Breast Pathology
Vikram Dhillon
Nova Southeastern University
Case
- 29 y/o Korean female (nullipara) presents with a progressively enlarging right breast lump found on self-examination.
Case
- Not taking any medication.
- She was unmarried, but reported being with two sexual partners in the last year.
- She did not drink alcohol and had a smoking history of 5 pack years.
Case
- No significant past medical history, but a maternal aunt with breast cancer.
Case
- Vitals: 98.6 F. BP of 120/88. Pulse at 90 bpm. Respiratory rate of 20 breaths.
- General: Patient is awake, alert, oriented and responsive.
- HEENT: No JVD, no carotid bruits. No conjunctival pallor
Case
- Breast: 2.9 cm round mass in the upper-outer quadrant
- Heart: S1, S2 present. Regular rate. S3 gallop present, no thrills.
- Lungs: CTA-B. Bronchovesicular breath sounds.
Case
- Abdomen: Soft and non-tender abdomen, no guarding, no rigidity
- Extremities: No cyanosis or edema noted in extremities.
- Neuro: CN 2-12 intact. 2+ DTRs
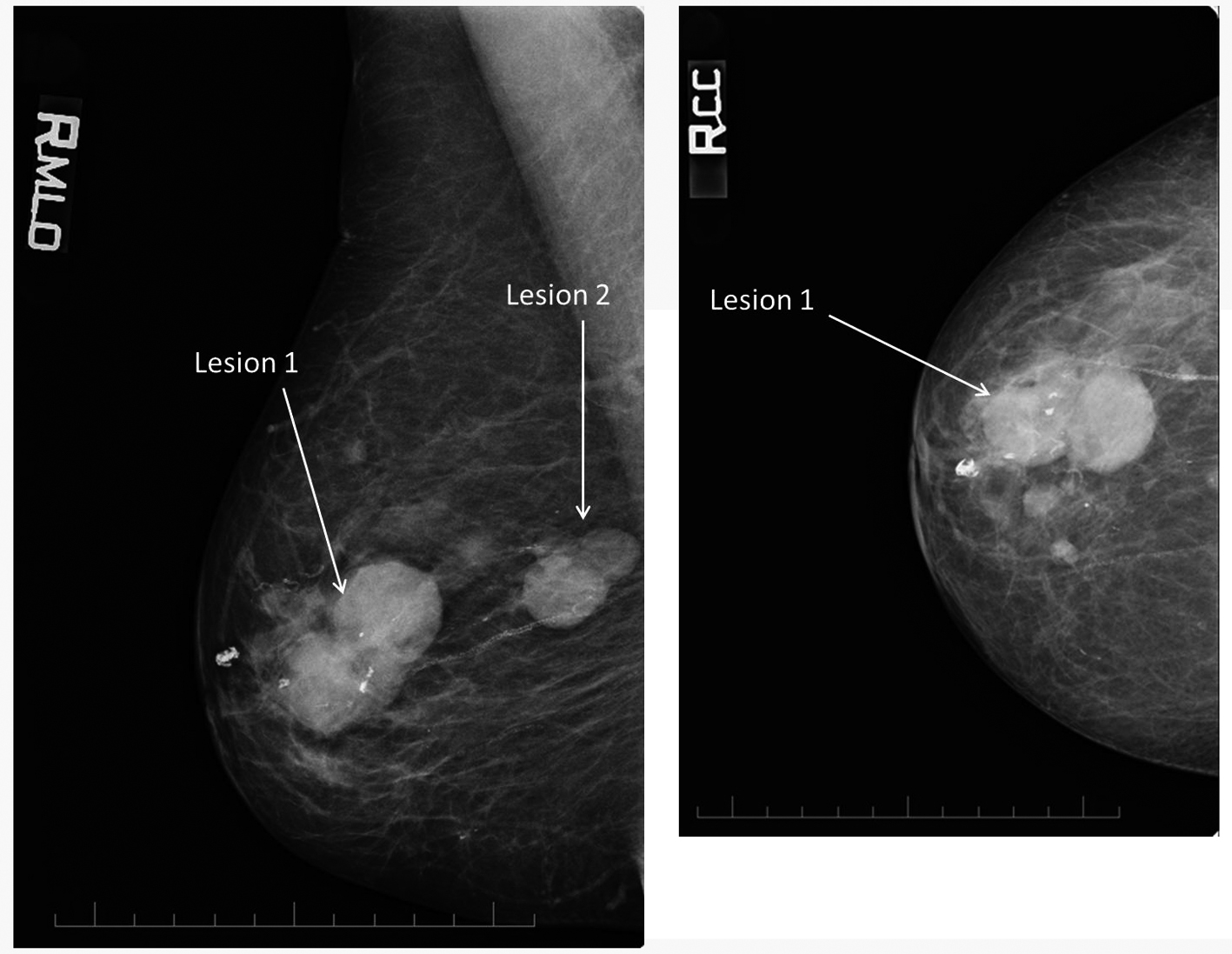
Peters et. al
Case
- Estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2)-positive.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy for 6 cycles followed by radiotherapy.
