String
字串
- 一個或以上的字元組成
- 不可使用slice切割(不是Python)
String
Char
- 單一字元
- 可轉換成ASCII碼
Contents
Iterator
- 迭代器
- 儲存向量的記憶體空間位址
Char
'A'、'B'、'a'、'b'、'0' 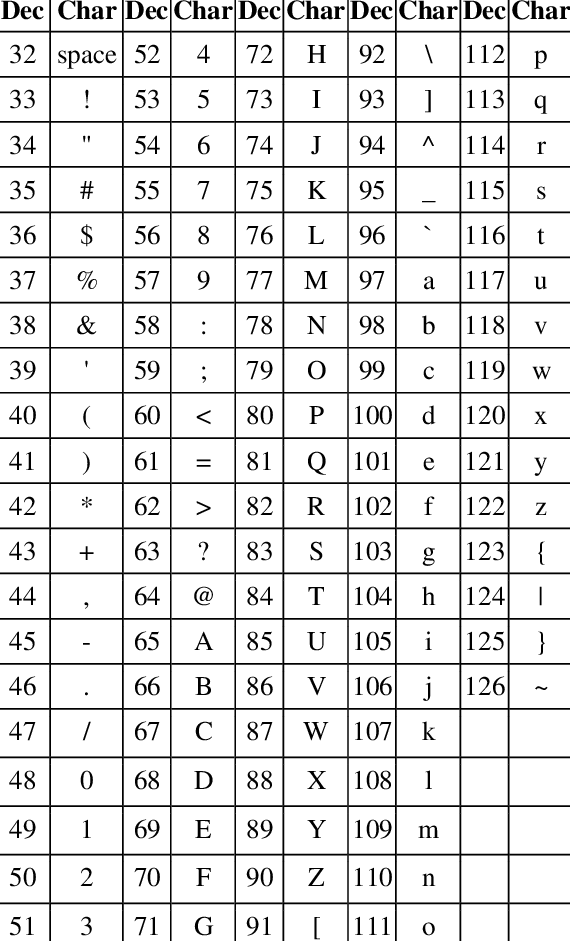
'A'=65、'Z'=90
'a'=97、'z'=122
'0'=48、'9'=57
tips:
判斷字元是大寫or小寫轉換成ASCII比較。
**不用記數字!!!**
只要記得a比z的ASCII小、A比Z的ASCII小就好了
小練習:
輸入一個字元,若為大寫輸出upper,小寫輸出lower,不是字元則輸出Not an alpha
char alpha;
if(alpha>=__ && alpha<=__) cout << upper << endl;
else if(alpha>=__ && alpha<=__) cout << lower << endl;
else cout << "Not an alpha" << endl;大小寫互換:
char alpha;
cin >> alpha;
if(alpha>=__ && alpha<=__)
cout << char(alpha-'A'+'a') << endl;
else if(alpha>=__ && alpha<=__)
cout << char(alpha-'a'+'A') << endl;
else cout << "Not an alpha" << endl;轉換大小寫之函式版本:
char alpha;
cin >> alpha;
if(alpha>='A' && alpha<='Z')
cout << char(tolower(alpha)) << endl;
else if(alpha>='a' && alpha<='z')
cout << char(toupper(alpha)) << endl;
else cout << "Not an alpha" << endl;String
- 使用雙引號(")
- 輸入時遇到空白停止
- 可相加
- 可取出其中的單一字元
- 宣告後可更改其中的內容(部分and全部)
- 可迭代
string str="Hello World!";//更改字元
string str="Hello World!";
str[1]='a';
cout << str;
//Hallo World!
//取出單一字元
string str="Hello World!";
char first=str[0];
char second=str[1];
cout << first <<" "<< second;
//H e//字串相加
string first="Hello ";
string second="World!";
cout << first+second;
//Hello World!Char Array
- C語言
- 字元陣列
- 若不做初始化數值則需規定長度
//字串初始化版
char arr[]="Hello World!";
//陣列初始化
char text[]={'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o','\0'};其他和字串特性皆相同
but 在C語言中不能使用string
使用字元陣列時須考慮到'\0'的空位:
//要輸入Hello
char arr[5+1];
cin >> arr;
cout << arr;初始化:
//設定內容空間數
char arr[數值];
//設定內容
char arr2[]="...."
//錯誤X
char arr3[];基礎常用函式:
//長度
string:字串.size()
char array:strlen(字串)
//判斷字串是否為空
字串.empty()
//空則回傳1
//比較
strcmp(字串1,字串2)
//相等回傳0
//strlen,strcmp皆為C語言函式
//需匯入#include <cstring>
//或者通用標頭 #include <bits/stdc++.h>**長度不包括結束符號'\0'
Homework 1:
~~迴文~~
請輸入一個字串,判斷其是否為迴文,是輸出yes,否輸出no
迴文定義:從前面念和從後面念相同
e.g. abba,abcba等
Iterator
迭代器
- 記憶體空間位址
- 常搭配指標使用
- 儲存向量如:陣列、字串、vector等
| 'H' | 'e' | 'l' | 'l' | 'o' | '\0' |
|---|
begin & end
|
|
'H' (0) | 'e' (1) |
'l' (2) |
'l' (3) |
'o' (4) |
'\0' |
|---|
假設一向量名為arr,此為它的內容。
arr.begin()
arr.end()
arr.rend()
arr.rbegin()
字串.insert(索引值,插入字串)
字串.erase(迭代起始,迭代終點)string grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Helloinsert & erase
(有頭無尾)
string grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Hellostring grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Hello| 'H' | 'e' | 'l' | 'l' | 'o' | '\0' |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| grt.begin() | grt.begin()+1 | grt.begin()+2 | grt.begin()+3 | grt.begin()+4 | grt.end() |
string grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Hello| 'H' | 'e' | 'l' | 'l' | 'o' | '\0' |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| grt.begin() | grt.begin()+1 | grt.begin()+2 | grt.begin()+3 | grt.begin()+4 | grt.end() |
不算到尾
erase
string grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Hello| 'H' | 'l' | 'o' | '\0' |
|---|---|---|---|
| grt.begin() | grt.begin()+1 | grt.begin()+2 | grt.end() |
string grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Hello| 'H' | 'l' | 'o' | '\0' |
|---|---|---|---|
| grt.begin() 索引值[0] |
grt.begin()+1 索引值[1] |
grt.begin()+2 索引值[2] |
grt.end() |
{'e','l'}
string grt="Hello";
grt.erase(grt.begin()+1,grt.begin()+3);
cout << grt << endl;
//Hlo
grt.insert(1,"el");
cout << grt;
//Hello| 'H' | 'e' | 'l' | 'l' | 'o' | '\0' |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| grt.begin() | grt.begin()+1 | grt.begin()+2 | grt.begin()+3 | grt.begin()+4 | grt.end() |
find
string grt="Hello";
string fnd="ll";
int idx=grt.find(fnd);
int len=fnd.size();
cout << idx << " " << len;
//2 2會回傳第一個索引值
Hw2:
輸入一字串,再輸入想刪去的內容,並輸出刪除後的結果。
string str,fnd;
cin >> str >> fnd;
int idx=__.find(__);
int len=__.size();
while(idx<__.size() && idx>=0){
str.erase(______,______);
idx=str.find(__);
}
cout << str << endl;Kahoot!