Version Control with Git
What is version control?
- A tool to track the history of a project
- who changed what when
- Individual or collaborative
Why do I can about the history of a project?
- Individual:
- fix (or undo) mistakes
- what was done and why
- definitive (final?) version
- hard to accidentally delete
- Collaborative:
- who to ask if you have questions
- work simultaneously
- hard to overwrite

Configuration
- git command format: git verb
- verb: config
- who you are
- --global
- apply everywhere
- color: color code output
- editor: set default editor
- you can change these setting at any time
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "YourEmail@email.edu"
git config --global color.ui "auto"
git config --global core.editor "nano"
git config --global core.autocrlf input #Mac and linux
git config --global core.autocrlf true #windows
git config --global init.defaultBranch mainThe Situation
- Dracula, Wolfman, and the Mummy
- research moving to another planet
- want to share their research

Creating a repository
- cd to your home directory
- make a directory called planets
- cd into planets directory
git init- make planets directory a repository
ls -a- .git directory is where git stores the history of the project
git statusTracking Changes to Files
- Create a file to track
- Open your text editor
- Type: cold and dry but everything is my favorite color
- save file as mars.txt
- Check in with git
- start tracking file
- Record current state
-
- -m : commit message inline
git statusgit add mars.txtgit commit -m "starting to think about mars"What are we doing?
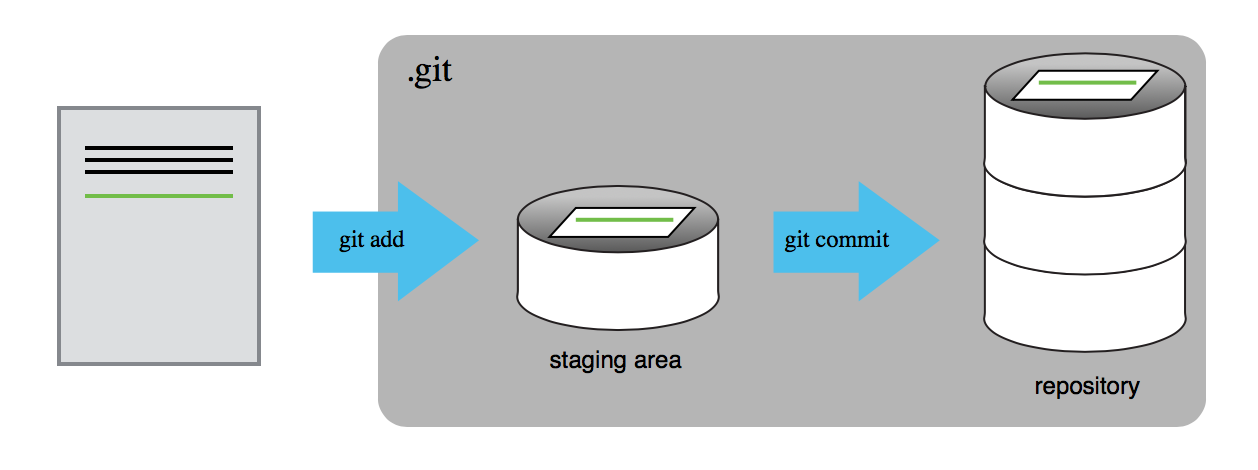
Exercise 1:
- Create a file called jupiter.txt with a sentence about jupiter in your planets directory
- start tracking and record the current state of jupiter.txt
- Put your green post-it up when you are done
git status
git add filename
git commit -m "commit message"Viewing your history
git logChanging a File
- Open your mars.txt file and add:
- The two moons may be a problem for Wolfman
- Check the status of your files
- View the changes you made
- Tell git which files you want to record changes in
- Save changes to revision history
git statusgit diff mars.txtgit add mars.txtgit commit -m "concerns about Mars' moons"What are we doing?
