ClojureScript
A better JavaScript for React/Redux
김동우 @NHNEnt
About Me
- 2006 ~ : Full Stack
- 2012 ~ : 방황
- 2015 ~ : Front-end
Clojure는...
2016년부터 (외롭게) 공부중
Spacemacs!
Clojure
LISP
- 현존하는 가장 오래된 언어 중 하나 (1958)
- LISP가 처음 소개한 개념들
- 조건문, 가비지 컬렉터, 동적 타이핑
- 긴 변수명, 리터럴 데이터 구조
- REPL, 일급함수, 재귀함수, 매크로
- Code As Data - 동형성 (homoiconic)
-
LISt Procesor : 문법 X, 리스트 O
- 전체 코드 : 표현식(Expression)의 트리
Lisp: 해커의 언어



Eric S. Raymond
Paul Graham
Alan Kay
Lisp 연대
1세대
- FORTRAN (1957)
- LISP (1958)
- ALGOL 58 (1958)
- COBOL (1959)
2세대
- Pascal (1970)
- C (1972)
- SmallTalk (1972)
- Scheme (1972)
80년대
- C++ (1980)
- Common Lisp (1984)
- Emacs Lisp (1985)
- Objective-C (1986)
90년대
- Python (1991)
- Racket (1994)
- Java (1995)
- JavaScript (1995)
최근
- Scala (2003)
- Clojure (2007)
- Go (2009)
- Swift (2014)
Clojure: Modern Lisp


LISP (1958)
John McCarthy
Clojure (2007)
Rich Hichey
Clojure
- 함수형 언어 : 불변 데이터형 + 일급 함수
- LISP++ : Code-as-data -> map, vector
- 다형성(Polymorphism) 지원
- 동적(Dynamic) 언어
- JVM 환경에서 실행 (공생 언어)
Why Clojure?
- A Lisp
- for Functional Programming
- symbiotic with an established Platform
- designed for Concurrency
By Rich Hickey
Why Clojure?
- 함수형 언어 : 멀티 스레딩 프로그래밍의 어려움 해결
- Lisp : 간결한 문법. Homoiconic
- JVM 환경에서 실행 : 기존 Java 코드와 호환
- STM 지원 : 동시성 문제 해결
- 성능 : 메모리를 공유하는 불변 데이터 구조 사용
- 지원 : 커뮤니티와 다양한 도구들
Persistent Data Structure

Example
(defn flatten-and-remove-nils
"`interceptors` might have nested collections, and contain nil elements.
return a flat collection, with all nils removed.
This function is 9/10 about giving good error messages."
[id interceptors]
(let [make-chain #(->> % flatten (remove nil?))]
(if-not debug-enabled?
(make-chain interceptors)
(do ;; do a whole lot of development time checks
(when-not (coll? interceptors)
(console :error "expected a collection of interceptors, got:" interceptors))
(let [chain (make-chain interceptors)]
(when (empty? chain)
(console :error "given an empty interceptor chain"))
(when-let [not-i (first (remove interceptor/interceptor? chain))]
(if (fn? not-i)
(console :error "got a function instead of an interceptor" not-i)
(console :error "expected interceptors, but got:" not-i)))
chain)))))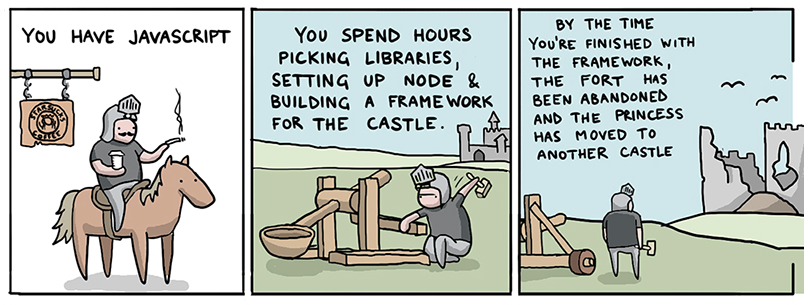
How to save the princess in...
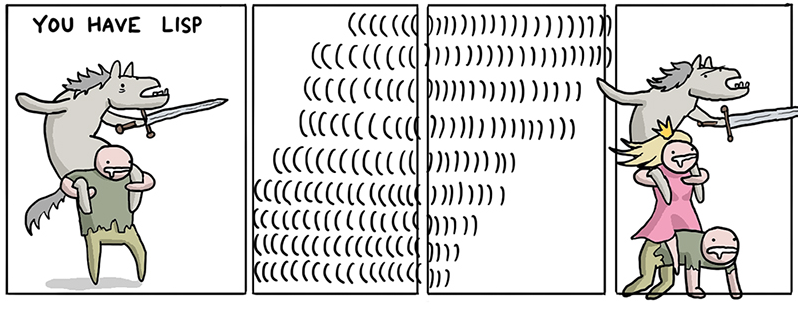
How to save the princess in...

