networking
Introduction to basic network concepts
osi layers
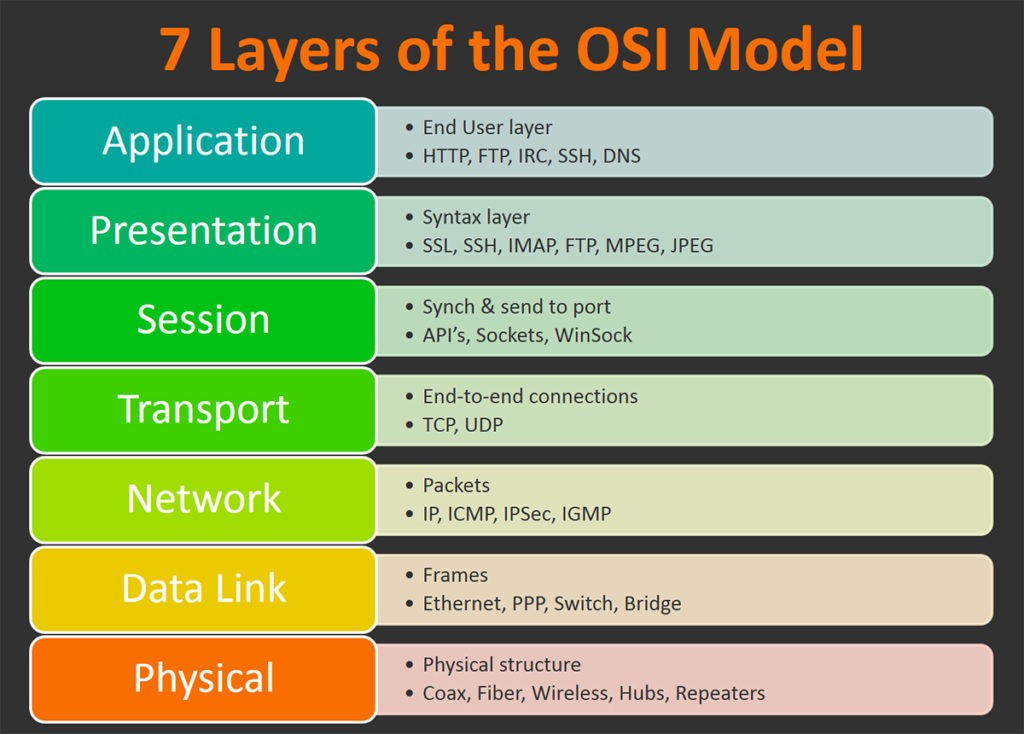
physical layer
Provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface.
physical layer
Defines the means of transmitting a stream of raw bits.
LInk LAYER
Provides transfer of data frames between hosts connected to the physical link.
LInk LAYER
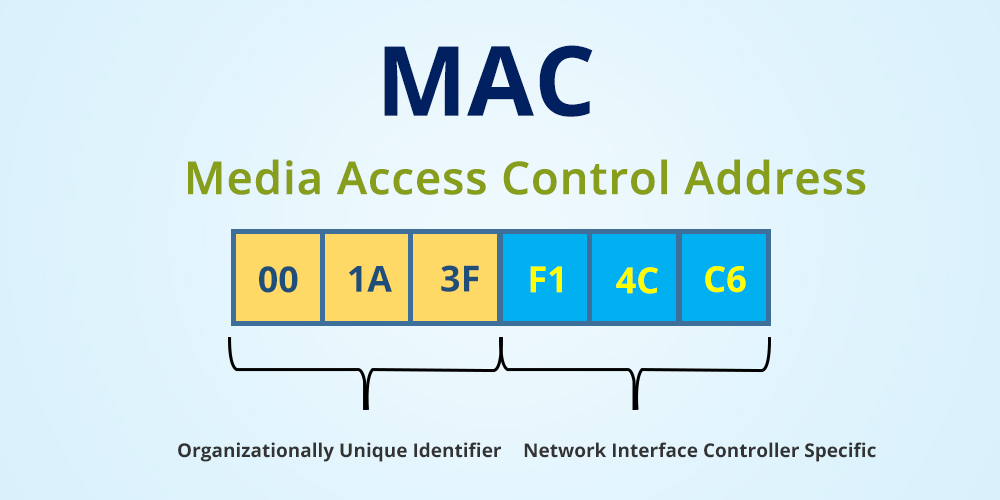
Media Access Control (MAC) address.
