150 coding challenges in 25 days
What I learned from attempting Advent of Code 2017, 2016 & 2015 all at one go.
Yong Jun
24 Jan 2018
About me




by Eric Wastl
Advent of Code a series of small programming puzzles for a variety of skill levels.
They are self-contained and are just as appropriate for an expert who wants to stay sharp as they are for a beginner who is just learning to code.
Each puzzle calls upon different skills and has two parts that build on a theme.
Leaderboard
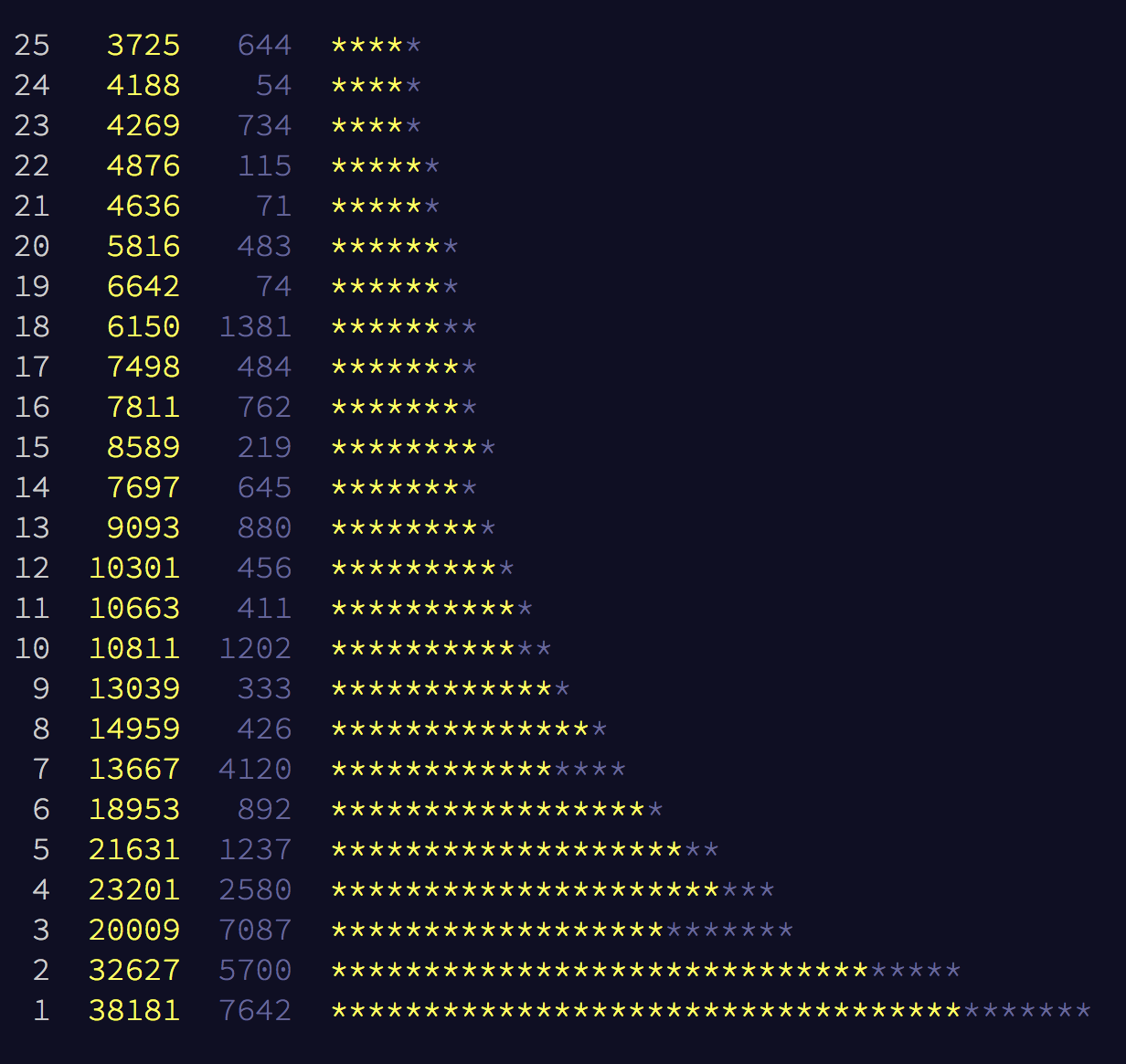
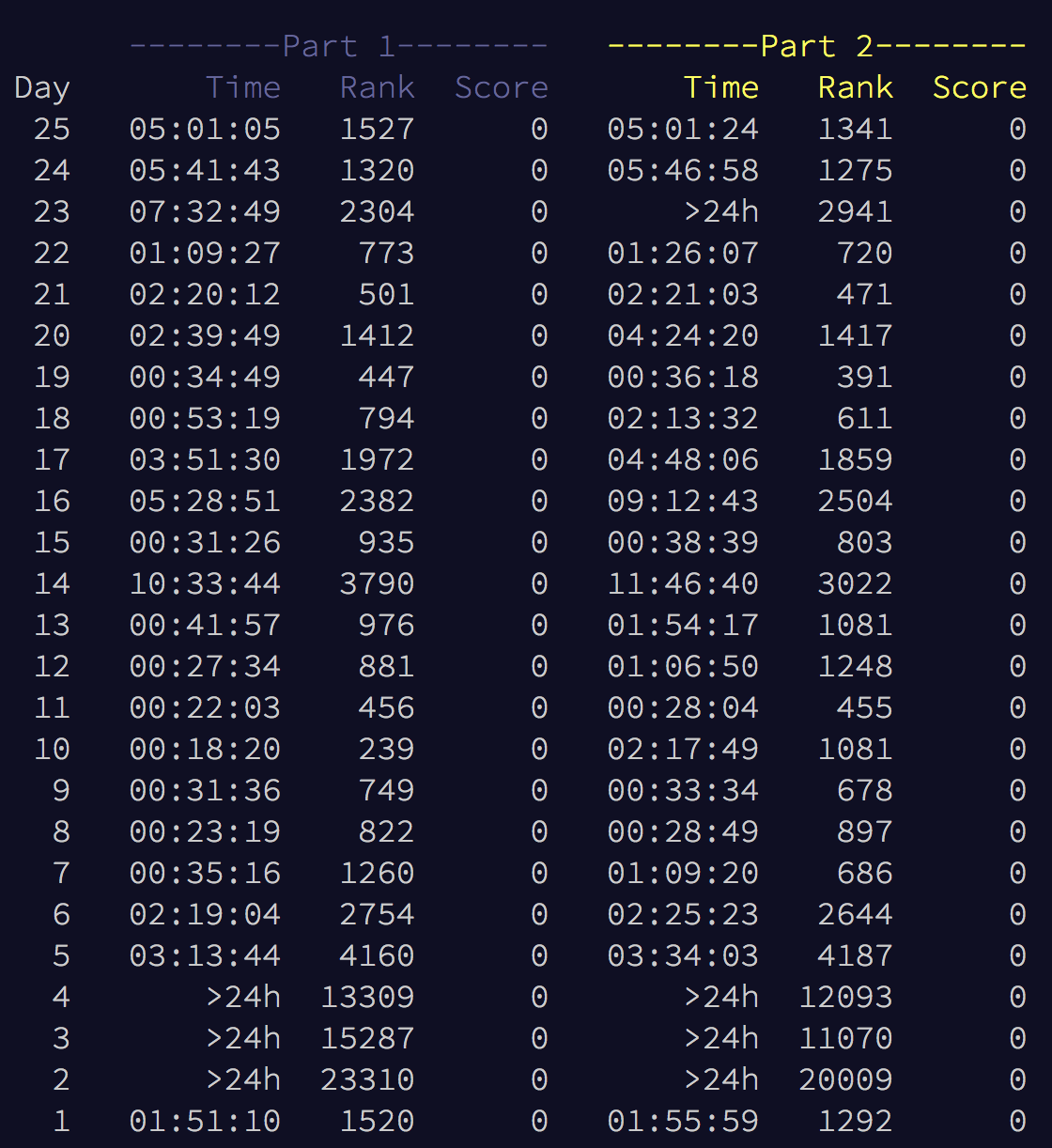
Personal Stat
Global Stat
If you need a little help
Some things I've learned
Generators
function* generator () {
// do something
yield 'someValue'
// do some more thing
yield 'anotherValue'
}
const iterator = generator()
console.log(iterator.next())
// {value: 'someValue', done: false}
console.log(iterator.next())
// {value: 'anotherValue', done: false}
console.log(iterator.next())
// {value: undefined, done: true}AoC 2017 Day 3: Spiral Memory

Right x 1
Up x 1
Left x 2
Down x 2
Right x 3
Up x 3
Left x 4
Down x 4
function * traverse () {
let step = 1
let x = 0
let y = 0
yield [x, y]
while (true) {
for (let right = step; right > 0; right--) {
yield [++x, y]
}
for (let up = step; up > 0; up--) {
yield [x, ++y]
}
step++
for (let left = step; left > 0; left--) {
yield [--x, y]
}
for (let down = step; down > 0; down--) {
yield [x, --y]
}
step++
}
}
function manhattanDistance (target) {
let coordinates
const location = traverse()
for (let i = 0; i < target; i++) {
coordinates = location.next().value
}
return Math.abs(coordinates[0]) + Math.abs(coordinates[1])
}Solution
Why use a generator?