JavaScript
JavaScript
- 1995년 Brendan Eich가 디자인
- 동적 / 약한 타입의 언어
- 멀티 패러다임 언어 : 객체지향 + 절차형 + 함수형
- 인터프리터 언어 (JIT)
Influenced by...
| C | 문법 (if, while, for, switch …) statement 와 expression 구분 |
| Java | 이름, 문법 (new…) Core 및 라이브러리 API (Math, Date…) |
| Scheme | Closure, Lexical Scope 일급함수, 동적 타입, (eval?) |
| Self | Prototype 상속 |
Most Popular Language

Most Popular Language
- 브라우저 환경에서 사용할 수 있는 유일한 언어
- Node.js : 백엔드 개발
- Electron : 데스크탑 어플리케이션 개발
- React Native : 네이티브 모바일 어플리케이션 개발
Any application that can be written in JavaScript, will eventually be written in JavaScript
- Jeff Atwood 2007 -
Most Blamed Language

Most Blamed Language
- Book: JavaScript Good Parts
- wtfjs
- JavaScript Gotchas
- Common JavaScript Errors
Most Blamed Language
- 처음에 단순한 스크립트 언어로 시작
- 웹: 하위호환성을 무시할 수 없음
- ES2015 부터 기존의 많은 문제점 개선
- 현재 아주 빠른 속도로 발전중
- 2017 Most loved Language 11위 (Clojure와 공동)
Caveats
Compile to JavaScript
- 2006 Google Web Toolkit
- 2007 CoffeeScript
- 2011 Dart
- 2011 ClojureScript
- 2012 TypeScript
- 2012 Elm
- 2013 PureScript
- 2016 BuckleScript / Reason
ClojureScript
Rational
- JavaScript’s Reach
- JavaScript is not Robust
- Client-service Applications are on the Rise
- JavaScript Engines Gain Power
- Google Leads the Way
- The Library Problem
ClojureScript
- Clojure 코드를 Javascript 로 변환하는 컴파일러
- Clojure 로 작성됨
- 컴파일을 위해 JVM 환경 필요 (크로스 컴파일러)
- Google Closure Library 사용
- Google Closure Compiler (GCC) 사용
Closure Library
- Google 서비스에 사용되는 오픈소스 라이브러리 셋
- 브라우저 호환성, 네임스페이스, OOP, Math, String, DOM 등 다양한 기능 제공
- ClojureScript 컴파일러가 생성하는 코드에서 사용됨
- Closure Compiler 에 최적화됨