- Hormonal therapy with daily tamoxifen 20 mg, and trastuzumab
Epidemiology
- Second leading cause of mortality in women
- 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer during their lifetime
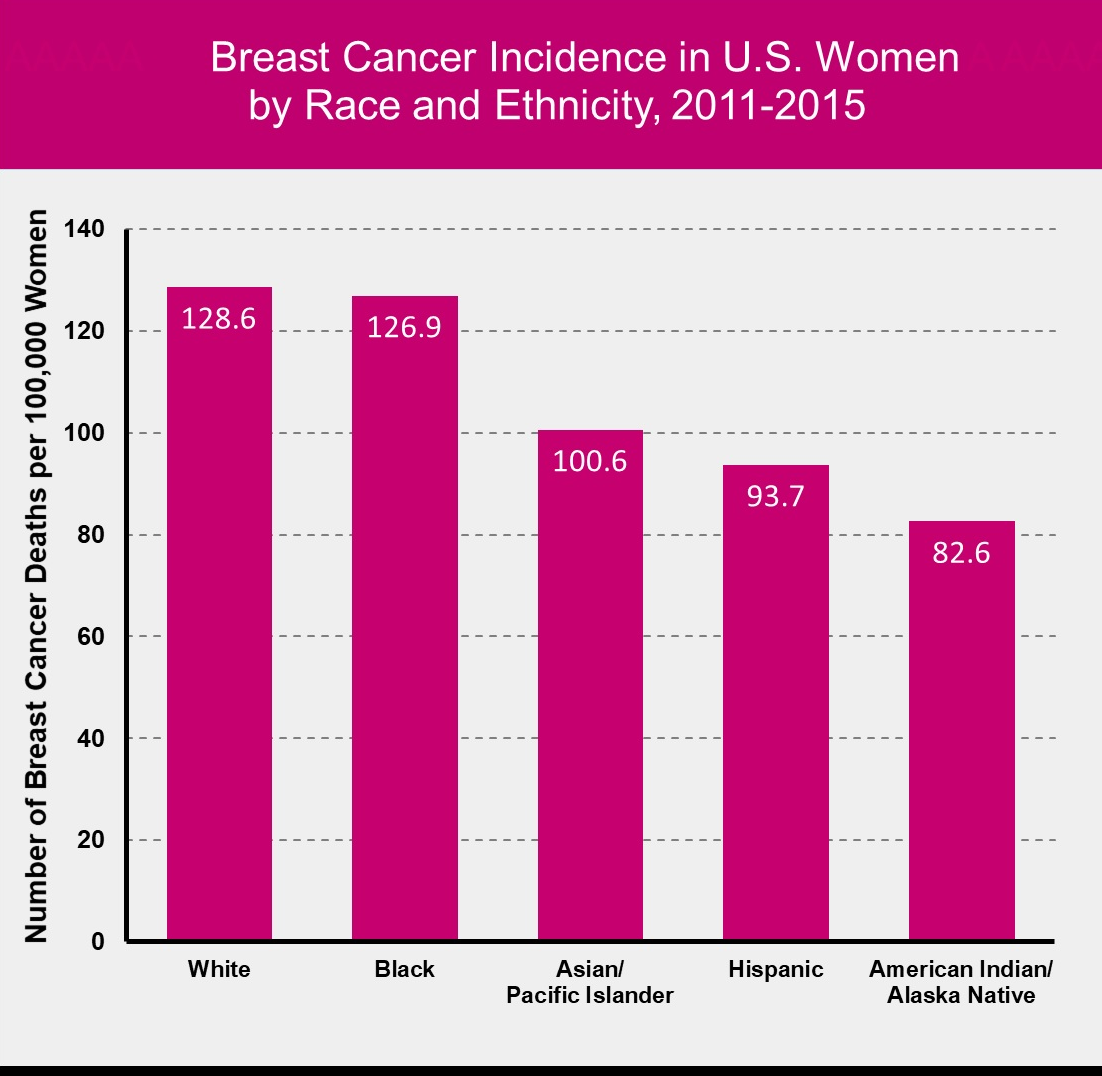
NCI 2015
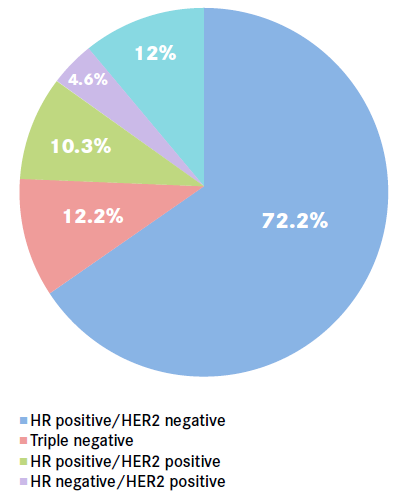
Key et. al.
Risk factors
Increased exposure to estrogen:
- Obesity
- Nulliparity