-
Rather than create an object that maintain internal state by variables assignment (explicit)
- Internal state can be implicit in the position of the yield statement
- Behave sort of like the goto statement from old school imperative programming
Another example
AoC 2015 Day 14:
Reindeer Olympics


function * reindeer (speed, fly, rest) {
let distance = 0
while (true) {
for (let i = 0; i < fly; i++) {
distance += speed
yield distance
}
for (let i = 0; i < rest; i++) {
yield distance
}
}
}RegEx
AoC 2016 Day 7:
Internet Protocol Version 7
Task:
Find ABBA
Solution:
function containsAbba (str) {
const match = str.match(/([a-z])([a-z])\2\1/)
if (!match) return false
if (match[1] !== match[2]) return true
return containsAbba(str.slice(match.index + 1))
}Tail Call
Optimization
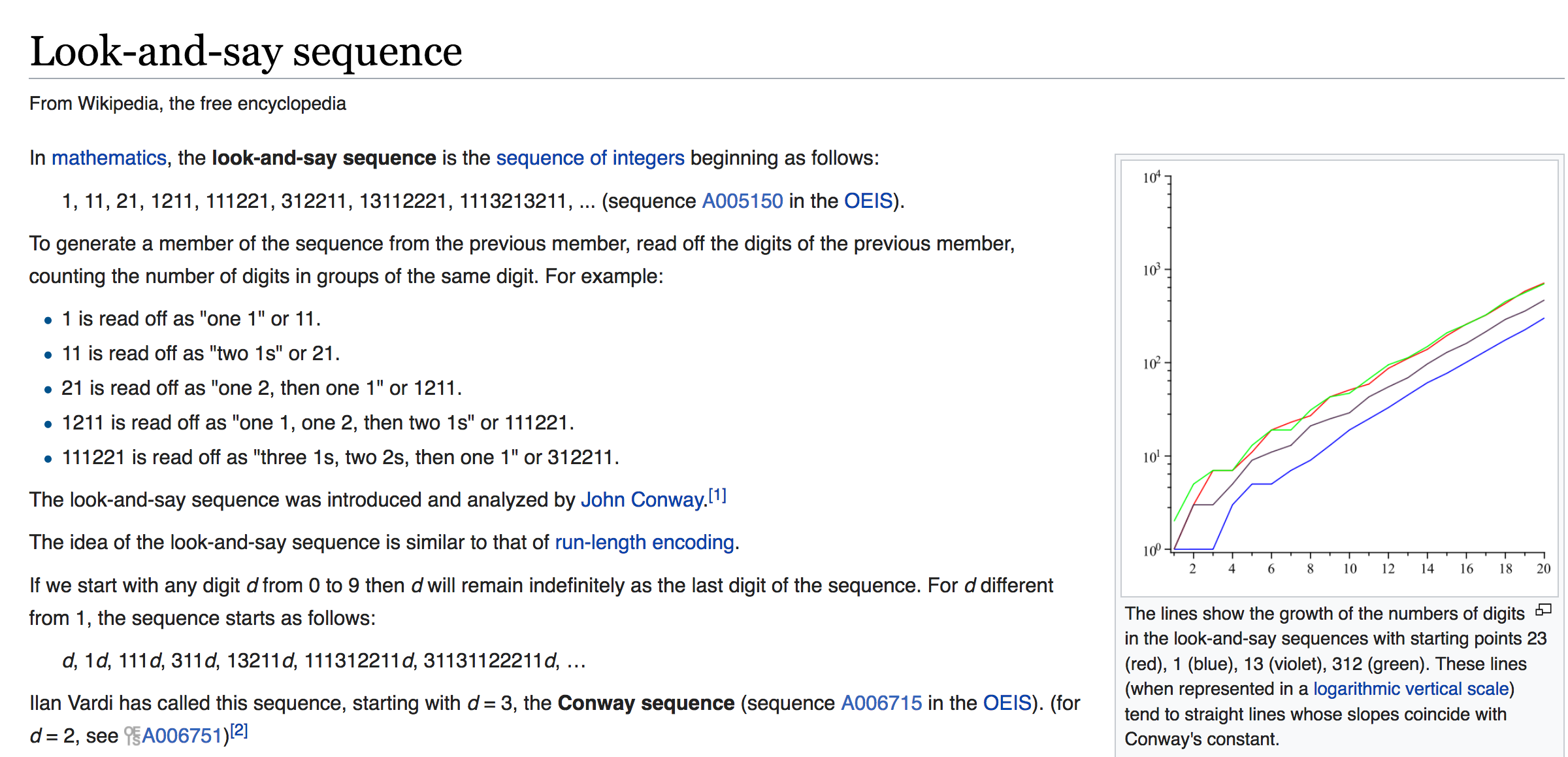
AoC 2015 Day 10:
Elves Look, Elves Say
Solution
// no proper tail call
function lookNsay (str) {
const match = str.match(/(.)(\1*)/)
if (match[0].length === str.length) return match[0].length + match[1]
return match[0].length + match[1] + lookNsay(str.slice(match[0].length))
