Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
How does it work?
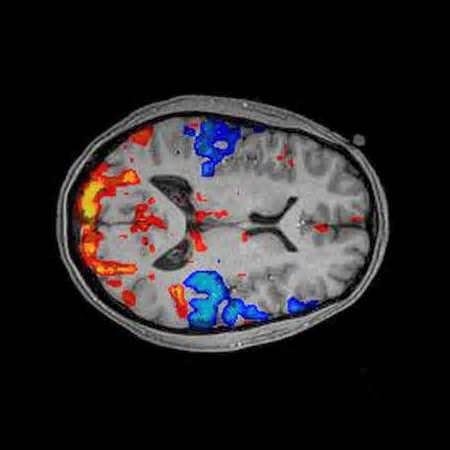
fMRI machines detect changes in blood oxygenation and blood flow that occurs in the brain as a result of neural activity.
When different areas of the brain are active, they require more blood flow (for oxygen)- this is the haemodynamic response.
What does it show?
fMRIs produce 3D images showing which part of the brain is active.
When would you use it?
-
for soft tissues (i.e. brain)
-
research into internal mental processes (i.e. memory/localisation of function of the brain)
-
NO claustrophobia
-
NO metal in their bodies (e.g. pacemaker)
Strengths!
-
NO radiation (unlike PET scans)
-
Non-invasive
-
Risk-free
-
High spatial resolution (mm)
Weaknesses
-
Expensive
-
Poor temporal resolution (5-second lag)
-
Requires to be very still during scan
-
Only measures bloodflow- not individual neuron activity