REACT IN 60 minutes
CONCEPTS AND CODE

React
A JAVASCRIPT LIBRARY FOR BUILDING USER INTERFACES*
* React isn't an MVC framework.
WHY*
BUILD COMPOSABLE COMPONENTS
SIMPLE and DECLARATIVE
* Facebook's official reasons
LEARN ONCE, WRITE ANYWHERE
WHO USE












Pretty TIME TO START

REACT
IMPLEMENTS a GROUP OF IDEAS AND CONCEPTS
- Virtual DOM
- JSX syntax
- ES6 support
- Component driven development
- Isomorphic React
virtual DOM
concept OF

VIRTUAL DOM
- Represent original DOM in memory
- Calculate diff with changed Virtual DOM
- Patch original DOM nodes
SoLVEs THE FOLLOWING TASKS
It is an abstraction of the real DOM
Virtual DOM. Diff Algorithm
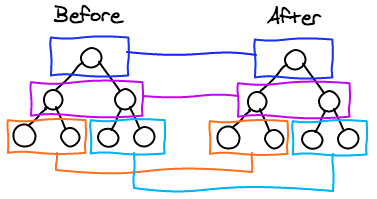
1. React only tries to reconcile trees level by level.
Tree diff algorithm has O(n^3) complexity*
2. React introduce the key attribute to help the diff algorithm do matching
React approach
Turn a O(n^3) problem into a O(n) one.
REACT APROACH. Batched DOM operations
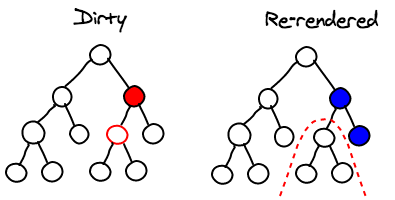
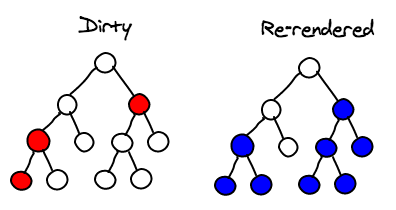
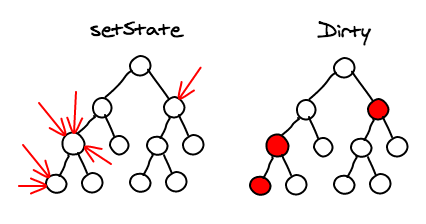
1. Whenever you set the state on a component, React will mark it as dirty.
2. The component rebuilds the virtual DOM for its children.
Sub-tree Rendering
Selective Sub-tree Rendering
React will optimize DOM mutation by using batching and change detection.
HOW WORK
With virtual DOM

var element = React.createElement('div', {
className: 'reactElement'
}, 'Hello world');
ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);React Elements
React.createElement = (type, props, children) => ReactElement;
ReactDOM.render = (ReactElement, HTMLElement | SVGElement) => ReactComponent;Code example
API Definitions
Render result (on jsfiddle)
<div id="reactContainerElement">
<div data-reactroot class="reactElement">Hello world</div>
</div>Light, stateless, immutable, virtual representation of a DOM Element
var divFactory = React.createFactory('div');
var element = divFactory({
className: 'reactElement'
}, 'Hello world');
ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);REACT FACTORIES
Code example
Render result (on jsfiddle)
<div id="reactContainerElement">
<div data-reactroot class="reactElement">Hello world</div>
</div>A ReactElement-factory is simply a function that generates a ReactElement with a particular type property
var element = React.DOM.div({
className: 'reactElement'
}, 'Hello world');
ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);REACT.DOM
Code example
Render result (on jsfiddle)
<div id="reactContainerElement">
<div data-reactroot class="reactElement">Hello world</div>
</div>React.DOM provides convenience wrappers around React.createElement for DOM components.
var MyComponent = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return React.DOM.div({className: 'reactElement'}, 'Hello world');
}
});
var element = React.createElement(MyComponent);
var component = ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);React Components
Code example
Render result (on jsfiddle)
<div id="reactContainerElement">
<div data-reactroot class="reactElement">Hello world</div>
</div>Haven't the access to the virtual DOM, but it can be easily converted to ReactElements
React EVENT SYSTEM
Your event handlers will be passed instances of SyntheticEvent,
a cross-browser wrapper around the browser's native event.
All event objects conform to the W3C spec, and all events (including submit) bubble correctly per the W3C spec.
XML-LIKE SYNTAX EXTENSION TO ECMASCRIPT