Can be impersonated.
network layer
Provides packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers.
network layer
Relaying datagrams across network boundaries.
Internet Protocol
network layer
Internet Protocol

network layer
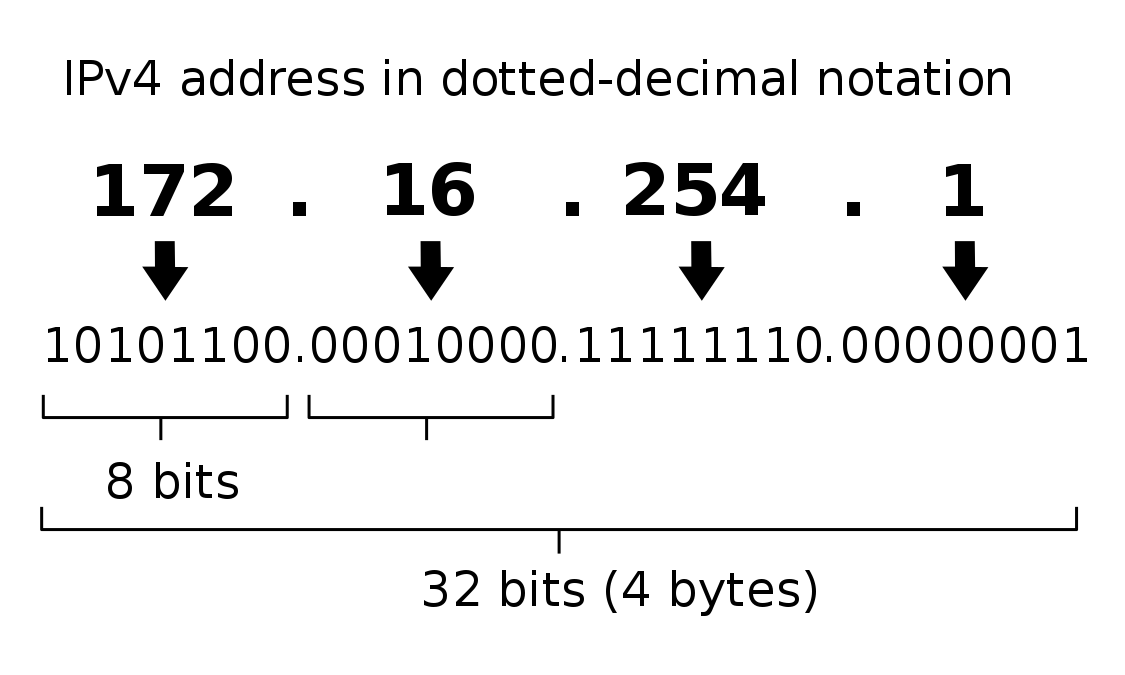
An IP mask identifies a range of IPs.
Internet Protocol: SUBNET
network layer
A mask is a number, from 8 to 32.
Internet Protocol: SUBNET
network layer
The mask specifies the IP starting bits that are "fixed".
Internet Protocol: SUBNET
network layer
Internet Protocol
network layer
Adheres to the end-to-end principle.
