Travel Agency Demo
Persistence with JPA
Christina Lin
Environment Setup
Install H2 database
Copy travelagency.mv.db to ~/h2 folder in your machine.
Setup Fabric authentication
Go to ~/.m2/settings.xml
Unser servers, add the following id/pwd information
<server>
<id>fabric8.upload.repo</id>
<username>admin</username>
<password>admin</password>
</server>
You can skip this part if you already done so

You can skip this part if you already done so
Setup JBoss Fuse
- Unzip you JBoss Fuse, (please use the one provided)
- Startup JBoss Fuse, by going to INSTALL_PATH/jboss-fuse-6.1.1.redhat-412/bin and start it
- Linux
- ./fuse
- Windows
- fuse.bat
- Linux
- In console create Fuse Fabric by typing
- fabric:create --wait-for-provisioning
- Stop your fuse by typing exit in console

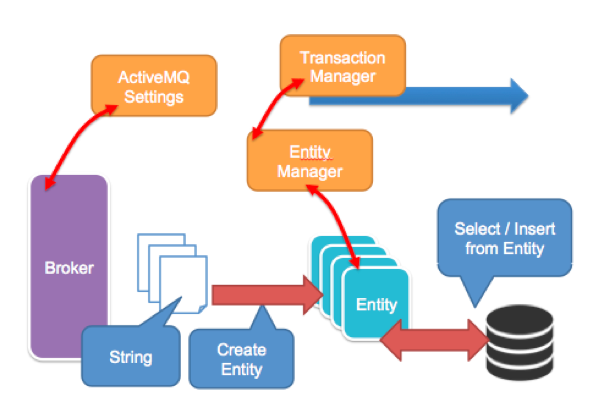
Create booking service, we are going to provide 2 functions in this service, Hotel booking and the other one is to cancel it. We are going to interact with our persistence layer with JPA.

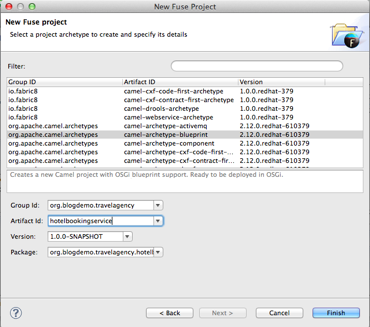
Choose the blueprint archetype,
GroupID: org.blogdemo.travelagency
ArtifactID: hotelbookingservice
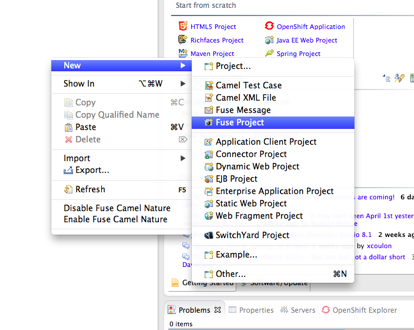
Create a Fuse project,

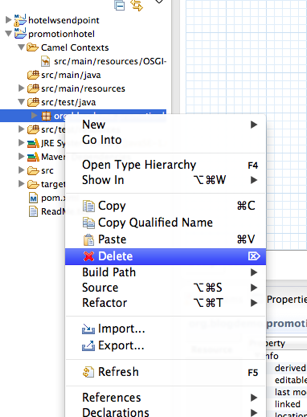
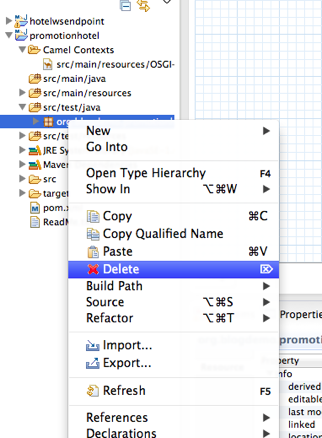
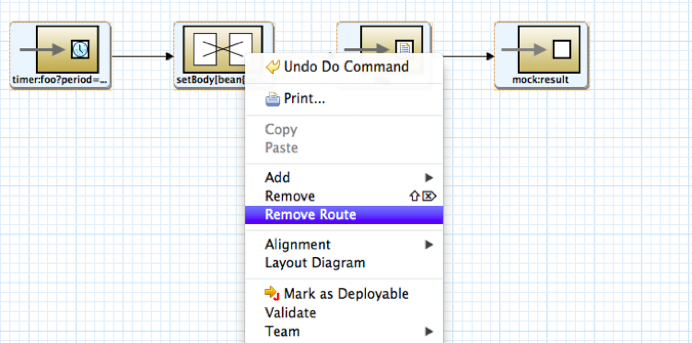
Open up /example/src/main/resources/OSGI-INF/blueprint/blueprint.xml and remove the route, so you are left with a blank canvas.
Remove the hellobean registry in the xml file. And delete all the java files.
<bean id="helloBean" class="com.mycompany.camel.blueprint.HelloBean"> <property name="say" value="Hi from Camel"/> </bean>
Remove everything under
src/java/* and src/test/*

