JavaScript Functional Programing
WeMo Scooter
Meng




Why?
- 你可能每天都在工作中使用到它。
- functional是一種觀念,有機會可以解決工作上遇到的問題
- 我們不必從頭學習所有東西就能開始撰寫程式。
- 想用就用,也不必一口氣完全導入
- JS完全有能力撰寫高級的 functional 程式碼。
- 借助一些第三方的library就可以實現functional programming的各種特性
導讀項目
-
Think functionally
- Becoming functional
- Higher-order JavaScript
-
Get functional
-
Few data structures, many operations
-
Toward modular, reusable code
-
Design patterns against complexity
-
-
Enhancing your functional skills
OO makes code understandable by encapsulating moving parts.
FP makes code understandable by minimizing moving parts.
Michael Feathers (Twitter)
Functional programming isn’t a framework or a tool, but a way of writing code, thinking functionally is radically different from thinking in object-oriented terms.
1.更接近人類的語言
2.更加模組化
3.更容易測試
Functional對我而言...
背景知識
- First Class Funtcion
- function可以當作變數傳入function當中
//
var getServerStuff = function(callback) {
return ajaxCall(function(json) {
return callback(json);
});
};
//
var getServerStuff = ajaxCall;return ajaxCall(callback);var getServerStuff = function(callback) {
return ajaxCall(callback);
};
背景知識
- Curry
- 只透過部分的參數呼叫一個 function,它會回傳一個 function 去處理剩下的參數。
let add = x => y => x + y;
var increment = add(1);
increment(1) // -> 2var add = function(x) {
return function(y) {
return x + y;
};
};
var increment = add(1);
increment(1) // -> 2簡單的例子
document.querySelector('#msg').innerHTML = '<h1>Hello World</h1>';function printMessage(elementId, format, message) {
document.querySelector(`#${elementId}`).innerHTML =
`<${format}>${message}</${format}>`;
}
printMessage('msg', 'h1','Hello World');var printMessage = run(addToDom('msg'), h1, echo);
printMessage('Hello World');pointfree
簡單的例子
將原本的程式修改
將msg 使用h2標籤 並且 重複 print 在console上面3次
var printMessage = run(addToDom('msg'), h1, echo);
