Introduction to Stationary Process
Yung-Sheng Lu
Mar 7, 2017
@NCKU-CSIE
Outline
-
Time Series
-
Stationarity
-
Stationary Process
-
References
Time Series
Definition
-
A time series is a variable indexed by the time :
-
Examples:
-
The time can be annual, monthly, daily...
-
Let be the annual GDP.
-
Let be the monthly temperature
-
Let be the daily stocks
-
-
Some Distinctions
-
The time series can:
-
Take discrete or continuous values.
-
Be measured at discrete or continuous time.
-
Be measured at regular or irregular intervals.
-
Description
-
To describe a time serie, we will concentrate on:
-
Data Generating Process (DGP)
-
The joint distribution of its elements
-
Its "moments":
-
Expected value
-
Variance
-
Autocovariance or autocorrelation of order
-
-
Description (cont.)
-
Definition of Variance
-
Definition of Autocovariance
-
Definition of autocorrelation of order
Stationarity
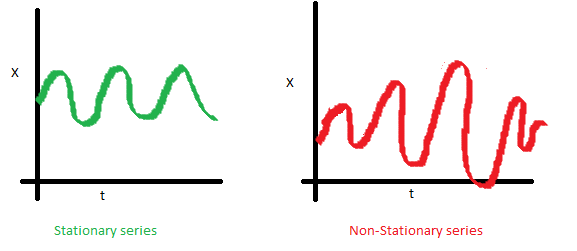
Stationary Series
-
The mean of the series should not be a function of time rather should be a constant.

-
The variance of the series should not be a function of time.
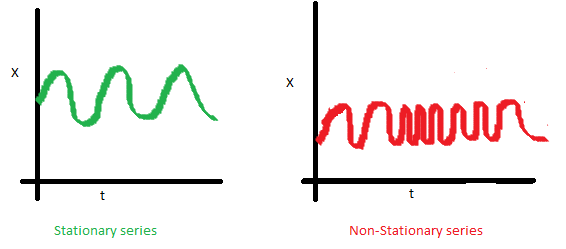
Stationary Series (cont.)
-
The covariance of the i-th term and the (i + m)-th term should not be a function of time.
Stationary Series (cont.)
-
Example
Imagine a girl moving randomly on a giant chess board. In this case, next position of the girl is only dependent on the last position.
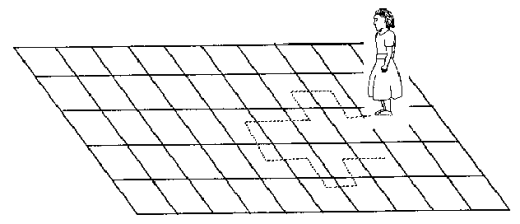
Random Walk
-
Questions
-
How to predict the position with time?
-
How accurate will be?
-
Random Walk (cont.)

-
The randomness brings at every point in time.
-
Recursively fit in all the
Random Walk (cont.)
-
Is the mean constant?
-
Expectation of any error will be 0 as it is random.
-
Random Walk (cont.)
-
Is the variance constant?
- The random walk is not a stationary process as it has a time variant variance.
- The covariance is also dependent on time.
Random Walk (cont.)
Stationary Process
-
Coefficient
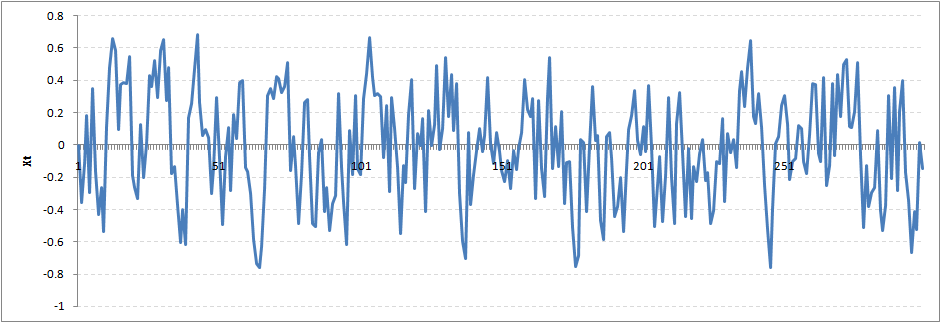
- Stationary series with .
Coefficient
- Stationary series with .
Coefficient (cont.)
- Stationary series with .
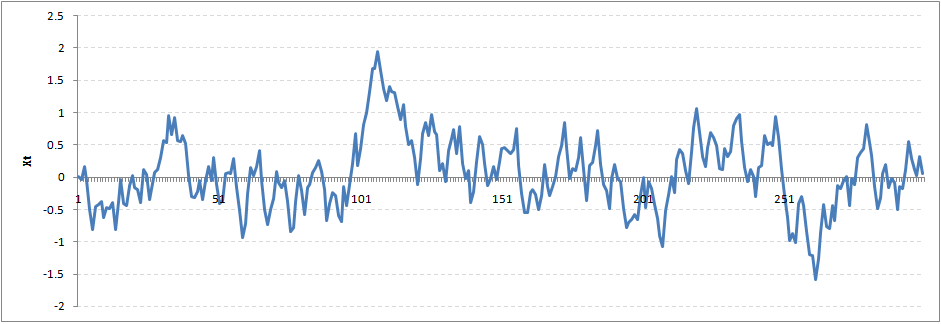
Coefficient (cont.)
- Stationary series with .
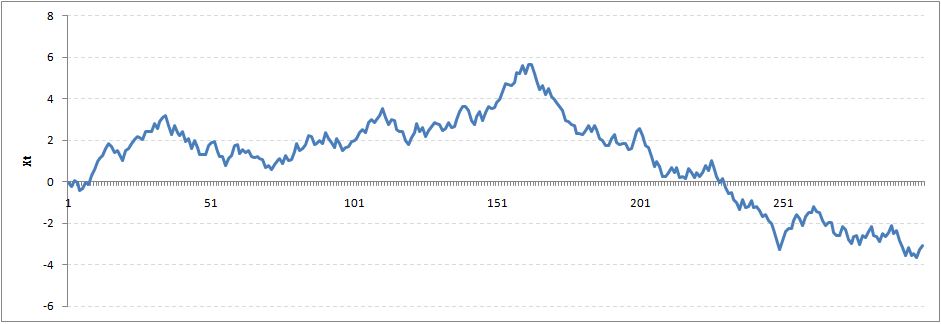
Coefficient (cont.)
-
如果有一個訊號 對於所有 都滿足以下條件,則我們稱此為一個平穩過程。
和 的聯合機率分布 (joint distribution),只和
和 的時間差有關,與其他參數都無關。
Definition
-
若為一個平穩隨機過程,則需滿足以下條件:
- 機率密度函數 (PDF) 在任意時間點 都是相同。
- 與時間無關 (time-independent) 的函式。
Definition (cont.)
-
白雜訊 (white noise)
-
功率密度為常數的隨機過程。
-
一個時間連續隨機過程 其中 為實數是一個白雜訊若且唯若滿足以下條件:
-
功率密度