Setup the dependencies in pom.xml
<!-- Database persistence-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-jpa</artifactId>
<version>2.12.0.redhat-610379</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.openjpa</groupId>
<artifactId>openjpa</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<version>1.4.181</version>
</dependency>
<!--Messaging from and to AMQ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.activemq</groupId>
<artifactId>activemq-camel</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0.redhat-610379</version>
</dependency>

Go back Camel route file, blueprint.xml, add activemq setting to connect to our messaging queue
<bean id="activemq" class="org.apache.activemq.camel.component.ActiveMQComponent">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/>
<property name="userName" value="admin"/>
<property name="password" value="admin"/>
</bean>
Inject JPA EntityManager and Transaction manager into camel context, and assign them to your Camel JPA component.
<bean id="jpa" class="org.apache.camel.component.jpa.JpaComponent">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
<property name="transactionManager" ref="jpaTxManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jpaTxManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"/>
</bean>

<bean id="entityManagerFactoryBean" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalEntityManagerFactoryBean" init-method="afterPropertiesSet">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="travelagency"/>
<property name="jpaDialect">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.OpenJpaDialect" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="entityManagerFactory" factory-ref="entityManagerFactoryBean" factory-method="getObject" />
With JPA, the most important part is the Entity itself, so create two entities.
Create an Entity
Package: org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice
Class name: Booking

package org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice;
import static javax.persistence.LockModeType.PESSIMISTIC_WRITE;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.NamedQuery;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@NamedQuery(name = "queryHotelBookingById", query = "select hotelbooking from Booking hotelbooking where hotelbooking.bookingid=:bookingid " , lockMode = PESSIMISTIC_WRITE)
@Table(name = "hotelbooking")
public class Booking {
@Column(name = "bookingid")
@Id
String bookingid;

@Column(name = "recieveDate")
Date recieveDate;
public String getBookingid() {
return bookingid;
}
public void setBookingid(String bookingid) {
this.bookingid = bookingid;
}
public Date getRecieveDate() {
return recieveDate;
}
public void setRecieveDate(Date recieveDate) {
this.recieveDate = recieveDate;
}
}

Create another entity
Package: org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice
Class name: CancelBooking
package org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "cancelhotelbooking")
public class CancelBooking {
@Column(name = "bookingid")
@Id
String bookingid;
@Column(name = "recieveDate")
Date recieveDate;
public String getBookingid() { bookingid;
public void setBookingid(String bookingid) {
this.bookingid = bookingid;
}
public Date getRecieveDate() { recieveDate;}
public void setRecieveDate(Date recieveDate) {
this.recieveDate = recieveDate;
}
}

