Cost-Effective Index Poisoning Scheme for P2P File Sharing Systems
Yuusuke Ookita and Satoshi Fujita
Department of Information Engineering, Hiroshima Univeristy, Higashi-Hiroshima, Japan
Presenter: Denffer (趙之宇)
2017@Department of Computer Science, University of Taipei
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Introduction
-
Index
-
Simple P2P
-
Index Poisoning
-
Purpose of Index Poisoning
-
Cost-Effective
Information containing the name, owner, size
and the other attributes of the file
Index
Introduction

A

B
query
Index
Simple P2P
Introduction
Introduction
Index Poisoning
A technique which alters the index of illegal files
so that they could not be reached by any peer which wishes to access them through P2P
Introduction
Purpose of Index Poisoning
To reduce the probability of correct identification
as much as possible by reducing the number of correct copies of the index of illegal files
Introduction
Cost-Effective
1. Network cost
Evaluated by the total number of messages and the load of agent to poison index
2. Spatial cost
Evaluated by the number of altered copies existing in the network
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Proposed Scheme
Overview
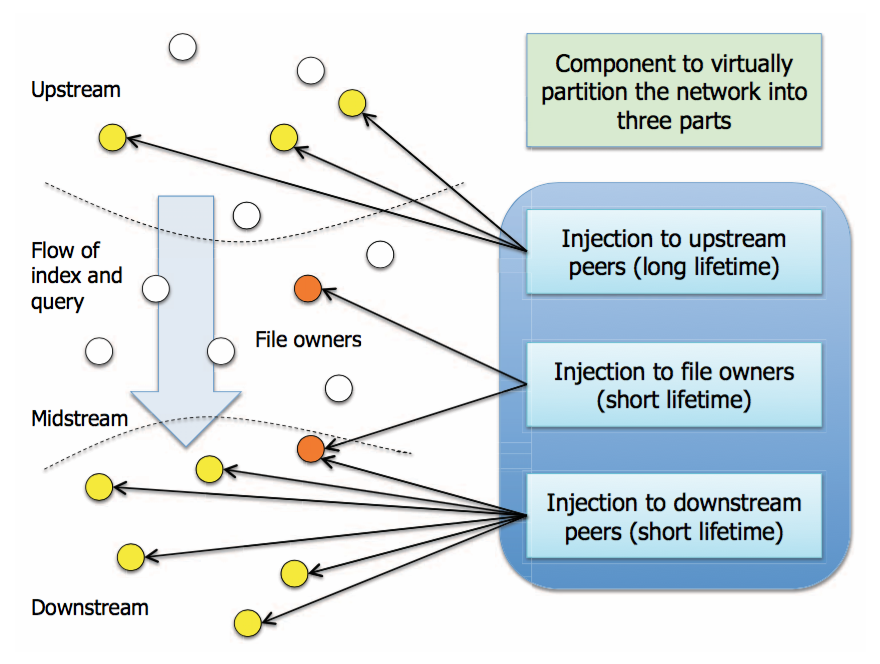
Proposed Scheme
Overview

The identification of upstream, midstream, and downstream peers can be realized by the behavior of each peer concerned with the index propagation
More concretely, this can be achieved by the software, Winny
Proposed Scheme
Overview

Proposed Scheme
Step 1: Injection to remove the seed of propagation
-
Target at the illegal file of the file owners
-
Overwrite a copy of the index held by the file owner with an altered one
-
Stop the new propagation of the correct index
Proposed Scheme
Step 2: Injection to remove propagated copies
-
Inject copies of altered index to upstream peers by setting a long lifetime
-
The altered index will then be received by many peers
Proposed Scheme
Step 3: Injection to remove propagated copies
-
Inject copies of altered index to downstream peers by setting a Short lifetime
-
Aim to overwrite the index of the illegal files previously received.