}
// with proper tail call
function lookNsay (str, prefix = '') {
const match = str.match(/(.)(\1*)/)
if (match[0].length === str.length) return prefix + match[0].length + match[1]
return lookNsay(str.slice(match[0].length), prefix + match[0].length + match[1])
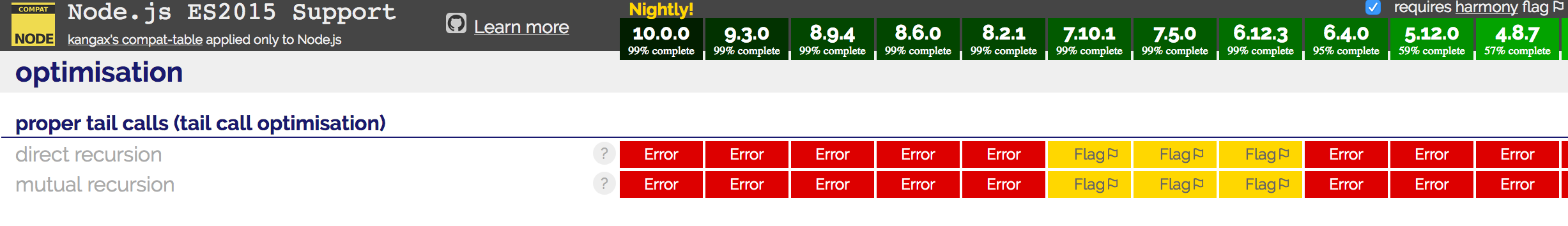
}Limitations
- 'use strict'
- --harmony ⚐
- Only node 6 & 7
Workaround
- rewrite recursion into iteration
- use a stack
- eg. Depth-first-search
Enumeration
AoC 2015 Day 17:
No Such Thing as Too Much
Task:
Given containers of various sizes (eg. 20, 15, 10, 5, and 5).
Find how many different combinations total up to a given capacity.
For example if required total is 25, four ways are possible:
- 15 and 10
- 20 and 5 (the first 5)
- 20 and 5 (the second 5)
- 15, 5, and 5
Solution:
Enumerate all possible assignment combination
Eg. 000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111
AoC 2015 Day 9:
All in a Single Night
Task:
Given distances between each location pair, find the
shortest route where every location is visited exactly once.
