High Altitude Ballooning (HAB)
High Altitude Ballooning (HAB)
A big latex balloon that is capable of carrying a bunch of objects to near space.
Filled with helium or hydrogen, the balloon expands as it ascends through Earth’s atmosphere.
The payload train is the objects that are attached to a HAB.
Each payload serves a particular purpose and include:
- a parachute
- radar reflector
- communication tracker
- camera
- science experiments
Over the next few weeks students will:
- Research the upper atmosphere
- Investigate satellites, sounding rockets & balloon payloads
- Form design teams and use the engineering design process to determine a problem and a solution for their experiment
- Research launch conditions
- Start to design and construct a balloon payload
- Calibrate instruments and determine atmospheric conditions that will affect their experiment
- Test components of the payload and prepare a pre-launch checklist
- Ready balloon and payload for launch and test equipment
- Recover payload after launch
- Evaluate data collected from the balloon and draw conclusions
- Present project
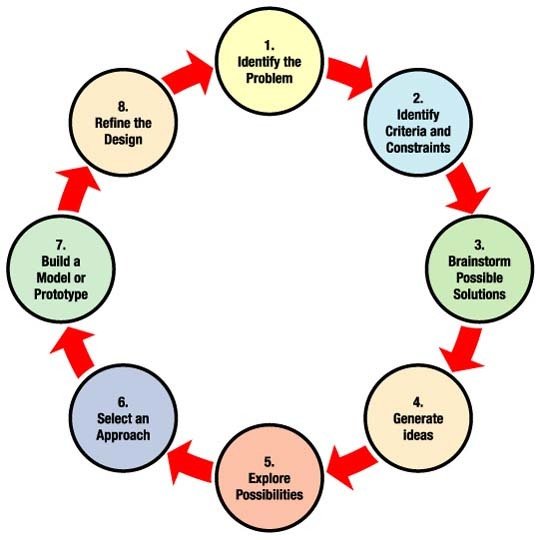
Engineering Design Process
Image from NASA
1. Identify the Problem
What is the problem that you are trying to solve? Try to be as specific as possible.
Describe the problem and explain why it needs to be solved.
What are the criteria and constraints that your project need to take into account for success?
2. Brainstorm Solutions
What are the criteria and constraints that your problem need to take into account?
How will you solve the problem? Brainstorm ideas to solve your problem.
3. Select a Solution
Examine your ideas and decide which one is the best. To decide, think about which
idea does the best job of solving your problem and which one makes the most sense.
Create a pro/con chart or a matrix to determine which idea best fits to solve the problem and meet your criteria and constraints.
4. Build a Model or Prototype
What will it look like? Draw or build your prototype (model, drawing, etc.). Your model should be made from easily found and low-cost materials, to show that your idea will work.
5. Evaluate
Test your solution, making changes when necessary, to refine your design. Continue to
record your findings in your design brief until you have designed andtested your final product.
6. Present Results
How did it turn out? Share your results and ask others what they think. Use their suggestions to make your solution better.
The Upper Atmosphere
Research features and data about the stratosphere, mesosphere and ionosphere such as:
• Basic facts, pressure, temperature, buoyancy, etc.
•Composition, weather
•Properties of the ionized component
•Aurora borealis, space weather
•Cosmic rays and X rays
The Upper Atmosphere
Gather information critical for a high altitude balloon space probe:
• How do balloon payloads communicate and conduct experiments
• Why does language play such an important role in communication
• How are balloon payloads designed to survive in harsh/hostile conditions
• How are balloon experiments designed and tested
Resources
Resources
Resources
Resources
Resources
Resources
- Sending a Weather Balloon to 95,000 ft
https://www.instructables.com/id/Sending-a-Weather-Balloon-to-95000-Feet/


