Intro to WordPress:
The Absolute Basics
Instructors: Gordon Seirup & Jess Quig

http://slides.com/gordonium/wp-intro-lesson-1
What is WordPress?
-
An open-source content management system (CMS)
-
-
Open-source:
-
Code is freely available (free to use, allowed to be edited)
-
Developed and supported by a volunteer community
-
-
CMS: Interface for creating/editing digital content; users don’t have to be coders
-
-
The most popular CMS - WP powers:
-
~27% of all websites
-
~50-60% of all websites using a CMS *
-

* Source: https://www.codeinwp.com/blog/wordpress-statistics/
Why WordPress?
-
WordPress is a publishing platform
-
Highly customizable (even without touching code)
-
Themes <-- more later!
-
Plugins <-- more later!
-
-
Easy to learn
-
Tons of support available in all forms (classes, text & video tutorials, forums…)
-
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) friendly
-
Can handle simple sites to (fairly) large e-commerce
WordPress.com vs WORDPRESS.org
| Hosting is provided | You get your own hosting |
|---|---|
| Free domain (___.wordpress.com) or pay extra for custom | Buy your own, custom domain |
| Limited flexibility (no plugins, no base code access) | Extremely flexible |
| Good if you just want to blog and custom functionality isn't important | Good if... <-- that's not good enough |
3 Main Parts of Wordpress: Core
CORE
Theme
Plugins
-
WordPress core: all of the files WordPress needs to run
- Download from wordpress.org (pre-installed on some hosting)
- Usually gets updated a few times a year (currently 4.6.1)
- You will never touch most of these files
3 Main Parts of Wordpress: THeme

CORE
Theme
Plugins
-
Themes: files layered on top of WordPress core that modify the appearance and (sometimes) functionality of a site (usually on the front-end, but sometimes on the backend, too - ex: Divi)
-
Free vs premium
-
3 Main Parts of Wordpress: Plugins

CORE
Theme
Plugins
-
Plugins: Software pieces that can be uploaded to your site to expand its functionality
-
Free vs premium vs custom
-
Ex: WordPress plugin library (free plugins)
-
Ex: Wellmont widgets (custom plugin)
-
Log into our test site!
-
USER: lcsclass
-
PASS: lovelandcreatorspacerocks
Try It Out!
Pages vs Posts
- Relatively static content (ex: About page, Contact page)
- Usually provide the base structure of your website
Both:
- Text editor
- Status (published, draft, etc)
- Visibility
- Publish date
- Featured image
- Usually time-oriented content that is updated often (ex: journal, announcements)
- Usually displayed in date order
- Can use tags and categories (user sorting)
- Displayed in RSS feed of site
TRY IT OUT!
Media
- Upload images, documents, and small videos:
- Drag & drop or regular media uploader
- Max upload size: 1MB
- (can also add to images folder in FTP)
- Edit:
- Very basic image editing (rotate, flip, resize)
- Use:
- Add in widget areas / page editor
STOP! Just Watch For This!
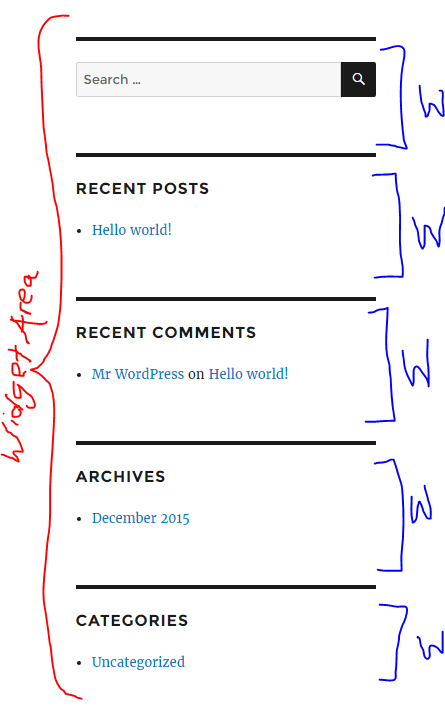
widgets
- To edit, go to Appearance > Widgets
-
Widget area: a specific location on a page or post that contains widgets
- Ex) Sidebar
-
Widget: a small area that serves a specific function
- Ex) Search bar
STOP! Just Watch For This!
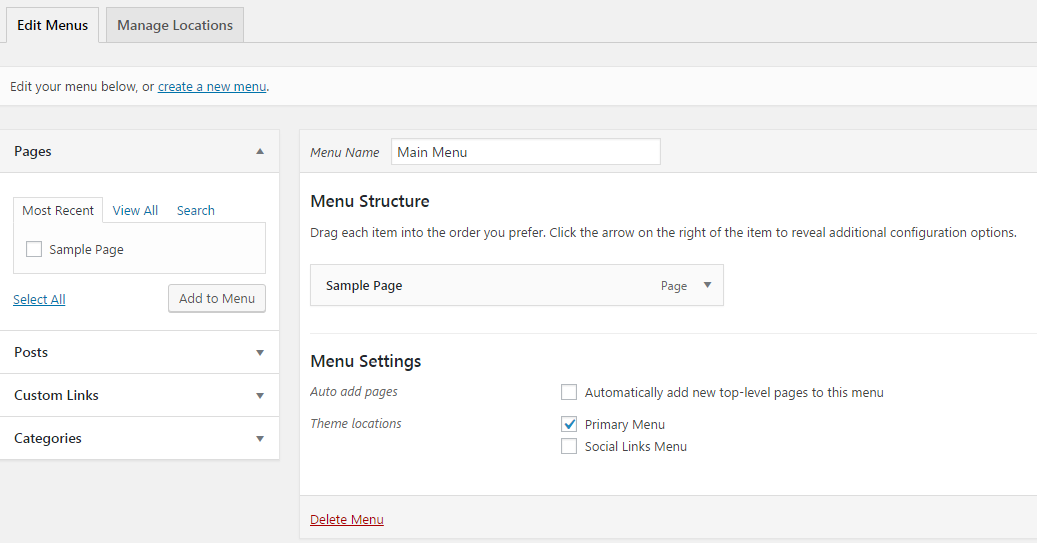
Menus
- To edit, go to Appearance > Menus
- Location options will vary by theme
STOP! Just Watch For This!
Settings
- General: Site title, tagline, timezone, etc
- Reading: Front page display, SE visibility, etc
- Discussion: Allow comments, etc
- Permalinks: Set to 'post name' unless you have good reason
Hosting
- Regular hosting: Stores your website on a server and makes it available on the internet
-
Managed WordPress hosting: Usually have beefed up services specifically targeted at the needs of WordPress sites
- Example services: WP-specific security, speed, updates, daily backups, website uptime monitors
Homework
- Pick WordPress.com or WordPress.org
- If .org, pick regular or Managed hosting (click linked images below)
- Set up an account, install WP (if not provided by host), dink around 'til next week.
- Questions? Things you'd like to cover?
- Email jess@copperleafcreative.com
- Subject: CreatorSpace class
WP Intro Course - Lesson #1: The Absolute Basics
By Gordon Seirup
WP Intro Course - Lesson #1: The Absolute Basics
- 1,339