Solution:
Enumerate all possible permutation
Eg. ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, CBA
AoC 2015 Day 13:
Knights of the Dinner Table
Task:
Find the ideal seating arrangement around a round
dining table
Solution:
Fix a start point and enumerate all possible
permutation that start and end with that point. Eg.
- A > B > C > D > A
- A > B > D > C > A
- A > C > B > D > A
- A > C > D > B > A
AoC 2015 Day 15:
Science for Hungry People
Task:
With exactly 100 teaspoons of ingredients. Find
the ideal recipe
Solution:
Enumeration all possible split combinations. Eg.
| 0/0/100 | |||
| 0/1/99 | 1/0/99 | ||
| 0/2/98 | 1/2/98 | 2/1/98 | |
| 0/3/97 | 1/2/97 | 2/1/97 | 3/0/97 |
Enumerate Assignment Combinations
- Count up from 0 to
- Convert number to binary representation using Number.prototype.toString(2)
- Left pad string with zeros
- Convert to array using String.prototype.split('')
function getAssignments (items, groups = 2) {
const combinations = []
const nCombinations = Math.pow(groups, items)
const zeroPad = '0'.repeat(items)
for (let i = 0; i < nCombinations; i++) {
const combiString = (zeroPad + i.toString(groups)).slice(-items)
const combination = combiString.split('')
if (groups === 2) combinations.push(combination.map(v => +v))
else combinations.push(combination)
}
return combinations
}Implementation
Enumerate Split Combination
- Instead of enumerating units, enumerate cuts. Eg.
- If you have k different ingredients, the number of cuts to enumerate will be k - 1
- Pick any position that is between last cut's position and N inclusive
- Cuts can overlap
- Subtract adjacent cut index to get units of ingredient
- i.e.
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
First cut is always at 0
Last cut is always at N
Second cut at 2
Third cut also at 2
Fourth cut at 5
Implementation
function getSplitCombinations (total, items) {
const combinations = []
function recurse (division, i) {
if (division.length < items - 1) {
while (i <= total) {
recurse(division.concat(i), i)
i++
}
} else {
division = [0, ...division, total]
const combination = []
for (let i = 1; i < division.length; i++) {
combination.push(division[i] - division[i - 1])
}
combinations.push(combination)