Closure Compiler
- Java 로 작성됨 (실행시 JVM 필요)
- Javascript 코드를 최적화해서 새로운 코드를 생성
- JSDoc 을 최적화 및 검사에 활용
- 문법, 타입 오류, 위험한 코드 검사
- Minify & Mangle
- Dead Code Elimination
- Code Spliting
Persistent Data Structure
JS vs CLJS
Similarities
- First Class Function
- Dynamic Typing
- Anonymous function (Lambda)
- Closure & Lexical Scoping
- Destructuring
- Rest Arguments
- Literal Syntax
- JS: Object / Array
- CLJS: Map / Vector / Set / List
Literal Syntax
// Object
{
name: 'Kim',
age: 32
}
// Array
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
;; Vector
[1 2 3 4 5]
;; List
'(1 2 3 4 5)
;; Map
{:name "Kim"
:age 32}
;; Set
#{1 2 3 4 5}
JS
CLJS
Function
// function declaration
function hello(name) {
return 'Hello, ' + name;
}
// function expression
const hello = function(name) {
return 'Hello, ' + name;
}
// arrow function (ES6)
const hello = (name) => 'Hello, ' + name;
// call
hello('Kim');
;; defn
(defn hello [name]
(str "Hello, " name))
;; def + fn
(def hello
(fn [name]
(str "Hello, " name)))
;; def + #()
(def hello #(str "Hello, " %))
;; call
(hello "Kim")
JS
CLJS
Mutable vs Immutable
const state = {count: 0}
state.count = state.count + 1
;; var
(def state {:count 0})
(def state-a (assoc state :count 1)}
(def state-b (update state :count inc)}
;; atom
(def state (atom {:count 0}))
(swap! state #(update % :count inc))
JS
CLJS
Reference vs Value
const personA = {
age: 32,
name: {first: 'John', last: 'Doe'}
}
const personB = {
age: 32,
name: {first: 'John', last; 'Doe'}
}
console.log(personA === personB)
// false
(def person-a {:age 32
:name {:first "John"
:last "Doe"}})
(def person-b {:age 32
:name {:first "John"
:last "Doe"}})
(println (= person-a person-b))
;; true
JS
CLJS
Core Library
JS
CLJS
map, map-indexed, mapcat, reduce, first, filter, find, flatten, get, get-in, group-by, identical?, interleave, interpose, juxt, keys, last, next, nfirst, nnest, partial, partition, partition-all, partition-by, take, take-last, take-nth, take-while, trampoline, transduce, vals....
map, filter, reduce, concat, assign, some, every, keys, find...
+
Lodash.js
(Ramda.js)
Async
JS
CLJS
core.async
Promise, Generator
Async / Await
+
js-csp
(RxJS)
Tools
| JS | CLJS | |
|---|---|---|
| Dependency | npm / yarn | Leiningen / Boot |
| Scaffolding | Yeoman / CRA | Leiningen / Boot |
| Compile | Babel / TypeScript | Leiningen / Boot |
| Bundling | Webpack / Rollup | Leiningen / Boot |
| Interactive Programming |
Webpack Dev Server | Figwheel |
Comparision
Hot Module Replace ++
Dead Code Elimination ++
Lisp!
Javascript
lodash.js
Immutable.js
js-csp
Babel
Webpack
npm / Yeoman
ClojureScript
Leiningen
Figwheel
JS Interop
Global Vars / API
(js/alert "Hello")
(js/document.getElementById "app")
(js/document.body.lastChild.innerHTML.charAt 7)
(js/some.of.my.libraries.api.method "args")
(js/$.ajax #js {:url "/"
:success (fn [res] (js/console.log res))})
Method / Property
;; same as javacript string
(def s "Hello Clojure")
;; method call
(.toUpperCase s) ;; "HELLO CLOJURE"
;; property access
(.-length s) ;; 13
;; chaning
(def my-div (js/document.querySelector "div"))
(.-length (.toUpperCase (.-innerHTML my-div)))
(->> my-div .-innerHTML .toUpperCase .-length)
(.. my-div -innerHTML toUpperCase -length)
Object / Array
;; macro
(def arr (array 1 2 3))
(def obj (js-obj "x" 1 "y" 2))
;; reader literal
(def arr #js [1 2 3])
(def obj #js {:x 1 :y 2})
;; clj->js function
(def arr (clj->js [1 2 3]))
(def obj (clj->js {:x 1 :y 2}))
;; jc->clj function
(def arr-clj (js->clj arr))
(def obj-clj (js->clj obj))
ClojureScript -> Javascript
React
Declarative
-
Imperative-> Declarative - Virtual-DOM (React Element)
- DOM을 직접 다루지 않고, 가상 DOM의 구조를 반환
- Reconcile 엔진이 변경을 최적화해서 DOM에 반영
Component Based
- Component를 합성하여 UI 구성
- State 와 Props 를 이용해서 정보 전달
-
Template-> JSX (JavaScript Data Structure)
Learn Once,
Write Anywhere
- React Native
- React VR
Sample Code
class Counter extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0
}
increase() {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => this.increase()}>
Count: {this.state.count}
</button>
</div>
);
}
}React
Functional Approach
JSX = JavaScript
<div>
<TodoInput />
<ul>
{todos.map(todo =>
<TodoItem todo={todo} />
)}
</ul>
<div>Completed: {completed.length}</div>
</div>
React.createElement(
"div",
null,
React.createElement(TodoInput, null),
React.createElement(
"ul",
null,
todos.map(function (todo) {
return React.createElement(
TodoItem, { todo: todo }
);
})
),
React.createElement(
"div",
null,
"Completed: ",
completed.length
)
);
Component = Function
- Input : Props
- Ouput : V-DOM(React Element) Tree
All React components must act like pure functions with respect to their props.
Immutable Props
- Props는 수정할 수 없음
Whether you declare a component as a function or a class,
it must never modify its own props
Immutable State
- this.state 직접 변경 금지
- this.setState() 를 호출해서 명시적 변경
Never mutate this.state directly,
as calling setState() afterwards may replace the mutation you made.
Treat this.state as if it were immutable.
SholuldComponentUpdate





