CMSC389L
Week 3
S3 + CloudFront
September, 15, 2017
Recap
- Week 2 Feedback Form: ter.ps/389l
- Codelab 2 (S3), due next Friday
11:59PM - Office Hours:
-
- Tuesdays 4-5PM (AVW 4101)
- Fridays 2-3PM (AVW 4101)
Class Today
- S3 Review
- Codelab Workshop
- CloudFront
- CloudFront Worksheet
S3 Review

S3
-
Simple Storage Service (S3): Key-value store for object storage at scale
- Bucket + Key : Object
- Object Storage: Any sequence of bytes (photos, videos, source code, ...)
-
Durability: 99.999999999%
- Replicated across data centers and AZs
- Features: ACLs, Metadata, Versioning, Encryption, ...
When to use S3?
-
S3 Use Cases: Think "file storage"
- Object Size: support for large files (up to 5TB)
- Integration with CloudFront CDN
- Support for archiving data (to Glacier)
- examples: website static content (HTML/CSS/etc.), log files
-
Non-S3 Use Cases: Databases -- think "queryable data"
- Object Size: Limited (f.e., 400Kb for DynamoDB)
- DBMS guarantees
- Support for indexes for querying
- Faster read/writes
- examples: user profile data, credentials
S3 Concepts
-
Object: Fundamental entity in S3
- Consists of object data + metadata
-
Metadata: name-value pairs that describe the object
- date last modified, content-type, etc.
-
Bucket: Container for objects stored in S3
- Bucket name must be globally unique
- Can store unlimited objects
- Key: Unique identifier of objects within buckets
S3 Atomicity
- Atomic: Reads to a previously updated object will return either the updated object or the previous object. Never partial or corrupted data.
S3 Consistency
-
Eventual Consistency: Update and delete operations are not available until fully replicated.
- For new keys, reads have read-after-write consistency
S3 Storage Types
| S3 Default | S3 RRS | S3 IA | Glacier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | 99.999999999% | 99.99% | 99.999999999% | 99.999999999% |
| Availability | 99.99% | 99.99% | 99.9% | 99.99% |
| Extra Fees * | None | None | Retrieval | None |
| Real-Time Access? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No (min to hours) |
| Frequently Accessed? | Yes | Yes | No | No |
* : Excludes the usual data storage (per-GB), external bandwidth (GB/month), and API call charges
Codelab Workshop
- Codelab 2 is available here: ter.ps/389l
- Work in groups of 2-3
CloudFront
CloudFront Concepts
-
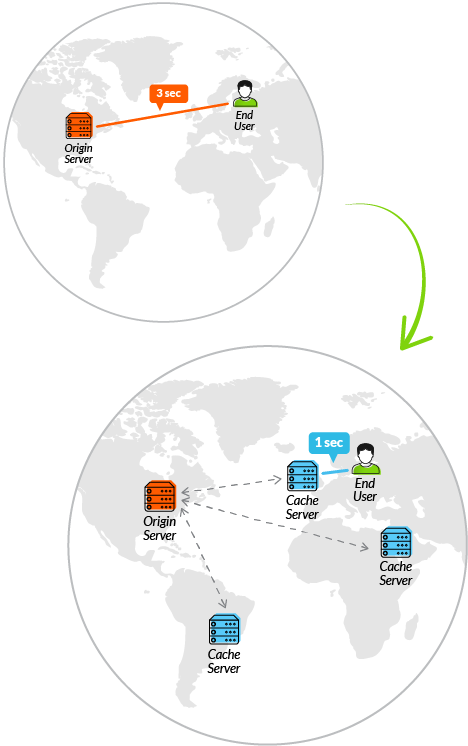
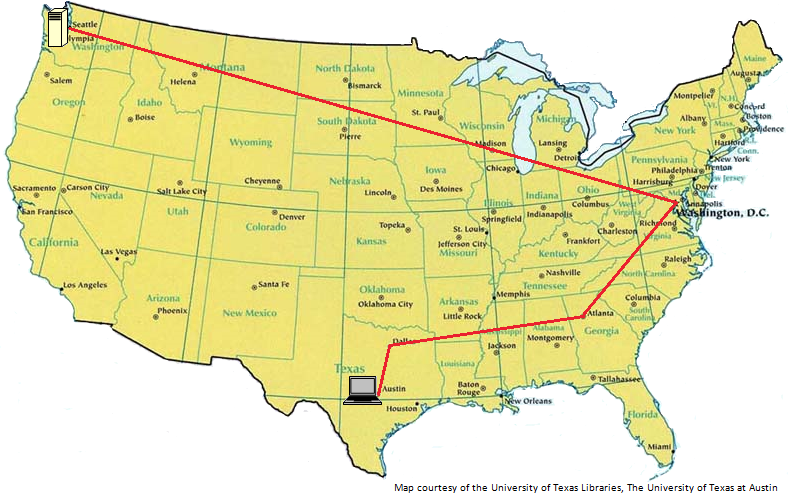
Content Delivery Networks (CDN): a globally-distributed network of proxy servers which cache content
- Use cases: web streaming, static content acceleration
CDN Metrics
- Latency: Time taken until the first byte is downloaded
- Data Transfer Rates: Rate at which data is transferred to the client
- Cache Hit Ratio: The percent of requests where the data can be retrieved from the cache
CloudFront Concepts
- Edge Locations: Proxy server in the CloudFront network
- Regional Edge Caches: Proxy servers that intermediates between origin server and edge locations.
