RGS | London
August 2016
Back to the Future
of Multimodelling
Sébastien Rey-Coyrehourcq | IDEES, Rouen
Romain Reuillon | ISCPIF, Paris
Clémentine Cottineau | UCL, London
slides @ http://goo.gl/gpJTtd
Why multimodelling ?

Validation Dragon !
[ Rey 2015, p11 - 184 ]
1960's - 2016
back to origin ?
Equifinality & self-organisation
[Bertalanffy 1950]
[Ashby 1947]
[Prigogine 1969]
[Foerster 1960]
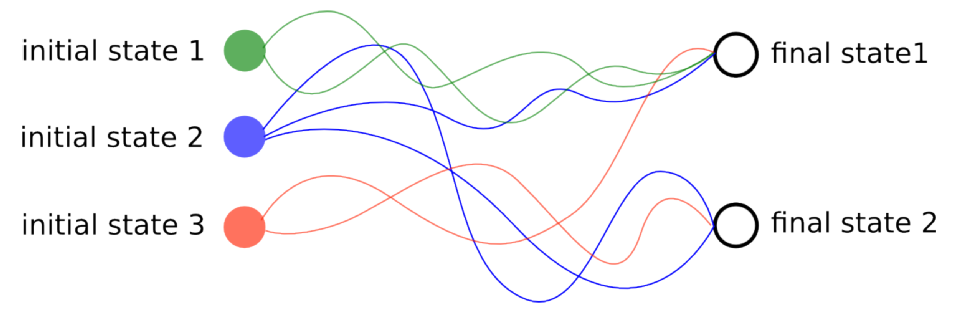
An Observational Dilemma
The Nature of Simulation
[Batty 1976]
[Morgan 2005]
[Phan 2008, 2010]
[Winsberg 2009]
[Guala 2008]
[Varenne 2001, 2013]
[Bulle 2005]
Early vision of MM
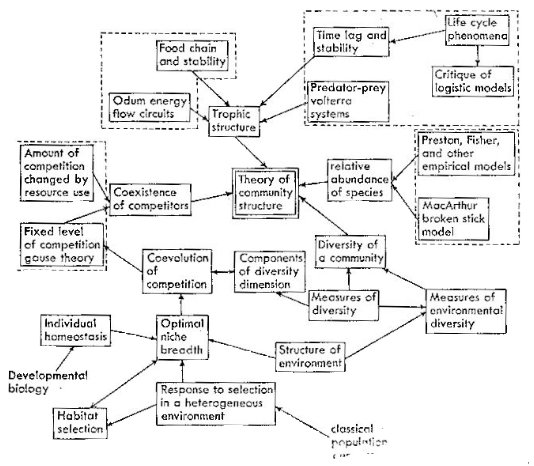
"Cluster of models" example applied to "ecological community"
Alternative (linked, nested, completary, concurrent, etc. ) models
Multiple Goals of Modelling, Validation != "True"
(see also Hermann 1967 !!)
generality vs realism vs precision
The strategy of model building in biology, Lewins R., 1966
Interdisciplinarity

Limited ressources
CDC 6000 "super"computers
Washington University IBM 650
& Northwestern's Vogelback computing center CDC 3400/ 6400
ask Swedish & American Simulation pioneers in 60's ...
[ex Hager III and Hager IV Fortran program]
3 MFlops ...
Openshaw 80's vision

“From data crunching to model crunching: the dawn of a new era”, 1983
The dream is of some kind of model-crunching machine which could be persuaded to search for interesting model specifications in the universe of all possible models relevant to a particular purpose
Openshaw 80's vision
“Building an automated modelling system (AMS) to explore a universe of spatial interaction models”, 1988
7 variables
5 parameterization
5 operators
15 functions
Blueprint to generate spatial interaction models
( up to 1 to 5 linked modules)
into module
1
1
1
2
combine
of
alternatives
Openshaw 80's vision
Models generated hard to interpret

“Building an automated modelling system (AMS) to explore a universe of spatial interaction models”, 1988
Openshaw 80's vision

Cray 1 vector supercomputer 1976
- 160 MFlops -
Random
vs
meta-heuristics
High Performance Computing (HPC)
“Building an automated modelling system (AMS) to explore a universe of spatial interaction models”, 1988
MM method
need
- fastest with less ressources
- find optimal / suboptimal
- explore diversity, uncertainty
better
Back to ecology
Robustness analysis: Deconstructing computational models for ecological theory and applications, Grimm et al. 2016
Complementory with Richard Levins' idea !
Know where and when
parameters and mechanisms break
base model
base model
choices
give different path (1, 2) to explain same pattern
( )
( )
Look back and challenge choices
Share your results
and challenge others

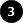
( )
Cumulative knowledge
Back to the future?
Ecology
Geography
2016
2036
1996
1976
1956
Levins
Hermann
Grimm al.
Openshaw
GeoDiver
City
Massive parrallelism era
?
Batty, Torrens
Theory and conceptual framework
Application
Vector processor era
HPC
Operational MM
"This project aims at tackling equifinality in systems dynamics by confronting different mechanisms with similar evaluation criteria [...] and by scanning automatically the parameter space along with the space of model structures (as combinations of modelled dynamics)."

