TypeScript
A little about me

-
I am a Javascript Engineer @Wix.com
- Passionate about Javascript, Typescript, Angular and React
- @yanivef
Yaniv Efraim
This lecture:
- What is TypeScript?
- How to use TypeScript
- Conclusion
How to use TypeScript
How to use TypeScript
What is TypeScript?
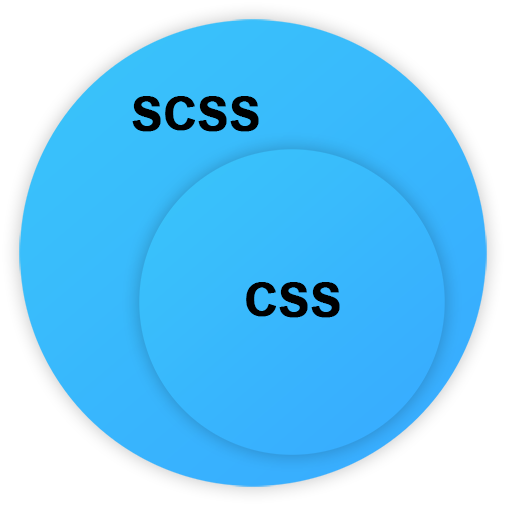
A JavaScript superset
with optional type system
Superset