var MyComponent = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return React.DOM.div({className: 'wrapper'},
React.DOM.div({className: 'container'},
React.DOM.div({className: 'reactElement'},
'Hello world'
)
)
);
}
});
var element = React.createElement(MyComponent);
var component = ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);<div id="reactContainerElement">
<div data-reactroot class="wrapper">
<div class="container">
<div class="reactElement">Hello world</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Render result (on jsfiddle)
Code example
React Component WITHOUT JSX
var Hello = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<div className='wrapper'>
<div className='container'>
<div style={{backgroundColor: 'green'}}>
Hello world
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<Hello />,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);
Code example
Render result (on jsfiddle)
<div id="reactContainerElement">
<div data-reactroot class="wrapper">
<div class="container">
<div class="reactElement">Hello world</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>React Component WITH JSX
React.createElement(
"div",
{ className: "navbar-header" },
React.createElement(
"button",
{ type: "button", className: "navbar-toggle"},
React.createElement(
"span",
{ className: "sr-only" },
"Toggle navigation"
),
React.createElement("span", { className: "icon-bar" }),
React.createElement("span", { className: "icon-bar" }),
React.createElement("span", { className: "icon-bar" })
),
React.createElement(
"a",
{ className: "navbar-brand", href: "#" },
"Project name"
)
);<div className="navbar-header">
<button type="button" className="navbar-toggle">
<span className="sr-only">Toggle navigation</span>
<span className="icon-bar"></span>
<span className="icon-bar"></span>
<span className="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
<a className="navbar-brand" href="#">Project name</a>
</div>JSX GENERATE REACT ELEMENTS
Return JSX content by render() method
Convert result
support

var Photo = React.createClass({
handleDoubleTap: function(e) { … },
render: function() { … },
});Classes definition syntax
class Photo extends React.Component {
handleDoubleTap(e) { … }
render() { … }
}The ES5 way
The ES6+ way
var Video = React.createClass({
getDefaultProps: function() {
return {
autoPlay: false,
maxLoops: 10,
};
},
getInitialState: function() {
return {
loopsRemaining: this.props.maxLoops,
};
},
propTypes: {
autoPlay: React.PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
maxLoops: React.PropTypes.number.isRequired,
posterFrameSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
videoSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
},
});Property initializers SYNTAX*
class Video extends React.Component {
static defaultProps = {
autoPlay: false,
maxLoops: 10,
}
static propTypes = {
autoPlay: React.PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
maxLoops: React.PropTypes.number.isRequired,
posterFrameSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
videoSrc: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired,
}
state = {
loopsRemaining: this.props.maxLoops,
}
}The ES5 way
The ES6+ way
* ES7+ Property Initializers
Arrow functions
var PostInfo = React.createClass({
handleClick: function(e) {
this.setState({
showOptionsModal: true
});
},
});class PostInfo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick(e) {
this.setState({
showOptionsModal: true
});
}
}ES5 Way: autobinding by React.createClass
class PostInfo extends React.Component {
handleClick = (e) => {
this.setState({
showOptionsModal: true
});
}
}ES6+ Way: no Autobinding
ES6+ Way: arrow functions
COMPONENT DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT
concept OF