Application

Application

What makes cities grow differentially?
Demographics
Local Resources
Economic Specialization
Politics
a. size effects
b. gen. trend
a. coal and ore
b. oil and gas
c. access to sea
a. State level
b. region level
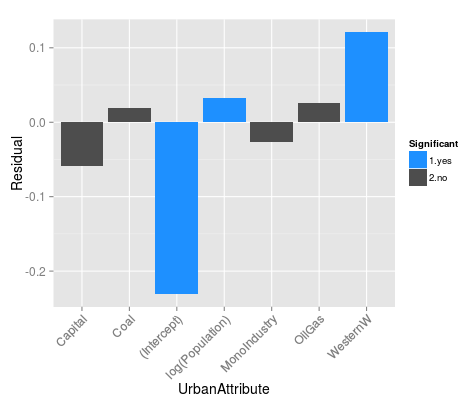
Example:
USSR 1959-1989
USSR 1989-2010
Experiment Design

Generate models
Confront models (structure + parameters) to evaluation target

Step 1
Step 2
Functional programming paradigm
and mixin methods (Scala)

How to Implement MultiModels?
trait T11
parameter 1 for trait T11
parameters for trait T22
ex: ressource extraction
ex: oil & gas multiplier
ex: degree of rural migration
trait T22
ex: urban transition
Model id
= composition
of mechanisms
What comes out of the calibration of MultiModels?
Model id
= composition
of mechanisms
Parameters
= calibrated values
given composition
Fitness
(for multiple
evaluation targets)
Best 3,200 instances
of 36,000,000 evaluated by GA
for each of the two simulation periods
1
2
...
3200
HPC Needed !!!
~ 1 week of computation
on a grid of 3000 cores

How to Analyse MultiModels ?
Interactive Visualisations & Explorations


shiny.parisgeo.cnrs.fr/VARIUS
A few answers
Are all mechanisms necessary?

Model id
= composition
of mechanisms
Fitness
(for multiple
evaluation targets)
~
A few answers
What are the parameter values of the 'best' parsimonious model?
Given
Fitness
(for multiple
evaluation targets)
~
Parameters
= calibrated values
given composition
Model id
= composition
of mechanisms
1959-1989
1989-2010


A few answers
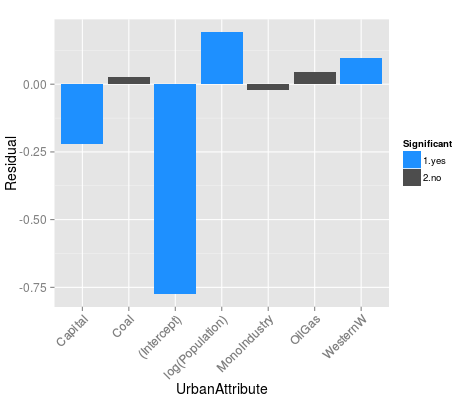
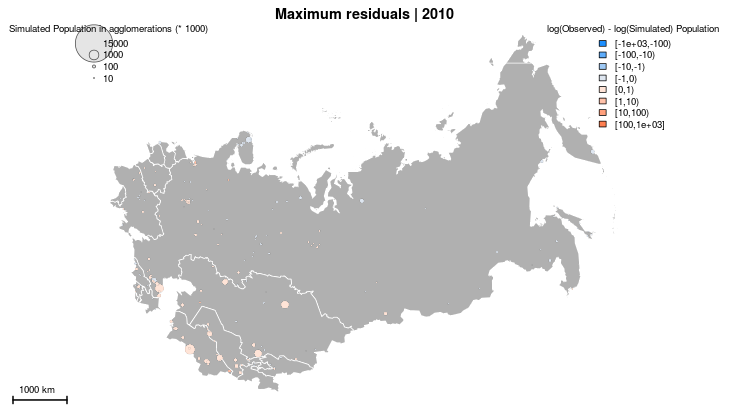
1959-1989
1989-2010
What is the 'best' model leaving out?
Significant attribute
Non-significant attribute
Large City
Non-Capital
Western
Profile of Cities w
Underestimated
Growth
Western City
Large City
Profile of Cities w
Underestimated
Growth
Perspectives
Build a library of mechanisms
Build a library of mathematical and logical functions
"There is always room for doubt as to whether a result depends on the essentials of a model or on the details of the simplifying assumptions." Levins 1966: 423
Combine and accumulate urban models at different scales
to facilitate the use of tested models for different purposes
"Ultimately, we might assemble libraries of tested submodels representing specific behaviours or processes." Thiele & Grimm 2015
The future has arrived – it’s just not evenly distributed yet."
William Gibson
@reyman64
@ClementineCttn
@romainreuillon
GitHub

https://github.com/openmole/family
slides @ http://goo.gl/gpJTtd
bibliography @ http://goo.gl/gRfGvG
London RGS Aout 2016
By sebastien rey coyrehourcq
London RGS Aout 2016
- 1,242



