull Requestのコミットを、golang.org/x/cryptoをフォークしたリポジトリにgit cherry-pickした上で、実装した「server-sig-algs」のコミットを追加
-
既存のプルリクエストのコミット
-
「server-sig-algs」を実装したコミッ卜
-
セキュリティチームと統合テストを実施
-
テスト完了後、無事に本番環境へリリース
-
後日、cherry-pickしたコミットを持つ既存のPull Requestは無事マージされていた
RFC8308 server-sig-algsを実装する
# 恒久的な対応の実施

-
問題の発覚
-
問題の調査
-
恒久的な解決方法の調査
-
恒久的な対応の実施
-
反省と今後の改善
Agenda
-
今や情報サービスにおいてOSSの活用は必要不可欠な時代
-
使用しているOSSの最新の動向を漏れなくキャッチして精査する仕組みが重
-
ヌーラボでは、使用しているライブラリや外部サービスのアップデートを、チャットBotで自動的にお知らせする仕組みを一部導入している
-
それらの既存の仕組みに倣い、セキュリティ系のツイートやミドルウェアのアップデート情報(RSSフィード等)を適切なChatトピックに集約して、確実に起票できるようなフローの整備を進める
# 反省と今後の改善
OSSの動向を漏れなく集約して精査するフローを整備する
-
今後、他のアルゴリズムが非推奨になる等の不確実性に素早く対応できる環境を整える
-
今回は見送った、前述のUpdateHostKeyの機能をサーバー側でサポートする準備も進めている
-
現在、GitのSSHサーバーで使用しているのはssh-rsaのホスト鍵のみだが、安全性や性能、普及具合を踏まえた上で、ecdsaやed25519のホスト鍵を追加して、段階的にセキュアな実装を目指す
-
# 反省と今後の改善
UpdateHostKeyでホスト鍵を追加する
NuCon> git commit -m "ご静聴ありがとうございましたʕ◔ϖ◔ʔ"