printMessage('Hello World');var printMessage = run(console.log, repeat(3), h2, echo);
printMessage('Get Functional');Functional基本概念
- Declarative programming
- Pure functions
- Referential transparency
- Immutability
Declarative programming
SELECT Id, OrderDate, CustomerId, TotalAmount
FROM [Order]
WHERE NOT (TotalAmount >= 50 AND TotalAmount <= 15000)
ORDER BY TotalAmount DESC敘述式的程式其實大家都很熟悉...
Declarative programming
var name = "peter";
var greeting = "Hi, I'm "
console.log(greeting + name);function greet(name) {
return "Hi, I'm " + name;
}
greet("Peter");
// => Hi, I'm Peter
命令式
敘述式
Declarative programming
var array = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
for(let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = Math.pow(array[i], 2);
}
array; //-> [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9].map((num) => Math.pow(num, 2))
array; //-> [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81
命令式
敘述式
Declarative programming
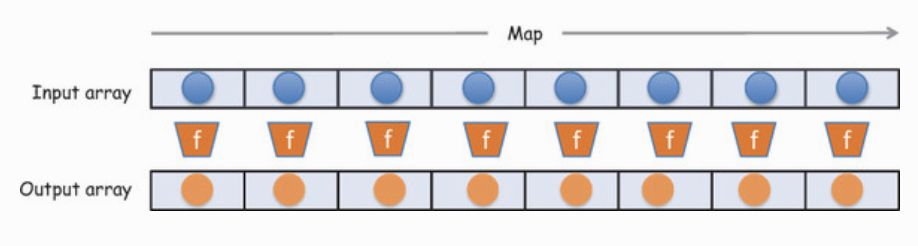
var numbers = [1, 5, 10, 15];
var roots = numbers.map(function(x){
return x * 2;
});
// roots is now [2, 10, 20, 30]
// numbers is still [1, 5, 10, 15]Declarative programming
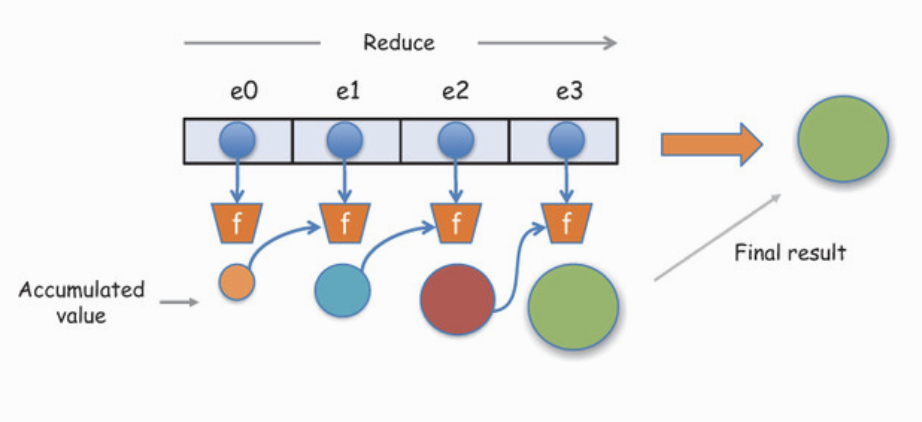
var sum = [0, 1, 2, 3].reduce(function(a, b) {
return a + b;
}, 0);
// sum is 6Declarative programming
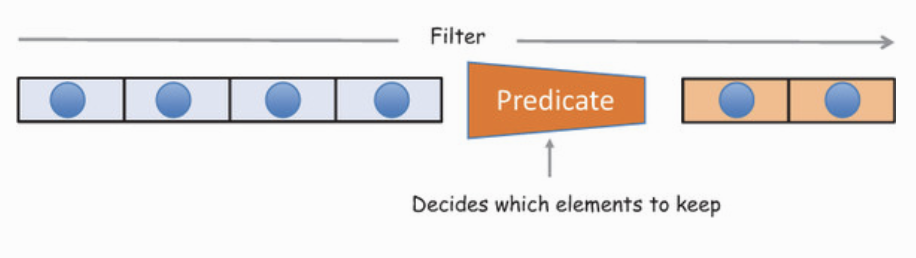
function isBigEnough(value) {
return value >= 10;
}
var filtered = [12, 5, 8, 130, 44].filter(isBigEnough);
// filtered is [12, 130, 44]Pure functions
var counter = 0;
function increment() {
return ++counter;
}避免 side effects
Impure
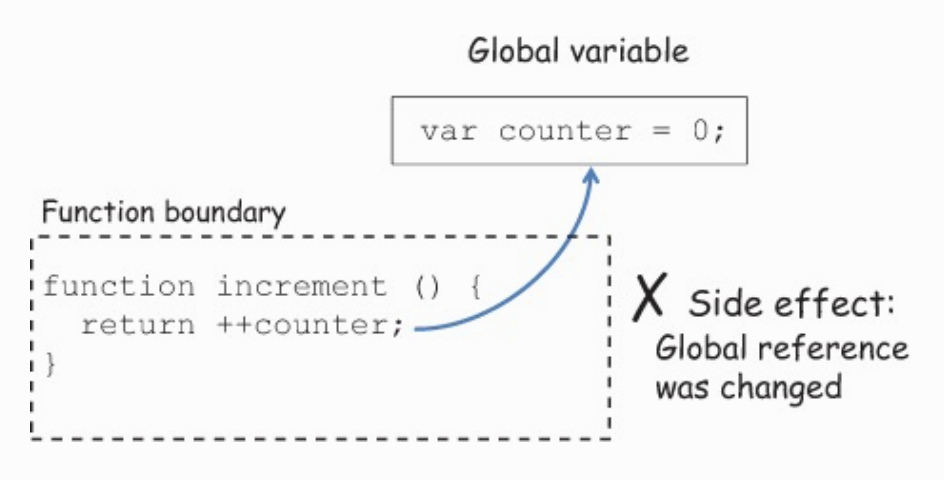
Pure functions
var xs = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// pure(純)
xs.slice(0, 3);
//=> [1, 2, 3]
xs.slice(0, 3);
//=> [1, 2, 3]