Internet Protocol
network layer
It's a ping!
icmp
transport layer
Provides end-to-end communication services for applications.
transport layer
Connection-oriented protocol.
tcp
transport layer
Ordered data transfer.
tcp
transport layer
Retransmission of lost/corrupted packets.
tcp
transport layer
Connectionless protocol.
udp
transport layer
Transaction oriented.
udp
transport layer
Stateless.
udp
transport layer
No guarantee of delivery.
udp
session layer
Session checkpointing and recovery.
session layer
Sockets are defined by an application programming interface (API) for the networking architecture.
session layer
Sockets are created only during the lifetime of a process of an application
session layer
Number assigned to uniquely identify a connection endpoint and to direct data to a specific service.
ports
session layer
Well-known ports 0-1023
Maintained by IANA.org.
ports
session layer
Registered ports 1024-49151
Registered with IANA.org.
ports
session layer
Ephemeral ports 49152–65535
Can not be registered with IANA.org.
ports
session layer
ports
| Number | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 21 | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Command Control |
| 22 | Secure Shell (SSH) Secure Login |
| 25 | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) email delivery |
| 53 | Domain Name System (DNS) service |
| 80 | Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) |
| 123 | Network Time Protocol (NTP) |
| 443 | HTTP Secure (HTTPS) HTTP over TLS/SSL |
session layer
Transport Protocol +
IP address +
Port number
socket address
presentation layer
Provides a bridge between session and application layer.
application layer
Provides communications protocols and interface methods used in process-to-process transmissions.
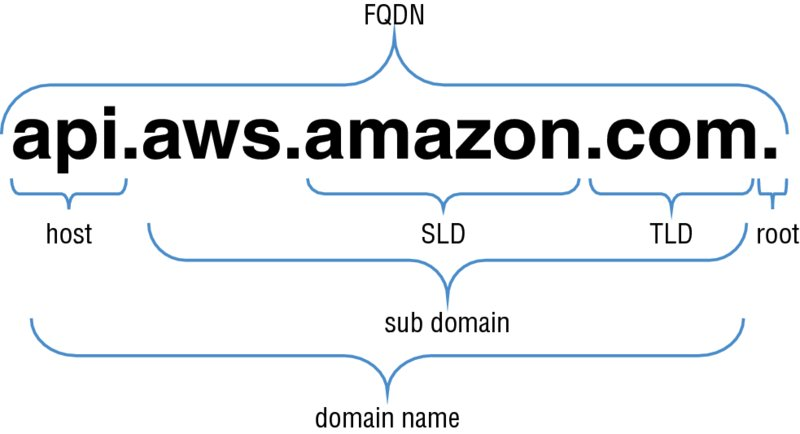
service: dns
Hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to identify computers reachable through Internet Protocol networks.
