Wprowadzenie do testowania w Meteorze
Maciek Stasiełuk

Plan szkolenia
- Teoria - czym są testy
- Teoria - w czym i jak można testować
- Praktyka - testy w Meteorze
Po co testujemy?
- Upewnienie się że soft działa :)
- Zapobieganie regresji i błędom.
- Pewność przy refactoringu i zmianach.
- Zapewnienie zgodności ze specyfikacją.
- Samoistna dokumentacja.
Podstawowe kroki podczas testów
- Set up - przygotowania środowiska przed testem
- Execute - wykonanie kodu aplikacji który chcemy przetestować
- Verify - sprawdzenie czy osiągnęliśmy zakładany rezultat
- Tear down - posprzątanie po sobie
Rodzaje testów
Sposób przeprowadzania
- Testy manualne
- Testy automatyczne
Metoda testowania
- Testowanie statyczne
- Testowanie dynamiczne
Metoda testowania
- White box
- Black box
- Gray box
Rodzaje testów /
Przeznaczenie testów
- Testy akceptacyjne (UAT)
- Alfa / beta testy
- Testy funkcjonalne
- Testy regresyjne
- Testy niefunkcjonalne
- Testy wydajnościowe
- Testy bezpieczeństwa (pentesty)
- Testy usability
- Testy A / B
- ...
Zakres testów
SUT - System Under Test
- Testy jednostkowe (unit tests)
- Testy integracyjne (integration tests)
- Testy systemowe (system tests, end-to-end tests)
Zakres testów
Testowana aplikacja

Testy jednostkowe

Testy integracyjne
Testy systemowe

Bibliografia ;)
Izolacja podczas testów
- Stub
- Mock
- Spy
- Fake
Test doubles

Stub
Stub jest najprostszym typem, jego zadaniem jest symulowanie innego obiektu poprzez zwracanie znanej z góry stałej wartości.
Możemy go użyć np. gdy chcemy sprawdzić czy nasz kod dobrze weryfikuje dane przychodzące z zewnątrz.
// Przygotowanie
var Posts = {
findOne: function (query) {
return {
_id: 'ABC',
title: 'My Post',
content: 'My post content'
};
}
};
// Testowany kod
var isValid = checkIfPostIsValid('ABC');
// Weryfikacja
if(!isValid) {
throw 'Błąd!';
}Fake
Fake jest podobny do stuba, jednak w przeciwieństwie do niego może ulegać zmianie w trakcie testowania.
// Przygotowanie
var Posts = {
doc: {
_id: 'ABC',
title: 'My Post'
},
findOne: function (query) {
return this.doc;
},
update: function (query, modifier) {
_(this.doc).extend(modifier.$set);
}
};
// Testowany kod
setPostTitle('ABC', 'New title');
// Weryfikacja
if(Posts.findOne().title !== 'New title') {
throw 'Błąd!';
}Mock
Rolą Mocków jest weryfikowanie zachowania naszego kodu.
Można w tym celu posłużyć się biblioteką np. Sinon.
Wpierw konfigurujemy spodziewane użycie naszego mocka, później możemy zweryfikować czy nasz kod dobrze obsługuje inne zależności.
// Przygotowanie
var Posts = {
findOne: function (query) {
return {
_id: 'ABC',
title: 'My Post'
};
}
};
sinon.mock(Posts)
.expects('findOne')
.once()
.withExactArgs({title: 'My Post'});
// Testowany kod
var post = findPostByTitle('My Post');
// Weryfikacja
Posts.findOne.verify();Spy
Szpieg jest bardzo podobny do mocka, z tą rożnicą iż korzysta z prawdziwego obiektu.
Nadpisuje jego wybrane metody i szpieguje, dzięki czemu możemy później sprawdzić jak nasz kod traktuje inne obiekty.
// Przygotowanie
var Posts = new Meteor.Collection('posts');
sinon.spy(Posts, 'findOne');
// Testowany kod
findPostByTitle('My Post');
// Weryfikacja
if(!Posts.findOne.calledOnce) {
throw 'Błąd!';
}
// Sprzątamy po sobie
Players.findOne.restore();Bibliografia ;)
W czym pisać testy?