- Early menarche (<11 y.o.)
- Late menopause (>50 y.o.)
- Late first pregnancy (>30 y.o.)
Risk factors
- Smoking
- Breast cancer in first degree relatives
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia
Risk factors
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
- Over-expression of ER/PR receptors
- Li-Fraumeni associated p53 loss
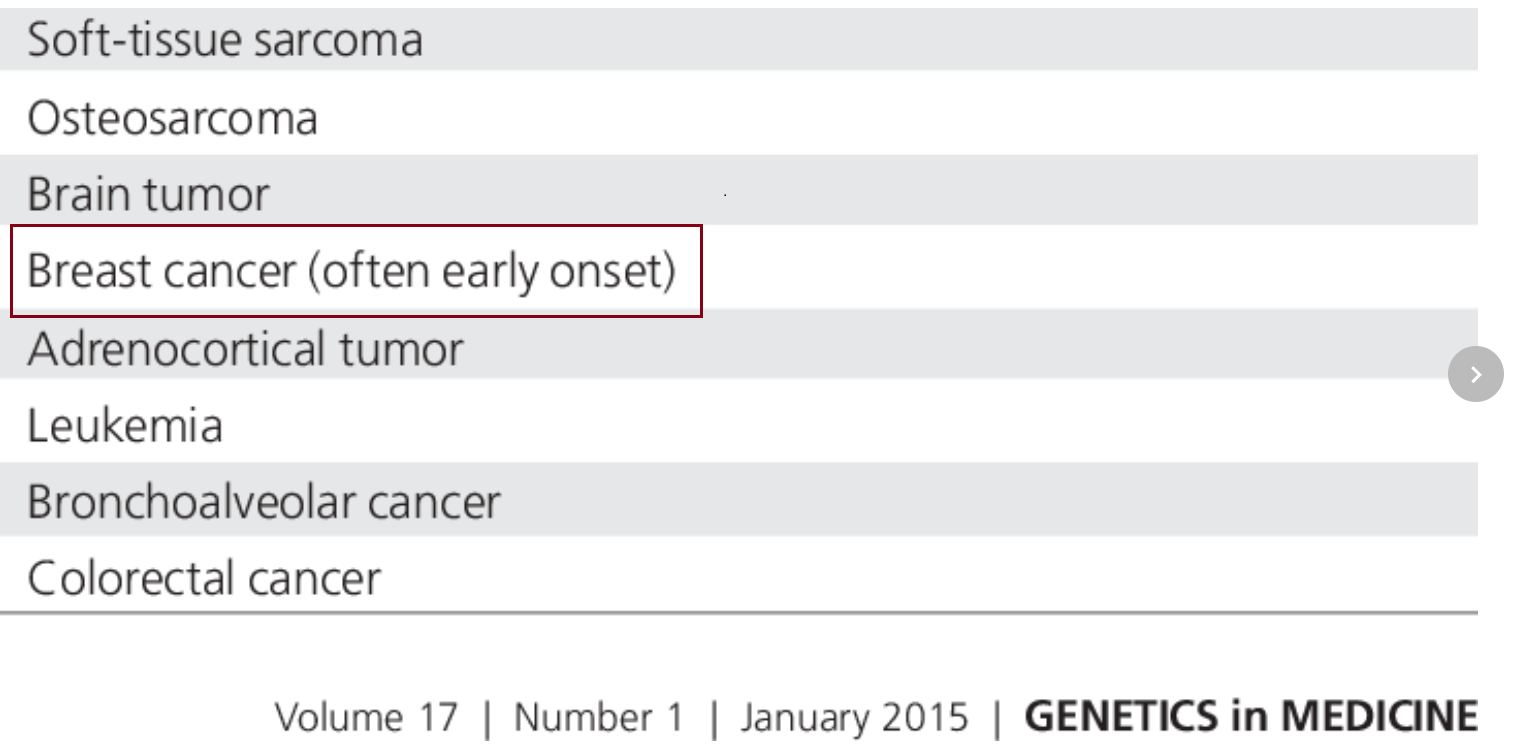

