Advanced
programming
Lecture 6


Måns Magnusson
Statistics and Machine learning
Department of computer and information science

Since last time?

Performant code

Writing fast code

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Time to write code
Speed is important!
Time to maintain code
Time to run code
Performance

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
1. Performance
2. Complexity
Complexity affects performance...
...but performance don't affect complexity
Computional complexity

Computational complexity

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Theoretical worst case
big-Oh notation
Basic operations
Relationship: operations to problem size
Big Oh

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
"How fast do a function grow"
n ~ number of operations
Big Oh

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Example
Complexities

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
| Big Oh | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| O(1) | constant | assignments |
| O(log(N)) | logarithmic | binary search |
| O(N) | linear | max |
| O(N^2) | quadratic | naive vector-matrix mult. |
| O(N^c) | polynomial | naive matrix-matrix mult. |
| O(c^n) | exponential | brute force |
Determine complexity

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
statement 1
statement 2
...
statement cif(a)
statement a
else
statement bfor(i in 1:N)
statement iDetermine complexity

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
for(i in 1:N)
for (j in 1:M)
statement i,jfor(i in 1:N)
g(i)
Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
1 function Dijkstra(Graph, source):
2
3 dist[source] ← 0 // Distance from source to source
4 prev[source] ← undefined // Previous node in optimal path initialization
5
6 create vertex set Q
7
8 for each vertex v in Graph: // Initialization
9 if v ≠ source: // v has not yet been removed from Q (unvisited nodes)
10 dist[v] ← INFINITY // Unknown distance from source to v
11 prev[v] ← UNDEFINED // Previous node in optimal path from source
12 add v to Q // All nodes initially in Q (unvisited nodes)
13
14 while Q is not empty:
15 u ← vertex in Q with min dist[u] // Source node in the first case
16 remove u from Q
17
18 for each neighbor v of u: // where v is still in Q.
19 alt ← dist[u] + length(u, v)
20 if alt < dist[v]: // A shorter path to v has been found
21 dist[v] ← alt
22 prev[v] ← u
23
24 return dist[], prev[]Example
Parallelism

What is parallelism?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Multiple cores
Each core work with its own part
Cores can exchange information
Why parallelism?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
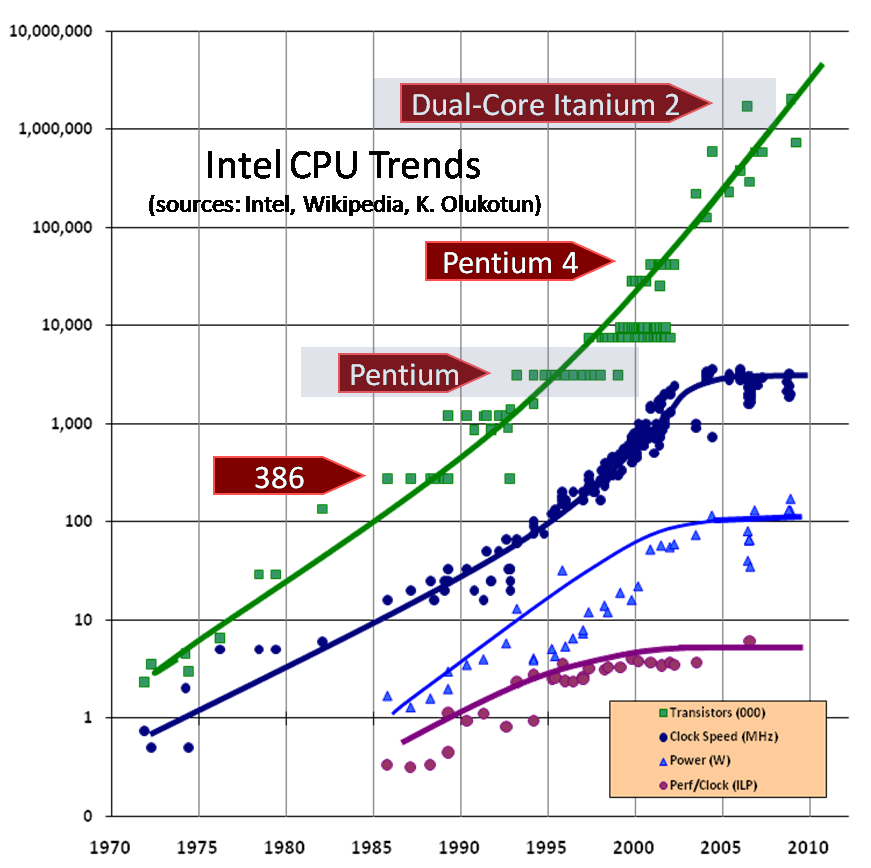
Why parallelism?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Single core limits
Handling larger data
Solving problems faster
More and more important
Types of parallelism

