Wege aus der
in-silico-Reproduzierbarkeitskrise
Johannes Köster
2016


Perspektive
- Promovierter Informatiker
- Bioinformatik seid 2008
Projekte:
- Algorithmische Bioinformatik
- Systembiologie (MPI Dortmund)
- Ökologie (Universität Duisburg-Essen)
- Medizin/Krebsforschung (Harvard Medical School, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Universitätsklinikum Essen)
Software und Daten(analyse) in der Wissenschaft

Software und Daten(analyse) in der Wissenschaft

in-silico Reproduzierbarkeitskrise
Automatisierungskrise

dataset
results
Datenanalyse
"Ich mache das schnell von Hand..."

dataset
results
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
"Ich mache das schnell von Hand..."

Datenanalyse
dataset
results
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
reproducibility
From raw data to final figures:
- document parameters, tools, versions
- execute without manual intervention
Datenanalyse
dataset
results
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
scalability
Handle parallelization:
execute for tens to thousands of datasets
Avoid redundancy:
- when adding datasets
- when resuming from failures
Datenanalyse
dataset
results
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
scalability
reproducibility
Workflow management:
formalize, document and execute data analyses
Datenanalyse


Genome of the Netherlands:
GoNL consortium. Nature Genetics 2014.
Cancer:
Townsend et al. Cancer Cell 2016.
Schramm et al. Nature Genetics 2015.
Martin et al. Nature Genetics 2013.
Ebola:
Park et al. Cell 2015
iPSC:
Burrows et al. PLOS Genetics 2016.
Computational methods:
Ziller et al. Nature Methods 2015.
Schmied et al. Bioinformatics 2015.
Břinda et al. Bioinformatics 2015
Chang et al. Molecular Cell 2014.
Marschall et al. Bioinformatics 2012.








dataset
results
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
dataset
Define workflows
in terms of rules
Define workflows
in terms of rules
rule mytask:
input:
"path/to/{dataset}.txt"
output:
"result/{dataset}.txt"
script:
"scripts/myscript.R"
rule myfiltration:
input:
"result/{dataset}.txt"
output:
"result/{dataset}.filtered.txt"
shell:
"mycommand {input} > {output}"
rule aggregate:
input:
"results/dataset1.filtered.txt",
"results/dataset2.filtered.txt"
output:
"plots/myplot.pdf"
script:
"scripts/myplot.R"Define workflows
in terms of rules
Define workflows
in terms of rules
rule mytask:
input:
"data/{sample}.txt"
output:
"result/{sample}.txt"
conda:
"software-envs/some-tool.yaml"
shell:
"some-tool {input} > {output}"rule name
refer to input and output from shell command
how to create output from input
(shell, Python, R)
Directed acyclic graph (DAG) of jobs

Publikation
Problem:
Keine festen Regeln in den Journal-Guidelines

Beispiel Nature:
Vorschlag
1. Git repository:
├── config.yaml
├── scripts
│ ├── script1.py
│ └── script2.R
└── Snakefile# clone workflow into working directory
git clone https://bitbucket.org/user/myworkflow.git
cd myworkflow
# execute workflow locally
snakemake --cores 24
# execute workflow on a cluster
snakemake --jobs 1000 --drmaa2. DOI zuweisen (figshare/Zenodo)
3. DOI im Manuskript zitieren
4. Resultate nachvollziehen und reproduzieren
Softwarekrise