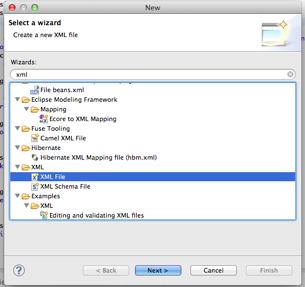
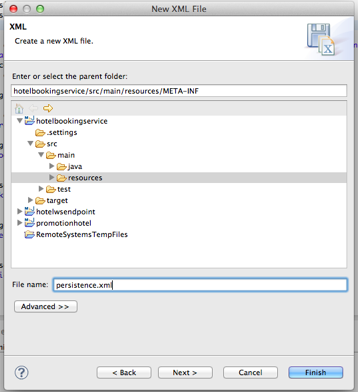
Same as in normal JPA project, we will need to declare the Entities, create a xml file under resource/META-INF called
persistence.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<persistence-unit name="travelagency" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<class>org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice.Booking</class>
<class>org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice.CancelBooking</class>
<properties>
<property name="openjpa.ConnectionDriverName" value="org.h2.Driver" />
<property name="openjpa.ConnectionURL" value="jdbc:h2:file:~/h2/travelagency;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE" />
<property name="openjpa.ConnectionUserName" value="sa" />
<property name="openjpa.ConnectionPassword" value="" />
<property name="openjpa.jdbc.SynchronizeMappings" value="buildSchema(SchemaAction='refresh')"/>
<property name="openjpa.Log" value="DefaultLevel=INFO, Runtime=INFO, Tool=INFO, SQL=TRACE"/>
<property name="openjpa.jdbc.DBDictionary" value="h2(useSchemaName=true)"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit> </persistence>

For booking, because we are inserting a new POJO, we are going to need a service to create these entities. This service also handles the necessary business logic in the booking service, such as generating random booking id and calculating fees.0
Create a java class
Package: org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice
Class name: BookingService
package org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Random;
public class BookingService {
private SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
public Booking createBooking(String someStringFromBPMS){
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
Booking booking = new Booking();
booking.setBookingid(genBookingId());
booking.setRecieveDate(cal.getTime());
return booking;
}

public CancelBooking createCancelBooking(String id){
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
CancelBooking cancelbooking = new CancelBooking();
cancelbooking.setBookingid(id);
cancelbooking.setRecieveDate(cal.getTime());
return cancelbooking;
}
private String genBookingId(){
return new BigInteger(130, secureRandom).toString(32);
}
public int cancelCharge(){
final Random random = new Random();
return random.nextInt((10-5)+1) + 5;
}
}

Register the service bean in camel context.
<bean id="bookingService" class="org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice.BookingService" />
<bean id="params" class="java.util.HashMap" />
Create the route to book the hotel
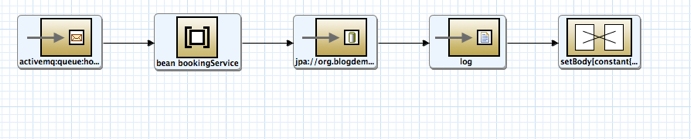

-
Activemq Endpoint
- Uri: activemq:queue:hotelbooking
-
Bean
- Bean Name: bookingService
- Method: createBooking
-
JPA endpoint
- Uri: jpa://org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice.Booking?consumeDelete=false
-
Log Endpoint:
- Message: ${body}
-
setBody
- Expression:OK
- Language: constant

Create the route to cancel booking,
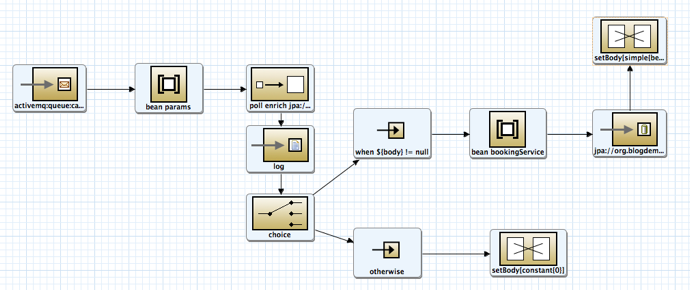
-
Activemq Endpoint
- Uri: activemq:queue:cancelhotelbooking
-
Bean
- Bean Name: params
- Method: put('bookingid',${body})
-
PollEnrich Endpoint
- Timeout: 2000
- Uri: jpa://org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice.Booking
- consumeDelete=false&consumer.namedQuery=queryHotelBookingById&consumer.parameters=#params

-
Log
- Message: try:[${body}]
-
Choice
-
When
- Expression: ${body} != null
- Language: simple
-
Bean
- Bean Name: bookingService
- Method: createCancelBooking(${body.bookingid})
-
JPA endpoint
- Uri: jpa://org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice.CancelBooking?consumeDelete=false
-
setBody
- Expression:bean:bookingService?method=cancelCharge
- Language: simple
-
When