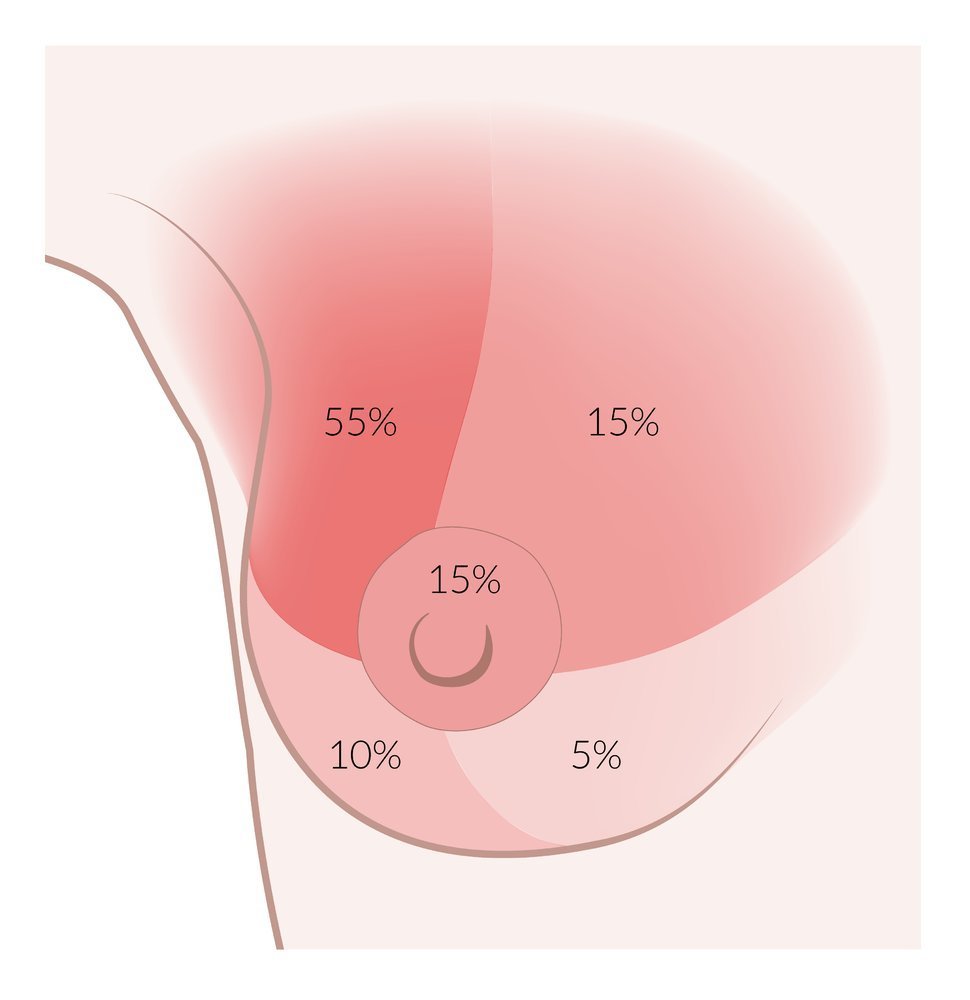
First Aid USMLE 2018
Step-Up to USMLE Step 2 CK

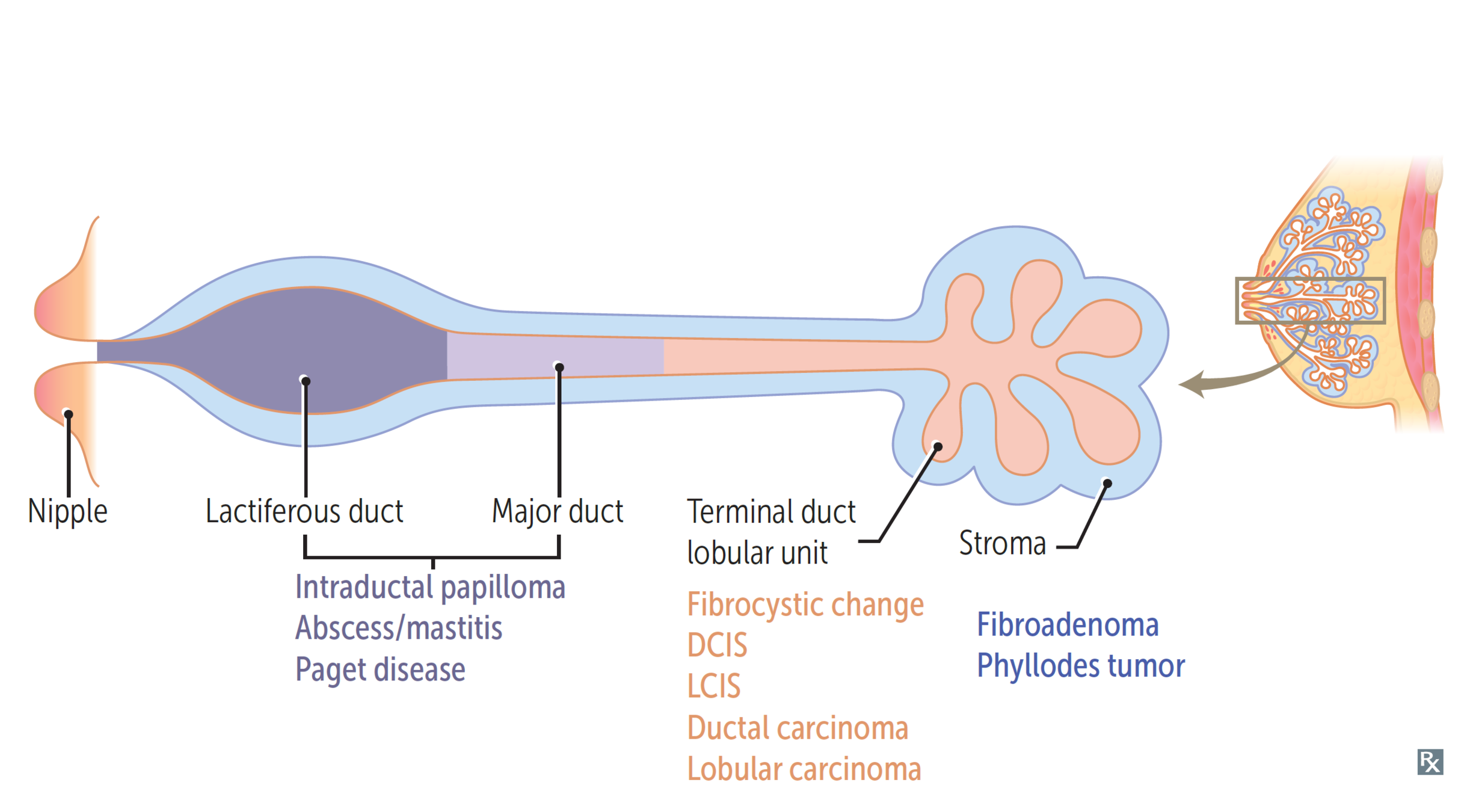
Benign disorders of breast
Ductal Carcinoma in-situ
- Rises from progression of ductal hyperplasia
- Non-palpable mass on PE
- Seen on mammography due to microcalcifications
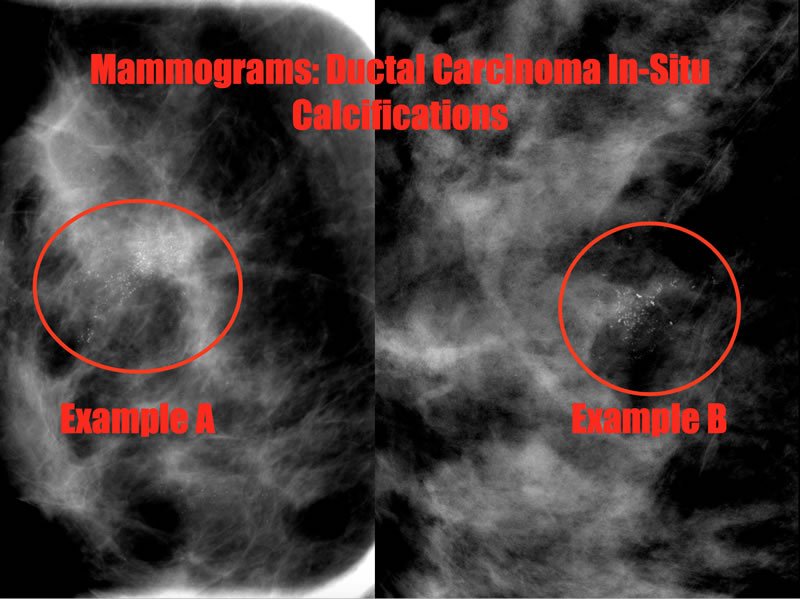
Bleiweiss et. al.

DCIS with central comedo-type necrosis.