SERVICE: dns
SERVICE: dns
They are configured in the DNS root zone as 13 named authorities.
root servers
SERVICE: dns
Server that gives answers in response to questions asked about names in a zone.
AUTHORITATIVE NAME servers
SERVICE: dns
To improve efficiency, reduce traffic, and increase performance in end-user applications the results can be cached with a TTL.
cache NAME servers
SERVICE: dns
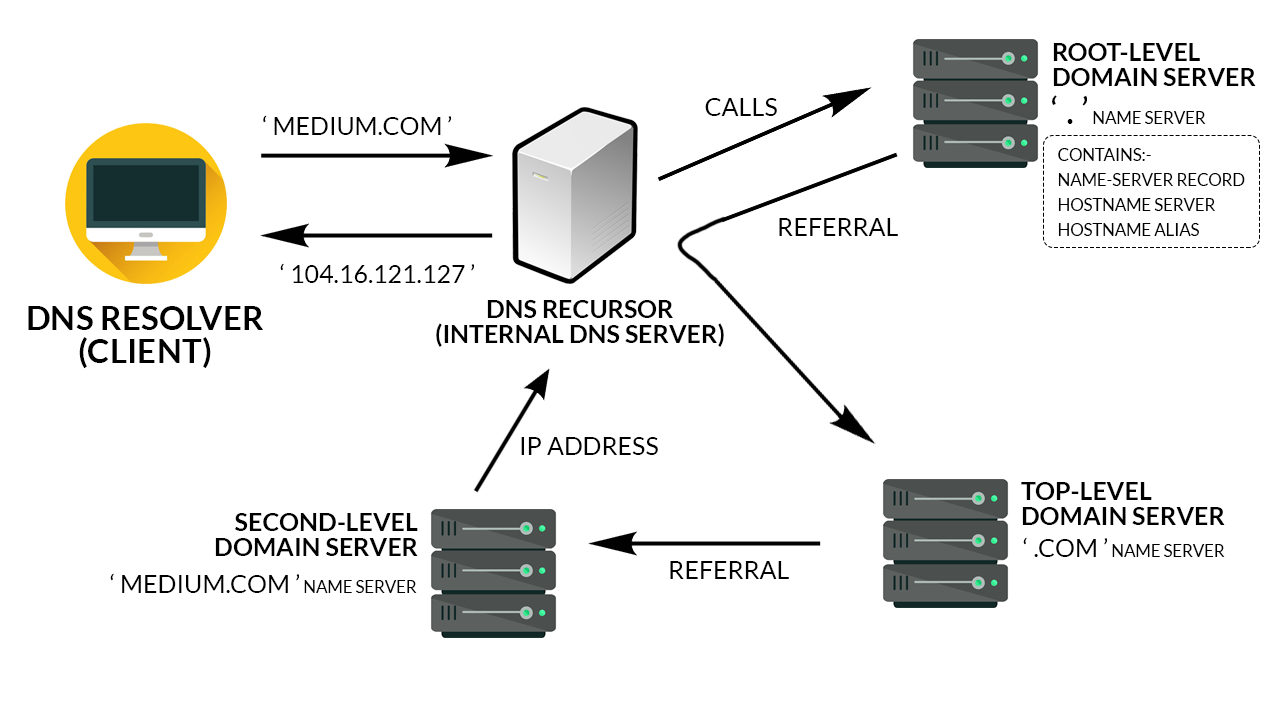
SERVICE: dns
Propagation unreliable.
protocol: tls/ssl
Provides security, including privacy (confidentiality), integrity, and authenticity through the use of cryptography.
protocol: tls/ssl
Runs over TCP.
protocol: tls/ssl
Negotiates cipher to use.
application layer
Handshake with an asymmetric cipher.
tls/ssl
application layer
Server provides identification in the form of a digital certificate.
tls/ssl
application layer
Certificate contains:
- server name
- the trusted certificate authority (CA) - the server's public encryption key
tls/ssl
