How does data get into your application?
- AJAX
- localstorage
- cookies
- IndexDB
- Embedded JSON
- User input
How does data get into the view?
- Data-Binding
- DOM Insertion (please don't, it's the jQuery way)
How do data changes propagate?

The path from database to view and back gets complicated
WTF?
Your application needs an entry point for data
Data consumers become ignorant of how data is obtained
Angular's Holy Grail
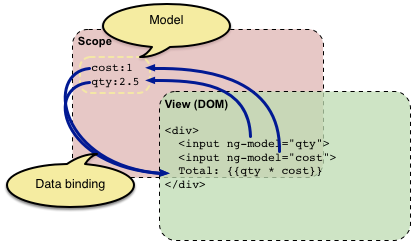
Views are purely reactive (declarative), bound to data in $scope
Views bind to a single source of truth (a single copy of any given piece of domain data)
When that single source of truth changes, all bound views update equally
Changes propagate via data-binding, not events or imperative programming
Example
angular.service('PostService', function ($http) { var posts = {}; return { getById: function (id) { if (!posts[id]) { this.find(id) }; return posts[id]; }, find: function (id) { return $http.get('posts/' + id).then(function (data) { posts[id] = data; return data; }); } };});
Example
angular.controller('PostCtrl', function ($scope, $routeParams, PostService) { $scope.$watch(function () { return PostService.getById($routeParams.id); }, function (post) { $scope.post = post; });});
This is one way to react to changes
in data owned by a Service
Data Synchronization
Easy to do between client persistence layer and client views.
Much harder to manage full synchronization between database and views.
Keep your data in your Angular Services.
Controllers and Directives expose your data to your views.
Changes to your data happen in your service layer.
You're building a Model layer
Something Angular doesn't provide.
A problem Ember Data is attempting to solve.
$resource, restangular, Breeze.js, Backbone Models, etc.
Other projects like Meteor and Tower are tackling database to view synchronization (isomorphic).
Caching
Why Cache?
Performance
Reduce latency from 200ms to 1 ms
Pages load near instant
Eliminate extra AJAX requests
Ease load on server
When/what to cache?
All the things!
Easy to cache individual items. e.g.
{ id: 5, name: 'John Smith'}
Collections are harder to cache, especially those that are the result of some query.
You can cache collection query results, but you may end up busting your cache often.
How?
angular.service('PostService', function ($http) { return { find: function (id) { return $http.get('posts/' + id, { cache: true }); } };});
PostService.find(5); // 233msPostService.find(5); // 1ms
$cacheFactory.get('$http').get('posts/5'); // cached item is here
$cachefactory doesn't support X ?
angular-cache has you covered
Remember...
Do you unto your data as
you would have done unto you