System's Architecture
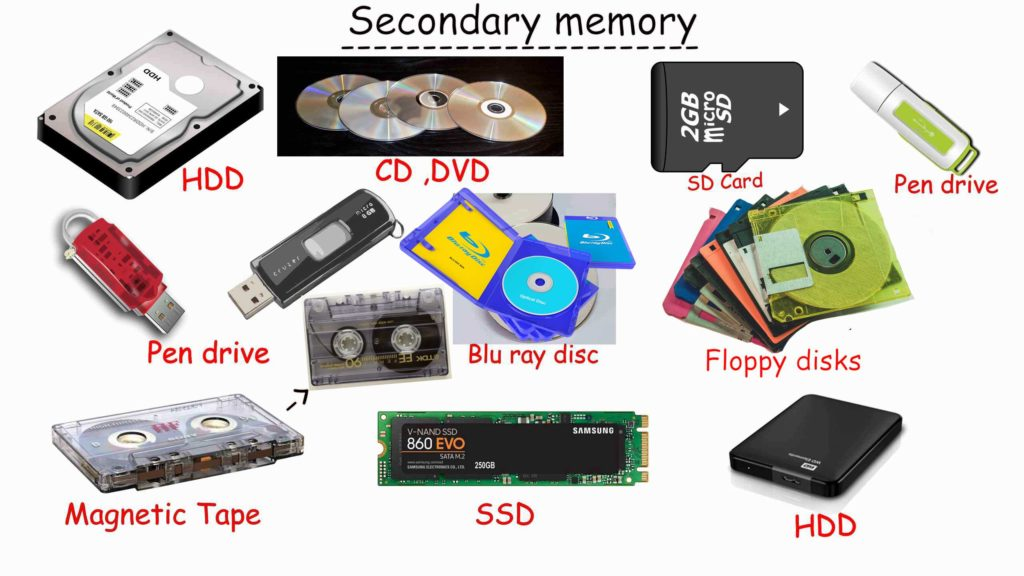
Secondary Storage

Secondary Storage
-
Any non-volatile, long-term storage mechanism not directly accessible by the CPU.
-
Without secondary storage all programs and data would be lost the moment the computer is switched off.
-
There are three main types of secondary storage in a computer system: solid state storage devices, optical storage devices, magnetic storage devices.
-
Not all computers require secondary storage. Embedded computers, such as those found in a washing machine or central heating system, do not need to store data when the power is turned off.
Questions
- Why do we need secondary storage?
- What is stored on secondary storage in a computer system?
Questions
- Why do we need secondary storage?
RAM is volatile, so will not store data when the power is removed. Secondary storage, will contain the you data/files for when the computer is switched on again.
- What is stored on secondary storage in a computer system?
The operating system, data, images, programs, documents, etc...
Magnetic Storage
-
Uses magnetism to store data.
-
Most common device is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
-
Reliable and low cost per GB.
-
Ideal for large amounts of storage.
-
Currently in the multi-terrabyte capacities.
-
Likely to be damaged by shock (dropped) and strong magnetic fields.

HDD Operation
-
Stack of disks, called platters, coated in a magnetic material.
-
Effectively billions of tiny magnets, north = 1 and south = 0.
-
The platters rotate and a set of sensors (heads) move across the platters sensing the change of north/south alignment of the magnets.

Solid-State Storage
-
Uses flash memory, electronic circuits to store data.
-
Very fast access times, due to no moving parts.
-
Relatively expensive compared to magnetic storage (changing rapidly).
-
Many different form factors (shapes): SD card, USB drive, SATA, M2...
-
Replacing magnetic drives for most systems, exception being very large storage requirements.

Solid-State Advantages
-
Magnetic drives have a delay (latency) in accessing data because the head needs to move across the platter, SSD do not have moving parts, reducing the latency.
-
The lack of moving parts also means the power consumption is lower and there is no heat or noise.
-
SSD's do not experience slow speeds due to data fragmentation.
-
SSD's are smaller and lighter, allowing more portable devices.
-
SSD's are more robust as they are not as affected by shocks.

Optical Storage
-
CDs, DVDs, Blu-Ray
-
Use light to read data
-
CD — 700 MB
-
DVD — 4.7 GB single layer or 8.5 GB dual layer
-
Blu-Ray — 25 GB single layer or 50 GB dual layer
-
Tend to be used to store data never to be changed.

Optical Storage
-
Lasers are used to write and read the data.
-
The surface of the disk is covered in billions of indentations.
-
When the light is shone on the disk the indentations will reflect differently depending on whether is hits an indentation or not.
-
This difference in the reflected light is interpreted as either a 1 or a 0 to represent binary data.

