Digital Media
3D Graphics
3D Modeling
3D Rendering
(This distinction seems to be slowly collapsing)
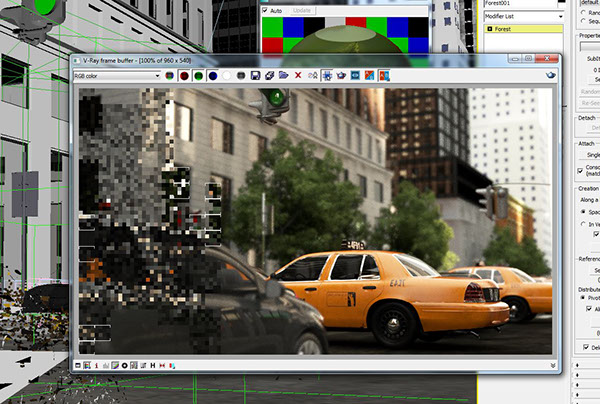
Non Real-time
Real-time
CPU
(e.g. Vray)
GPU
(e.g. Rhino Interface)
Know the difference!

Memory
HDD
GPU
Memory
CPU
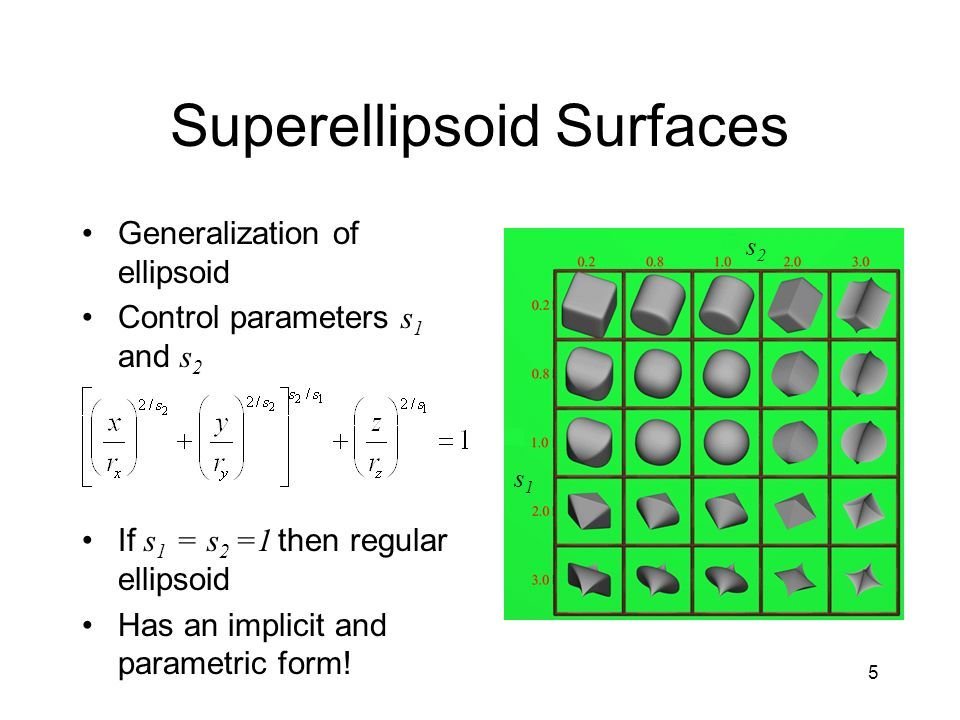
Polygons vs. NURBS
Polygonal Modeling
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational Basis Spline)
Based on Mathematical Model, Higher Level, More Intuitive
Points (Vertices) > Curves > Surfaces (Abstraction that's ultimately rendered as polygons)
Points (Vertices) > Triangles (Mesh)
Lower Level, Less Intuitive, More Efficient for 3D Rendering
Know the difference!
NURBS vs. Polygons
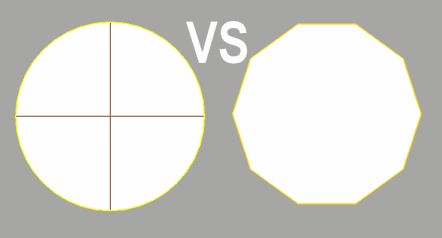
NURBS vs. Polygons



