How Redis Implement
- String, List
Wenzhi Xu
CityU Seattle
https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/
written by c language.
Start a redis server
Open a terminal
Common usage of string
redis> set foo "Hello World"
OK
redis> get foo
Hello World
redis> strlen foo
11
redis> append foo !
12
redis> get foo
Hello World!
redis>
- set
- get
- get string length
- append
How to design it ?
C
1. Low-level language manage memory fastly
2. Use '\0' as the end of a string which means we need to ensure that the end of the string must be \0. No efficient string library in c standard library
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char* school = "CityU Seattle.";
printf("%s\n", school);
printf("%d", strlen(school)); // O(n)
return 0;
}
/** Output
* CityU Seattle.
* 14
*/
How Redis Design
struct sdshdr {
unsigned int len;
unsigned int free;
char buf[];
};
redis> set foo "Hello World"
struct sdshdr {
unsigned int len 11 + 1;
unsigned int free 0;
char buf[] = "Hello World\0";
};
redis> strlen foo
11
redis> get foo
Hello World
Redis Object
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* lru time (relative to server.lruclock) */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
/* Object types */
#define REDIS_STRING 0
#define REDIS_LIST 1
#define REDIS_SET 2
#define REDIS_ZSET 3
#define REDIS_HASH 4
/* Objects encoding. Some kind of objects like Strings and Hashes can be
* internally represented in multiple ways. The 'encoding' field of the object
* is set to one of this fields for this object. */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_RAW 0 /* Raw representation */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_INT 1 /* Encoded as integer */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_HT 2 /* Encoded as hash table */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_ZIPMAP 3 /* Encoded as zipmap */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST 4 /* Encoded as regular linked list */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_ZIPLIST 5 /* Encoded as ziplist */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_INTSET 6 /* Encoded as intset */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_SKIPLIST 7 /* Encoded as skiplist */
#define REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR 8 /* Embedded sds string encoding */Common Usage of List
redis> lpush task "CT"
1
redis> rpush task "DB"
2
redis> rpush task "KC"
3
redis> rpush task "PE"
4
redis> lrange task 0 10
0 CT
1 DB
2 KC
3 PE
redis> lpush task "MP"
5
redis> lrange task 0 10
0 MP
1 CT
2 DB
3 KC
4 PE
redis> llen task
51. Lpush : Push from left
2. Rpush : Push from right
3. lrange: Returns the specified elements of the list stored at key.
4. Llen : Get length of the list
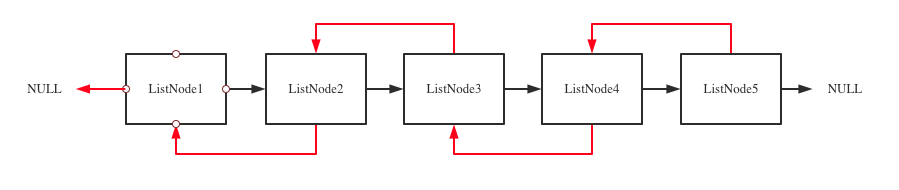
How Redis Design
typedef struct list {
listNode *head;
listNode *tail;
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr);
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
unsigned long len;
} list;
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev;
struct listNode *next;
void *value;
} listNode;
typedef struct listIter {
listNode *next;
int direction;
} listIter;
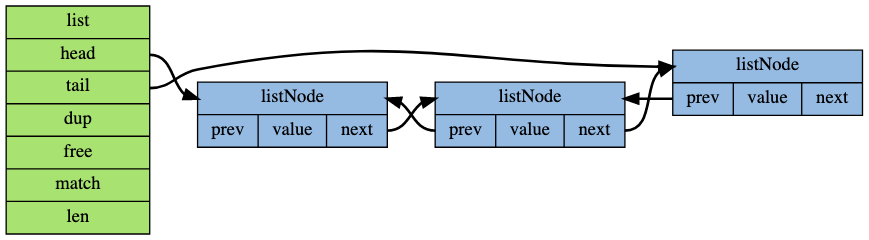
1. Every list object has a list structure
2. Struct ListNode is the chain to store values
3. listIter is for traverse elements in specific range
List source code
More
Redis source code is the best library to learn low-level technology.
1. Data types implements(string, list, hash, set, and zset)
2. Network architecture (select, epoll on Unix-types OS or kqueue on MacOS and why redis is single-threaded?)
3. Memory management (how to manage memory efficiently
4. ...
Q&A
Thanks!
References:
https://redis.io/documentation
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cprogramming/c_bit_fields.htm