REACT COMPONENT

LIKE A LEGO BRICK
class Root extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Parent childName="Slim Shady" />
<hr />
<Parent childName="Michael Jackson" />
</div>
);
}
}
class Parent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>There's my child {this.props.childName}</div>
<Child name={this.props.childName} />
</div>
);
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>Hi, I'm child and my name is {this.props.name}</div>
);
}
}Code example (on jsfiddle)
REACT COMPONENT PROPERTIES
REACT COMPONENT PROPERTIES
Used for communication and passed from parent to child components
ROOT
component
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component
props
props
props
props
props
props
React COMPONENT PROPERTIES. VALIDATION
React.PropTypes exports a range of validators
that can be used to make sure the data you receive is valid
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
optionalArray: React.PropTypes.array,
optionalBool: React.PropTypes.bool,
optionalFunc: React.PropTypes.func,
optionalNumber: React.PropTypes.number,
optionalUnion: React.PropTypes.oneOfType([
React.PropTypes.string,
React.PropTypes.number,
React.PropTypes.instanceOf(Message)
]),
requiredFunc: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired,
customProp: function(props, propName, componentName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(props[propName])) {
return new Error('Invalid prop `' + propName + '`. Validation failed.');
}
}
};
}React COMPONENT CHILDREN propertY
class Wrapper extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
children: React.PropTypes.element.isRequired
}
render() {
return (
<div className="wrapper">
{this.props.children}
</div>
);
}
}
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Wrapper>
My component content
</Wrapper>
);
}
}With React.PropTypes.element you can specify
that only a single child can be passed to a component as children*
* Use React.Children deal with the this.props.children opaque data structure.
React COMPONENT. STATE
this.state should only contain the minimal amount of data needed to represent your UI's state.
To mutate component state use "this.setState" method*
* It does not mutate state immediately. There is no guarantee of synchronous operation of calls to setState and calls may be batched for performance gains.
React COMPONENT. STATE
class LikeButton extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
liked: false
};
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState({
liked: !this.state.liked
});
}
render() {
const text = this.state.liked ? 'liked' : 'haven\'t liked';
return (
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>
You {text} this. Click to toggle.
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<LikeButton />,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);Code example (on jsfiddle)*
* Example from react official documentation
React STATELESS COMPONENT
const HelloMessage = (props) => <div>Hello, {props.name}</div>;
HelloMessage.propTypes = {
name: React.PropTypes.string
}
HelloMessage.defaultProps = {
name: 'John Doe'
}
ReactDOM.render(<HelloMessage name="Agent Smith"/>, mountNode);You may also define your React compoment (class) as a plain JavaScript function.
Code example
const HelloMessage = (props) => <div>Hello {props.name}</div>;
ReactDOM.render(<HelloMessage name="Sebastian" />, mountNode);However, you may still specify .propTypes and .defaultProps by setting them as properties on the function, just as you would set them on an ES6 class.
REACT COMPONENT LIFECYCLE
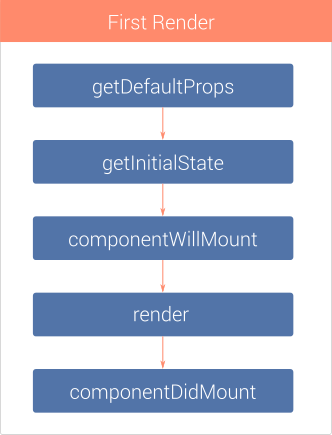
REACT COMPONENT LIFECYCLE. MOUNTING
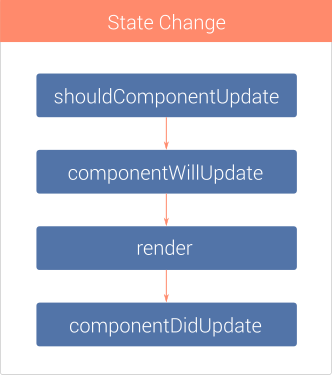
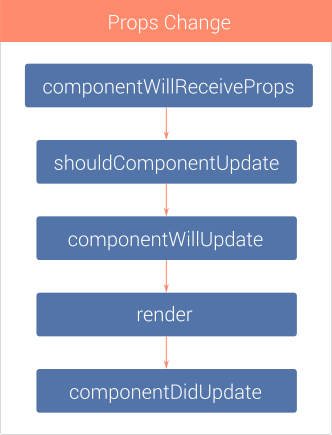
REACT COMPONENT LIFECYCLE. UPDATING

REACT COMPONENT LIFECYCLE. UNMOUNTING
Reusability
Composition
Easy testing
React COMPONENT aproach
Communication
GIVES advantageS
NEEDS
React Components. composition
class Avatar extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<PagePic pagename={this.props.pagename} />
<PageLink pagename={this.props.pagename} />
</div>
);
}
}
class PagePic extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<img src={'https://graph.facebook.com/' + this.props.pagename + '/picture'} />
);
}
}
class PageLink extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<a href={'https://www.facebook.com/' + this.props.pagename}>
{this.props.pagename}
</a>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Avatar pagename="Engineering" />,
document.getElementById('reactContainerElement')
);Example (on jsfiddle) of Avatar component which shows a Facebook page picture and name using the Facebook Graph API.
* Example from react official documentation
REACT COMPONENTS
COMMUNICATION


React Components. COMMUNICATION
- Props usage
- Refs usage
Parent TO CHILD
Techniques of communication:
React Components. COMMUNICATION
Parent TO CHILD. REFS
class Parent extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.refs.childRef.makeRed();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>Make it red</button>
<Child ref='childRef' />
</div>
);
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
color: 'greed'
}
}
makeRed() {
this.setState({
color: 'red'
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>My color is {this.state.color}</div>
);
}
}Code example (on jsfiddle)