xs.slice(0, 3);
//=> [1, 2, 3]
// impure(不純)
xs.splice(0, 3);
//=> [1, 2, 3]
xs.splice(0, 3);
//=> [4, 5]
xs.splice(0, 3);
//=> []避免 side effects
Pure functions
function showStudent(ssn) {
var student = db.get(ssn);
if(student != null) {
document.querySelector(`#$(elementId)`).innerHTML =
`${student.ssn},
${student.firstname},
${student.lastname}`;
}
else {
throw new Error('Student not found!');
}
}
showStudent('444-44-4444');·使用外部函式
從DB取得資料,假設該函式為同步函式
若找不到資料則拋出例外
找出學生資料並顯示在畫面當中
避免 side effects
Pure functions
function showStudent(ssn) {
var student = db.get(ssn);
if(student != null) {
document.querySelector(`#$(elementId)`).innerHTML =
`${student.ssn},
${student.firstname},
${student.lastname}`;
}
else {
throw new Error('Student not found!');
}
}
showStudent('444-44-4444');·會讓程式中止
db來自外部,有可能不存在。
相同參數每次得到的結果可能不同
來自外部的變數
無法確定內容
直接改變了HTML的內容
problem with side effects
Pure functions
problem with side effects
var find = curry((db, id) => {
var obj = db.get(id);
if(obj === null) {
throw new Error('Object not found!');
}
return obj;
});
var csv = (student) => {
return `${student.ssn}, ${student.firstname}, ${student.lastname}`;
};
var append = curry((elementId, into) => {
document.querrySelector(elementId).innerHTML = info;
})
var showStudent = run(
append('#student-info'),
csv,
find(db)
)
showStudent('444-44-4444')更易讀
pure/ impure function隔離
可重複使用
可追蹤
Referential transparency
var counter = 0;
function increment() {
return ++counter;
}
increment();
increment();
...
print(counter); //-> ?var increment = counter => counter + 1;
var plus2 = run(increment, increment);
print(plus2(0));counter來自外部,在呼叫時無法直接觀察其變化,從程式碼上較難得知會影響的外部變數
不會改動外部的變數
Referential transparency
var input = [80, 90, 100];
var average = (arr) => divide(sum(arr), size(arr));
average (input); //-> 90
var input = [80, 90, 100];