Test Framework
Oprogramowanie które wyznacza pewne ramy i zasady pomagające w pisaniu testów. Przykłady:
Test Runner
Biblioteki asercji
Przykłady testów
TinyTest 🔗
Tinytest.add('Template.leaderboard.players()', function (test) {
var someLocalCollectionCursor = {};
Players.find = function (selector, options) {
test.equal(options.sort.score, -1);
test.equal(options.sort.name, 1);
return someLocalCollectionCursor;
};
test.equal(Template.leaderboard.players(), someLocalCollectionCursor);
});
Tinytest.add('Template.leaderboard.selected_name()', function (test) {
// returns player when player is found and has a name
Players.findOne = function () {
return {name: 'Tom'};
};
test.equal(Template.leaderboard.selected_name(), "Tom");
// returns undefined when player.name isn't present
Players.findOne = function () {
return {};
};
test.equal(Template.leaderboard.selected_name(), undefined);
// returns undefined when player doesn't exist
Players.findOne = function () {
return undefined;
};
test.equal(Template.leaderboard.selected_name(), undefined);
});
Tinytest.add('Template.player.selected()', function (test) {
// returns selected when the selected player in the session matches
// player in the current template
Template.player._id = 1234;
Session.set('selected_player', 1234);
test.equal(Template.player.selected(), "selected");
// returns empty string when the selected player in the session doesn't
// matches player in the current template
Template.player._id = 4321;
Session.set('selected_player', 1234);
test.equal(Template.player.selected(), "");
});
Na przykładzie domyślnej aplikacji Meteora: Leaderboard
Mocha 🔗
MochaWeb.testOnly(function () {
function waitFor(testFn, callbackFn) {/**/}
var assert = chai.assert;
describe('Accounts', function () {
var testUser = {
email: Random.id(4) + '@example.com',
password: Random.id(6)
};
describe('Register form', function () {
before(function (done) {
Meteor.logout(done);
});
it('should be able to navigate to', function (done) {
FlowRouter.go('register');
waitFor(function () {
return FlowRouter.current().route.name === 'register';
}, done);
});
it('should be visible', function (done) {
waitFor(function () {
return $('form.ui.form').length === 1;
}, done);
});
it('should contain email and passwords inputs', function () {
assert.lengthOf($('form.ui.form input[type="email"]'), 1);
assert.lengthOf($('form.ui.form input[type="password"]'), 2);
});
it('should be able to create new account', function (done) {
$('form.ui.form input[type="email"]').val(testUser.email);
$('form.ui.form input[type="password"]').val(testUser.password);
$('form.ui.form button[type="submit"]').click();
waitFor(function () {
return !!Meteor.userId();
}, done);
});
it('should redirect to profile page after creating new account', function (done) {
waitFor(function () {
return FlowRouter.current().route.name === 'uniProfilesFullview';
}, done);
});
it('should be able log out', function (done) {
Meteor.logout(done);
});
});
describe('Login form', function () {
before(function (done) {
Meteor.logout(done);
});
it('should be able to navigate to', function (done) {
FlowRouter.go('login');
waitFor(function () {
return FlowRouter.current().route.name === 'login';
}, done);
});
it('should be visible', function (done) {
waitFor(function () {
return $('form.ui.form').length === 1;
}, done);
});
it('should contain email and password inputs', function () {
assert.lengthOf($('form.ui.form input[type="email"]'), 1);
assert.lengthOf($('form.ui.form input[type="password"]'), 1);
});
it('should be able to log in', function (done) {
$('form.ui.form input[type="email"]').val(testUser.email);
$('form.ui.form input[type="password"]').val(testUser.password);
$('form.ui.form button[type="submit"]').click();
waitFor(function () {
return !!Meteor.userId();
}, done);
});
});
});
});Na przykładzie projektu
SCL Tigers
Demo
// Analiza statyczna //
eslint .