React Components. COMMUNICATION
Child to Parent
- Callback functions
Techniques of communication:
React Components. COMMUNICATION
CHILd TO PARENT
class Parent extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
color: 'Green'
};
}
mutateColor() {
this.setState({
color: 'Red'
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
My color is {this.state.color}
<Child handleClick={this.mutateColor.bind(this)} />
</div>
);
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div onClick={this.props.handleClick}>
Change parent
</div>
);
}
}Code example (on jsfiddle)
React Components. COMMUNICATION
Sibling to Sibling

- Parent Component
Techniques of communication:
React Components. COMMUNICATION
SIBLING TO SIBLING. PARENT COMPONENT
class Parent extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
propA: 'A',
propB: 'B'
};
}
mutatePropA() {
this.setState({
propA: 'A modified'
});
}
mutatePropB() {
this.setState({
propB: 'B modified'
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<SiblingA
myProp={this.state.propA}
myFunc={this.mutatePropB.bind(this)}
/>
<SiblingB
myProp={this.state.propB}
myFunc={this.mutatePropA.bind(this)}
/>
</div>
);
}
}Code example (on jsfiddle)
React Components. COMMUNICATION
Any to Any

- Context
Techniques of communication:
Works similarly to props, but it can be used to provide data to an entire subtree.
class Root extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
locale: 'en'
};
}
getChildContext() {
return {
setLocale: locale => this.setState({
locale: locale
}),
locale: this.state.locale
}
}
render() {
return <Parent />
}
}
Root.childContextTypes = {
setLocale: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired,
locale: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired
};Code example (on jsfiddle)
class Parent extends React.Component {
render() {
return <Child />;
}
}
class Child extends React.Component {
render() {
const {setLocale, locale} = this.context;
const setRussianLocale = () => setLocale('ru');
return (
<div>
<div>Application state is '{locale}'!</div>
<button onClick={setRussianLocale}>
Set russian locale
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
Child.contextTypes = {
setLocale: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired,
locale: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired
}
React Components. COMMUNICATION
ANY TO ANY. CONTEXT
React Components. TESTING
- React-addons-test-utils, official Facebook library
- Enzyme, by airbnb
Testing libraries
import React from 'react';
import sinon from 'sinon';
import { mount } from 'enzyme';
import MyComponent from './MyComponent';
import Foo from './Foo';
describe('<Foo />', () => {
it('allows us to set props', () => {
const wrapper = mount(<Foo bar="baz" />);
expect(wrapper.props().bar).to.equal('baz');
wrapper.setProps({ bar: 'foo' });
expect(wrapper.props().bar).to.equal('foo');
});
it('simulates click events', () => {
const onButtonClick = sinon.spy();
const wrapper = mount(
<Foo onButtonClick={onButtonClick} />
);
wrapper.find('button').simulate('click');
expect(onButtonClick).to.have.property('callCount', 1);
});
});Enzyme example usage
ISOMORHIC REACT
concept OF

ISOMORHIC APPLICATION
Charlie Robbins suggested the term “Isomorphic JavaScript” used to describe JavaScript code that “can execute both on the client and the server”.
And nobody knew what the hell it meant.
But now instead of just writing JavaScript the people were writing Isomorphic JavaScript.