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Multicore systems
Distributed systems
Graphical processing units (GPU)
Speedup

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
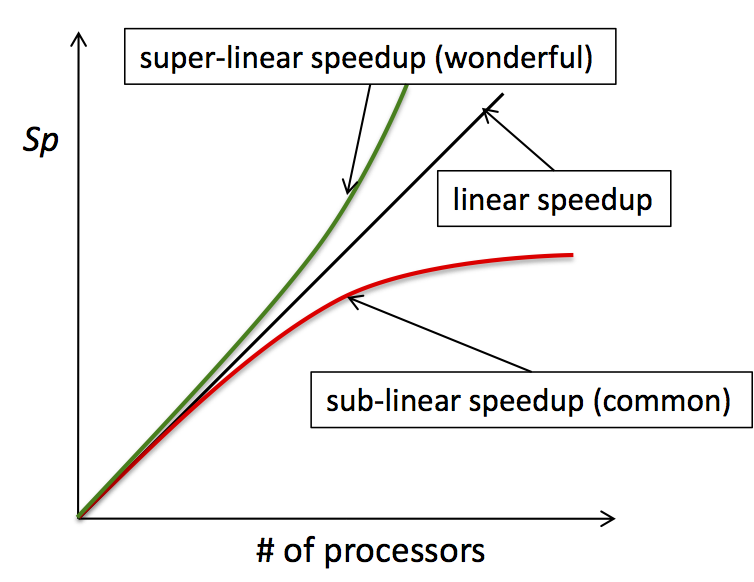
Theoretical limits

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Strong scaling: Almdahls law
Weak scaling: Gustafsons law
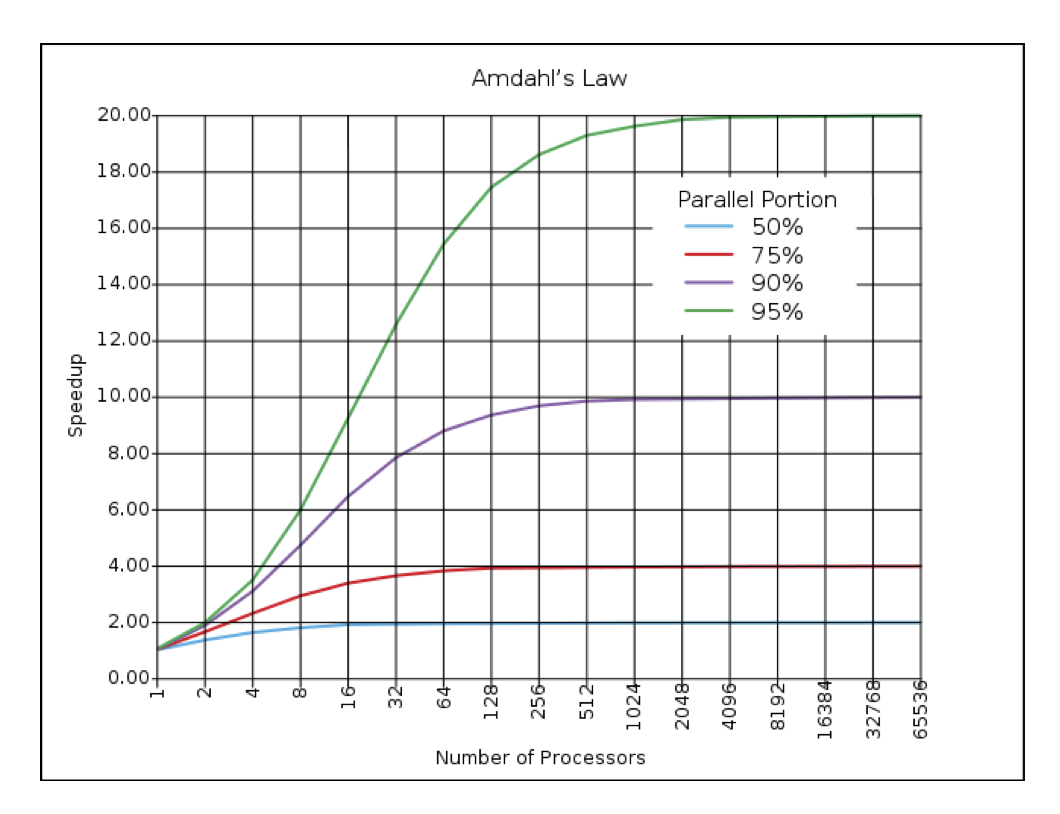
Aldahls law

