Chemistry
Vocab
Atom
A source of nuclear energy

Nucleus
Central core of an atom that consists of protons, neutrons and it's containing nearly all its mass.
Neutron
A particle about the same mass as a proton that doesn't have an electrical charge , is present in atomic nuclei except those with ordinary hydrogen

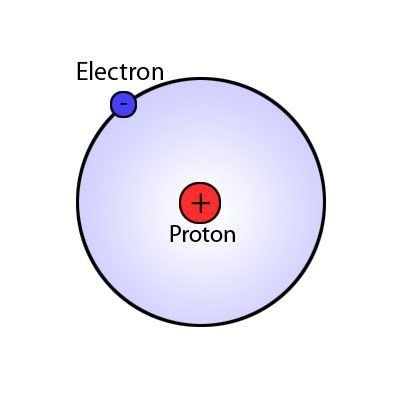
Proton
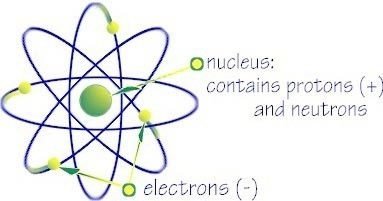
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge found in all atoms acting as a the primary carrier of electricity in solids.
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.

Mass number
The total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus.

Element
Each of one or more hundred substances that can not be chemically broken down into smaller/simpler substances.
Chemical Symbol

Periodic Table

Period
The name given to a horizontal row in the periodic table. There is seven Periods in the periodic table.

Group/Family
A column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements.

Metal
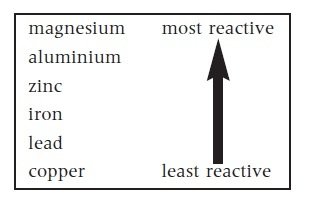
Reactivity
The state or power of being reactive or the degree to when something is reactive.
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together , representing the smallest fundamental unit of the chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction.
Property
A characteristic or quality in a substance that has been observed.
Non-metal
Element or substance that does not contain metal

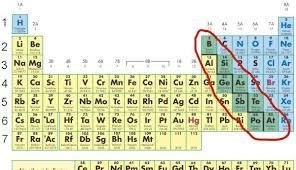
Metalloid
An element whose properties are intermediate between metals and non-metal solids.
luster
The way light interacts with crystal, rock or mineral.

Malleable
A material like metal that was able to be pushed/pressed permanently out of shape without being broken or cracked.

Ductile
Being able to bend with out loosing toughness.

Conductivity
Material able to conduct electricity or some type of form of energy.
Magnetism
One aspect of the combined electromagnetic force. The force called by magnets.

Corrosion
The process of corroding metal, stone or other materials.

Indicate
Point out or show

Individual
Single or separate.
Chemistry
By Jillian Sperico
Chemistry
- 911