-
No propagation, and therefore shorter lifetime will be more cost-effective
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Evaluation
Tools
-
PeerSim
- an open source P2P simulator -
Winny
- a monitor to compare the performance of the proposed scheme
Evaluation
Configuration
-
Number of peers: 1000
-
Kind of files: 500
-
Number of keys initially held by each peer: 2
-
Maximum number of keys held by each peer:
- 500 for downstream peers
- 300 for midstream peers
- 100 for upstream peers
-
Number of peers of each type:
- 235 are downstream peers
- 485 are midstram peers
- 280 are upstream peers -
Default lifetime of index: 1500 seconds
-
Simulation time: 3870 seconds
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Results
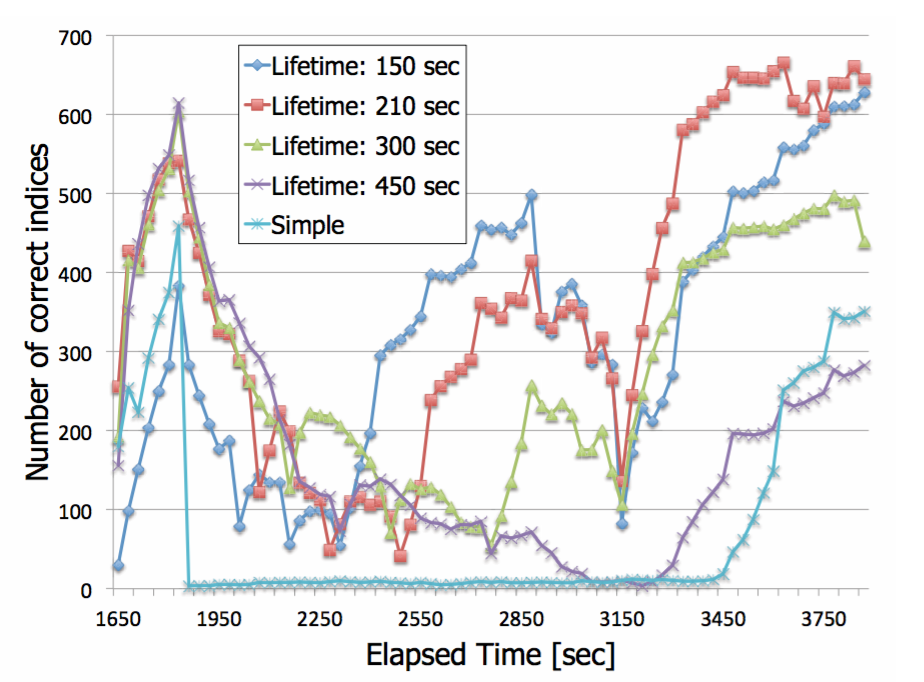
Time variation of the number of correct copies vs simple scheme
Results
The effect of the injection to downstream peers
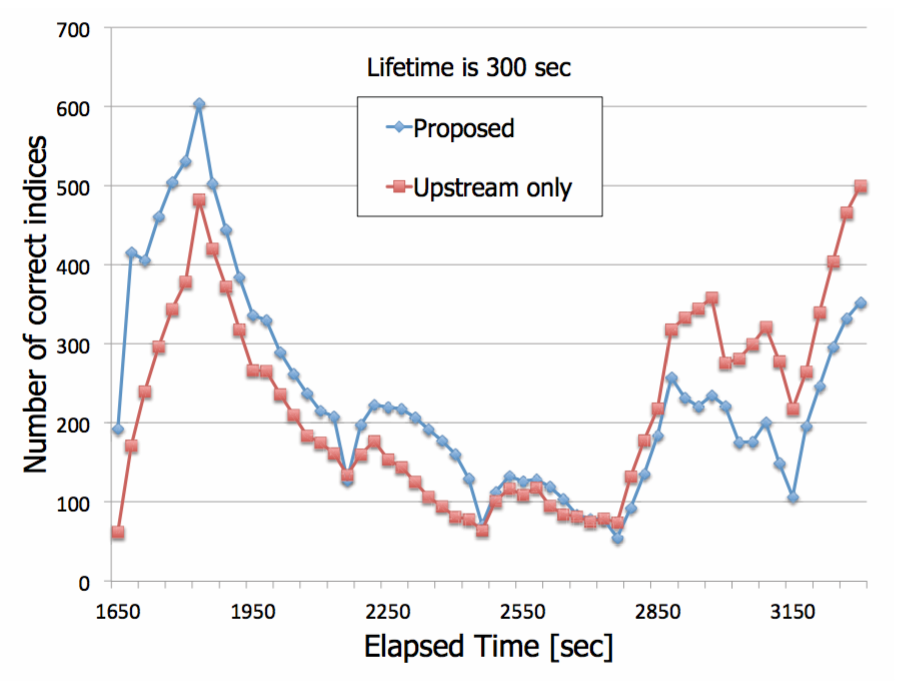
Results
Impact of the update interval of file owner
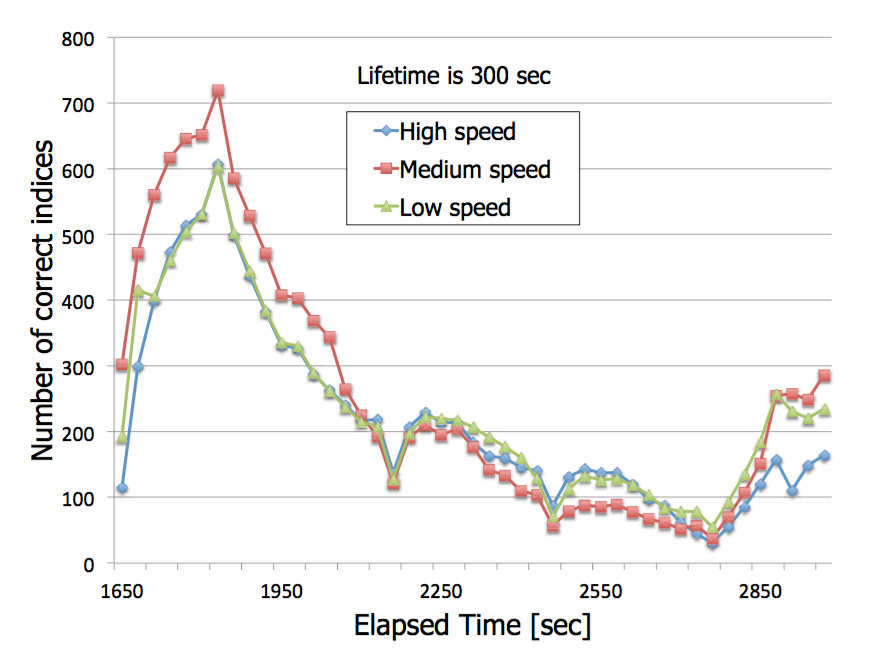
Results
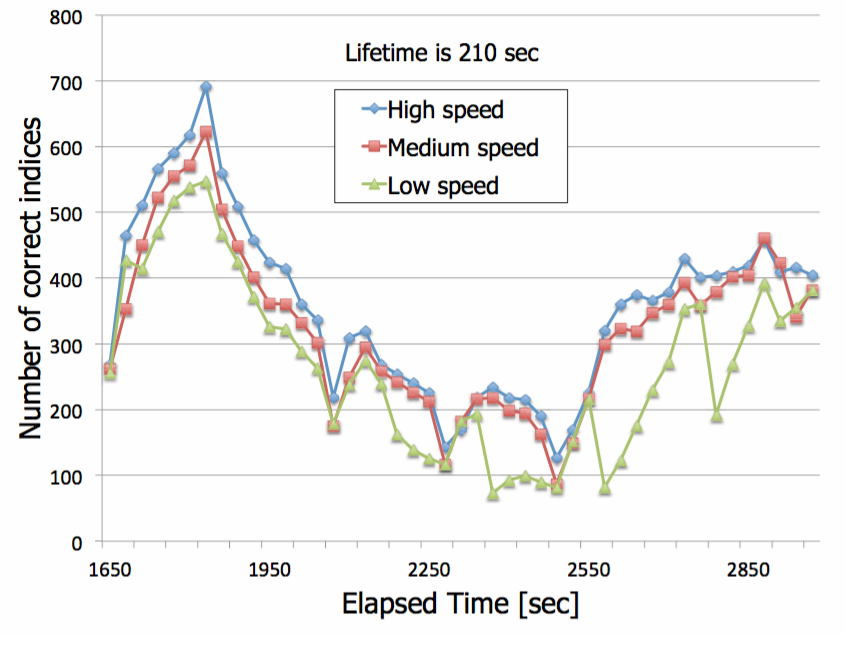
Impact of the update interval of file owner
Results
Hit rate of queries requesting the correct index of illegal file
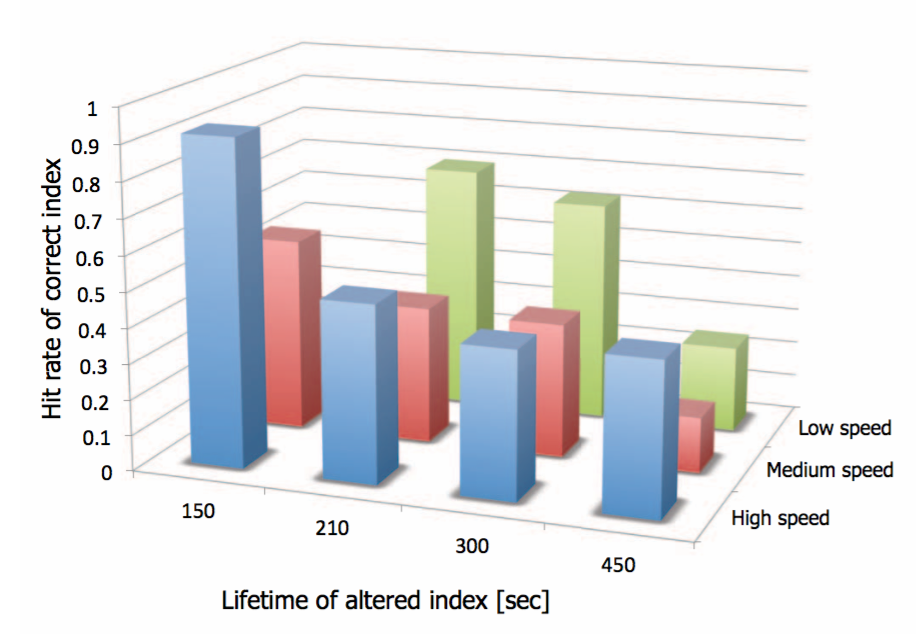
Results