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
where
serial fraction of code
paralleliziable fraction of code
number of cores
Almdahls law

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Gustafsons law

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
where
the largest non-parallelizable fraction of any parallel process
number of cores
Practical problems

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Costs of parallelism
communication
load balancing
scheduling
fine-grained vs embarrisingly paralell
Practical problems

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
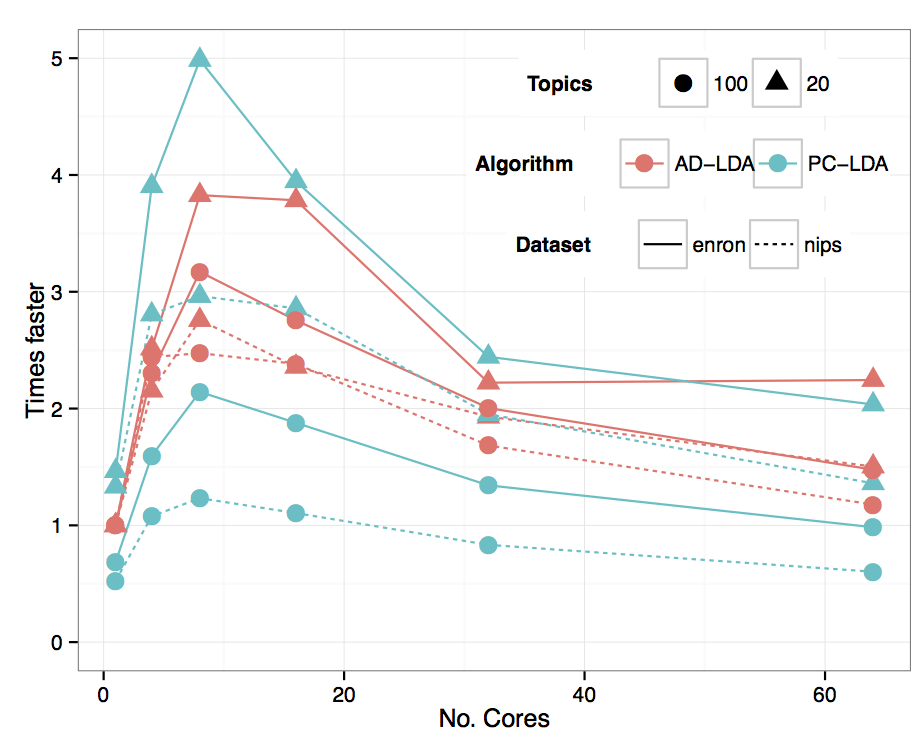
Real speedup
Improving R code


Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
“Programmers waste enormous amounts of time thinking about, or worrying about, the speed of noncritical parts of their programs, and these attempts at efficiency actually have a strong negative impact when debugging and maintenance are considered.”
— Donald Knuth
Performance

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Depend on many things:
1. Code
2. Complexity
3. Compiler
4. Hardware
5. Language
If you don't measure, you don't optimize!
Cost of operations

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
> library(microbenchmark)
> x <- runif(1000)
> y <- runif(1000)
> microbenchmark(x + y, x - y, x * y, x / y, sqrt(x),
+ log(x), exp(x), x^0.5, runif(1000), rnorm(1000))
Unit: nanoseconds
expr min lq mean median uq max neval
x + y 926 1055.5 1347.52 1132.5 1224.5 13870 100
x - y 976 1078.5 1267.14 1123.5 1302.0 3562 100
x * y 956 1073.0 1353.20 1145.5 1350.0 4939 100
x/y 4057 4104.5 4369.95 4152.0 4248.5 7440 100
sqrt(x) 4021 4081.0 4384.78 4111.5 4191.5 7578 100
log(x) 9663 9776.0 11216.16 9837.0 9908.5 39500 100
exp(x) 7978 8055.0 8550.31 8086.5 8161.0 27445 100
x^0.5 32216 32322.5 34261.14 32383.5 32465.0 67052 100
runif(1000) 30042 32391.5 53390.19 33862.0 54642.0 257249 100
rnorm(1000) 72569 74031.5 155968.90 82078.0 209345.0 1496669 100How to optimize

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
1. Write code that works
2. Profile your code for bottlenecks
3. Try to eliminate the bottle necks
4. Redo 2-3 until fast enough
Profiling