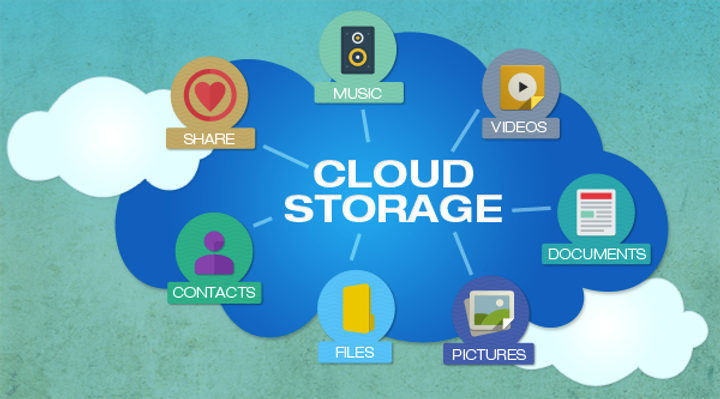
Cloud Storage
-
Data that is accessed via the internet rather than being stored locally on your computer, phone, etc.
-
A network of servers that store data or run applications, that are housed in huge data centres around the world.
-
Users generally do not know the geographical location of the data storage.
-
Storage: Google Drive, One Drive, iCloud Drive, DropBox
-
Applications: Google Docs, Office 365, GMail
Cloud Storage - Advantages
-
Files and applications can be accessed from anywhere in the world with an internet connection.
-
Applications are kept up to date without the user having to update anything themselves.
-
Reduces the workload for network managers and technical support staff.
-
Storage space is flexible, users can buy more storage as they need it.
-
Improved security, the hosting company is responsible for keeping users data backed up.
-
Sharing files with others is easier.

Cloud Storage - Disadvantages
-
Can only access files whilst there is an internet connection.
-
Users no longer control the security of their files. Hackers more likely to attack a hosting company with many users data than an individuals computer system.
-
Not always clear who owns the data (read about Facebook's terms and conditions).
-
Hosting companies may change their terms and conditions, prices and even cease to exist.
-
Can become expensive in the long term.

Questions
- State what is meant by cloud computing
- Identify two services that can be accessed via the internet.
- Explain two disadvantages of storing your data in the cloud.
Questions
- State what is meant by cloud computing
The use of storage, services and applications that are accessed via the internet rather than being accessed locally on a device.
- Identify two services that can be accessed via the internet.
File storage, e.g. Google Drive
Applications, e.g. Google Docs
Questions
- An internet connection is required to access the data.
- Not much control over the security of the data or where it is stored.
- Terms and conditions can be changed with little notice.
- Can be more expensive in the long term.
- Explain two disadvantages of storing your data in the cloud.
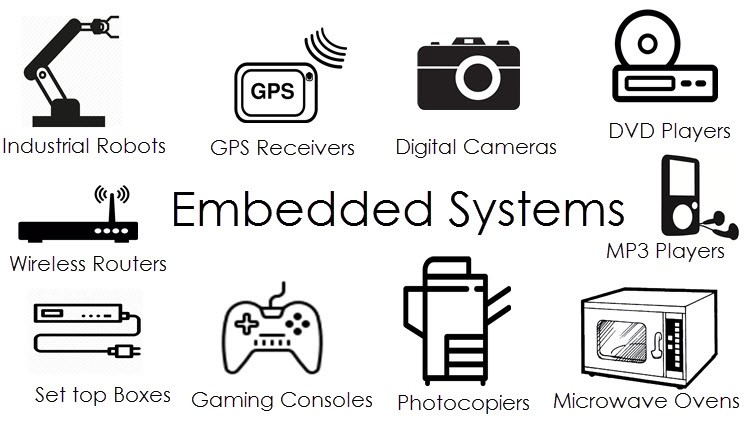
Embedded Systems
-
A computer system that has a dedicated function as part of a larger device.
-
Generally a single chip (microcontroller), with some circuitry.
-
Size and cost can be reduced if a system only needs a fixed range of tasks.
-
Includes some ROM to store the program.
-
May include some RAM to store user inputs/outputs.
Embedded Systems
-
Low power, so can operate with a small power source (mobile phone)
-
Small in size, so can fit into portable devices (fitness watch)
-
Rugged, so can operate in harsh environments (car engine management)
-
Low cost, so suitable for mass production (microwave ovens)

Questions
- Explain why embedded systems can have both ROM and RAM.
- Identify one input and one output from the embedded system in a microwave oven.
- Give two examples of systems that use embedded computer systems and explain why it is the most appropriate type of computer system to use in each case.
Questions
- Explain why embedded systems can have both ROM and RAM.
- Identify one input and one output from the embedded system in a microwave oven.
ROM is non-volatile, so will store the data and instructions needed to operate the device.
RAM is volatile, so will store the inputs/outputs for the user.
User selection for time, power level,...
Display user selections, timer countdown, ping,...
Questions
- Give two examples of systems that use embedded computer systems and explain why it is the most appropriate type of computer system to use in each case.
Many options, discuss: power, size, rugged, cost
4e Systems Architecture - Secondary Storage
By David James
4e Systems Architecture - Secondary Storage
Computer Science - Computer Systems - Systems Architecture - Secondary Storage
- 990