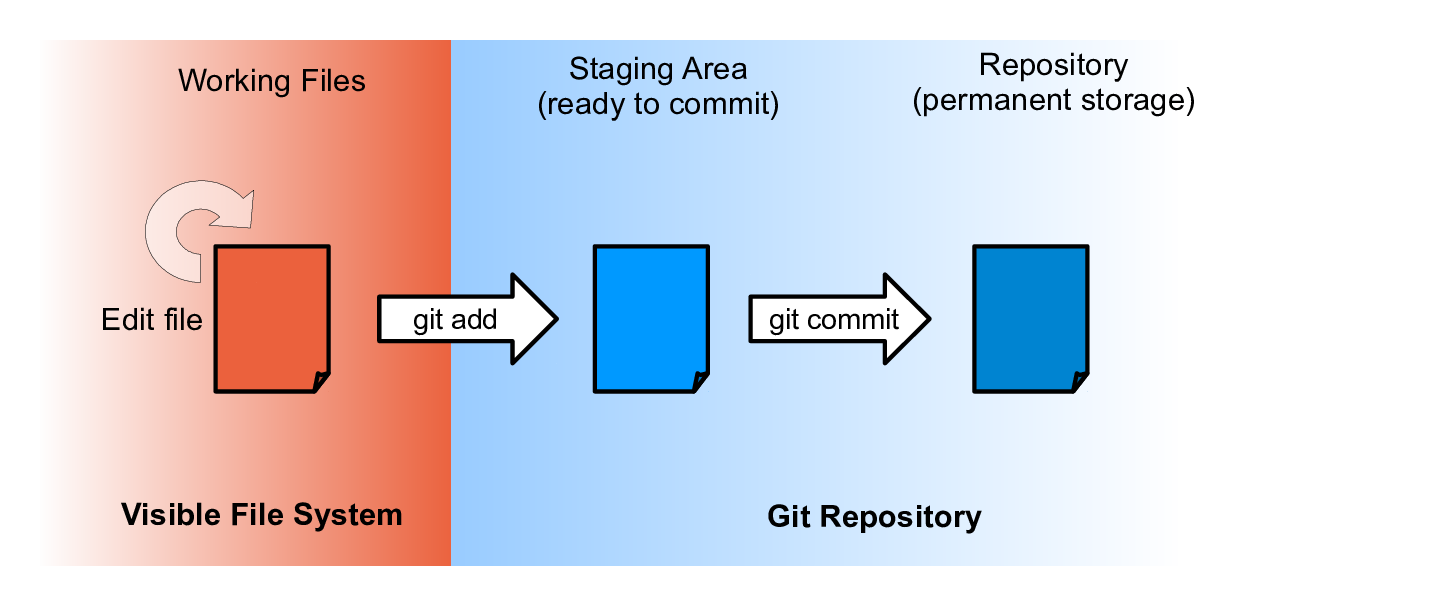
Exercise 2
- Open file jupiter.txt in your text editor
- Add a line
- View the change you made using git
- Record your changes in the project's history
- View your project's history
- Put up your green post-it
- Bonus:
- make another change
- try any one of these variations:
- commit without adding
- view changes between adding and committing
- commit without the -m
A note on viewing changes
-
- changes between working directory and what was last staged
-
- changes between staging area and last commit
git diffgit diff --stagedReferencing different versions
- Shorthand for different versions of a repository (refers to commits)
- Current Version (most recent commit): HEAD
- Version before current: HEAD~1
- Version before that: HEAD~2
- Each of these also has a commit hash
- use git log to get appropriate hash
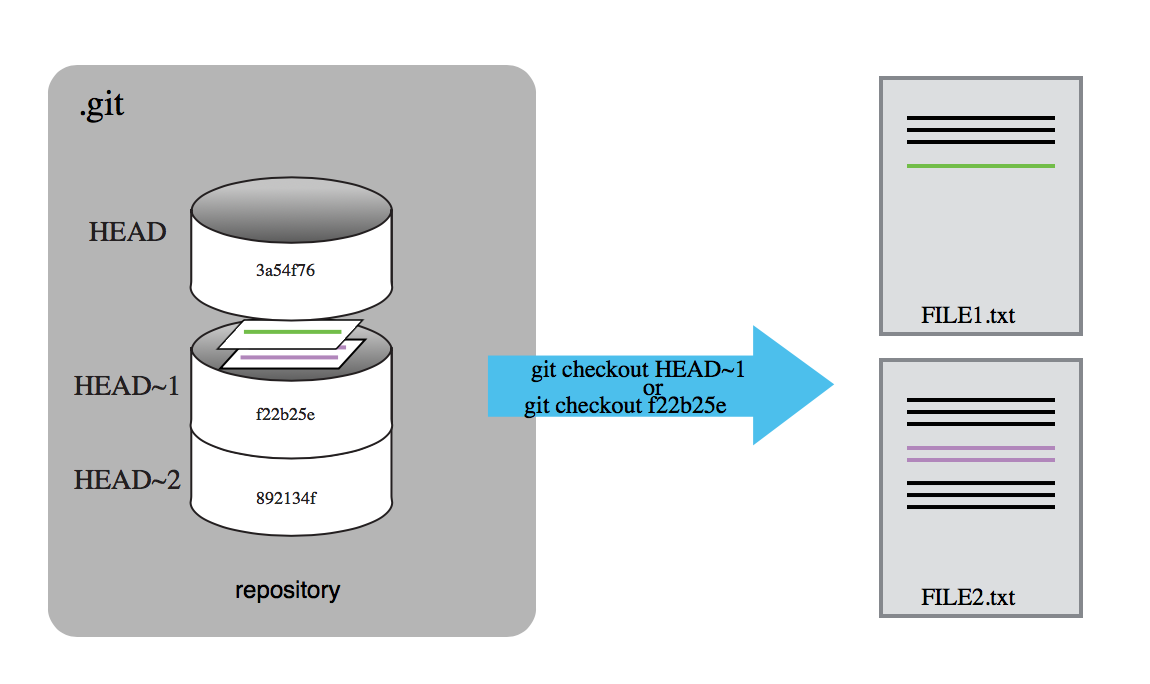
Exploring History
- Changes made in the last commit
- Changes made in the last 2 commits
- Changes made in the last 3 commits
- Changes made since commit hash...
