Writing Systems

History of Writing Systems
Origins
- Writing systems were developed independently by separate civilizations
- Writing systems start out as drawings, evolve into more abstract symbols

Evolution
- Egyptian hieroglyphs -> Phoenician alphabet -> Greek alphabet -> Roman alphabet
Directionality
- Left-to-right (Roman, Greek)
- Right-to-left (Arabic, Hebrew)
- Top-to-bottom (Chinese, Mongolian)
- Bottom-to-top (Hanunó'o)
- Variable (Egyptian hieroglyphs)
- Boustrophedon (Ancient Greek)
Types of Writing Systems
- Alphabets
- Abjads
- Abugidas
- Syllabaries
- Semanto-phonetic
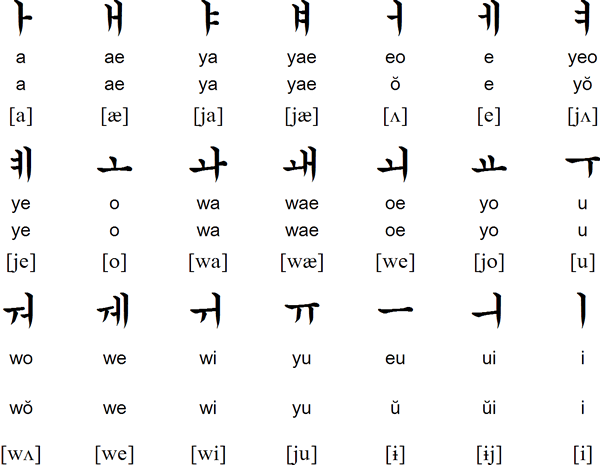
Alphabets
- Sets of letters that represent consonants and vowels
- Same letter can represent different sounds, while same sounds can be written with different combinations
-
Examples:
- Roman alphabet
- Cyrillic alphabet
- Greek alphabet
- Georgian alphabet
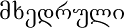
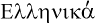
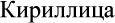
Abjads
- "Consonant alphabets"
- Set of letters that only represent the consonants
- Vowels are denoted through context, or diactritics
-
Examples:
- Arabic script
- Hebrew script

Abugidas
- "Syllabic alphabets"
- The syllable is the main element
- Symbols are modified to denote different vowels, ending consonants, etc.
-
Examples:
- Devanagari
- Burmese
- Inuktitut syllabics

Inuktitut syllabics
- Used in Inuit languages of north and east Canada
- Symbols are rotated to give them different vowels


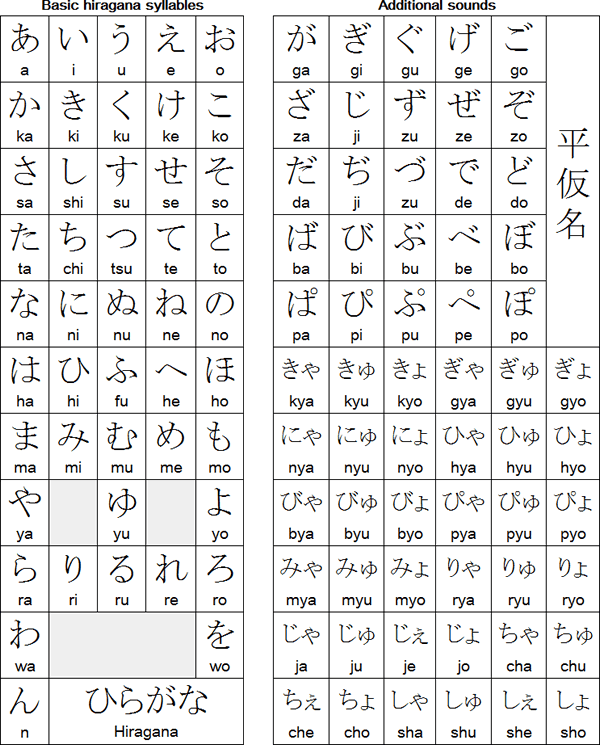
Syllabaries
- The syllable is the main element
- Each syllable is denoted by a unique symbol
-
Examples:
- Japanese (Hiragana, Katakana)
- Cherokee

Semanto-phonetic
- Symbols can represent both meaning and pronunciation
- Pictograms/logograms: simplified drawings
- Ideograms: abtract ideas
- Examples
- Egyptian hieroglyphs
- Chinese characters

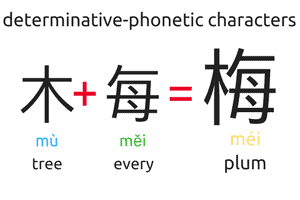
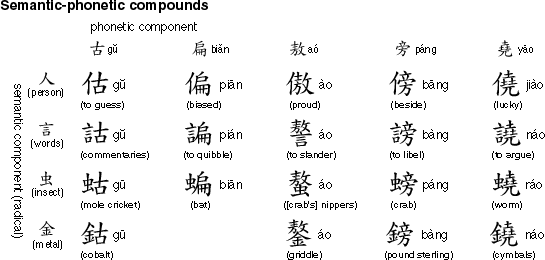
Compound characters
- Most of the Chinese characters
- Contains both a semantic element and a phonetic element
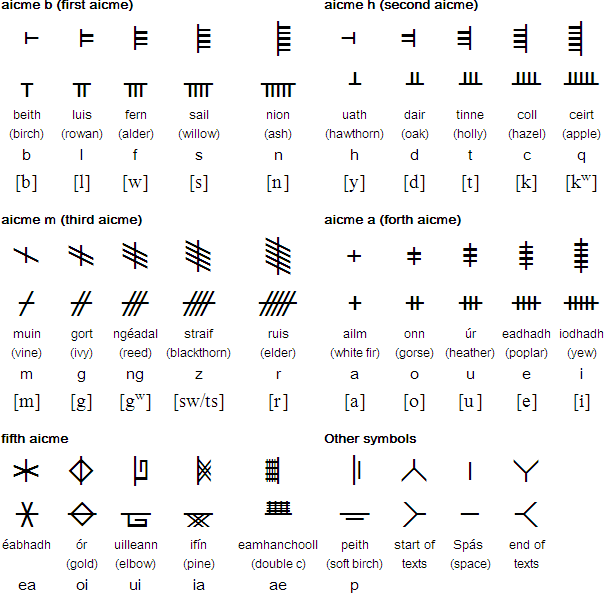
Guess the type of writing system!
Ogham (᚛ᚑᚌᚐᚋ᚜)
- Used to write Old Irish, Old Welsh, Pictish, Latin
- Can be written horizontally or vertically
- 25 letters, words linked together by a solid line
Alphabet
Ge'ez (ግዕዝ)
- Used to write Amharic, other East African languages
- Written left to right
- The basic signs are modified in a number of different ways to indicate the various vowels
Abugida

- Ethiopian name for the Ge'ez script
- Taken from four letters of the script (አቡጊዳ)
Thaana (ތާނަ)
- Used to write Dhivehi
- Written from right to left
- Letters represent consonants, vowels denoted with diacritics
- Derived from the Arabic script and indigenous scripts
Abjad

Hangul (한글)
- Used to write Korean
- Created during the reign of King Sejong in 1444
- Written from top to bottom until the 1980s, now written from left to right
- Symbols denoting vowels and consonants are put into a symbol block representing one syllable
Alphabet / Syllabary