Impact of the update interval of file owner
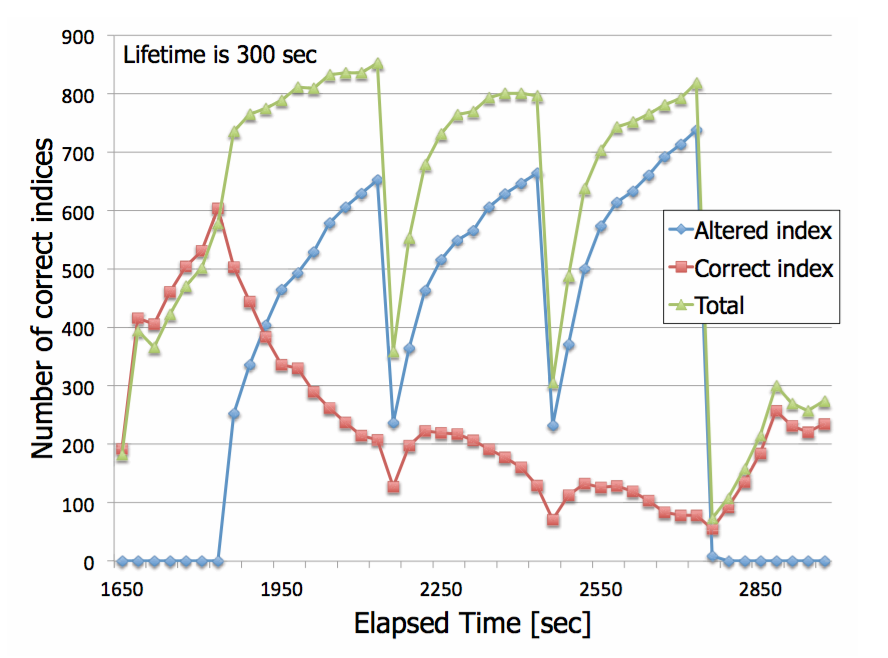
Results
Impact of the update interval of file owner

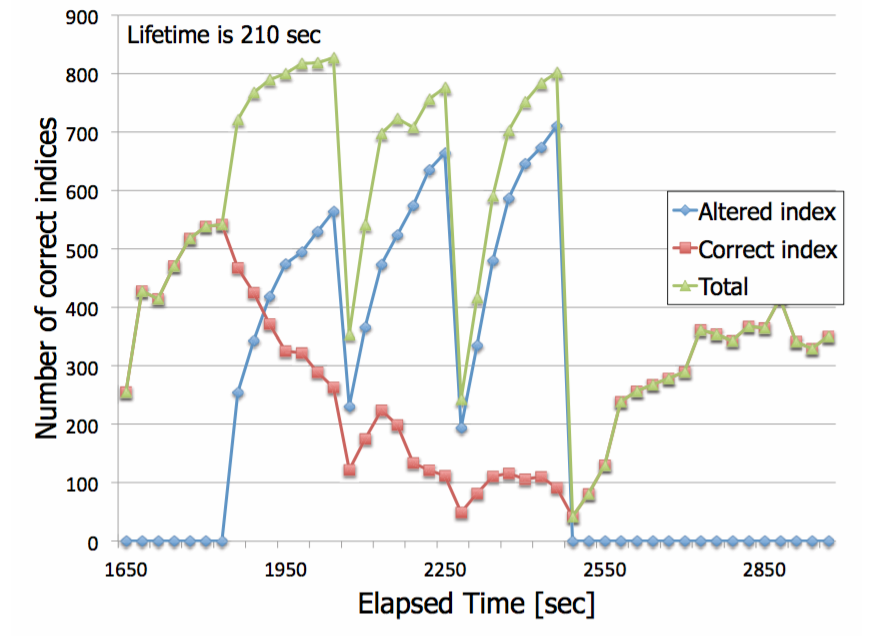
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Proposed Scheme
-
Evaluation
-
Result
-
Conclusion
Conclusion
The proposed scheme could attain almost the same performance with a simple (but expensive) scheme in which altered index with a sufficiently long lifetime is directly injected to all peers in the system
Presenter: Denffer (趙之宇)
2017@Department of Computer Science, University of Taipei
Thank you
index-poisoning
By Denffer
index-poisoning
- 260