}
}
recurse([], 0)
return combinations
}More enumeration helpers
How about lazy enumeration?
AoC 2015 Day 24:
It Hangs in the Balance
Task:
Split cargo (28 pieces) into 3 groups of equal weight.
Pick combination with least items in the first group.
Analysis:
Total possible combinations is !!!
Takes too long to enumerate every possible combination.
Need a way to exit early once a match is found.
Iterables
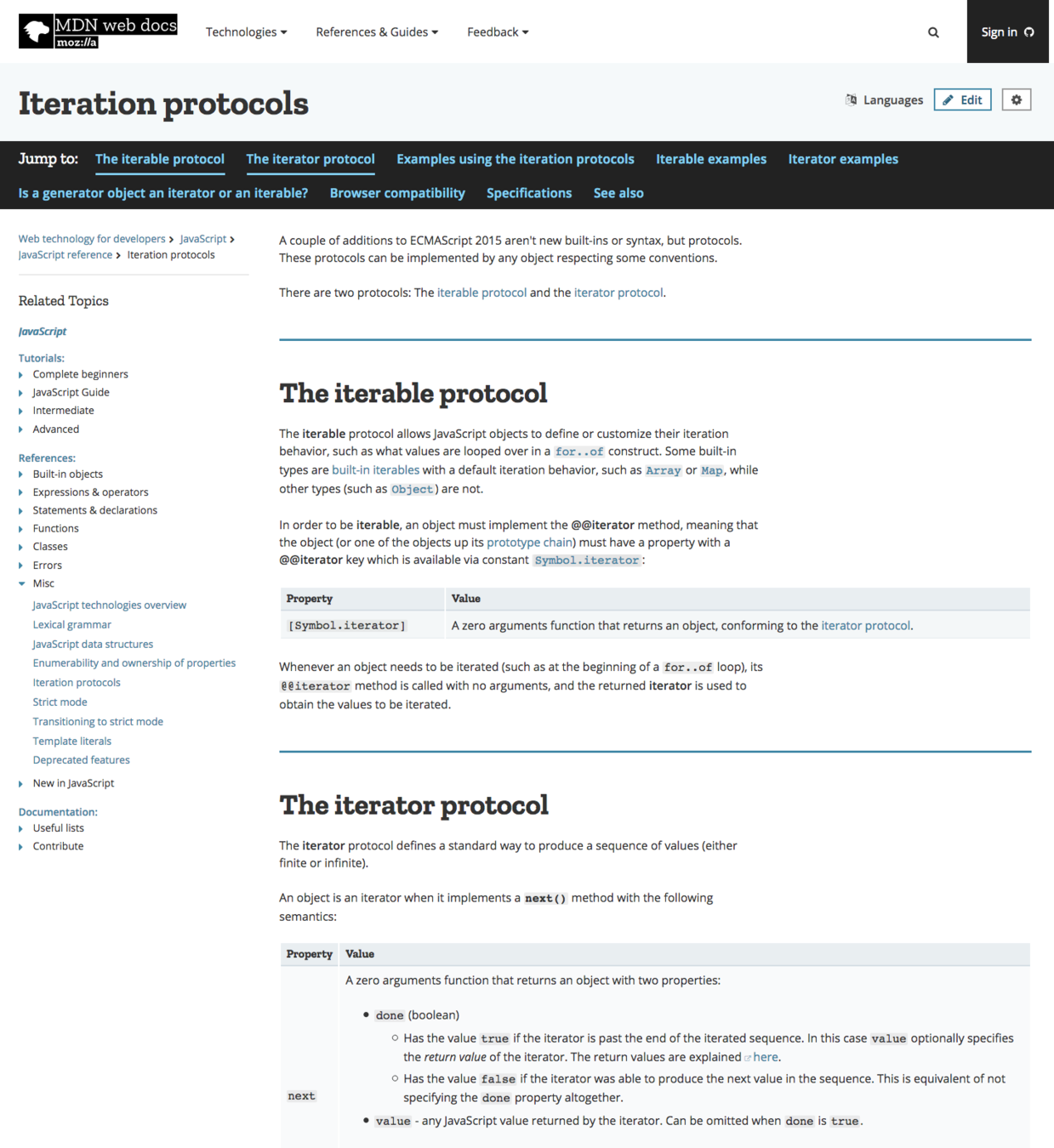
const iterable = {
[Symbol.iterator]: function* () {
let n = 0
while (true) {
yield n++
}
}
}
for (let n of iterable) {
if (n >= 10) break
}Example
// lazy version of assignment enumerator
function getAssignments (items, groups = 2) {
const nCombinations = Math.pow(groups, items)
const zeroPad = '0'.repeat(items)
return {
[Symbol.iterator]: function* () {
for (let i = 0; i < nCombinations; i++) {
const combiString = (zeroPad + i.toString(groups)).slice(-items)
const combination = combiString.split('')
if (groups === 2) yield combination.map(v => +v)
else yield combination
}
}
}
}// wrong use
const iterable = getAssignment(n)
Array.from(iterable)
[...iterable]// correct use
const iterable = getAssignment(n)
for (let item of iterable) {
if (/* condition met */) return item
}
Graph search
Breadth-First-Search
Depth-First-Search
function bfs (root) {
const visited = {}
const unvisited = []
unvisited.push([root, 0])
while (unvisited.length > 0) {
const [next, steps] = unvisited.shift()
if (next in visited) continue
visited[next] = 1
if (found) return steps
next.children
.forEach(child => {
unvisited.push([child, steps + 1]
})
}
}function dfs (root) {
const visited = {}
const unvisited = []
unvisited.push([root, 0])
while (unvisited.length > 0) {
const [next, steps] = unvisited.pop()
if (next in visited) continue
visited[next] = 1
if (found) return steps
next.children
.sort(sortFunc)
.reverse()
.forEach(child => {
unvisited.push([child, steps + 1]
})
}
}Dealing with coding task of the assembly language kind
- Use Chrome inspector
- node --inspect-brk script.js
- Add debugger statement
Wrapping up
- Work it out on paper
- Premature optimization
- Readability & Extensibility > Efficiency & Speed
- Some knowledge of computation complexity is helpful