SCU
Immutability for Performance
- Shallow 비교만으로 변경여부를 알 수 있음
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
const isPropsChanged = shallowEqual(this.props, nextProps);
const isStateChanged = shallowEqual(this.state, nextState);
return isPropsChanged || isStateChanged;
}
render() {
return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>;
}
}
class MyComponent extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
return <div className={this.props.className}>foo</div>;
}
}
Reagent
- 함수만으로 컴포넌트를 작성
- vector, map 만으로 (Hickup) DOM 구조 표현
- State 관리를 위한 r/atom 제공 (atom 확장)
- 변경될 때마다 deref 하는 컴포넌트를 자동으로 Re-render
- Value 비교를 통한 성능 최적화
Simple React Wrapper
Reagent provides a minimalistic interface between ClojureScript and React.
Sample Code
(def click-count (r/atom 0))
(defn counting-component []
[:div
"The atom " [:code "click-count"] " has value: "
@click-count ". "
[:input {:type "button" :value "Click me!"
:on-click #(swap! click-count inc)}]])
(defn hello-component [name]
[:p "Hello, " name "!"])
(defn say-hello []
[hello-component "world"])React vs Reagent
Simple Component
function simpleComponent() {
return (
<div>
<p>I am a component!</p>
<p className="someclass">
I have
<strong>bold</strong>
<span style={{color: "red"}}> and red</span>
text.
</p>
</div>
)
}
React
Simple Component
(defn simple-component []
[:div
[:p "I am a component!"]
[:p.someclass
"I have "
[:strong "bold"]
[:span {:style {:color "red"}} " and red "]
"text."]])
Reagent
Nested Component
const todos = [
'Learn ClojureScript',
'Learn Reagent',
'Learn Reframe'
];
function TodoItem(props) {
return <li className="todo-item">{props.todo}</li>;
}
function TodoList() {
return (
<ul className="todo-list">
{todos.map(todo => <TodoItem todo={todo} />)}
</ul>
);
}
React
Nested Component
(def todos ["Learn ClojureScript"
"Learn Reagent"
"Learn Reframe"])
(defn todo-item [todo]
[:li {:class "todo-item"} todo])
(defn todo-list []
[:ul {:class "todo-list"}
(for [todo todos] [todo-item todo])])
Reagent
State
function TodoItem({todo, deleteTodo}) {
return (
<li className="todo-item">
{todo.text}
<button onClick={() => deleteTodo(todo.id)}>X</button>
</li>
);
}
class TodoList extends React.Component {
state = {
todos: [
{id: 1, text: 'Learn ClojureScript'},
{id: 2, text: 'Learn Reagent'},
{id: 3, text: 'Learn Reframe'}
]
}
deleteTodo = (targetId) => {
const {todos} = this.state;
this.setState({
todos: todos.filter(({id}) => targetId !== id)
});
}
render() {
return (
<ul className="todo-list">
{this.state.todos.map(todo =>
<TodoItem
key={todo.id}
todo={todo}
deleteTodo={this.deleteTodo} />
)}
</ul>
);
}
}React
State
(def todos (r/atom [{:id 1, :text "Learn ClojureScrpt"}
{:id 2, :text "Learn Reagent"}
{:id 3, :text "Learn Reframe"}]))
(defn delete-todo [todo]
(swap! todos (partial remove #(= todo %))))
(defn todo-item [todo]
[:li {:class "todo-item"}
(:text todo)
[:button {:on-click #(delete-todo todo)} "X"]])
(defn todo-list []
[:ul
(for [todo @todos]
^{:key (:id todo)} [todo-item todo])])
Reagent
Controlled Component
React
class TodoInput extends React.Component {
state = {value: ''}
onChange = ev => {
this.setState({value: ev.target.value});
}
onKeyPress = ev => {
if (ev.which === 13) {
this.props.addTodo(this.state.value);
}
}
render() {
return (
<input type="text"
onChange={this.onChange}
onKeyPress={this.onKeyPress}
value={this.state.value} />
);
}
}
Controlled Component
Reagent
(defn todo-input []
(let [value (r/atom "")
on-change #(reset! value (.. % -target -value))
on-key-press #(if (= (.-which %) 13)
(add-todo @value))]
(fn []
[:input {:type :text
:on-change on-change
:on-key-press on-key-press
:value @value}])))
Performance
React
class Counter extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
const {idx, increase, data: {info, value}} = this.props;
return (
<button onClick={() => increase(idx)}>
{info.name} : {value}
</button>
);
}
}
class CounterApp extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
counters: [
{info: {name: "counter1", step: 5}, value: 0},
{info: {name: "counter2", step: 10}, value: 0},
{info: {name: "counter3", step: 15}, value: 0}
]
}
increase = idx => {
const counters = [...this.state.counters];
const target = counters[idx];
counters[idx] = {
...target,
value: target.value + target.info.step
}
this.setState({counters});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.state.counters.map((data, idx) =>
<Counter key={idx} idx={idx}
data={data} increase={this.increase} />
)}
</div>
);
}
}
Performance
Reagent
(def counters (r/atom [{:info {:name "count1" :step 5} :value 0}
{:info {:name "count2" :step 10} :value 0}
{:info {:name "count3" :step 15} :value 0}]))
(defn counter [idx {{:keys [name step]} :info value :value}]
(let [increase #(+ step value)
on-click #(swap! counters update-in [idx :value] increase)]
[:button {:on-click on-click}
(str name " : " value)]))
(defn counter-app []
[:div
(map-indexed (fn [idx data]
^{:key idx} [counter idx data]) @counters)])
Conclusion
| React | Reagent | |
|---|---|---|
| HTML | JSX (Syntax) | Hiccup (Data) |
| Component | function, Class | function |
| Data 전달 | props (this.props) 객체 | arguments |
| State 변경 | this.setState() | r/atom 변경 |
| State 변경 (부모) | this.setState() 호출하는 함수를 props로 전달 | r/atom 변경 |
| 성능 | showComponentUpdate() PureComponent |
자동 최적화 |
Redux
React의 State 관리
- React만으로는 State 관리가 어려움
- State를 관리하는 별도의 레이어가 필요
- Redux, Relay, MobX 등을 사용