var average = divide(270, 3); //-> 90
average (input); //-> 90
相同的輸入必得到相同的答案
程式碼可以替換成它執行後所得到的結果,而且不改變整個程式行為
immutable
var sortDesc = function (arr) {
return arr.sort(function (a, b) {
return b - a;
});
}
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
sortDesc(arr); //-> [9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1]
arr; //-> [9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1]資料建立後就不能更改,目的是避免side-effect
Functional的基本模式
compose
f • g = f(g(x))
var showStudent = compose(append('#student-info'), csv, find(db));
showStudent('444-44-4444');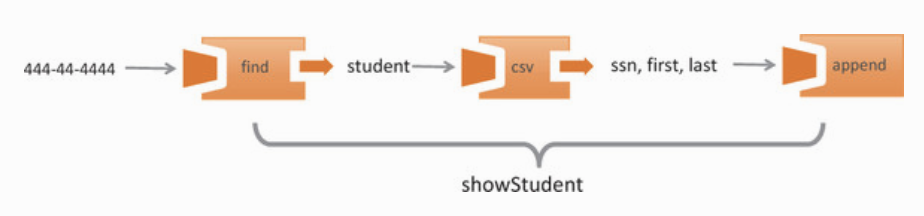
Functional的基本模式
compose
f • g = f(g(x))
var compose = function(f, g) {
return function(x) {
return f(g(x));
};
};
// 結合律(associativity)
var associative = compose(f, compose(g, h)) == compose(compose(f, g), h);
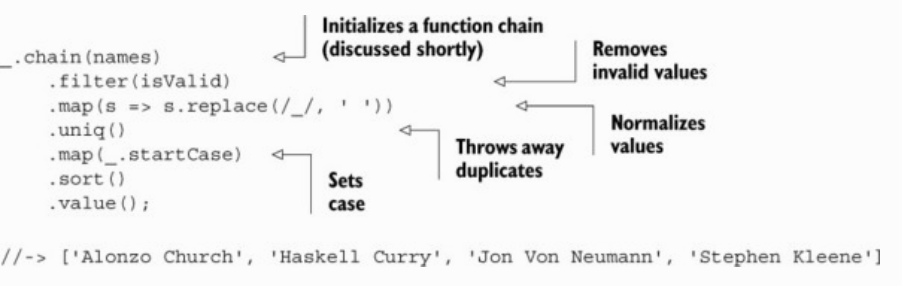
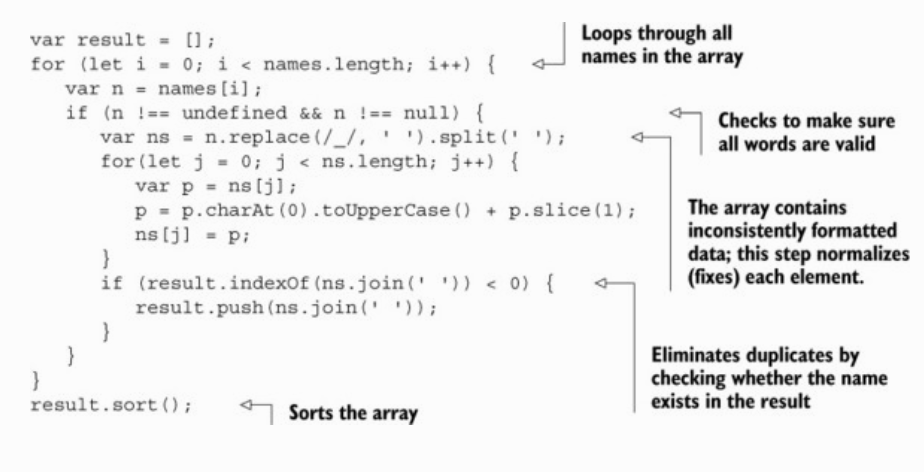
// trueProcessing data using fluent chains
let enrollment = [
{enrolled: 2, grade: 100},
{enrolled: 2, grade: 80},
{enrolled: 1, grade: 89}
];var totalGrades = 0;
var totalStudentsFound = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < enrollment.length; i++) {
let student = enrollment [i];
if(student !== null) {
if(student.enrolled > 1) {
totalGrades+= student.grade;
totalStudentsFound++;
}
}
}
var average = totalGrades / totalStudentsFound;
//-> 90_.chain(enrollment)
.filter(student => student.enrolled > 1)
.pluck('grade')
.average()
.value(); // -> 90
// (Underscore.js)Functional的基本模式
Functional的基本模式
const map = fn => array = > array.map(fn);
const multiply = x => y => x * y;
const pluck = key => object => object[key];
const discount = multiply(0.98);
const tax = multiply(1.0925);
const customRequest = request({
header:{ 'X-Custom': 'myKey'
});
customRequest({url: '/cart/items' })
