The ABC's of The Constitution
Yessenia Gutierrez
Sept. 26 2016

Table of Contents
- A-Articles of the Constitution
- B-Branches of Government
- C-Constitutional Convention
- D-Declaration of Independence
- E-Eminent Domain
- F-Federalism
- G-Great Compromise
- H-Hamilton (Alexander Hamilton)
- I-Individual Rights
- J-Judicial Power
- K-
- L- Legislative Power
- M-Magna Carta
- N-Ninth Amendment
- O-Oath of Office
- P-Preamble
- Q-Quartering of troops (3rd Amen)
- R-Ratification
- S-State and Local Governments
- T-Tranquility (Domestic Tranquility)
- U-Unitary System
- V-Voting (Women's rights)
- X-XV (Fourteenth Amendment)
A Articles of the Constitution
The Articles of the Constitution are divided into 7 parts and they all include different sections. Article 1 establishes the Legislative power, Article 2 establishes Executive power and Article 3 establishes Judicial power.

B-Branches of Government
In order for the government to not be controlled by one single power, our Founding Fathers created the three branches of our government. The three branches balance power within each other they are: the Executive Branch, Legislative Branch and Judicial Branch.

C Constitutional Convention
The first ever Constitutional Convention was called in 1787 by Congress to revise Articles of Confederation. The United States was still a young country and the government in place (A of C) was not working, at the convention the delegates ended up creating the Constitution instead of revising the Articles of Confederation.

D Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence announced it's separation from Great Britain. It included all the wrong doings of Great Britain to the colonists and announced it's official separation from Great Britain and recognized itself as its own country.

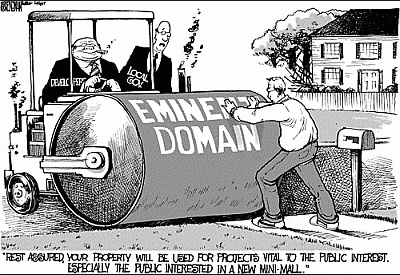
E-Eminent Domain
Eminent Domain allows for condemnation of someone's private property for public use with compensation. According to the Fifth Amendment of the Constitution, the government is required to provide compensation to the owner if his/her private property is taken.
F- Federalism Powers
The 10th Amendment of the Constitution restates the Principle of federalism. Federalism states that citizens are subject to the powers of governmental units and it is the highest governmental power.

G-Great Compromise
The Great Compromise created a Bicameral Legislature. It allowed the House of Representatives based on Population and Senate with 2 members.

H- Hamilton (Alexander Hamilton)
Alexander Hamilton was one of the Founding Fathers of the Constitution. He was also the nation's first secretary of treasury.

I- Individual Rights
According to John Locke, citizens have the right to life, liberty and property. Our nation protects our Individual rights with the Bill of Rights.

J-Judicial Power
The Judicial Branch of government establishes the court systems. The Judicial Power involves court cases of the Constitution, Federal law, foreign treaties, international law and bankruptcies.

L-Legislative Power
The Legislative Branch is responsible for passing laws. The Legislative Branch includes the 17th amendment which allows citizens to directly elect Senators.
M-Magna Carta
The Magna Carta= Limited Government
Protects citizens from cruel punishment and levying of unfair taxes.

N-Ninth Amendment
The Ninth Amendment states that all powers are not spelled out in Constitution. This allows for amendments to be made to the constitution throughout time.

O-Oath of Office
When a President takes Oath in Office, he agrees to many different responsibilities. Some of these responsibilities include limited responsibilities for example, making Treaties with Advice and Consent of the Senate.

P-Preamble
"We the People of the United States in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility.." The Preamble was signed in convention on Sept. 17, 1787 and ratified June 21, 1788.

Q-Quartering of Troops (3rd Amendment)
The third Amendment states that no soldiers can take over your home. This amendment was important during early wars of our country like the American Revolution.

R- Ratification
Article VII or Ratification was important for the Establishment of the Constitution. The Constitution had to be ratified or approved by the first nine States.

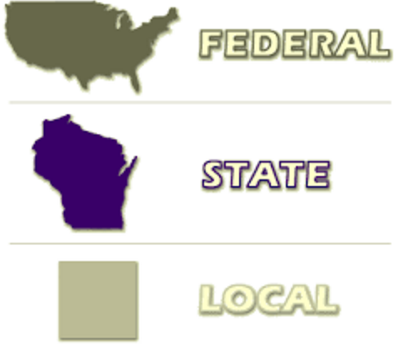
S-State and Local Governments
Not all powers are reserved to to the federal government. Powers are also reserved for the states, this is is established in the 10th Amendment.
T-Tranquility (Domestic)
After Shay's Rebellion, the Preamble in the Constitution established "Domestic Tranquility" in an effort to prevent civilian unrest. Peace at home was key for survival of the nation.

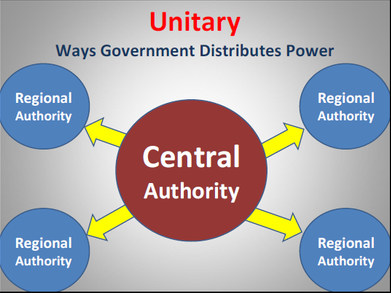
U-Unitary System
A Unitary System is a government that gives all key powers to the national or central government. Sovereign states are governed as a single entity.
V-Voting (Women's right to vote)
Women were given the right to vote in 1920. Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Alice Paul were important ladies who pushed for women's rights including equality in the work force and the right to vote.

W-Washington (George Washington)
George Washington not only our first president but he was also the commander of the Continental Army and president of the Constitutional convention. His leadership greatly influenced the Constitution.

X- XV (The fourteenth Amendment)
The fourteenth Amendment gave citizens the right to vote not denied by race. This Amendment came after abolishment of slavery (13th Amendment).