- first 7 characters
- use git log to find commit you want
git diff HEAD~1git diff HEAD~2git diff HEAD~3git diff 0b0d55eRecovering Older Versions
- Overwrite mars.txt:
- Recover last recorded version:
- checkout HEAD = revert to version in HEAD
- can use commit hash to revert to even older version
- mars.txt: tells git which file to revert
- in git status they list this option with -- instead of HEAD. This is a shortcut.
echo 'the mummy will like the dry air' > mars.txt
cat mars.txtgit checkout HEAD mars.txtWhat is going on here:
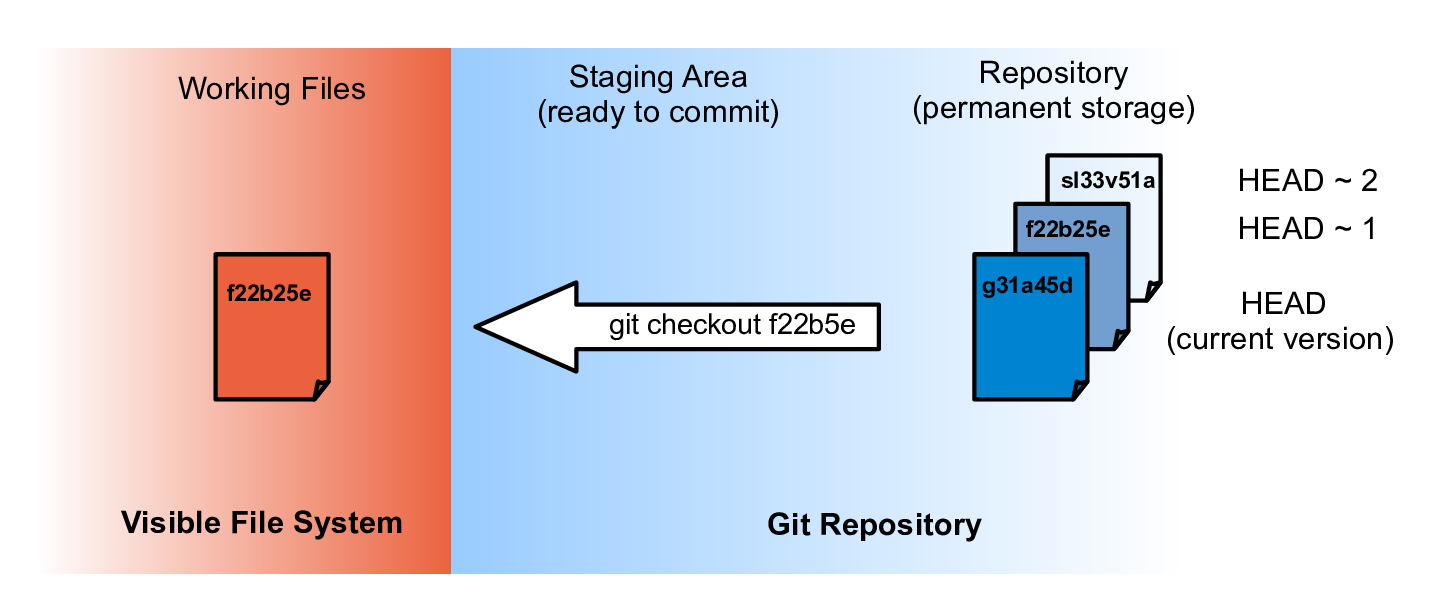
Exercise 3:
- Overwrite and recover jupiter.txt
- Put up your green post-it
- Bonus:
- revert to the first saved version of jupiter.txt
- switch back to the most recent version of jupiter.txt
Variations
- git show: changes and commit message "show me what I did in this commit"
- git revert <hash>: undo commit <hash> as a new commit
- DETACHED HEAD:git checkout main
local_version_control
By abostroem
local_version_control
- 5,016