.then(map(pluck('price')))
.then(map(discount))
.then(map(tax));
Promise chains
[
{price: 5},
{price: 10},
{price: 3}
][
5,
10,
3
][
5 * 0.98,
10 * 0.98,
3 * 0.98
]Functional的基本模式
const map = fn => array = > array.map(fn);
const multiply = x => y => x * y;
const pluck = key => object => object[key];
const discount = multiply(0.98);
const tax = multiply(1.0925);
const customRequest = request({
header:{ 'X-Custom': 'myKey'
});
customRequest({url: '/cart/items' })
.then(map(pluck('price')))
.then(map(discount))
.then(map(tax));
Promise chains
customRequest({url: '/cart/items' })
.then(
map(compose(tax, discount, pluck('price')))
);
比較functional與OO
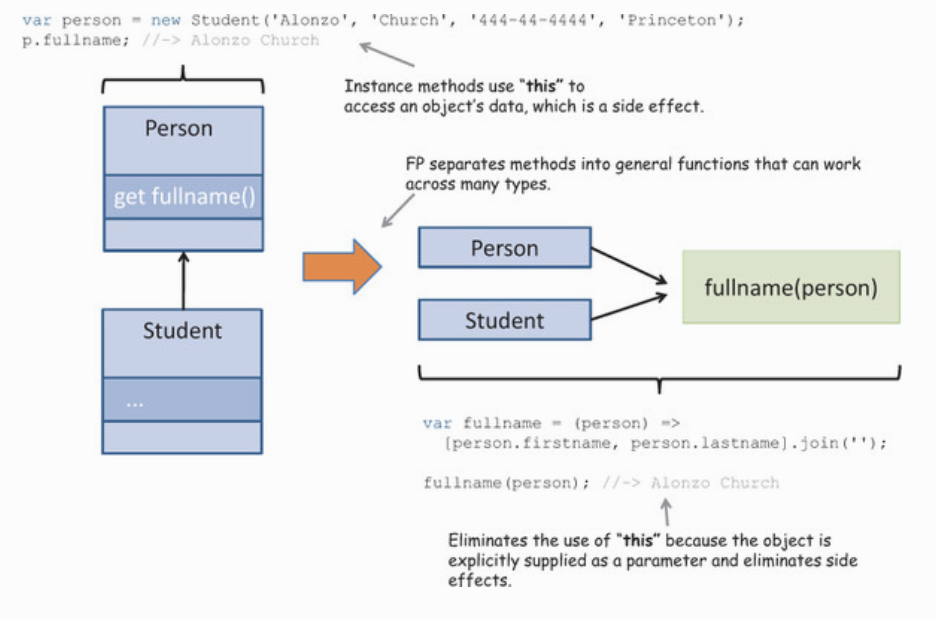
OO遇到的問題
class Person {
constructor (firstname, lastname ,ssn){
this._firstname = firstname;
this._lastname = lastname;
this._ssn = ssn;
this.address = null;
}
get address() {
return this._address;
}
set address(addr) {
this._address = addr;
}
.....
}class Student extends Persion {
constructor (firstname, lastname, ssn, school){
super(firstname, lastname ,ssn);
this._school = school
}
get school() {
return this._school;
}
}OO遇到的問題
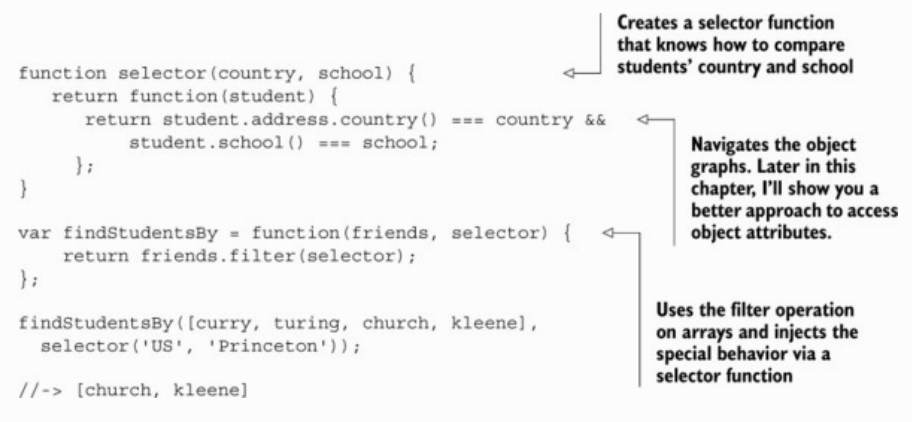
// Person class
peopleInSameCountry(friends) {
var result = [];
for(let idx in friends) {
var friend = friends[idx];
if(this.address.country === friend.address.country){
result.push(friend);
}
}
return result;
};
// Student class
peopleInSameCountryAndSchool(friends) {
var closeFriends = super.peopleInSameCountry(friends);
var result = [];
for (let idx in closeFriends) {
var friend = closeFriends[idx];
if(this.school === friend.school){
result.push(friend)
}
}
return result;
}OO遇到的問題
Functional Library



Lodash
Ramda
underscore.js
Functional Programing in ES6
By MengWei Chen
Functional Programing in ES6
- 1,306