NURBS vs. Polygons
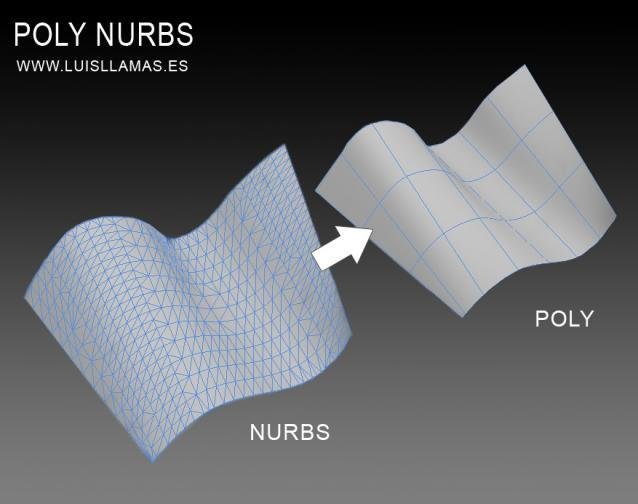
A
B
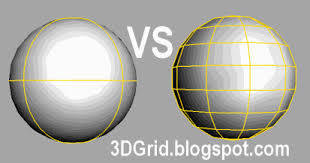
NURBS vs. Polygons
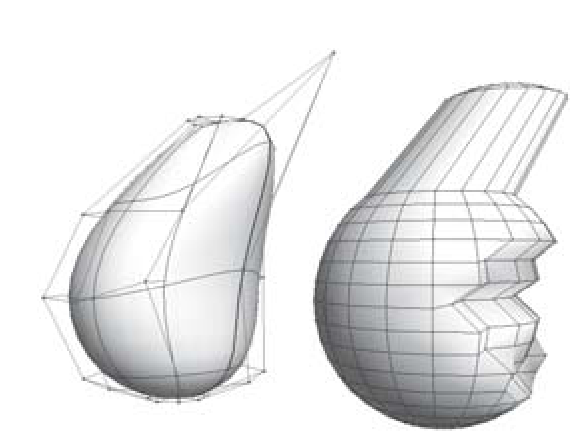
B
A
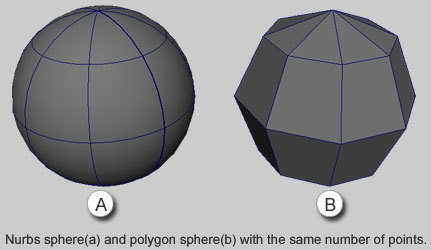
NURBS vs. Polygons
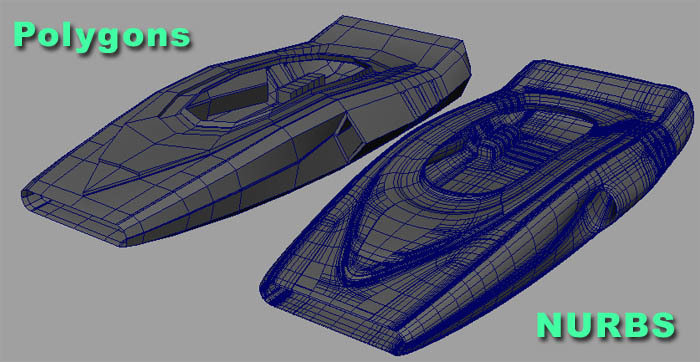
B
A
NURBS vs. Polygons



Polygons
NURBS
NURBS
Polygons
Polygons vs. NURBS
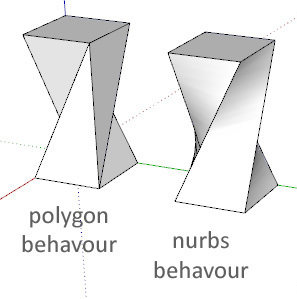
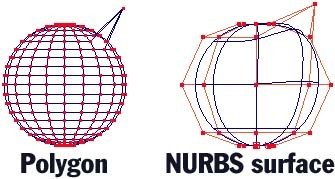
NURBS
Behavior
Polygon
Behavior
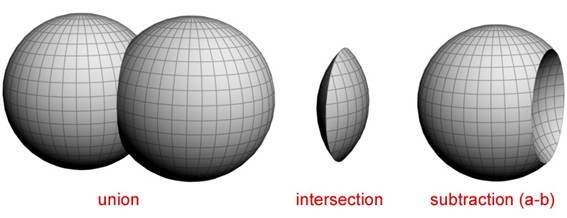
Solid Modeling
Emphasis on Physical Fidelity
Can Be Based on
Mathematical Functions

Solid Modeling
Boolean Geometric Operations
Solid Modeling
Boolean Geometric Operations
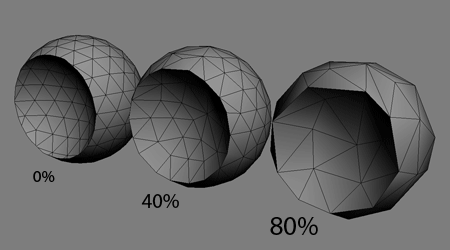
All 3D computer graphics abstractions are fundamentally comprised of small triangles (facets, faces, etc.)
Through the process of Tesellation