Redux - Concept
- 단방향 데이터 흐름
- 단일 스토어
- CQRS / Event Sourcing

Redux
기존 MVC

Single source of truth
- 전체 어플리케이션의 상태를 단일 트리 형태로 저장
- 전체 상태를 관리하고, 서버 등의 환경과 공유하기 쉬움
- 개발도구에서 상태가 변경된 모든 이력을 확인
console.log(store.getState())
/*
{
visibilityFilter: 'SHOW_ALL',
todos: [
{
text: 'Consider using Redux',
completed: true,
},
{
text: 'Keep all state in a single tree',
completed: false
}
]
}
*/State is Read-Only
- State를 직접 변경할 수 없음 (setter X)
- 오직 Action(데이터 객체) 을 발생시켜서 State를 변경
- Event Sourcing -> 전체 변경내역을 관리하기 용이
- 하나의 Action에 하나의 변경 -> 복잡한 상호관계가 없음
store.dispatch({
type: 'COMPLETE_TODO',
index: 1
})
store.dispatch({
type: 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER',
filter: 'SHOW_COMPLETED'
})Pure function & Immutable State
- Reducer는 순수 함수 (Side Effect 없음)
- 각 Action에 맞게 항상 새로운 state 반환
function todos(state = [], action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD_TODO':
return state.concat([{ text: action.text, completed: false }])
case 'TOGGLE_TODO':
return state.map(
(todo, index) =>
action.index === index
? { text: todo.text, completed: !todo.completed }
: todo
)
default:
return state
}
}Why Immutable?
- Performance
- 상태의 변경을 확인할 때, 레퍼런스만으로 Shallow 비교가 가능
- React가 추구하는 방식과 잘 어울림
- Time-Travel Debugging
- 상태 변경의 모든 이력을 저장하기 쉬움
- Time-Travel 디버깅 가능
- Hot Module Replacement
- 테스트가 용이
Immutability
in Javascript
Example
const state = {
artist: {
name: {
first: 'Michael',
last: 'Jackson'
},
born: '1958-08-29'
},
genre: ['pop', 'soul', 'disco', 'rock'],
albums: []
}
Plain Javascript
function updateLastName(state, lastName) {
return {
...state,
artist: {
...state.artist,
name: {
...state.artist.name,
last: lastName
}
}
};
}
const state1 = updateLastName(state, 'Jordan');
const state2 = updateLastName(state, 'Jordan');
console.log(state1 === state2); // false
Lodash-fp / Ramda
import _ from 'lodash/fp'
function updateLastName(state, lastName) {
return _.set(state, ['artist', 'name', 'last'], lastName);
}
const state1 = updateLastName(state, 'Jordan');
const state2 = updateLastName(state, 'Jordan');
console.log(state1 === state2); // false
Immutable.js
// Immutable 객체로 변경
const stateIM = Immutable.Map(state);
function updateLastName(state, lastName) {
return state.setIn(['artist', 'name', 'last'], lastName);
}
// 비교
const state1 = updateLastName(staetIM, 'Jordan');
const state2 = updateLastName(staetIM, 'Jordan');
console.log(state1 === state2); // false
console.log(state1.equal(state2)); // true
// 일반 JS로 변경
const stateJS = stateIM.toJS();
ClojureScript
(def state
{:artist {:name {:first "Michael"
:last "Jackson"}
:born "1958-08-29"}
:genre ["pop" "soul" "disco" "rock"]
:albums []})
(defn update-last-name [state last-name]
(assoc-in state [:artist :name :last] last-name))
(def state1 (update-last-name state "Jordan"))
(def state2 (update-last-name state "Jordan"))
(js/console.log (= state1 state2)) ;; true