// Velocity //
// uruchomienie meteora wraz z testami
meteor
// uruchomienie meteora bez testów bo muli :)
VELOCITY=0 meteor
// uruchomienie samych testów
meteor --test
// TinyTest //
// przetestowanie paczek i raport w formie strony www
meteor test-packages
// przetestowanie paczek i raport w konsoli
spacejam test-packages
Continuous Integration
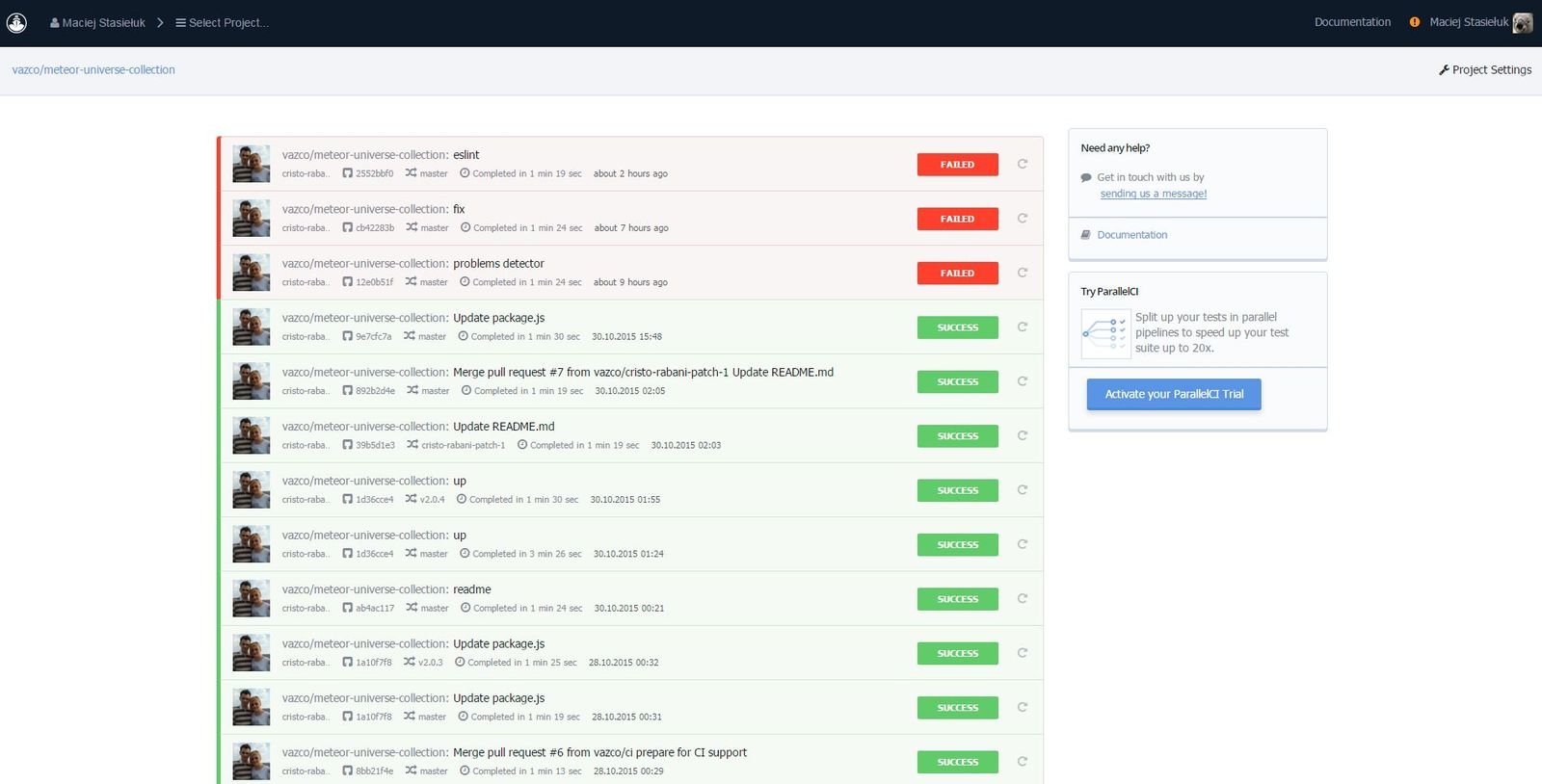
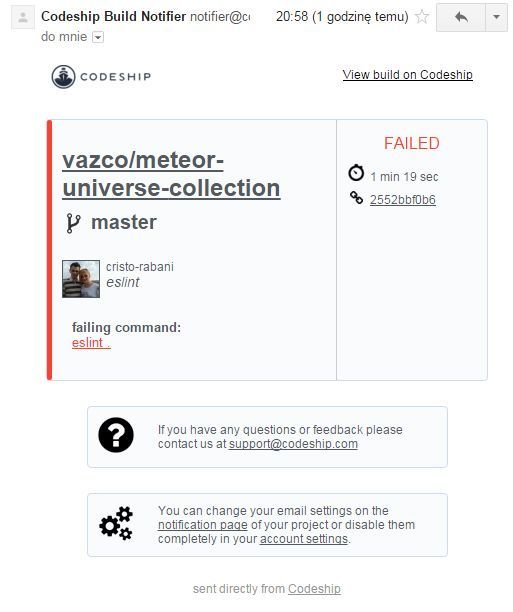
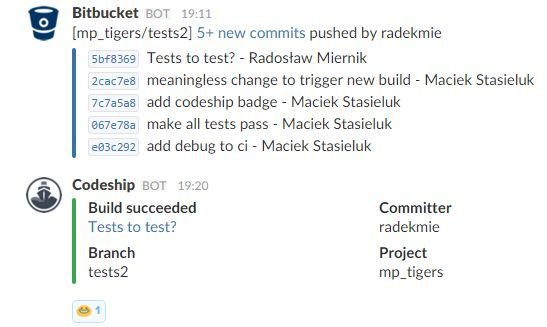
Spacejam
spacejam: spawning meteor
[[[[[ Tests ]]]]]
=> Started proxy.