First Aid USMLE 2018
Paget's disease
- Extension of DCIS into lactiferous ducts and skin of nipple
- Eczematous patches on nipple

Eczematous patches of Paget's disease
First Aid USMLE 2018
- Histology shows Paget cells: Large cells in epidermis with clear halo

First Aid USMLE 2018
Lobular carcinoma in-situ
- Non-palpable mass
- No calcifications - Doesn't show on mamogram
- Completely incidental finding
- Often bilateral
Histology shows distended lobules with neoplastic cells without BM penetration
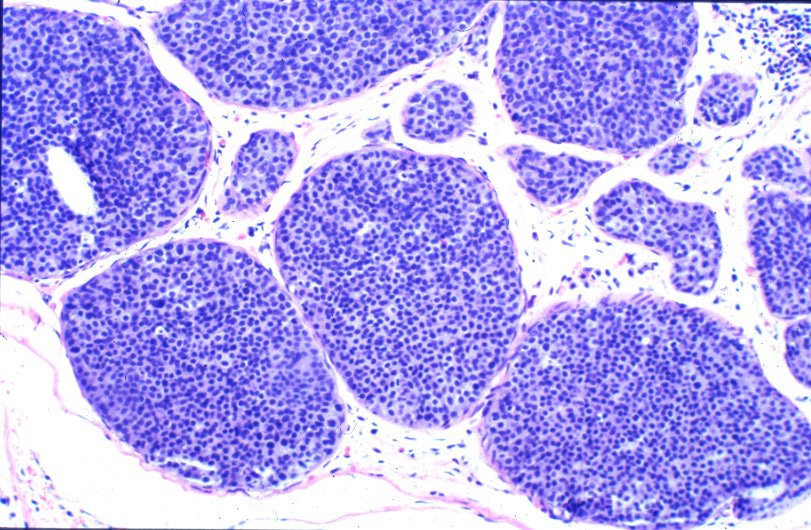
First Aid USMLE 2018
Invasive lobular
- Often multiple lobes and bilateral
- Loss of e-cadherin - Responsible for forming cell clusters
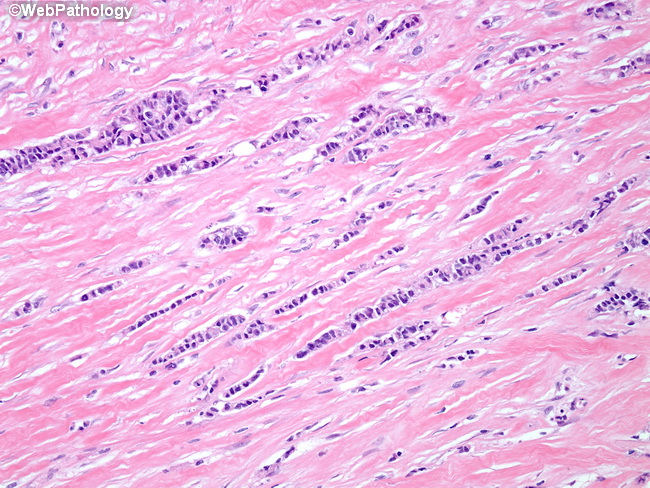
Orderly lines
First Aid USMLE 2018
Inflammatory
- Poor prognosis (50% survival at 5 years)
