DEEP LEARNING BACKGROUND
Andrew Beam, PhD
Department of Biomedical Informatics
Harvard Medical School
March 21st, 2018

twitter: @AndrewLBeam
WHAT IS A NEURAL NET?

NEURAL NETWORKS ARE AN OLD IDEA

One of the very first ideas in machine learning and artificial intelligence
- Date back to 1940s
- Many cycles of boom and bust
- Repeated promises of "true AI" that were unfulfilled followed by "AI winters"

Are today's neural nets any different than their predecessors?
"[The perceptron is] the embryo of an electronic computer that [the Navy] expects will be able to walk, talk, see, write, reproduce itself and be conscious of its existence." - Frank Rosenblatt, 1958
MILESTONES


A PARTIAL ACCOUNT

Please read Schmidhuber's perspective on the history of deep learning: http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Deep_Learning

- This history focuses on what happened on this side of the atlantic in North America and is incomplete
- In Europe, a different community of researchers were exploring similar ideas, some times with better results
- Notably, Jurgen Schmidhuber's lab in Switzerland did important research on neural nets, including the invention of the LSTM
- These research communities have different accounts on the history of deep learning
IN THE BEGINNING... (1940s-1960s)


Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts (1943)
Thresholded logic unit with hardcoded weights
Intended to mimic "integrate and fire" model of neurons
IN THE BEGINNING... (1940s-1960s)

Rosenblatt's Perceptron, 1957

- Initially very promising
- Came with provably correct learning algorithm
- Could recognize letters and numbers
THE FIRST AI WINTER (1969)



Minsky and Papert show that the perceptron can't even solve the XOR problem
Kills research on neural nets for the next 15-20 years
THE BACKPROPAGANDISTS EMERGE (1986)


Rumelhart, Hinton, and Willams show us how to train multilayered neural networks

REBRANDING AS 'DEEP LEARNING' (2006)

Unsupervised pre-training of "deep belief nets" allowed for large and deeper models

Image credit: https://www.toptal.com/machine-learning/an-introduction-to-deep-learning-from-perceptrons-to-deep-networks
THE BREAKTHROUGH (2012)

Imagenet Database
- Millions of labeled images
- Objects in images fall into 1 of a possible 1,000 categories
- Relatively high-resolution
- Bounding boxes giving exact location of object - useful for both classification and localization
Large Scale Visual
Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)
- Annual Imagenet Challenge starting in 2010
- Successor to smaller PASCAL VOC challenge
- Many tracks including classification and localization
- Standardized training and test set. Competitors upload predictions for test set and are automatically scored
CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETS (CNNs)

Dates back to the late 1980s
- Invented by in 1989 Yann Lecun at Bell Labs - "Lenet"
- Integrated into handwriting recognition systems
in the 90s - Huge flurry of activity after the Alexnet paper


THE BREAKTHROUGH (2012)

Pivotal event occurred in an image recognition contest which brought together 3 critical ingredients for the first time:
- Massive amounts of labeled images
- Training with GPUs
- Methodological innovations that enabled training deeper networks while minimizing overfitting
THE BREAKTHROUGH (2012)

In 2011, a misclassification rate of 25% was near state of the art on ILSVRC
In 2012, Geoff Hinton and two graduate students, Alex Krizhevsky and Ilya Sutskever, entered ILSVRC with one of the first deep neural networks trained on GPUs, now known as "Alexnet"
Result: An error rate of 16%, nearly half what the second place entry was able to achieve.
The computer vision world immediately took notice
THE ILSVRC AFTERMATH (2012-2014)


Alexnet paper has ~ 20,000 citations since being published in 2012!
NETS KEEP GETTING DEEPER (2012-2016)


WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
Several key advancements has enabled the modern deep learning revolution

WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
Several key advancements have enabled the modern deep learning revolution

Availability of massive datasets
with high-quality labels
Standardized benchmarks of progress and open source tools
Community acknowledgment that
open data -> everyone gets better

WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
Several key advancements have enabled the modern deep learning revolution
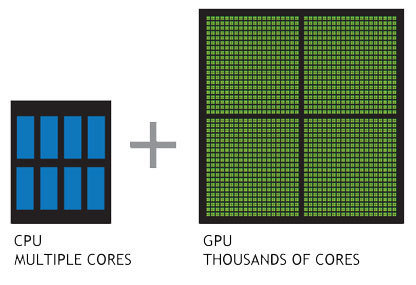
Advent of massively parallel computing by GPUs. Enabled training of huge neural nets on extremely large datasets



WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
Several key advancements have enabled the modern deep learning revolution
Methodological advancements have made deeper networks easier to train

Architecture

Optimizers

Activation Functions

WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
Several key advancements have enabled the modern deep learning revolution
Robust frameworks and abstractions make iteration faster and less error prone
Automatic differentiation allows easy prototyping





WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
This all leads to the following hypothesis
Deep Learning Hypothesis: The success of deep learning is largely a success of engineering.

WHAT'S CHANGED? WHY NOW?
Fitting Analogy?



APPLICATIONS

DEEP LEARNING HAS MASTERED GO





DEEP LEARNING HAS MASTERED GO


Source: https://deepmind.com/blog/alphago-zero-learning-scratch/

Human data no longer needed
DEEP LEARNING CAN PLAY VIDEO GAMES



DEEP LEARNING CAN PLAY VIDEO GAMES


DEEP LEARNING CAN PLAY VIDEO GAMES


DEEP LEARNING CAN IMITATE STYLE


DEEP LEARNING CAN DIAGNOSE PATIENTS


DEEP LEARNING CAN DIAGNOSE PATIENTS




DEEP LEARNING CAN UNLOCK INFORMATION


MANY MEDICAL IMAGING EXAMPLES


DEEP LEARNING CAN DIAGNOSE PATIENTS

What does this patient have?
A six-year old boy has a high fever that has lasted for three days. He has extremely red eyes and a rash on the main part of his body in addition to a swollen and red strawberry tongue. Remaining symptoms include swollen lymph nodes in the neck and Irritability
DEEP LEARNING CAN DIAGNOSE PATIENTS

What does this patient have?
A six-year old boy has a high fever that has lasted for three days. He has extremely red eyes and a rash on the main part of his body in addition to a swollen and red strawberry tongue. Remaining symptoms include swollen lymph nodes in the neck and Irritability

Image credit: http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
DEEP LEARNING CAN DIAGNOSE PATIENTS


What does this patient have?
A six-year old boy has a high fever that has lasted for three days. He has extremely red eyes and a rash on the main part of his body in addition to a swollen and red strawberry tongue. Remaining symptoms include swollen lymph nodes in the neck and Irritability
DEEP LEARNING CAN DIAGNOSE PATIENTS


What does this patient have?
A six-year old boy has a high fever that has lasted for three days. He has extremely red eyes and a rash on the main part of his body in addition to a swollen and red strawberry tongue. Remaining symptoms include swollen lymph nodes in the neck and Irritability
We are evaluating this system on questions from the US medical licensing exam!
DEEP LEARNING IS VALUABLE


DEEP LEARNING IS VALUABLE



EVERYONE IS USING DEEP LEARNING



HOW CAN YOU STAY CURRENT?
The field moves fast, staying up to date can be challenging


http://beamandrew.github.io/deeplearning/2017/02/23/deep_learning_101_part1.html
DEEP LEARNING AND YOU
Barrier to entry for deep learning is actually low

... but a few things might stand in your way:
- Need to make sure your problem is a good fit
- Lots of labeled data and appropriate signal/noise ratio
- Access to GPUs
- Must "speak the language"
- Many design choices and hyper parameter selections
- Know how to "babysit" the model during learning phase
- You're in this class so you're off to a good start!
CONCLUSIONS

- Deep learning is real and probably here to stay
- Could potentially impact many fields -> understand concepts so you have deep learning "insurance"
- Long history and connections to other models and fields
- Prereqs: Data (lots) + GPUs (more = better)
- Deep learning models are like legos, but you need to know what blocks you have and how they fit together
- Need to have a sense of sensible default parameter values to get started
- "Babysitting" the learning process is a skill
BMI 707 - Lecture 1: History and Background
By beamandrew
BMI 707 - Lecture 1: History and Background
- 2,153