Softwarekrise
Wissenschaftliche Software wird häufig...
- unzureichend dokumentiert
- ineffizient programmiert
- nicht gewartet
Beispiel:
ISMB 2016 "Wall of Shame"
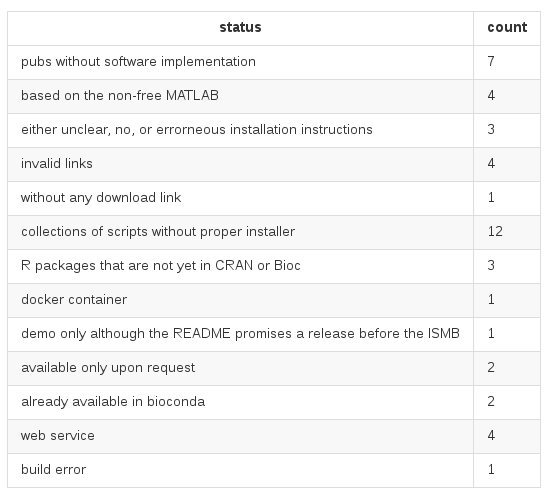
Von 47 open-access Publikationen, ...
Ursache I
Zeitverträge, wechselnde Projekte und Mitarbeiter
Zu Lasten von:
- Tests
- Wartung
Ursache II
Programmierung als wissenschaftliche "Allgemeinbildung"
Problem:
Programmierung != Informatik
Zu Lasten von:
- algorithmischer Qualität (Effizienz)
- Code/Architekturqualität (Wiederverwendbarkeit)
- Distribution (Lizenz, Paketierung)
Regeln
Style-Guides beachten:
def make_complex(*args):
x, y = args
return dict(**locals())def make_complex(x, y):
return {'x': x, 'y': y}vs
Regeln
Code-Duplikation vermeiden:
Vererbung oder Delegation anstatt Copy-Paste
Testen:
Unit- und Integration-Tests für möglichst 100% des Programms
Regeln
Das Rad nicht neu erfinden:
data = dict()
with open("somefile.tsv") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.split("\t")
key, fields = line[0], line[1:]
data[key] = [float(field) for field in fields]import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_table("sometable.tsv", index_col=0)vs
Wahl der Programmiersprache
Ziel:
Effiziente, ressourcenschonende, und fehlerfreie Software
Wahl der Programmiersprache
Ziel:
Effiziente, ressourcenschonende, und fehlerfreie Software
Strategie I:
Klassische maschinennahe Sprachen
(C, C++, ...)
Problem:
komplex und fehleranfällig (Speichermanagement, Thread safety, ...)

Wikipedia
Wahl der Programmiersprache
Ziel:
Effiziente, ressourcenschonende, und fehlerfreie Software
Strategie II:
Skriptsprachen (Python, Ruby, ...)
Problem:
langsam und fehleranfällig
(keine Typsicherheit,
nur Laufzeitfehler, ...)
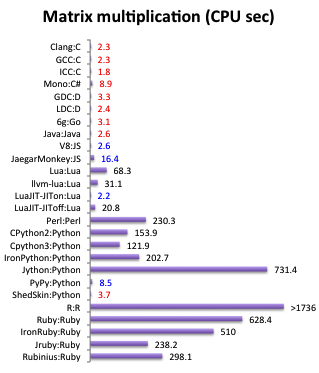
https://attractivechaos.github.io/plb/
Rust
- vereinfachte, C++-ähnliche Syntax
- Automatische Typ-Inferenz
- Elemente aus Skriptsprachen
- Sehr strikter Compiler der Speicher- und Threadsicherheit garantiert
Ergebnis:
Entwicklungszeit verschiebt sich vom Debugging zum Kompilieren.
Software ist leichter zu warten.


Rust-Bio

Software installation is heterogeneous
source("https://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R")
biocLite("DESeq2")easy_install snakemake./configure --prefix=/usr/local
make
make installcp lib/amd64/jli/*.so lib
cp lib/amd64/*.so lib
cp * $PREFIXcpan -i bioperlcmake ../../my_project \
-DCMAKE_MODULE_PATH=~/devel/seqan/util/cmake \
-DSEQAN_INCLUDE_PATH=~/devel/seqan/include
make
make installapt-get install bwayum install python-h5pyinstall.packages("matrixpls")Der Conda-Paketmanager
source or binary
package:
name: seqtk
version: 1.2
source:
fn: v1.2.tar.gz
url: https://github.com/lh3/seqtk/archive/v1.2.tar.gz
requirements:
build:
- gcc
- zlib
run:
- zlib
about:
home: https://github.com/lh3/seqtk
license: MIT License
summary: Seqtk is a fast and lightweight tool for processing sequences
test:
commands:
- seqtk seqpackage
Normalisierung von Installationsroutinen über "Recipes":
- Installationen ohne Admin-Rechte
- Isolierte Softwareumgebungen

Already over 1600 bioinformatics related conda packages
(C, C++, Python, R, Perl, ...)

Over 130 contributors


Integrated with 3 popular workflow management systems:




CONDA-FORGE

Partner project for general purpose software:
Zusammenfassung

In-silico-Reproduzierbarkeitskrise:
Automatisierungskrise:
- Workflow Management mit Snakemake
- Regeln für die Publikation von Datenanalysen
Softwarekrise:
- Besserer Code mit Rust
- Distribution mit Conda
Wege aus der in-silico Reproduzierbarkeitskrise
By Johannes Köster
Wege aus der in-silico Reproduzierbarkeitskrise
Keynote at Helmholz workshop "Nachhaltige Softwareentwiklung"
- 2,893



