資訊學科能力競賽
複賽題解
猜猜我出哪幾題
CHSH-nhspc112-PRI
CHSH X HARC
ysh 2023
ST
A. Walk
給你一條線 y=ax+b
問你從 (0,0) 在剛好走 k 步的情況下有沒有辦法到達這條線
首先,可以發現如果前一次在線上,代表這次不可能在線上
所以,我們試圖讓點到達線上
也就是先求出點到線的(最短)計程車距離
因為斜率必為1或-1,於是直接比大小
最後看看k跟b的奇偶性是否相同即可
# Author : ysh
# 2023/07/27 Thu 17:03:44
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
print = sys.stdout.write
b = abs([int(i) for i in input().split()][1])
for i in range(int(input())):
n = int(input())
if n < b:
print('NO\n')
continue
if n & 1 == b & 1:
print('YES\n')
else:
print('NO\n')
quit()B. Vendor
給你 n 個點
\displaystyle 請求出 \min \big[\sum_{k=1}^n \sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}\big]
問題
(x_i,y_i),\ 1 \leq i \leq n
爆搜
有一堆方法
O(4 \times 10^{12} \times n)\ O(2 \times 10^6 \times n)
Fun Fact
直接輸出第一個座標就可以獲得三分
但沒人要做
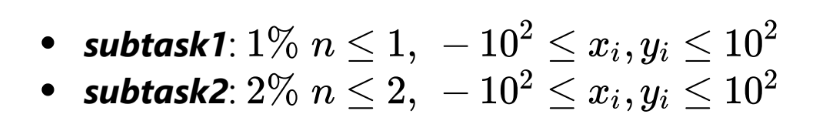
Fun Fact
爆搜就可以獲得 10 分
但同樣沒人要做
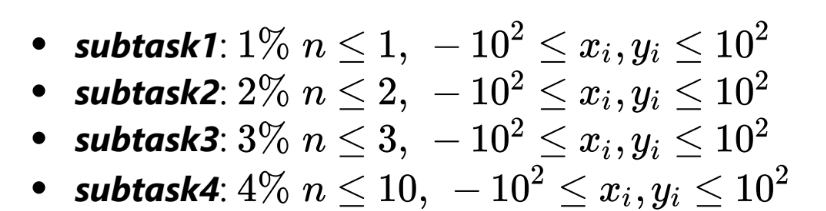
Fun Fact
有所有點都在同一條線上的測資
仍然沒人要做
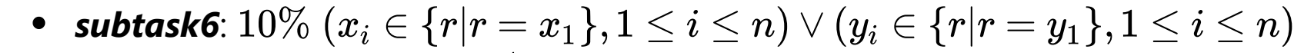
subtask 1,2
直接輸出第一個座標
subtask 3
算外心,找出附近四個點中總距離最小的
subtask 6
直接輸出最中間的那個座標
subtask 7
二分搜包二分搜
O(n (log_2^{2 \times 10^6})^2)
怎麼二分搜?
對 x 座標做二分搜
每次搜出
當 x 座標為 ?? 的時候
總距離最小值出現在哪裡
// Author : ysh
// 2023/08/03 Thu 14:22:59
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define dt(i,j,k,l) ((i - k) * 1LL * (i - k) + (j - l) * 1LL * (j - l))
long double alldt(vector<pair<int,int>>&f,int x,int y) {
long double ans = 0;
for(auto &i : f) {
ans = ans + sqrtl(abs(dt(i.first,i.second,x,y)));
}
return ans;
}
int check(vector<pair<int,int>>&f,int x,int l,int r) {
if(l == r) return l;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
bool c = alldt(f,x,mid) > alldt(f,x,mid + 1);
if(c) return check(f,x,mid + 1,r);
else return check(f,x,l,mid);
}
int ck(vector<pair<int,int>>&f,int l,int r) {
if(l == r) return l;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int left = check(f,mid,-int(1e6),int(1e6));
int right = check(f,mid + 1,-int(1e6),int(1e6));
bool c = alldt(f,mid,left) > alldt(f,mid + 1,right);
if(c) return ck(f,mid + 1,r);
else return ck(f,l,mid);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;cin>>n;
vector<pair<int,int>>f(n);
for(auto &i : f) {
cin>>i.first>>i.second;
}
int x = ck(f,-int(1e6),int(1e6));
int y = check(f,x,-int(1e6),int(1e6));
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<"\n";
return 0;
}為什麼可以這麼做?