Graphic Tessellation
Architectural Tessellation

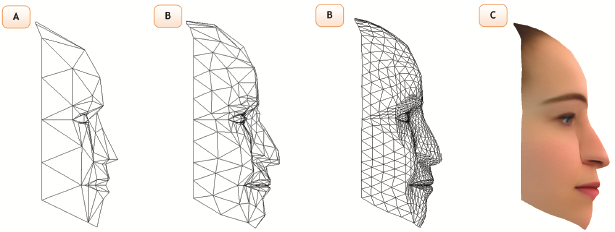
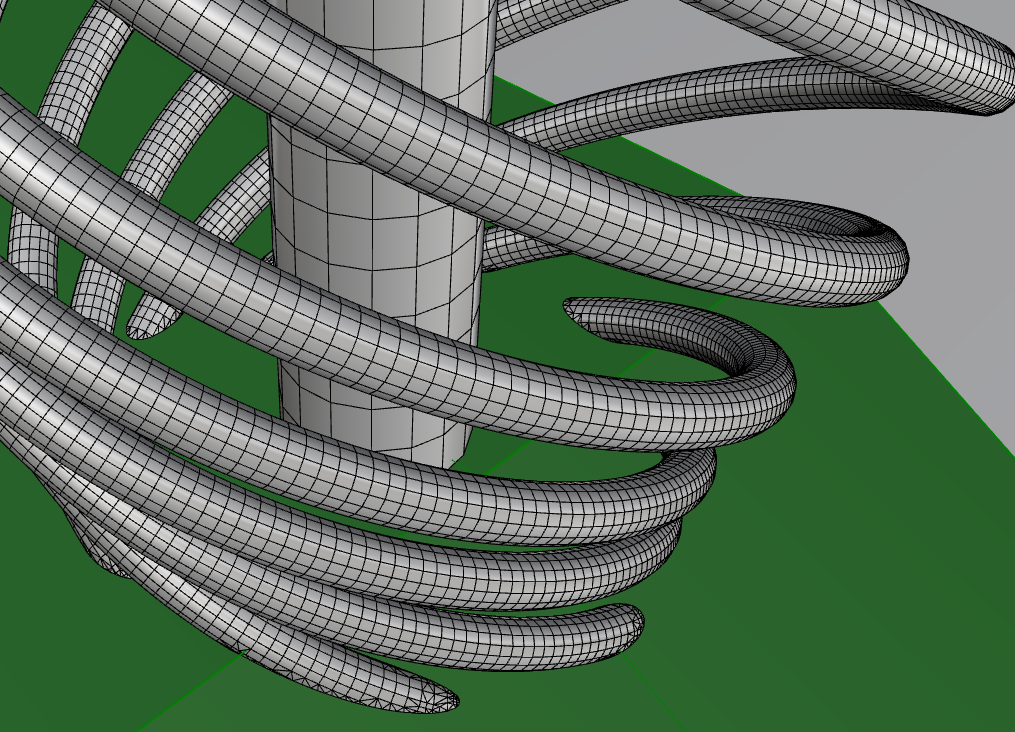
Number of vertices needed grows with the amount of curvature in the geometry.
Try to imagine how many vertices/faces would be needed to model thin "piped" geometries.
e.g. Modeling hair is a difficult computational problem.
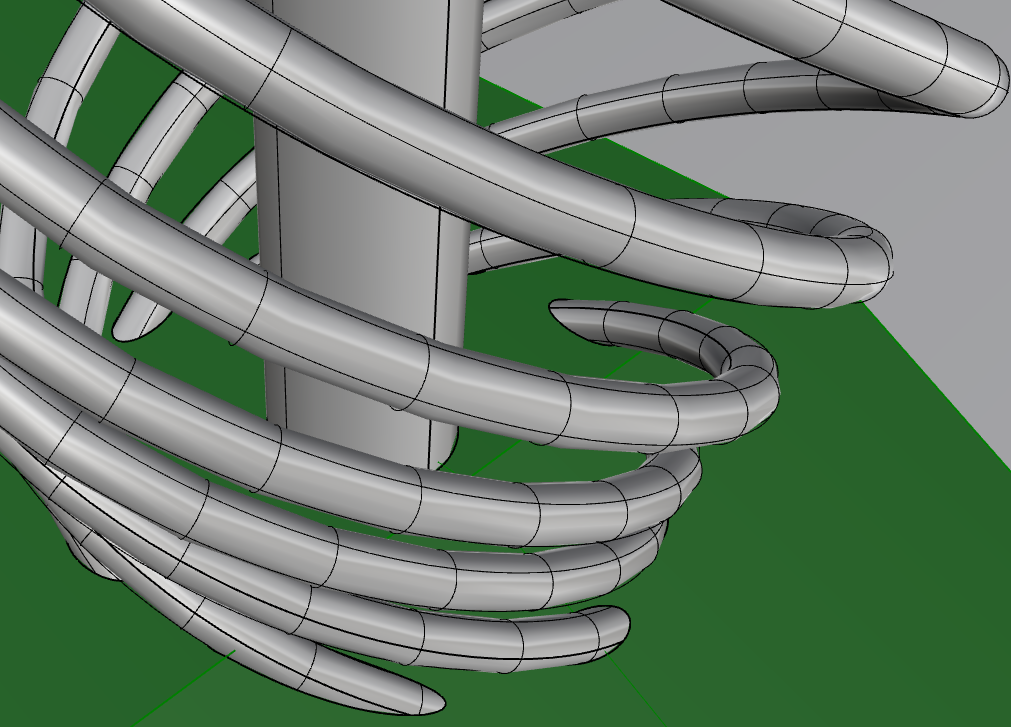
NURBS
Mesh (Polygons)
3D Graphics
By Eddy Man Kim
3D Graphics
- 1,717