- Dermal lymphatic invasion and blockage by tumor
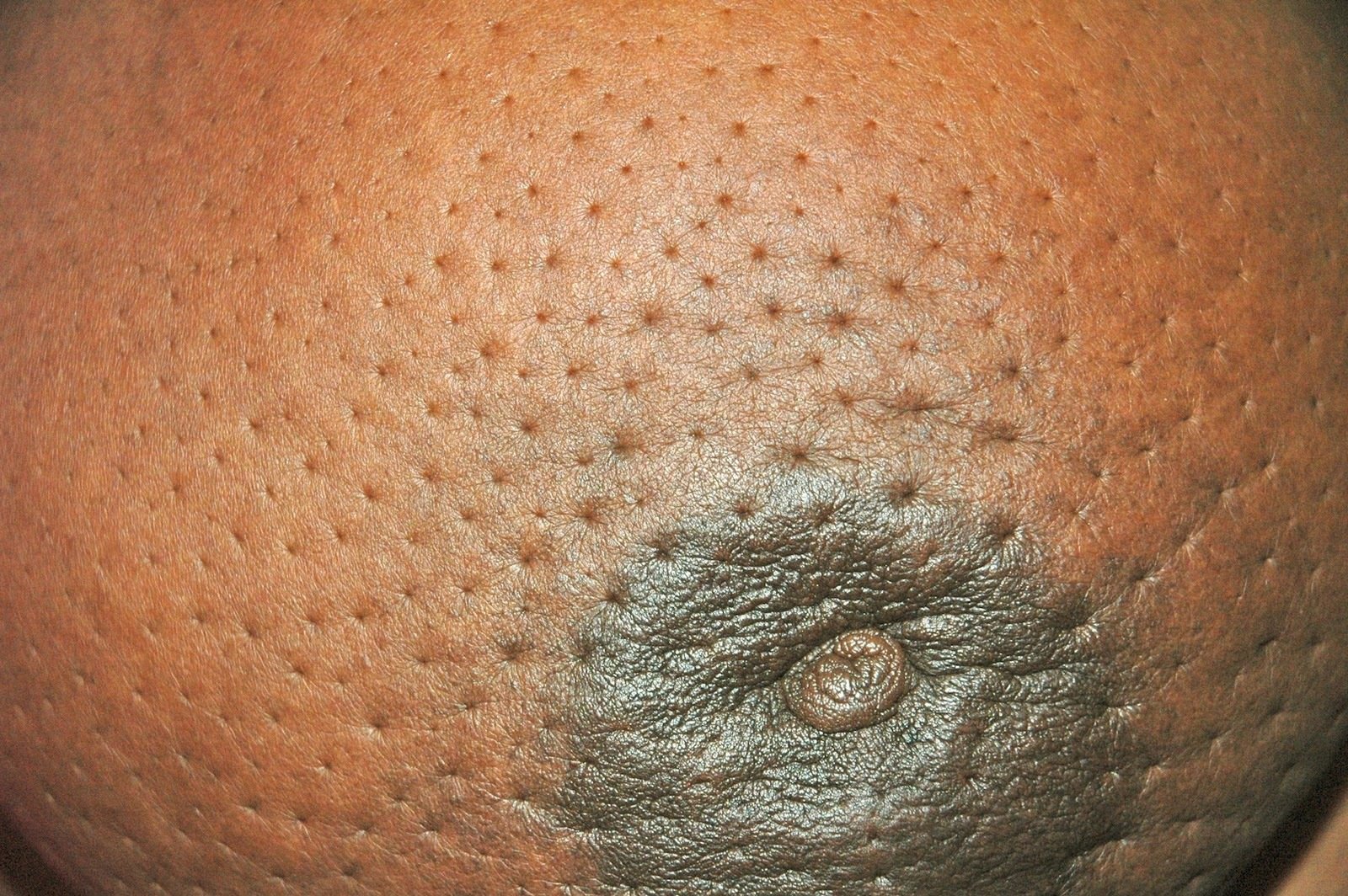
Peau d'orange
First Aid USMLE 2018
References
- Peters, G., & Jones, C. M. (2012). Unusual Mammographic and Ultrasound Findings in a Patient With Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS). Journal of Medical Cases, 3(4), 270-273.
- Key, T. J., Verkasalo, P. K., & Banks, E. (2001). Epidemiology of breast cancer. The lancet oncology, 2(3), 133-140.
- Jenkins B, McInnis M, Lewis C. Step-Up to USMLE Step 2 CK. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2015.
- Bleiweiss IJ. Pathology of breast cancer. In: Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pathology-of-breast-cancer. Last updated June 17, 2016. Accessed Feb 1, 2019
Breast Pathology
By dhillonv10
Breast Pathology
- 527