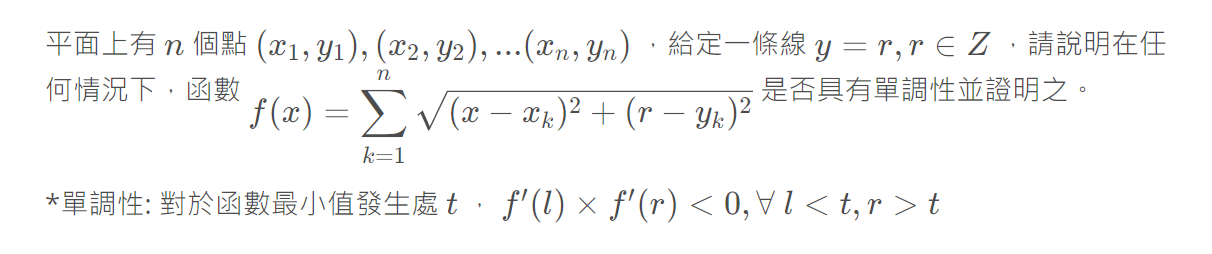
首先讓我們分開來看
\sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}
在 y 座標固定的情況下
是個凹函數
所以對 x 微分
[\sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}]'\\
= \frac{1}{2}[(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2] ^ {-\frac{1}{2}} \times 2(x - x_i)\\
= [(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2] ^ {-\frac{1}{2}}(x - x_i)\\
= \frac{(x - x_i)}{\sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}}
\displaystyle
\text{let } \frac{(x - x_i)}{\sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}} = f'(x)\\
\frac{(x - x_i)}{\sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}} = 0\\
\lim_{x \rightarrow x_i-} f'(x) < 0 \text{ and } \lim_{x \rightarrow x_i+} f'(x) > 0\\
\text{When } x = x_i,\ f(x) \text{ has minimum value } f(x_i)
可得其為凹函數
由 凹函數與凹函數相加為凹函數 可知
\displaystyle\sum_{k = 1}^n \sqrt{(x - x_i)^2+(y - y_i)^2}
為凹函數
但是還是太慢了
嘿嘿我多卡了一個 log
有沒有發現
其實不用每次都對 y 座標做完整的二分搜
於是就誕生了另一套演算法
倍增
由 二的次冪之和 可以為任意正整數
可以推得
只需要不斷向 上下左右 移動二的次冪個單位
就可以不斷獲得最小值
從而達成整體最小值
// Author : ysh
// 2023/08/12 Sat 16:23:21
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int xx[] = {-1,0,1,0};
const int yy[] = {0,1,0,-1};
vector<pair<int,int>>f;
#define dt(i,j) sqrtl((i.first * 1LL - j.first) * (i.first - j.first) + (i.second * 1LL - j.second) * (i.second - j.second))
long double alldt(pair<int,int>j) {
long double ans = 0;
for(auto &i : f) {
ans = ans + dt(i,j);
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;cin>>n;
f = vector<pair<int,int>>(n);
for(auto &i : f) {
cin>>i.first>>i.second;
}
int mask = (1 << 20);
pair<int,int>now = make_pair(0,0);
long double ans = alldt({0,0});
while(mask != 0) {
for(int j = 1;j<=2;j++) {
for(int i = 0;i<=3;i++) {
auto pre = make_pair(now.first + (xx[i] * mask),now.second + (yy[i] * mask));
auto t = alldt(pre);
if(t < ans) {
ans = t;
now = pre;
}
}
}
mask = mask >> 1;
}
cout<<now.first<<" "<<now.second<<"\n";
return 0;
}結論
Mingyee 欠我一客冰炫風
F. Practice
首先
不唬爛 這題來自AIME
DP
DPDP
Math
// Author : ysh
// 03/23/2023 Thu 14:00:18.03
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int check(int x,bool c = 0,bool d = 0) {
if(x == 0) {
return c;
}
int ans = 0;
if(!c && d) ans += check(x - 1,1,1);
if(!d) ans += check(x - 1,c,1);
ans += check(x - 1,c,0);
return ans;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;cin>>n;
cout<<check(n,0,0);
return 0;
}// Author : ysh
// 03/23/2023 Thu 14:00:18.03
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int R = ((int) 1e9) + 7;
vector<int>mark;
#define int long long
int check(int x,bool c = 0,bool d = 0) {
if(x == 0) {
return c;
}
if(mark.at(((x - 1) << 2) + ((int) c << 1) + ((int) d)) != -1) return mark.at(((x - 1) << 2) + ((int) c << 1) + ((int) d));
int ans = 0;
if(!c && d) ans += check(x - 1,1,1);
if(!d) ans += check(x - 1,c,1);
ans += check(x - 1,c,0);
return mark.at(((x - 1) << 2) + ((int) c << 1) + ((int) d)) = ans % R;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;cin>>n;
mark.resize(n << 2,-1);
cout<<check(n,0,0);
return 0;
}#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int R = ((int) 1e9) + 7;
#define int long long
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;cin>>n;
if(n == 2) {
cout<<1;
return 0;
}
vector<int>f(n);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) {
if(i == 0) f.at(0) = 1;
else if(i == 1) f.at(1) = 2;
else {
f.at(i) = f.at(i - 1) + f.at(i - 2);
f.at(i) = f.at(i) % R;
}
}
long long ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n - 3;i++) {
ans = ans + (f.at(i - 1) * f.at(n - i - 3)) % R;
}
ans = ans + (f.at(n - 3) << 1);
ans = ans % R;
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}# Author : ysh
# 03/23/2023 Thu 13:56:24.23
import sys
R = int(1e9) + 7
a = [1,2]
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
if n == 1:
sys.stdout.write('0')
quit()
if n == 2:
sys.stdout.write('1')
quit()
for i in range(2,n):
a.append((a[len(a) - 2] + a[len(a) - 1]) % R)
ans = 0
for i in range(1,n - 2):
ans = (ans + (a[i - 1] * a[n - i - 3]))
ans = ans + (a[n - 3] << 1)
ans = ans % R
sys.stdout.write(str(ans))#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int R = (int) 1e9 + 7;
#define hck(i,j) check(i + j - 1,j)
#define int long long
int fp(int a,int b) {
if(b == 0) return 1;
int tmp = fp(a,b >> 1);
if(b & 1) return (((tmp * tmp) % R) * a) % R;
return (tmp * tmp) % R;
}
vector<int>mark({1});
int fl(int x) {
if(mark.size() >= x + 1) return mark.at(x);
mark.push_back((fl(x - 1) * x) % R);
return mark.at(x);
}
int check(int a,int b) {
return (((fl(a) * fp(fl(a - b),R - 1 - 1)) % R) * fp(fl(b),R - 1 - 1)) % R;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;cin>>n;
n = n - 1;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = (n + 1) >> 1;i>=1;i--) {
int left = n - (i - 1) - i;
ans = ans + hck(i + 1,left) * i;
ans = ans % R;
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}