-
Otherwise
-
setBody
- Expression:0
- Language: constant
-
setBody
Because we are using OpenJPA as our JPA library, we need to enhance the byte-code at build time. Go to your pom.xml and add the plugin in your plugin setting
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.openjpa</groupId>
<artifactId>openjpa-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
<configuration>
<includes>org/blogdemo/*.class</includes>
<addDefaultConstructor>true</addDefaultConstructor>
<enforcePropertyRestrictions>true</enforcePropertyRestrictions>
</configuration>

<executions>
<execution>
<id>enhancer</id>
<phase>process-classes</phase>
<goals>
<goal>enhance</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.openjpa</groupId>
<artifactId>openjpa</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>

Writing test code
Under src/test/java create 2 classes, one is the helper class to setup messaging queue and the other is the actual testing code.
Package: org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice
Class name: CamelJmsTestHelper
package org.blogdemo.travelagency.promtionhotel;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import org.apache.activemq.pool.PooledConnectionFactory;
public final class CamelJmsTestHelper {
private static AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
private CamelJmsTestHelper() {
}

public static ConnectionFactory createConnectionFactory() { return createConnectionFactory(null);}
public static ConnectionFactory createConnectionFactory(String options) {
int id = counter.incrementAndGet();
String url = "vm://test-broker-" + id + "?broker.persistent=false&broker.useJmx=false";
if (options != null) { url = url + "&" + options; }
ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(url);
connectionFactory.setCopyMessageOnSend(false);
connectionFactory.setOptimizeAcknowledge(true);
connectionFactory.setOptimizedMessageDispatch(true);
connectionFactory.setUseAsyncSend(false);
connectionFactory.setAlwaysSessionAsync(false);
PooledConnectionFactory pooled = new PooledConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
pooled.setMaxConnections(8);
return pooled;
}
}

Package: org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice
Class name: RouteTest
package org.blogdemo.travelagency.hotelbookingservice;
import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory;
import static org.apache.camel.component.jms.JmsComponent.jmsComponentAutoAcknowledge;
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.test.blueprint.CamelBlueprintTestSupport;
import org.junit.Test;
public class RouteTest extends CamelBlueprintTestSupport {
protected String componentName = "activemq";
@Override
protected String getBlueprintDescriptor() { return "/OSGI-INF/blueprint/blueprint.xml"; }
protected CamelContext createCamelContext() throws Exception {
CamelContext camelContext = super.createCamelContext();
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = CamelJmsTestHelper.createConnectionFactory();
camelContext.addComponent(componentName, jmsComponentAutoAcknowledge(connectionFactory));
return camelContext; }

@Test
public void testBooking() throws Exception {
String out = template.requestBody("activemq:queue:hotelbooking", "12345", String.class);
assertTrue(out.length()==26);
}
@Test
public void testSuccessfulCancelBooking() throws Exception {
String bookingId = template.requestBody("activemq:queue:hotelbooking", "12345", String.class);
Integer out = template.requestBody("activemq:queue:cancelhotelbooking", bookingId, Integer.class);
assertTrue(out > 0);
}
@Test
public void testProblemCancelBooking() throws Exception {
Integer out = template.requestBody("activemq:queue:cancelhotelbooking", "12345", Integer.class);
assertTrue(out==0);
}
}

Right click on the RouteTest.java and select JUnit Test
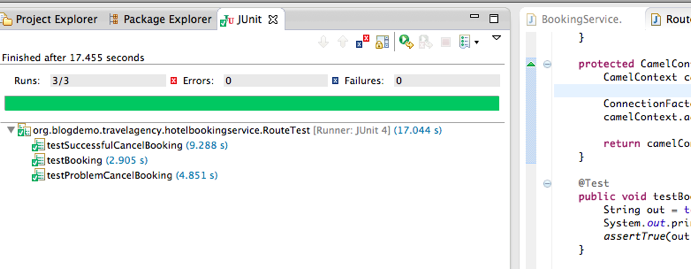
You should see all three test has passed in the Junit Test view

Lab Complete!