=> Started MongoDB.
spacejam: meteor mongodb is ready
=> Started your app.
=> App running at: http://localhost:4096/
spacejam: meteor is ready
spacejam: spawning phantomjs
I20151030-14:52:29.656(0)? test-in-console listening
phantomjs: Running tests at http://localhost:4096/local using test-in-console
S: tinytest - UniCollection - database error reporting. STRING : OK
S: tinytest - UniCollection - basics, STRING : OK
S: tinytest - UniCollection - fuzz test, STRING : OK
S: tinytest - UniCollection - stop handle in callback, STRING : OK
S: tinytest - UniCollection - recursive observe throws, STRING : OK
S: tinytest - UniCollection - cursor dedup, STRING : OK
[...]
C: tinytest - UniCollection - Remote Methods - collection : OK
C: tinytest - UniCollection - Remote Methods - document : OK
C: tinytest - UniCollection - Remote Methods - without latency compensation : OK
C: tinytest - UniCollection - Remote Methods - trusted stack : OK
C: tinytest - UniCollection - Hooks collection and context : OK
C: tinytest - UniCollection - Hooks inserts and doc metchods : OK
passed/expected/failed/total 199 / 0 / 0 / 199
##_meteor_magic##state: done
spacejam: phantomjs exited with code: 0
spacejam: killing meteor
spacejam: meteor killed with signal: SIGTERMVelocity
stream error Network error: ws://localhost:3000/websocket: connect ECONNREFUSED
I20151127-18:16:48.110(0)? [velocity] mocha is starting a mirror at http://localhost:50932/.
I20151127-18:16:48.118(0)? [velocity] *** Meteor Tools is installing ***
I20151127-18:16:48.119(0)? This takes a few minutes the first time.
I20151127-18:16:48.119(0)? [velocity] You can see the mirror logs at: tail -f /home/rof/src/bitbucket.org/vazco/mp_tigers/.meteor/local/log/mocha.log
PASSED mocha : Register form:Accounts => should be able to navigate to
PASSED mocha : Register form:Accounts => should be visible
PASSED mocha : Register form:Accounts => should contain email and passwords inputs
PASSED mocha : Register form:Accounts => should be able to create new account
PASSED mocha : Register form:Accounts => should redirect to profile page after creating new account
PASSED mocha : Register form:Accounts => should be able log out
PASSED mocha : Login form:Accounts => should be able to navigate to
PASSED mocha : Login form:Accounts => should be visible
PASSED mocha : Login form:Accounts => should contain email and password inputs
PASSED mocha : Login form:Accounts => should be able to log in
PASSED mocha : Example server tests => should have a Meteor version defined
PASSED mocha : Example client tests => should respect equality
TESTS RAN SUCCESSFULLYDokumentacja na temat CI:
https://bitbucket.org/snippets/vazco/AAznq/vazco-ci-cd-systems
Pytania?
Meteor Testing
By Maciej
Meteor Testing
Wprowadzenie w świat testów ogólnie i testowania w Meteorze
- 1,399