https://hackernoon.com/functional-programming-in-javascript-is-an-antipattern-58526819f21e

https://hackernoon.com/functional-programming-in-javascript-is-an-antipattern-58526819f21e
Reframe
Reframe
- Redux 와 비슷한 시기에 등장 (2015)
- Reagent 기반 (Ratom 사용)
- Redux와의 유사성
- 단방향 데이터 흐름
- 단일 State / Event Sourcing
- Redux와의 차이점
- Event + Effect (vs Action)
- Subscription
- 모든 것은 Data (Effect, Interceptor)
Action
- type 을 갖는 순수 객체
- Reducer로 바로 전달되면 Store를 변경시킴
- 다른 Side Effect 위해서는 Middleware 사용
{
type: 'ADD_TODO',
text: 'Learn Reframe'
}
{
type: 'TOGGLE_TODO',
id: 10
}Event
- Vector 형식의 데이터
- Event Handler 가 처리 -> Effect 발생
- 어플리케이션의 상태에 영향을 끼칠 수 없음
[:add-todo "Learn Reframe"]
[:toggle-todo 10]
Effect
- Side Effect 를 위한 데이터 (Map)
- Effect Handler가 실제 Effect 를 발생
{:db {:todos [{:id 1
:text "Learn Reframe"
:completed false}]}
:http {:method :post
:url "http://my.app/todos"
:on-success [:process-response]
:on-fail [:failed-todos]}}
Subscription
Redux (+ Reselect)
import { createSelector } from 'reselect'
const getShowing = (state) => state.showing
const getTodos = (state) => state.sortedTodos
export const getVisibleTodos = createSelector(
[getShowing, getTodos],
(showing, todos) => {
switch (showing) {
case 'ALL':
return todos
case 'DONE':
return todos.filter(t => t.completed)
case 'ACTIVE':
return todos.filter(t => !t.completed)
}
}
)
Subscription
Reframe
(ns todoapp.subs
(:require [re-frame.core :refer [reg-sub]]))
(reg-sub :showing #(:showing %))
(reg-sub :todos #(vals (:sorted-todos %)))
(reg-sub :visible-todos
:<- [:showing]
:<- [:todos]
(fn [[showing todos] _]
(filter (case showing
:done :done
:active (complement :done)
:all identity) todos)))Redux vs Reframe


Redux
Reframe
Conclusion
Redux
Reselect
Reframe
Javascript
Immutable.js
lodash.js
ClojureScript
React
Recompose
Reagent
npm / webpack
Babel / react-create-app
Leiningen
Figwheel
And...
- 간결한 문법
- macro
- Clojure 라이브러리
- Interactive Programming
- clojure.spec
- core.async
But...
- 어려워...요..
- JVM...
- 디버깅...
Companies
감사합니다 :)
clojurescript-reagent-reframe
By DongWoo Kim
clojurescript-reagent-reframe
- 1,871