ISOMORHIC APPLICATION
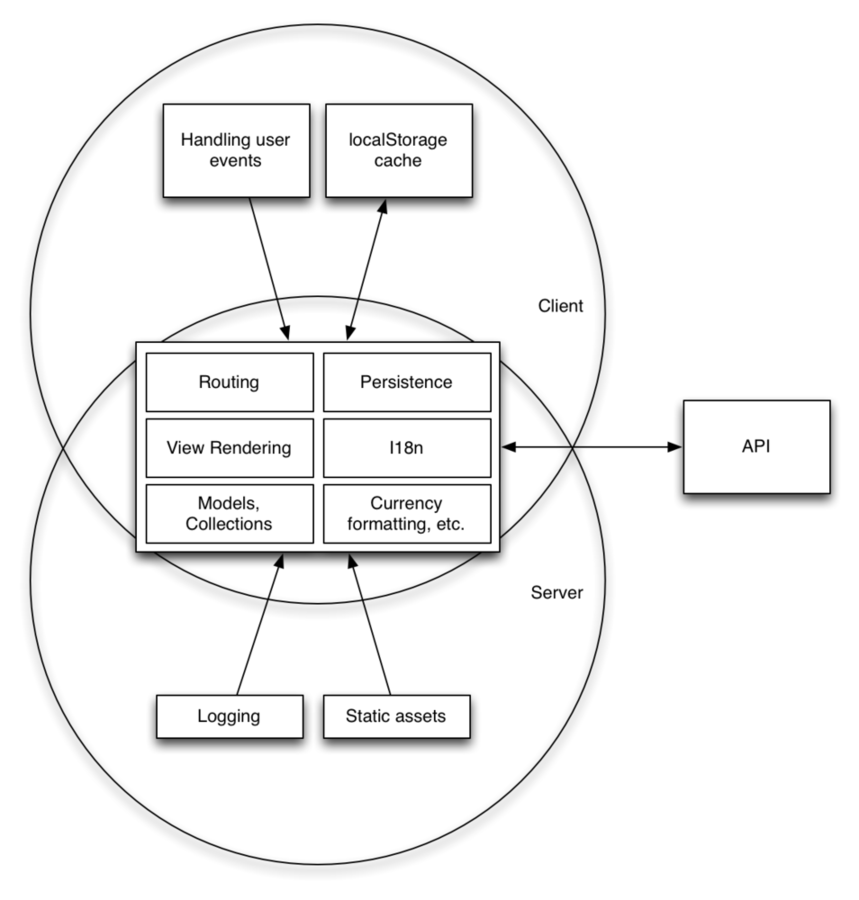
Application schema from presentation
Building a Single-Page App: Backbone, Node.js, and Beyond, by Spike Brehm
REACT Is not a framework
You will have to build application by yourself brick by brick*
*Not all of the libraries can be used as isomorhic
ISOMORHIC APPLICATION ISSUEs
Routing
Rendering
Data fetching
Persistence
Configuration
Localization
ISOMORHIC react. SERVER side RENDER
- C#, ReactJS.NET
- JVM, Nashorn
- React-PHP-V8Js
var React = require('react');
var ReactDOMServer = require('react-dom/server');
var element = React.createElement('div', null, 'Hello World!');
console.log(ReactDOMServer.renderToString(element));ReactDOMServer.renderToString = (ReactElement) => string;
ReactDOMServer.renderToStaticMarkup = (ReactElement) => string;API Defenitions
The react-dom/server package allows you to render your components on the server.
Usage example
NodeJS
ISOMORHIC react. Routing
There's a React Router. A complete routing library for React
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { Router, Route, Link, browserHistory } from 'react-router';
const App = React.createClass({/*...*/});
const Users = React.createClass({/*...*/});
const User = React.createClass({/*..*/});
const NoMatch = React.createClass({/*...*/});
render((
<Router history={browserHistory}>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<Route path="users" component={Users}>
<Route path="/user/:userId" component={User} />
</Route>
<Route path="*" component={NoMatch}/>
</Route>
</Router>
), document.getElementById('reactContainer'));Usage example
ISOMORHIC react. LOCALIZATION
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { I18nextProvider } from 'react-i18next';
import App from './App'; // your entry page
import i18n from './i18n'; // initialized i18next instance
ReactDOM.render(
<I18nextProvider i18n={i18n}><App /></I18nextProvider>,
document.getElementById('app')
);Usage example
Library react 18next
Higher-order components and components for React when using i18next.
import React from 'react';
import { translate } from 'react-i18next';
function TranslatableView(props) {
const { t } = props;
return (
<div>
<h1>{t('keyFromDefault')}</h1>
<p>{t('anotherNamespace:key.from.another.namespace', { /* options t options */ })}</p>
</div>
)
}
export default translate(['defaultNamespace', 'anotherNamespace'])(TranslatableView);USE NON-react LIBRARIES
What about other issues?
It was the only beginning
NOW You are on THE REACT way
Resources
Recomended
Used
- The React.js Way: Getting Started Tutorial
- Big names using React.js
- React Perfomance
- React Architecture – OSCON
- React on ES6+
- React Guide. Props vs State
- Execution sequence of a React component’s lifecycle methods
- 8 no-Flux strategies for React component communication
- Is “Isomorphic JavaScript” a good term?
- The Pain and the Joy of creating isomorphic apps in ReactJS
Any questions?