Type System
Optional


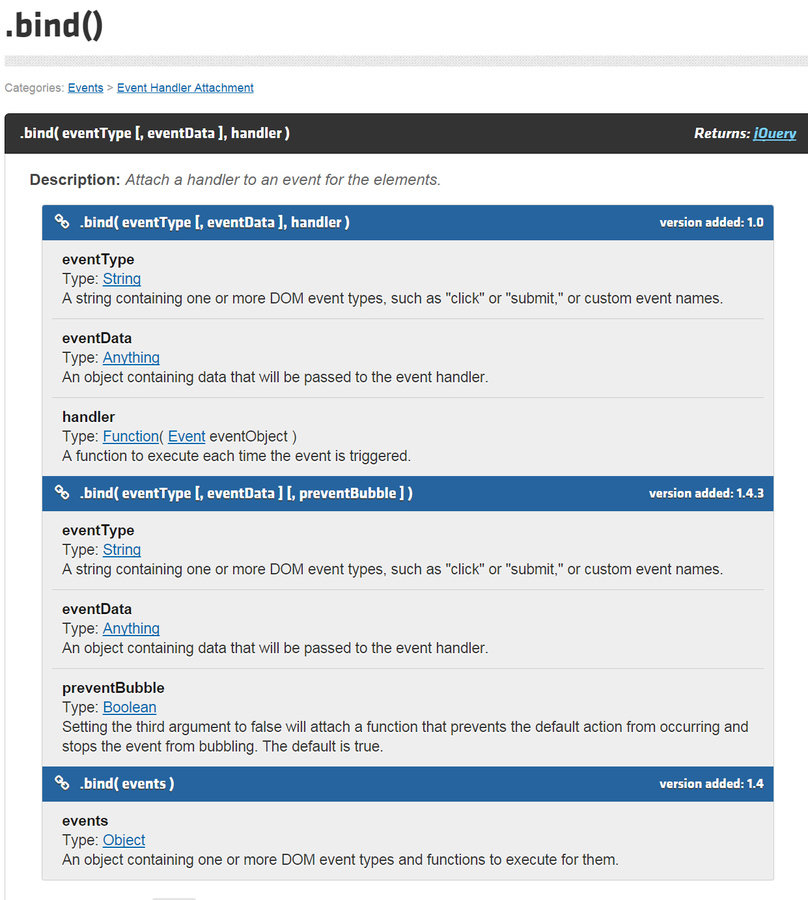
Java Types
Crazy OOP diagrams

Aren't we already using Types?
Angular docs

React docs

HTMLInputElement on MDN


Dev-Time only
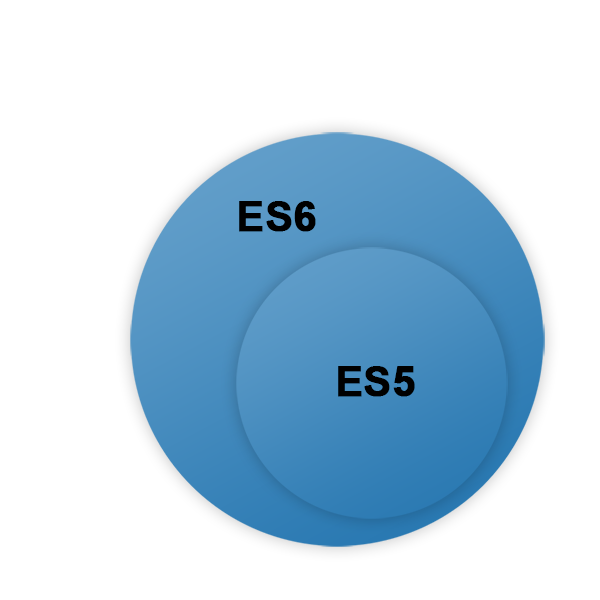
ES6 features
Gradual integration
TypeScript
(It's a superset)
Syntax is similar to ECMAScript4, C#
Basic Types
Basic Types
var x: string;
var y: number;
var z: boolean;
var foo: any;
var bar; // Same as "any"var x;
var y;
var z;
var foo;
var bar;Arrays
var a: any[];
var b: string[];
var p: Product[];
var a;
var b;
var p;function addTax(tax:number, products: Product | Products[]) {
.
.
.
}function addTax(tax, products) {
.
.
.
}
var a: any[];
var b: string[];
var p: (Product | Order)[];Functions as types
var func : (name:string) => number;
function process(x: () => string){
x().toLowerCase();
}
var func;
function process(x){
x().toLowerCase();
}Structures
Structural types
function process(x: {a:string; b:number}){
return x.a.length;
}interface IThing {
a: number;
b: string;
}
function process(x: IThing){
return x.a.length;
}
Interfaces
function process(x){
return x.a.length;
}
function process(x){
return x.a.length;
}
Structural vs Interface
interface IProduct {
name : string;
price : number;
}
function hasName(product: IProduct){
return product.name.length > 0;
}
var isNamed = hasName({name:'iPhone', price:1000});
function hasName(product){
return product.name.length > 0;
}
var isNamed = hasName({name:'iPhone', price:1000});Optional fields
interface IPerson {
age : number;
name : string;
address? : string; // <-- optional field
}
function getName(p: IPerson){
return p.name;
}
var name = getName({age:10, name:'Me'});Function fields
interface IPerson {
age : number;
name : string;
address : string;
walk(distance:number): number; // <-- a Function
}Function overloads
interface IPerson {
age : number;
name : string;
address : string;
walk(distance:number): number;
walk(destination:string): number;
walk(location:{x:number, y:number}): number;
}Type inference
Where inference takes over?
var x = 3; // x is a numberclass MyClass {
name = "Foo"; // name is a string
}function foo(value = false) { // value is a boolean
}function calc() {
return 55; // calc returns a number
}
var x = calc(); // x is also a numberbackward inference
interface IHuman {
age: number;
walk(distance:number):void;
}
var man : IHuman = {
age : 120,
walk: function(distance) {
console.log(distance); // distance inferred to be a number
}
}backward inference #2
window.onmousedown = function(mouseEvent) {
// mouseEvent inferred as MouseEvent
console.log(mouseEvent.button);
};Inference can cause errors
var x = 3; // x is a number
x = "45"; // compiler errorvar foo = {};
foo.description = 'I am FOO'; // compiler errorvar x : any = 3; // x can be anything
x = "45";var foo : any = {};
foo.description = 'I am FOO'; // compiler is happyany
var x; // x is any forever
x = '45'; // x is still anyfunction process(x) { // x is any
return x+x*3; // return type is any
}
process(42); // this does not change the type of xType Guards
Type Guards
var x: any;
if (typeof x === 'string') {
console.log(x.subtr(1)); // Error
}
// x is still any here
x.unknown(); // OKinstanceof
class Animal { name:string }
class Cat extends Animal { meow() { } }
var pet: Animal = new Cat();
if (pet instanceof Cat) {
pet.meow(); // OK
} else {
pet.meow(); // Error
}Ambient Types
Example for ambient type
declare var angular : any; lib.d.ts a gift from TypeScript
-
17K lines of ambient declarations
eval, parseInt, encodeURI
Math, Date, RegExp
Full DOM declarations
And many more...
interface Math {
/** The mathematical constant e. This is Euler's number, the base of natural logarithms. */
E: number;
/** The natural logarithm of 10. */
LN10: number;
/** The natural logarithm of 2. */
LN2: number;
/** The base-2 logarithm of e. */
LOG2E: number;
/** The base-10 logarithm of e. */
LOG10E: number;
/** Pi. This is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. */
PI: number;DefinitelyTyped a gift from the comunity
-
1458 contributors
-
15K commits
-
Thousands of definition files
-
node.d.ts
Things I didn't talk about
So what?!

Refactor
List parameters
Find occurrences
Go to definition
Code completion
inline errors