application layer
Client confirms the validity of the certificate with the CA provided.
tls/ssl
application layer
Generation of a shared session secret key.
tls/ssl
application layer
Communication is encrypted using a symmetric cipher with the shared session secret key.
tls/ssl
protocol: http
Provides distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems interconnection.
protocol: http
Runs over TCP.
protocol: http
Allows redirections.
protocol: http
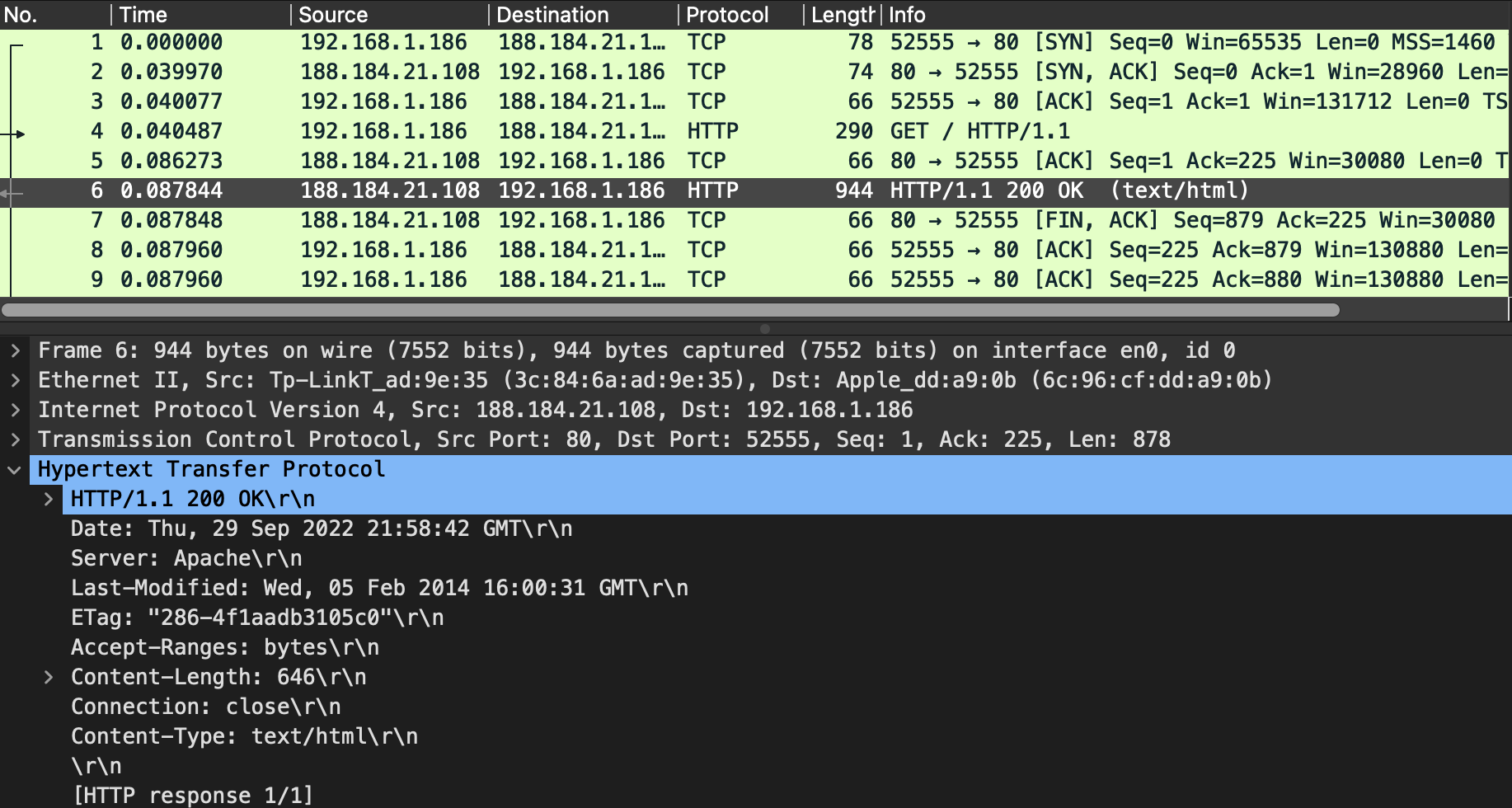
protocol: https
HTTP over TLS.
protocol: https
Everything goes encrypted over TLS.
protocol: https
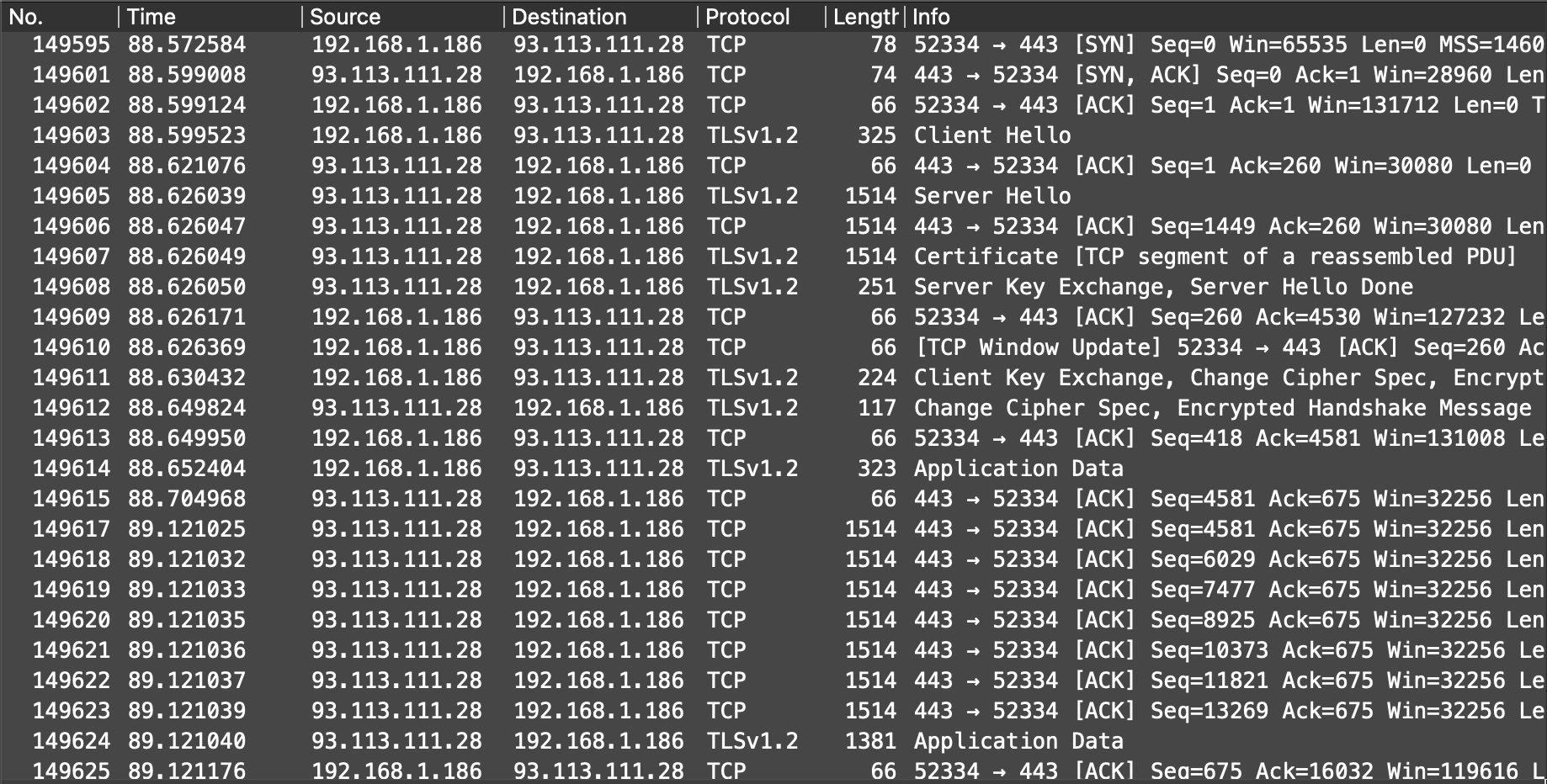
protocol: https
Used to terminate and/or establish TLS (or DTLS) tunnels by decrypting and/or encrypting communications.
tls proxy
protocol: https
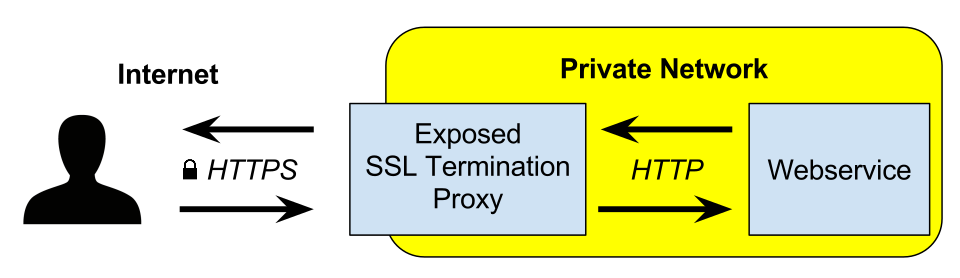
tls proxy
protocol: https
tls proxy
It can modify requests.
sources
Networking
By Gorka Guridi
Networking
Introduction to testing with pytest
- 78