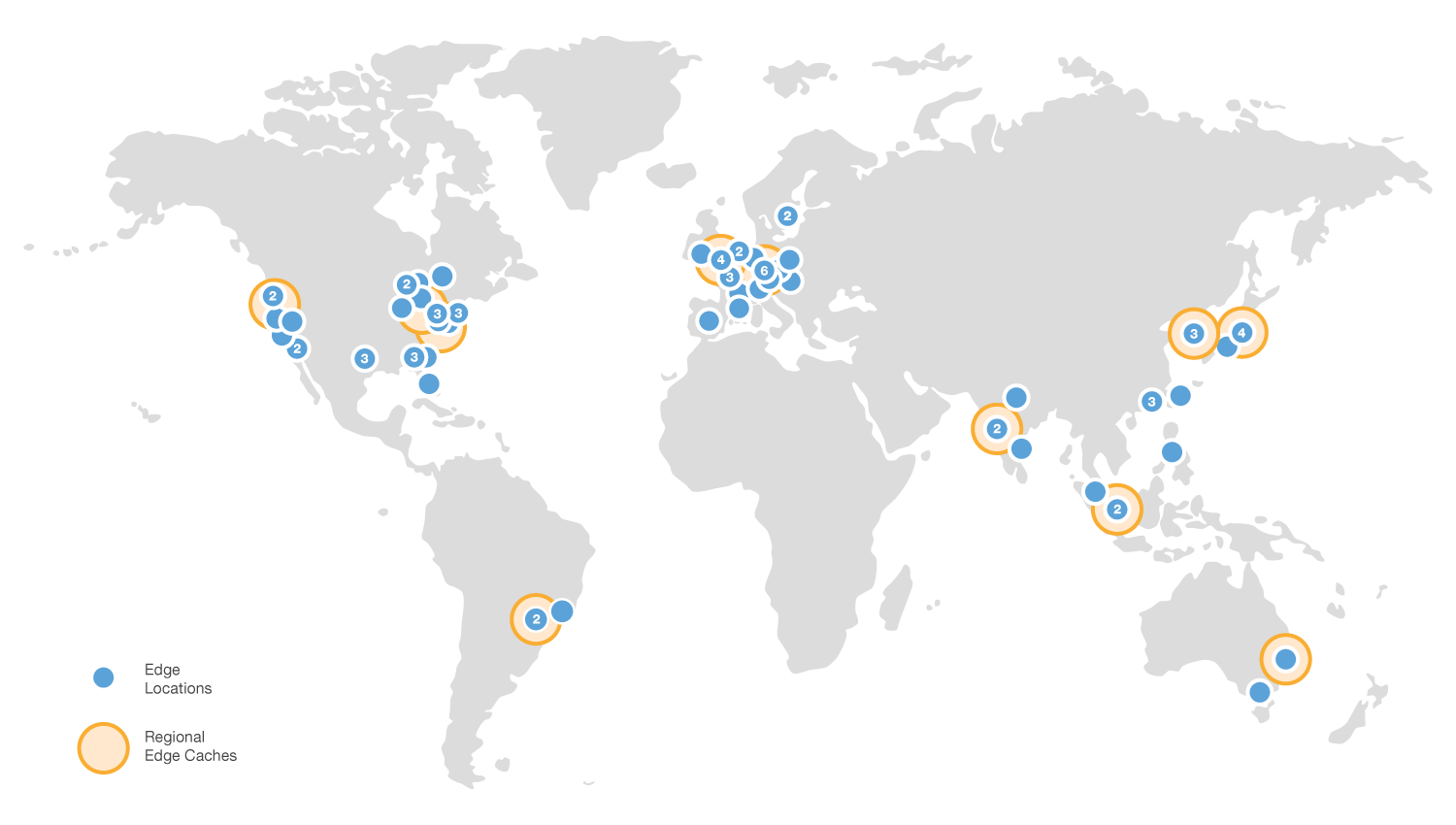
CloudFront Concepts
- Origin Server: The definitive store of content that CloudFront will accelerate (f.e., S3 or EC2 web server)
-
Distribution: Configuration specifying your origin server, cache invalidation rules, etc.
- Shared with edge locations
CloudFront Costs
- Transfer from CloudFront to Internet: $0.085 / GB
- Varies by region and throughput
- Drops to $0.020 / GB
- Varies by region and throughput
- Transfer from AWS (S3, etc.) to CloudFront: Free
- Per-request fee: $0.01 / 10k requests
Worksheet: CloudFront
Complete the worksheet on CloudFront.
Closing Notes
- Codelab 2: due next Friday 11:59PM
- No Codelab this week
- Project 1: postponed until we start EC2 next week
- Turn in your worksheets
- Fill out the feedback form for week 3
- Offce hours in this room until 3PM
CMSC389L Week 3
By Colin King
CMSC389L Week 3
- 865