MAKING PHYSICS GAMES in HTML5
Before we Start...
SIGN UP AT PLAYCANVAS.COM
MozFest 2013:
Making Physics-based HTML5 Games
in 30 Minutes
Making Physics-based HTML5 Games
in 30 Minutes
Will Eastcott, Co-founder, @willeastcott
Agenda
PlayCanvas Brain Dump
30 minutes
Exercise: Build A Game in 30 Minutes
30 minutes
A brief history of will
1998-2004: Criterion software
Senior Software Engineer: RenderWare
Head of Consultancy
2004-2007: EA


Product Manager: RenderWare Physics
2007-2009: SonY

Consultant: PlayStation Home
2009-2011: Activision



Technical Director for Europe
What is PlayCanvas?
A
cloud-hosted, collaborative,
3D game engine
powered by HTML5
WHY DEVELOP in the cloud?
- Access your projects from any device
- Collaborate in realtime with your team
- Get instant help and feedback
- Browse and iterate public projects
Terminology
- Pack - A level or scene.
- Entity - A thing in your game.
- Component - Adds behavior to an entity.
- Attribute - A property of a component.
Exercise 1: Publish your 1st App
Get people playing your games!
(That's the point, right?)

Time to publish your first PlayCanvas app!
Graphics
- Ambient, directional, point and spot lights
- Static and skinned meshes (up to 256 bones)
- Wireframe rendering
-
Map types: diffuse, specular, emissive, normal
- Per-pixel fog
- Skyboxes
- Full screen effects
Primitives
Basic shapes: box, sphere, cylinder, cone, capsule
Very useful for prototyping
Can make entire games with them:
Models
3D content that you upload to PlayCanvas
Recommendations:
Supply models in FBX format
Ensure textures are embedded in FBX
Ensure no meshes have >65535 vertices
Material Editing
You can edit materials in Designer
Click once to select entity
Click again to select the material on selected mesh

Scripting
- Add custom behavior to entities
- JavaScript API
Workflows
2 available options:
- Edit scripts on playcanvas.com
- Edit scripts on your filesystem
and sync using Github or Bitbucket
Anatomy of a Script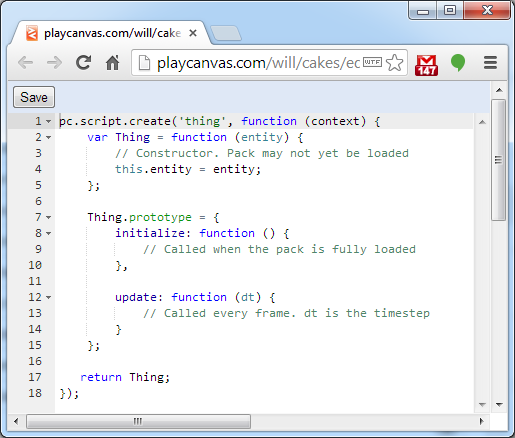
Debugging Scripts

Debugging Scripts

Take Care in the Script Editor

Collaborative script editing is not yet enabled
If you are working with other coders, be mindful that the most recent save overwrites the previous
TO BE RESOLVED VERY SOON!
Physics
Allows you to quickly create complex and
realistic behaviour and interactions
realistic behaviour and interactions
From the Classics...

...TO the CONTEMPORARY
Rigid BOdy
Idealised representation of a physical object
in which deformation is ignored
in which deformation is ignored
Properties:
- position and orientation
- linear and angular velocity
- mass, friction, restitution
Actions:
- apply forces and impulses
- apply torque and torque impulses
Body Types
- Static
- Dynamic
- Kinematic
Let's see each type in action...
Collision Primitives
A body needs to be linked to a collision primitive:
- Sphere
- Box
- Capsule
- Triangle Mesh
Let's take a look
Contact Detection
Useful for triggering events
e.g. audio, particles
e.g. audio, particles
initialize: function () {
// When another body comes into contact with this one,
// call the onCollision function
this.entity.collision.on('collisionstart', this.onCrash, this);
},
onCrash: function (result) {
this.entity.audiosource.play('crash');
},
Trigger Volumes
Entities that have a collision component but no rigidbody component are trigger volumes
initialize: function () { this.entity.collision.on('triggerenter', this.springTrap, this); }, springTrap: function (entity) { // If it is the player that has entered the trigger volume, // make him fall to his doom! if (entity.getName() === 'Player') { this.openTrapDoor(); }},
Let's make A BounCing Ball!
- Create a new project called 'ball'
-
Create a new pack
-
Create a camera
-
Create a static floor
(components: primitive, collision and rigidbody) -
Create a dynamic ball above floor
(same components as above) - Set ball rigid body type to 'Dynamic'
- Set 'Restitution' on floor and ball to 1
-
Launch!
Ladies and Gentlemen:
The Main Event
Let's make a classic Pong game!
MozFest 2013:
Making Physics-based HTML5 Games
in 30 Minutes
Making Physics-based HTML5 Games
in 30 Minutes
Will Eastcott, Co-founder, @willeastcott