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Sample based
Rprof(tmp <- tempfile(), line.profiling = TRUE, memory.profiling = TRUE)
test_data <- pxweb::get_pxweb_data(
url = "http://api.scb.se/OV0104/v1/doris/sv/ssd/BE/BE0101/BE0101A/BefolkningNy",
dims = list(Region = c('*'),
Civilstand = c('*'),
Alder = c('*'),
Kon = c('*'),
ContentsCode = c('*'),
Tid = as.character(1970)),
clean = TRUE)
Rprof()
summaryRprof(tmp, lines = "show", memory = "both")
Profiling

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
$by.self
self.time self.pct total.time total.pct mem.total
get_pxweb_data.R#102 1.96 39.2 1.96 39.2 579.2
get_pxweb_data_internal.R#42 1.16 23.2 1.16 23.2 405.0
get_pxweb_data.R#56 0.52 10.4 0.52 10.4 31.3
get_pxweb_data.R#80 0.38 7.6 0.38 7.6 29.1
get_pxweb_data.R#82 0.32 6.4 0.32 6.4 40.7
get_pxweb_data_internal.R#48 0.26 5.2 0.26 5.2 73.2
get_pxweb_data_internal.R#74 0.26 5.2 0.26 5.2 29.8
get_pxweb_data.R#83 0.08 1.6 0.08 1.6 17.2
api_catalogue.R#75 0.02 0.4 0.02 0.4 0.0
get_pxweb_data_internal.R#44 0.02 0.4 0.02 0.4 12.6
get_pxweb_data_internal.R#71 0.02 0.4 0.02 0.4 16.0Improvements

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
1. Look for existing solutions.
2. Do less work.
3. Vectorise.
4. Parallelise.
5. Avoid copies.
Parallelism in R

Parallelism in R

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Based on lapply()
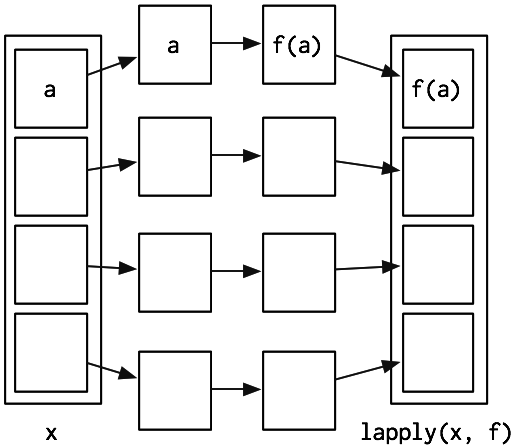
parallel package

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Two approaches:
mclapply()
parLapply()
mclapply()

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Pros
Simple to use
Low overhead (startup)
Cons
Do not work with windows
Only multicore
parLapply(type="psock")

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Pros
Works everywhere
Good for testing/developing
Cons
Slow on multiple nodes
parLapply(type="mpi")

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Pros
Good for multiple computers
Good for production
Cons
Can be used interactively
Needs Rmpi package
Example

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Rcpp

Rcpp

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Using C++ code in R
Need C++ compiler (look here)
Often called interfacing
Similar can be done with Java and Fortran
Extremely fast!
But just handle bottlenecks!
Fibonacci

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
R

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
f <- function(n) {
if (n < 2) return(n)
f(n-1) + f(n-2)
}
system.time(fr(30))
user system elapsed
2.246 0.171 2.451 C++

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
library(Rcpp)
cppFunction(code = '
int fcpp(int n) {
if (n < 2) return(n);
return(fcpp(n-1) + fcpp(n-2));
}
')
system.time(fcpp(30))
user system elapsed
0.007000000 0.000000000 0.006999999 memoise

Memoization

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
A simple optimization technique
Store results of function calls
If called again, returns old value
Depend on functional programming
Memoise in R

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
> library(memoise)
> a <- function(x) runif(1)
> replicate(3, a())
[1] 0.6709919 0.3490709 0.4772027
> b <- memoise(a)
> replicate(3, b())
[1] 0.1867441 0.1867441 0.1867441> c <- memoise(function(x) { Sys.sleep(1); runif(1) })
> system.time(print(c()))
[1] 0.7816399
user system elapsed
0.003 0.004 1.001
> system.time(print(c()))
[1] 0.7816399
user system elapsed
0.001 0.000 0.000
> forget(c)
[1] TRUE
> system.time(print(c()))
[1] 0.9234995
user system elapsed
0.003 0.004 1.001 Advanced R - Lecture 6
By monsmagn
Advanced R - Lecture 6
Lecture 6 in the course Advanced R programming at Linköping University.
- 1,908



